TEPADINA 400 mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSION

How to use TEPADINA 400 mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
TEPADINA 400 mg powder and solvent for solution for infusion
tiotepa
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contentsof the package leaflet:
- What is TEPADINA and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use TEPADINA
- How to use TEPADINA
- Possible side effects
- Storage of TEPADINA
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is TEPADINA and what is it used for
TEPADINA contains tiotepa as the active substance, a medicine that belongs to the group of alkylating agents.
TEPADINA is used to prepare the patient for a bone marrow transplant. It works by destroying the cells in the bone marrow. This allows the patient to receive a transplant of new bone marrow cells (haematopoietic stem cells), which in turn enable the body to produce healthy blood cells.
TEPADINA can be used in adults, children, and adolescents.
2. What you need to know before you use TEPADINA
Do not use TEPADINA
- if you are allergic to tiotepa,
- if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant,
- if you are breast-feeding,
- if you are going to receive the yellow fever vaccine with live virus and bacterial vaccines.
Warnings and precautions
Tell your doctor if you have:
- liver or kidney problems,
- heart or lung problems,
- seizures/epileptic fits or have had them in the past (if you have been treated with phenytoin or fosphenytoin).
Since TEPADINA destroys the bone marrow cells responsible for producing blood cells, you will need to have regular blood tests during treatment to check your cell counts.
To prevent and treat infections, you will be given anti-infectives.
TEPADINA may cause another type of cancer in the future. Your doctor will explain this type of risk to you.
Other medicines and TEPADINA
Tell your doctor if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding, and fertility
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant before receiving TEPADINA. You must not use TEPADINA during pregnancy.
Both women and men using TEPADINA must use effective contraceptive methods during treatment. Men must not father a child during treatment with TEPADINA or for up to one year after treatment has finished.
It is not known if this medicine is excreted in breast milk. As a precaution, women must not breast-feed during treatment with TEPADINA.
TEPADINA may affect male and female fertility. Male patients should seek advice on sperm preservation before starting treatment.
Driving and using machines
Some side effects of tiotepa, such as dizziness, headache, and blurred vision, may affect your ability to drive and use machines. Do not drive or use machines if you are affected.
TEPADINA contains sodium
This medicine contains 1,418 mg (61.6 mmol) of sodium per bag, equivalent to 70.9% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for adults.
3. How to use TEPADINA
Your doctor will calculate the dose based on your body surface area or weight and your disease.
How TEPADINA is administered
TEPADINA must be administered by a qualified healthcare professional via intravenous infusion (drip into a vein) after dilution of each vial. Each infusion lasts 2 to 4 hours.
Frequency of administration
You will receive infusions every 12 or 24 hours. The treatment may last up to 5 days. The frequency of administration and the duration of treatment will depend on your disease.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, TEPADINA can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some of the more serious side effects of treatment with TEPADINA or the transplant procedure are:
- decrease in blood cell counts (expected effect of the medicine as preparation for your transplant)
- infection
- liver problems, such as blockage of a liver vein
- graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)
- respiratory complications
Your doctor will monitor your blood cell counts and liver enzymes regularly to detect and treat these events.
The side effects of TEPADINA are frequent, which are defined as follows:
Very common side effects (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- increased risk of infections
- generalized inflammation (septicemia)
- decrease in white blood cell, platelet, and red blood cell count (anemia)
- graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)
- dizziness, headache, blurred vision
- uncontrolled body tremors (seizures)
- tingling, numbness, or prickling sensation (paresthesia)
- partial loss of mobility
- cardiac arrest
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- inflammation of the oral mucosa (mucositis)
- irritation of the stomach, esophagus, intestine
- inflammation of the colon
- loss of appetite, decreased appetite
- elevated blood glucose
- rash, itching, peeling
- skin color change (not to be confused with jaundice - see below)
- redness of the skin (erythema)
- hair loss
- back and abdominal pain, pain
- muscle and joint pain
- abnormal heart rhythm
- inflammation of lung tissue
- enlargement of the liver
- altered function of some organs
- blockage of a liver vein (veno-occlusive disease, VOD)
- yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- hearing impairment
- lymphatic obstruction
- high blood pressure
- enlargement of the liver, elevated kidney and digestive enzymes
- abnormal blood electrolyte values
- weight gain
- fever, general weakness, chills
- bleeding (hemorrhage)
- nasal bleeding
- general swelling due to fluid retention (edema)
- pain or inflammation at the injection site
- eye infection (conjunctivitis)
- decreased sperm count
- vaginal bleeding
- absence of menstrual periods (amenorrhea)
- memory loss
- delayed weight and height gain
- bladder problems
- insufficient production of testosterone
- insufficient production of thyroid hormones
- reduced activity of the pituitary gland
- state of confusion
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- anxiety, confusion
- abnormal dilation of one of the arteries in the brain (intracranial aneurysm)
- elevated creatinine
- allergic reactions
- blockage of a blood vessel (embolism)
- abnormal heart rhythm
- heart failure
- cardiovascular disability
- oxygen deficiency
- fluid accumulation in the lungs (pulmonary edema)
- lung bleeding
- respiratory arrest
- blood in the urine (hematuria) and moderate kidney failure
- inflammation of the urinary bladder
- discomfort while urinating and decreased urine production (dysuria and oliguria)
- increased blood nitrogen components (elevated BUN)
- cataracts
- liver failure
- cerebral hemorrhage
- cough
- constipation and stomach discomfort
- intestinal obstruction
- stomach perforation
- changes in muscle tone
- general lack of coordination of muscle movements
- bruises associated with low platelet count
- menopausal symptoms
- cancer (secondary primary malignancies)
- altered brain function
- male and female infertility
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- inflammation and peeling of the skin (erythrodermic psoriasis)
- delirium, nervousness, hallucinations, agitation
- gastrointestinal ulcer
- inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis)
- abnormal heart disease (myocardial disease)
Frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- increase in blood pressure in the arteries (blood vessels) of the lungs (pulmonary arterial hypertension)
- severe skin damage (e.g. severe lesions, blisters, etc.) that can affect the entire body surface, which can be fatal
- damage to a component of the brain (so-called white matter) that can be potentially fatal (leukoencephalopathy).
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of TEPADINA
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use the medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton, packaging, and bag after EXP.
The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Store and transport refrigerated (2°C-8°C). Do not freeze.
After activation and reconstitution of the bag, the medicine remains stable for up to 48 hours when stored at 2°C-8°C and up to 6 hours when stored at 25°C. From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. The unused product and waste should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
6. Contents of the pack and additional information
Composition of TEPADINA
- The active ingredient is thiotepa.
A bag contains 400 mg of thiotepa. After reconstitution with the solvent, each ml of solution contains 1 mg of thiotepa.
- The other ingredients are sodium chloride and water for injectable preparations (see section 2 "TEPADINA contains sodium").
Appearance of the product and contents of the pack
TEPADINA is supplied in a two-chamber bag with 400 mg of thiotepa and 400 ml of sodium chloride 9 mg/ml (0.9%) injectable solution in the other chamber.
After reconstitution, the bag contains a clear and colorless solution for infusion.
Each bag is placed inside an aluminum packaging. Each box contains 1 bag.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
ADIENNE S.r.l. S.U.
Via Galileo Galilei, 19 20867 Caponago (MB) Italy Tel: +39 02 40700445
You can request more information about this medicine by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Belgium/Belgique/Belgien Accord Healthcare bv Tel: +32 51 79 40 12 | Lithuania Accord Healthcare AB Tel: +46 8 624 00 25 |
Poland Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 577 28 00 | Luxembourg/Luxemburg Accord Healthcare bv Tel: +32 51 79 40 12 |
Czech Republic Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 577 28 00 | Hungary Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 577 28 00 |
Denmark Accord Healthcare AB Tel: +46 8 624 00 25 | Malta Accord Healthcare Ireland Ltd Tel: +44 (0) 208 901 3370 |
Germany Accord Healthcare GmbH Tel: +49 89 700 9951 0 | Netherlands Accord Healthcare B.V. Tel: +31 30 850 6014 |
Estonia Accord Healthcare AB Tel: +46 8 624 00 25 | Norway Accord Healthcare AB Tel: +46 8 624 00 25 |
Greece Accord Healthcare Italia Srl Tel: +39 02 943 23 700 | Austria Accord Healthcare GmbH Tel: +43 (0)662 424899-0 |
Spain Accord Healthcare S.L.U. Tel: +34 93 301 00 64 | Poland Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 577 28 00 |
France Accord Healthcare France SAS Tel: +33 (0)320 401 770 | Portugal Accord Healthcare, Unipessoal Lda Tel: +351 214 697 835 |
Croatia Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 577 28 00 | Romania Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 577 28 00 |
Ireland Accord Healthcare Ireland Ltd Tel: +44 (0)1271 385257 | Slovenia Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 577 28 00 |
Iceland Accord Healthcare AB Tel: +46 8 624 00 25 | Slovakia Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 577 28 00 |
Italy Accord Healthcare Italia Srl Tel: +39 02 943 23 700 | Finland Accord Healthcare Oy Tel: +358 10 231 4180 |
Cyprus Accord Healthcare S.L.U. Tel: +34 93 301 00 64 | Sweden Accord Healthcare AB Tel: +46 8 624 00 25 |
Latvia Accord Healthcare AB Tel: +46 8 624 00 25 | United Kingdom Accord-UK Ltd Tel: +44 (0)1271 385257 |
Date of last revision of this leaflet:
Other sources of information
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency website http://www.ema.europa.eu.
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
PREPARATION GUIDE
TEPADINA 400 mg powder and solvent for solution for infusion
thiotepa
Read this guide before preparing and administering TEPADINA.
- Presentation
A bag contains 400 mg of thiotepa.
After reconstitution with the solvent, each ml of solution contains 1 mg of thiotepa. TEPADINA must be reconstituted before administration.
- Dosage and administration
Calculation of the TEPADINA dose
TEPADINA is administered in different doses and in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents to patients who are to receive a conventional hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) for hematological diseases or solid tumors.
The recommended dosage of TEPADINA in adult and pediatric patients depends on the type of HSCT (autologous or allogeneic) and the disease.
If necessary, the adjustment of the TEPADINA dose will be made according to the specific application.
If the calculated necessary dose is higher than 400 mg but less than a multiple of that amount, the user must add the required mg of TEPADINA vials through a dedicated luer port (step 5 of the instructions for use in the leaflet).
If the calculated necessary dose is less than 400 mg, the user must remove the excess mg from the 1 mg/ml reconstituted solution or place an infusion pump with the amount of medicinal product to be administered in ml.
Dosage in adults
AUTologous HSCT
Hematological diseases
The recommended dose in hematological diseases varies between 125 mg/m2/day (3.38 mg/kg/day) and 300 mg/m2/day (8.10 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 2 to 4 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 900 mg/m2 (24.32 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
LYMPHOMA
The recommended dose varies between 125 mg/m2/day (3.38 mg/kg/day) and 300 mg/m2/day (8.10 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 2 to 4 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 900 mg/m2 (24.32 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
LYMPHOMA OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS)
The recommended dose is 185 mg/m2/day (5 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 2 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 370 mg/m2 (10 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment. MULTIPLE MYELOMA
The recommended dose varies between 150 mg/m2/day (4.05 mg/kg/day) and 250 mg/m2/day (6.76 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 3 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 750 mg/m2 (20.27 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
Solid tumors
The recommended dose in solid tumors varies between 120 mg/m2/day (3.24 mg/kg/day) and 250 mg/m2/day (6.76 mg/kg/day) divided into one or two daily infusions, administered for 2 to 5 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 800 mg/m2 (21.62 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
BREAST CANCER
The recommended dose varies between 120 mg/m2/day (3.24 mg/kg/day) and 250 mg/m2/day (6.76 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 3 to 5 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 800 mg/m2 (21.62 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
TUMORS OF THE CNS
The recommended dose varies between 125 mg/m2/day (3.38 mg/kg/day) and 250 mg/m2/day (6.76 mg/kg/day) divided into one or two daily infusions, administered for 3 to 4 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 750 mg/m2 (20.27 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
OVARIAN CANCER
The recommended dose is 250 mg/m2/day (6.76 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 2 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 500 mg/m2 (13.51 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment. STEM CELL TUMORS
The recommended dose varies between 150 mg/m2/day (4.05 mg/kg/day) and 250 mg/m2/day (6.76 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 3 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 750 mg/m2 (20.27 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
Allogeneic HSCT
Hematological diseases
The recommended dose in hematological diseases varies between 185 mg/m2/day (5 mg/kg/day) and 481 mg/m2/day (13 mg/kg/day) divided into one or two daily infusions, administered for 1 to 3 consecutive days before an allogeneic HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 555 mg/m2 (15 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
LYMPHOMA
The recommended dose is 370 mg/m2/day (10 mg/kg/day) divided into two daily infusions before an allogeneic HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 370 mg/m2 (10 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
MULTIPLE MYELOMA
The recommended dose is 185 mg/m2/day (5 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion before an allogeneic HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 185 mg/m2 (5 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
LEUKEMIA
The recommended dose varies between 185 mg/m2/day (5 mg/kg/day) and 481 mg/m2/day (13 mg/kg/day) divided into one or two daily infusions, administered for 1 or 2 consecutive days before an allogeneic HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 555 mg/m2 (15 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
THALASSEMIA
The recommended dose is 370 mg/m2/day (10 mg/kg/day) divided into two daily infusions, administered before an allogeneic HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 370 mg/m2 (10 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
Dosage in pediatric patients
AUTologous HSCT
Solid tumors
The recommended dose in solid tumors varies between 150 mg/m2/day (6 mg/kg/day) and 350 mg/m2/day (14 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 2 to 3 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 1,050 mg/m2 (42 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
TUMORS OF THE CNS
The recommended dose varies between 250 mg/m2/day (10 mg/kg/day) and 350 mg/m2/day (14 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 3 consecutive days before an autologous HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 1,050 mg/m2 (42 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
Allogeneic HSCT
Hematological diseases
The recommended dose in hematological diseases varies between 125 mg/m2/day (5 mg/kg/day) and 250 mg/m2/day (10 mg/kg/day) divided into one or two daily infusions, administered for 1 to 3 consecutive days before an allogeneic HSCT, depending on the combination with other chemotherapeutic agents, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 375 mg/m2 (15 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
LEUKEMIA
The recommended dose is 250 mg/m2/day (10 mg/kg/day) divided into two daily infusions, administered before an allogeneic HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 250 mg/m2 (10 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
THALASSEMIA
The recommended dose varies between 200 mg/m2/day (8 mg/kg/day) and 250 mg/m2/day (10 mg/kg/day) divided into two daily infusions, administered before an allogeneic HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 250 mg/m2 (10 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment. REFRACTORY CYTOPENIA
The recommended dose is 125 mg/m2/day (5 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 3 consecutive days before an allogeneic HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 375 mg/m2 (15 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment. GENETIC DISEASES
The recommended dose is 125 mg/m2/day (5 mg/kg/day) through a single daily infusion, administered for 2 consecutive days before an allogeneic HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 250 mg/m2 (10 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA
The recommended dose is 250 mg/m2/day (10 mg/kg/day) divided into two daily infusions, administered before an allogeneic HSCT, without exceeding the maximum accumulated dose of 250 mg/m2 (10 mg/kg) during the entire conditioning treatment.
Activation of the bag and reconstitution
TEPADINA 400 mg must be reconstituted with 400 ml of sodium chloride 9 mg/ml (0.9%) solution for injection. The final reconstituted solution is obtained after breaking the seal of the two-chamber bag and mixing the contents of both (powder solvent), until the complete dissolution of the powder.
After reconstitution with the solvent, each ml of solution contains 1 mg of thiotepa. Only colorless and particle-free solutions should be used.
Do not use the medicine if you observe any signs of deterioration.
Administration
TEPADINA solution for infusion must be visually inspected for the presence of particles before administration. Solutions containing precipitates must be discarded.
The infusion solution must be administered to patients using an infusion device equipped with a 0.2 µm in-line filter. The filtration does not alter the potency of the solution.
TEPADINA must be administered in aseptic conditions through infusion for 2-4 hours at room temperature (approximately 25 °C) and under normal lighting conditions.
Before and after each infusion, the permanent catheter must be flushed with approximately 5 ml of injectable solution with 9 mg/ml of sodium chloride (0.9%).
- SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL AND OTHER HANDLING
Generalities
Appropriate handling and disposal procedures for antineoplastic medicines will be taken into account. All transfer procedures will strictly follow aseptic techniques, preferably using a vertical laminar flow safety cabinet. As with other cytotoxic compounds, extreme caution will be exercised during the handling and preparation of TEPADINA solutions to avoid accidental contact with the skin or mucous membranes. Topical reactions associated with accidental exposure to thiotepa may occur. Therefore, the use of gloves is recommended during the preparation of the infusion solution. If the thiotepa solution comes into accidental contact with the skin, it should be washed thoroughly with water and soap immediately. If thiotepa comes into accidental contact with the mucous membranes, they should be washed thoroughly with water.
Disposal
The unused product and waste must be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
| |
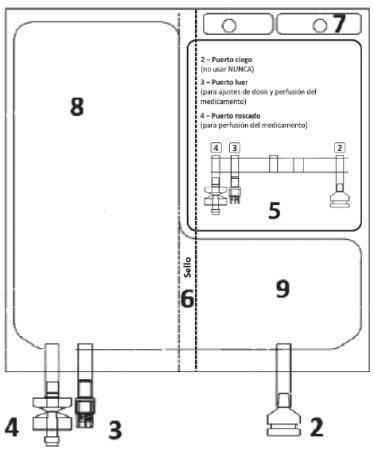
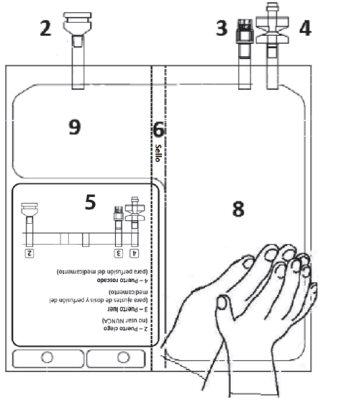
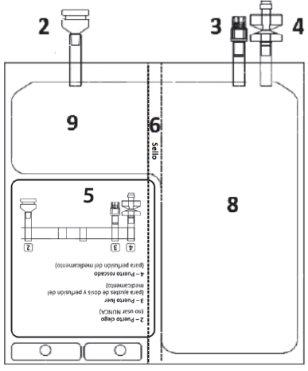
Figure A 1 – Notches on the outer bag
| Figure B 2 – Blind port (never use) 3 – Luer port
8 – Chamber with the solvent 9 – Chamber with the powder
|
| |||||||
|
| ||||||
|
| ||||||
|
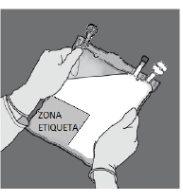
Place the bag on a clean and stable surface with the text facing up and the ports away from you, as shown in Figure E.
Check that there are no liquid leaks or product leaks from connection ports 2, 3, 4or from chamber 8, 9.
Verify the integrity of seal 6by checking that there is no liquid in chamber 9
Figure E |
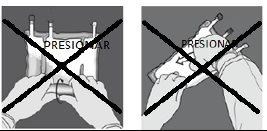
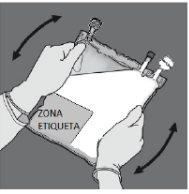
Place one hand over the other on the lower part of chamber 8(as in Figure F). Press firmly and uniformly until seal 6is fully activated (seal 6may take up to 5 seconds of continuous pressure to break).
|
BAG BEFORE ACTIVATION | BAG AFTER ACTIVATION | |
|
| |
DO NOT squeeze or press forcefully. | Figure I
| |
4 – CHECK THE BAG TO CONFIRM ACTIVATION. | ||
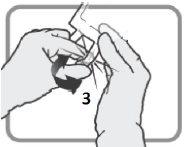
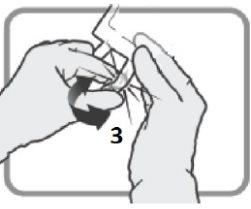
Check that seal 6is fully activated. Chambers 8and 9have been joined. | Mix gently until the product is completely dissolved. | |
Figure J
| Figure K
| |
5 – ADJUST THE DOSE – Refer to sections 2. “Posology and method of administration” and 3. “Special precautions for disposal and other handling” | ||
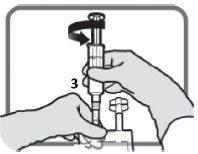
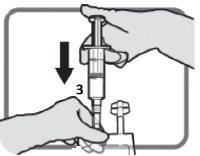
Identify the luer port 3, if necessary, adjust the dose. Remove the plastic cap from the luer port.
Figure L | Screw the device with the luer lock as in Figure M. Do not use devices with non-luer locks on port 3.
Figure M Make sure the connection is properly placed and tightened | Adjust the dose as described in sections 2and 3
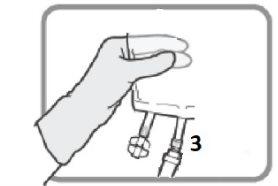
Figure N Unscrew the device when finished. Put the plastic cap over the luer port 3before proceeding with the infusion |
6 – CONNECTION - The infusion set can be connected to the bag via the luer connector or the spike connector. | |
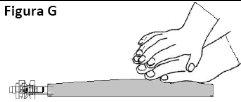
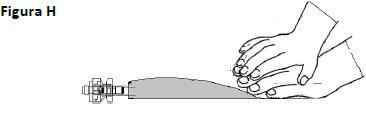
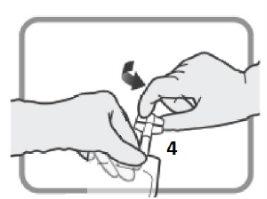
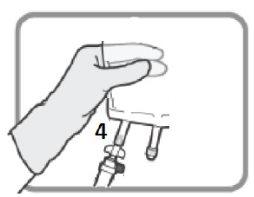
OPTION A – SPIKE CONNECTION Identify the threaded port 4if you are going to use an infusion set with a spike. Turn and remove the plastic cap before inserting the spike.
Figure O Insert the spike connector.
Figure P | OPTION B – LUER CONNECTION Select the luer port 3if you are going to use an infusion set with a luer connector. Remove the plastic cap from the luer port 3before inserting the luer connector.
Figure Q Insert the luer connector.
Figure R Make sure the connection is properly placed and tightened. |
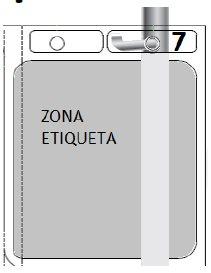
7 – HANG THE BAG | |
Hang the bag by the hole 7. | Figure S
|
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to TEPADINA 400 mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mgActive substance: thiotepaManufacturer: Adienne S.R.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 15 mgActive substance: thiotepaManufacturer: Adienne S.R.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mgActive substance: thiotepaManufacturer: Esteve Pharmaceuticals GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for TEPADINA 400 mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about TEPADINA 400 mg POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions