
SULIQUA 100 units/mL + 50 micrograms/mL pre-filled pen solution for injection

How to use SULIQUA 100 units/mL + 50 micrograms/mL pre-filled pen solution for injection
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Suliqua 100 units/ml + 50 micrograms/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen
Insulin glargine + lixisenatide
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Suliqua and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Suliqua
- How to use Suliqua
- Possible side effects
- Storing Suliqua
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Suliqua and what is it used for
Suliqua is an injectable medicine for diabetes that contains two active substances:
- Insulin glargine: a long-acting insulin that helps control blood sugar levels (glucose) throughout the day.
- Lixisenatide: a "GLP-1 receptor agonist" that helps your body produce its own extra insulin in response to rising blood sugar levels and decreases sugar absorption from meals.
Suliqua is used to treat adult patients with type 2 diabetes, to help control blood sugar levels when they are too high, as an addition to diet and exercise. It is given with metformin with or without sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors (gliflozins), when other medicines are not sufficient to control blood sugar levels.
2. What you need to know before you use Suliqua
Do not use Suliqua
- If you are allergic to insulin glargine or lixisenatide, or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before you start using Suliqua if:
- You have type 1 diabetes, as Suliqua is used for type 2 diabetes and this medicine will not be suitable for you.
- You have diabetic ketoacidosis (a complication of diabetes that occurs when your body is unable to use glucose because there is not enough insulin), as this medicine will not be suitable for you.
- You have a severe intestinal or stomach problem, such as a stomach muscle disease called "gastroparesis" that leads to delayed stomach emptying. Because Suliqua can cause stomach side effects (see section 4), it has not been studied in patients with severe stomach or intestinal problems. See information related to medicines that should not stay in your stomach for a long time in the section Other medicines and Suliqua.
- If you are going to have surgery, inform your doctor that you are taking Suliqua.
- If you have severe kidney disease or are on dialysis, as the use of this medicine is not recommended.
Follow your doctor's instructions exactly regarding dosage, monitoring (blood and urine tests), diet, and physical activity (work and exercise) and injection technique.
You must pay special attention to the following:
- Low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia). If your blood sugar level is too low, follow the guidelines for hypoglycemia (see information in the box at the end of this leaflet).
- High blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). If your blood sugar level is too high, follow the guidelines for hyperglycemia (see information in the box at the end of this leaflet).
- Make sure you use the correct medicine. Always check the label before each injection to avoid confusion between Suliqua and other insulins.
- If you have vision problems, see section 3.
While using this medicine, pay attention to the following and talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before using Suliqua if:
- You have severe stomach pain that does not go away. This may be a sign of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
- You experience fluid loss (dehydration), for example, due to vomiting and diarrhea. It is important to drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration, especially during the first few weeks of treatment with Suliqua.
Skin changes at the injection site
The injection site should be rotated to avoid skin changes, such as lumps under the skin. Insulin may not work as well if it is injected into a lumpy area (see How to use Suliqua). Contact your doctor if you are currently injecting into a lumpy area, before starting to inject into a different area. Your doctor may tell you to check your blood sugar levels more closely and adjust your insulin or the dose of your other diabetes medicines.
Travel
Before traveling, consult your doctor. You may need to discuss:
- If your medicine is available in the country you are visiting.
- How to get your medicine, needles, and other supplies.
- How to store your medicine properly during travel.
- The timing of meals and administration of your medicine.
- The potential effects of traveling across time zones.
- Health risks in the countries you will visit.
- What to do in emergency situations if you do not feel well or become ill.
Children and adolescents
There is no experience with the use of Suliqua in children and adolescents under 18 years of age; therefore, the use of Suliqua is not recommended in this age group.
Other medicines and Suliqua
Tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines. If you use another diabetes medicine, talk to your doctor if you should stop using that medicine when you start treatment with Suliqua.
Some medicines may change your blood sugar level. This may mean that your doctor may need to change your dose of Suliqua. Therefore, before taking a medicine, ask your doctor if it will affect your blood sugar level and what action to take if necessary. You also need to be careful when you stop taking a medicine.
The effect of some of the medicines you take may be affected by Suliqua. You may need to take some medicines, such as antibiotics, oral contraceptives, statins (such as atorvastatin to lower cholesterol), tablets, capsules, granules, powders, or oral suspensions that should not stay in your stomach for too long, at least one hour before or four hours after injecting Suliqua.
Your blood sugar level may decrease (hypoglycemia) if you take:
- Other medicines to treat diabetes.
- Disopyramide, for certain heart problems.
- Fluoxetine, for depression.
- Antibiotics of the sulfonamide group, to treat infections.
- Fibrates, to lower high blood fat levels.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), for depression or Parkinson's disease.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, for heart problems or high blood pressure.
- Pain relievers and fever reducers such as pentoxifylline, propoxyphene, and salicylates (such as acetylsalicylic acid).
- Pentamidine, for certain parasitic infections. This can cause low blood sugar levels that may be followed by high blood sugar levels.
Your blood sugar level may increase (hyperglycemia) if you take:
- Corticosteroids such as cortisone and prednisolone, for inflammation.
- Danazol, for endometriosis.
- Diazoxide, for high blood pressure.
- Protease inhibitors, for HIV.
- Diuretics, for high blood pressure or fluid retention.
- Glucagon, for very low blood sugar levels.
- Isoniazid, for tuberculosis.
- Somatropin, a growth hormone.
- Thyroid hormones, for thyroid gland problems.
- Estrogens and progestogens, such as in birth control pills or estrogens used for bone loss (osteoporosis).
- Clozapine, olanzapine, and phenothiazine derivatives, for mental health problems.
- Sympathomimetic medicines such as epinephrine (adrenaline), salbutamol, and terbutaline, for asthma.
Your blood sugar level may increase or decrease if you take:
- Betablockers or clonidine, for high blood pressure.
- Lithium salts, for mental health problems.
Medicines that may reduce the warning signs of low blood sugar
Betablockers and some medicines (such as clonidine, guanethidine, reserpine - for high blood pressure) may make it more difficult to recognize the warning signs of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). They may even hide or interrupt the early warning signs that your blood sugar level is too low.
If any of the above applies to you (or you are not sure), contact your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before using this medicine.
Warfarin and other anticoagulants
Tell your doctor if you are taking warfarin or other anticoagulants (medicines used to prevent blood clots), as you may need to have blood tests more often to check your blood clotting (called "International Normalized Ratio" or INR control).
Suliqua and alcohol
Your blood sugar levels may rise or fall if you drink alcohol. You should check your blood sugar level more often.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Suliqua should not be used during pregnancy. It is not known if Suliqua harms your unborn baby.
Suliqua should not be used during breastfeeding. It is not known if Suliqua passes into breast milk.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Low or high blood sugar levels (see the information in the box at the end of this leaflet) may affect your ability to drive and use tools or machines. Your concentration may be affected. This can be dangerous for you and others.
Ask your doctor if you can drive if:
- Your blood sugar level is often too low.
- If you find it difficult to recognize when your blood sugar level is too low.
Suliqua contains sodiumThis medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per dose, which is essentially "sodium-free".
Suliqua contains metacresol
This medicine contains metacresol, which may cause allergic reactions.
3. How to use Suliqua
Follow your doctor's instructions exactly regarding the administration of this medicine. Your doctor may tell you to use a different dose of Suliqua than your previous dose of insulin or your glucose-lowering medicine, if you use one. If you are in doubt, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Based on your lifestyle, blood sugar control, and previous insulin use, your doctor will tell you:
- How much Suliqua you need each day and at what time.
- When to check your blood sugar level and if you need to do urine tests.
- When you may need higher or lower doses.
Your doctor may tell you to use Suliqua with other medicines for high blood sugar.
How much to use
Suliqua 100 units/ml + 50 micrograms/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen:
- This pen delivers doses of 10 to 40 dose steps in one injection, in 1 dose step increments.
- Each selected dose step contains 1 unit of insulin glargine and 0.5 micrograms of lixisenatide.
Your dose of Suliqua is given in "dose steps". The dose window of the pen shows the number of dose steps.
Do not inject a dose less than 10 dose steps. Do not inject a dose more than 40 dose steps. If you need a dose more than 40 dose steps, your doctor will prescribe a different pen. For dose steps of 30-60 units, Suliqua 100 units/ml + 33 micrograms/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen is available.
Many factors can influence your blood sugar level. You should know these factors so that you can react correctly to changes in your blood sugar level and prevent it from rising or falling too much. For more information, see the box at the end of this leaflet.
Use in elderly patients (65 years and older)
If you are 65 years or older, inform your doctor, as you may need a lower dose.
If you have kidney or liver problems
If you have kidney or liver problems, inform your doctor, as you may need lower doses.
When to inject Suliqua
Use Suliqua once a day, within the hour before a meal. Preferably inject Suliqua before the same meal every day, when you have chosen the most suitable meal.
Before injecting Suliqua
- Read the "Instructions for Use" in this leaflet and use the pen as described.
- If you do not follow these instructions, you may get too much or too little Suliqua.
To avoid errors, always check the packaging and label of the pen before each injection to make sure you have the correct pen, especially if you inject more than one medicine.
If you are in doubt, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How to inject
- Suliqua is injected under the skin (subcutaneously or "SC").
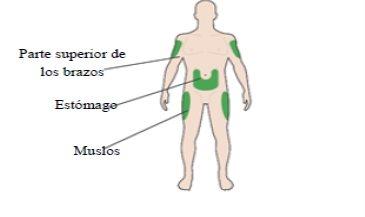
- Inject it into the front of your thighs, the top of your arms, or the front of your waist (abdomen).
- Change the injection site every day within an injection area. This will reduce the risk of lumps or bumps appearing at the injection site (for more information, see "Other side effects" in section 4).
Do not use Suliqua
- if particles appear in Suliqua. The solution should be clear, colorless, and water-like.
Other important information about using pre-filled pens
- Always use a new needle for each injection. Reusing needles increases the risk of blockage that can lead to underdose or overdose. Dispose of the needle safely after each use.
- To prevent the transmission of infections, pens should never be used by more than one person, even if the needle is changed.
- Only use needles compatible with the Suliqua pen (see "Instructions for Use").
- A safety test must be performed before each injection.
- Dispose of the used needle in a puncture-resistant container or as your pharmacist or local authority told you.
Never use a syringe to withdraw the solution from the pen, to avoid dosing errors and potential overdose.
If your pen is damaged, has not been stored correctly, if you are not sure it is working correctly, or if you notice that your blood sugar control is getting worse for no apparent reason:
- Discard the pen and use a new one.
- If you think you have problems with your pen, inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
If you use more Suliqua than you should
If you have injected too much medicine, your blood sugar level may drop too much (hypoglycemia). Check your blood sugar level and eat more to prevent your blood sugar level from dropping too much (hypoglycemia). If your blood sugar level drops too much, see the box at the end of this leaflet.
If you forget to use Suliqua
If you have missed a dose of Suliqua or if you have not injected enough insulin, your blood sugar level may rise too much (hyperglycemia):
When necessary, Suliqua can be injected before the next meal.
- Do not inject a double dose to make up for missed doses.
- Do not do two injections per day.
- Check your blood sugar level and inject your next dose at the usual time.
- For more information on treating hyperglycemia, see the box at the end of this leaflet.
If you stop using Suliqua
Do not stop your treatment without consulting your doctor. If you do, it may lead to very high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) and an increase in blood acid (ketoacidosis).
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
If you notice signs that your blood sugar level is too low (hypoglycemia),act immediately to raise your blood sugar level (see the box at the end of this prospectus).
Hypoglycemia can be very severe and is very frequent with medicines that contain insulin (it can affect more than 1 in 10 people).
Low blood sugar means that there is not enough sugar in the blood.
If your blood sugar level drops too low, you can faint (lose consciousness).
If the blood sugar level continues to be very low for too long, it can cause brain damage and can be potentially fatal. For more information, see the box at the end of this prospectus.
Other Adverse Effects
Inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse if you notice any of the following adverse effects:
Changes in the skin at the injection site:
If insulin is injected too frequently in the same place, the fatty tissue can shrink (lipoatrophy) or become thicker (lipohypertrophy). Lumps under the skin can also occur due to the accumulation of a protein called amyloid (cutaneous amyloidosis). It is unknown how frequently these skin changes can occur. Insulin may not work very well if injected into a lumpy area. Change the injection site to help avoid these skin changes.
Frequent(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Feeling of dizziness
- Feeling of nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Skin reactions and allergic reactions at the injection site: signs may include redness, intense pain when injecting, itching, hives, swelling, or inflammation. These reactions can spread around the injection site. Most minor insulin reactions usually disappear within a few days or weeks.
Infrequent(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Cold, runny nose, sore throat
- Hives (urticaria)
- Headache
- Indigestion (dyspepsia)
- Stomach pain
- Fatigue
- Gallstones
- Inflammation of the gallbladder
- Change in taste.
Rare(may affect 1 in 1000 people)
- Delayed emptying of the stomach.
Reporting Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible adverse effect that is not listed in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Suliqua
Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the packaging and on the label of the pen after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the indicated month.
Before First Use
Store in the refrigerator (between 2 °C and 8 °C).
Do not freeze or place near the freezer compartment or a cold accumulator.
Keep the preloaded pen in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
After First Use or if Carried as a Reserve
Keep your pen in use below 25 °C for a maximum of 28 days. Discard the pen after this period.
Do not put the pen back in the refrigerator and do not freeze it. Keep the pen away from direct heat or direct light. Always put the pen cap on when not in use to protect it from light.
Do not leave the pen in a car on an exceptionally hot or cold day.
Do not store the pen with the needle attached.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
What Suliqua Contains
- The active substances are insulin glargine and lixisenatide.
Each pen contains 300 units of insulin glargine and 150 micrograms of lixisenatide in a 3 ml solution. Each ml contains 100 units of insulin glargine and 50 micrograms of lixisenatide. Each dose step of Suliqua contains 1 unit of insulin glargine and 0.5 micrograms of lixisenatide.
The other components are: glycerol 85%, methionine, metacresol, zinc chloride, hydrochloric acid, and sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment) and water for injections. See also section 2 "What you need to know before you start using Suliqua" for more information on sodium and metacresol.
Appearance and Container Contents of the Product
Suliqua is an injectable solution (injection), clear and colorless in a glass cartridge within a pre-filled pen (SoloStar).
Packs of 3, 5, and 10 pre-filled pens.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Needles are not included in this pack.
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
82 avenue Raspail
94250 Gentilly
France
Manufacturer
Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH
Industriepark Höchst - 65926 Frankfurt am Main
Germany
You can request more information about this medicinal product from the local representative of the marketing authorisation holder:
Belgium/Belgique/Belgien Sanofi Belgium Tel: +32 (0)2 710 54 00 | Lithuania Swixx Biopharma UAB Tel: +370 5 236 91 40 |
Swixx Biopharma EOOD Tel: +359 (0)2 4942 480 | Luxembourg/Luxemburg Sanofi Belgium Tel: +32 (0)2 710 54 00 (Belgique/Belgien) |
Czech Republic Sanofi s.r.o. Tel: +420 233 086 111 | Hungary SANOFI-AVENTIS Zrt. Tel: +36 1 505 0050 |
Denmark Sanofi A/S Tel: +45 45 16 70 00 | Malta Sanofi S.r.l. Tel: +39 02 39394275 |
Germany Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH Tel: 0800 52 52 010 Tel from abroad: +49 69 305 21 131 | Netherlands Sanofi B.V. Tel: +31 20 245 4000 |
Estonia Swixx Biopharma OÜ Tel: +372 640 10 30 | Norway sanofi-aventis Norge AS Tel: +47 67 10 71 00 |
Greece Sanofi-Aventis Μονοπρóσωπη ΑΕΒΕ Tel: +30 210 900 16 00 | Austria sanofi-aventis GmbH Tel: +43 1 80 185 – 0 |
Spain sanofi-aventis, S.A. Tel: +34 93 485 94 00 | Poland Sanofi Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 280 00 00 |
France Sanofi Winthrop Industrie Tel: 0 800 222 555 Call from abroad: +33 1 57 63 23 23 | Portugal Sanofi - Produtos Farmacêuticos, Lda Tel: +351 21 35 89 400 |
Croatia Swixx Biopharma d.o.o. Tel: +385 1 2078 500 | Romania Sanofi Romania SRL Tel: +40 (0) 21 317 31 36 |
Ireland sanofi-aventis Ireland Ltd. T/A SANOFI Tel: +353 (0) 1 403 56 00 | Slovenia Swixx Biopharma d.o.o. Tel: +386 1 235 51 00 |
Iceland Vistor hf. Tel: +354 535 7000 | Slovakia Swixx Biopharma s.r.o. Tel: +421 2 208 33 600 |
Italy Sanofi S.r.l. Tel: 800 131212 (technical questions) 800 536389 (other questions) | Finland Sanofi Oy Tel: +358 (0) 201 200 300 |
Cyprus C.A. Papaellinas Ltd. Tel: +357 22 741741 | Sweden Sanofi AB Tel: +46 (0)8 634 50 00 |
Latvia Swixx Biopharma SIA Tel: +371 6 616 47 50 | United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) sanofi-aventis Ireland Ltd. T/A SANOFI Tel: +44 (0) 800 035 2525 |
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet:<{MM/AAAA}><{month AAAA}>.
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency web site: http://www.ema.europa.eu/
HYPERGLYCEMIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA
If you are taking insulin, you should always carry:
- Foods that contain sugar, such as glucose tablets or a sugary drink (at least 20 grams).
- Information that indicates you have diabetes.
Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels)
If your blood sugar level is too high (hyperglycemia), you may not have injected enough insulin.
Reasons why hyperglycemia may occur
Some examples:
- You did not inject Suliqua or did not inject enough.
- Your medicine is less effective, for example because it was not stored correctly.
- Your pen is not working properly.
- You are doing less exercise than usual.
- You are under stress - such as emotional distress or nervousness.
- You have an injury, infection, or fever, or have had an operation.
- You are taking or have taken certain medications (see section 2, "Using Suliqua with other medications").
Warning signs of hyperglycemia:
Thirst, increased need to urinate, fatigue, dry skin, redness of the face, loss of appetite, low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, and presence of glucose and ketone bodies in the urine. Stomach pain, deep and rapid breathing, feeling sleepy or passing out (loss of consciousness) can be signs of a serious condition (ketoacidosis) caused by lack of insulin.
What to do if you experience hyperglycemia
- Check your blood sugar level, if it is high, as your doctor or nurse told you, check your ketone level in your urine as soon as you notice any of the warning signs mentioned above.
- Contact your doctor immediately if you have severe hyperglycemia or ketoacidosis. This should always be treated by a doctor, usually in a hospital.
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar levels)
If your blood sugar level drops too low, you may pass out (lose consciousness). Severe hypoglycemia can cause a heart attack or brain damage and can be life-threatening. You should learn to recognize the signs that indicate your blood sugar level is dropping, so you can take the necessary measures to prevent the situation from getting worse.
Reasons why hypoglycemia may occur
Some examples:
- You inject too much Suliqua.
- You miss meals or delay them.
- You do not eat enough, or eat foods that contain fewer carbohydrates than usual. Artificial sweeteners are not carbohydrates.
- You drink alcohol, especially if you do not eat much.
- You lose carbohydrates due to vomiting or diarrhea.
- You are doing more exercise than usual or a different type of physical activity.
- You are recovering from an injury, operation, or other types of stress.
- You are recovering from an illness or fever,
- You are taking or have stopped taking certain medications (see section 2, "Other medications and Suliqua").
It is also more likely that hypoglycemia will occur if:
- You have just started treatment with Suliqua – if hypoglycemia occurs, it is more likely to happen in the morning.
- Your blood sugar levels are almost normal or unstable.
- You change the area of the skin where you inject Suliqua. For example from the thigh to the upper arm.
- You have a serious kidney or liver disease, or some other disease such as hypothyroidism.
Warning signs of hypoglycemia:
The first signs can be generally in your body. Examples of signs that your blood sugar level is dropping too low or too quickly are: sweating, damp and sticky skin, anxiety, rapid and irregular heartbeat, high blood pressure, and palpitations. These signs often occur before the signs of low blood sugar in the brain.
The signs in your brain include: headache, feeling very hungry, nausea, vomiting, feeling tired, drowsiness, agitation, sleep problems, aggressive behavior, difficulty concentrating, reduced reaction capacity, depression, feeling confused, difficulty speaking (sometimes, complete loss of speech), change in vision, tremors, inability to move (paralysis), tingling in hands or arms, feeling numb and tingling often around the mouth, feeling dizzy, loss of self-control, inability to take care of oneself, convulsions, loss of consciousness.
Situations in which the signs of hypoglycemia may be less clear:
The first warning signs of hypoglycemia may change, weaken, or be absent if:
- You are an elderly person.
- You have had diabetes for a long time.
- You have a certain type of nerve disease (called "diabetic autonomic neuropathy").
- You have recently had a large drop in blood sugar (for example, the day before).
- Your blood sugar level remains low.
- Your blood sugar level is always more or less "normal" or your diabetes control has improved significantly recently.
- You have recently changed from an animal insulin to an industrial insulin like Suliqua.
- You are taking or have taken certain medications (see section 2, "Other medications and Suliqua").
In these cases, you may experience severe hypoglycemia (and even pass out) before you realize what is happening. Always be familiar with your warning signs. If necessary, you may need to perform blood sugar tests more frequently. This can help identify mild hypoglycemic episodes. If you have difficulty recognizing your warning signs, you should avoid situations (such as driving a car) that could put you or others at risk due to hypoglycemia.
What to do if you experience hypoglycemia
- Do not inject insulin. Immediately ingest 15 to 20 grams of sugar, such as glucose, sugar cubes, or a sugary drink. Do not drink or eat foods that contain artificial sweeteners (such as diet drinks), as they do not help treat low blood sugar.
- You may need to eat something (such as bread or pasta) that increases your blood sugar level in the long term, especially if your next meal is not suitable. Ask your doctor or nurse if you are not sure what to eat.
With Suliqua, recovery from low blood sugar may be delayed because it contains a long-acting insulin (insulin glargine).
- Check your blood glucose level after 10-15 minutes of taking sugar. If your glucose levels are still too low (<4 mmol/l) or if hypoglycemia recurs, take another 15 to 20 grams of sugar.
- Consult a doctor immediately if you are unable to control hypoglycemia or if it recurs.
What others should do if you experience hypoglycemia
Inform your family, friends, and people close to you that you need urgent medical help if you are unable to swallow or if you pass out (lose consciousness).
You will need glucose or glucagon (a medication that increases blood sugar levels). It should be administered even if you are not sure if you are experiencing hypoglycemia.
You should check your blood sugar level immediately after ingesting glucose to confirm that you are actually experiencing hypoglycemia.
Suliqua 100 units/ml + 50 micrograms/ml solution for injection in pre-filled pen (10-40).
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Read the Leaflet and these Instructions for Use before the First Use of Suliqua
Suliqua (10-40) SoloStar pen contains insulin glargine and lixisenatide. The combination of medications in this pen is for daily injection of 10 to 40 dose steps of Suliqua.
- Never reuse needles.If you do, you may not get your full dose (underdose) or get too much dose (overdose), as the needle may become blocked.
- Never use a syringe to withdraw the medication from your pen.If you do, you may not get the correct dose of medication.
Keep these Instructions for Use for future reference.
Important Information
- Never share your pen - it is for you only.
- Never use your pen if it is damaged or if you are not sure it is working properly.
- Always perform a safety test. See STEP 3.
- Always carry a spare pen and spare needles, in case they are lost or stop working.
- Always check the label on the pen before using it to make sure you have the correct pen.
Learning to Inject
- Ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse how to inject yourself before using your pen.
- Ask for help if you have problems handling the pen, for example if you have vision problems.
- Read all these instructions before using your pen. If you do not follow all these instructions, you may receive too much or too little medication.
Do you need help?
If you have questions about Suliqua, the pen, or diabetes, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Additional Items You Will Need:
- a new sterile needle (see STEP 2).
- a puncture-resistant container for needles (see Dispose of the pen).
Injection Sites
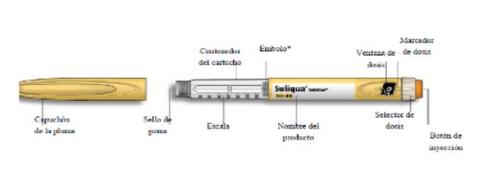
Know Your Pen
- You will not see the plunger until you have injected a few doses
STEP 1: Check Your Pen
For the first use of a new pen, take a new pen out of the refrigerator at least 1hour before your injection. Injecting the medication when it is cold is more painful. After use, the pen will be stored below 25°C.
- Check the name and expiration date on the label of your pen.
- Make sure you have the correct medication. This pen is peach-colored with an orange injection button.
- Do not use this pen if you need a daily dose of less than 10 dose steps or if you need more than 40 dose steps. Agree with your doctor which pen is suitable for your needs.
- Do notuse the pen after the expiration date.

- Remove the pen cap.
- Check that the medication is clear.
- Look at the transparent cartridge container. Do notuse the pen if the medication is cloudy, has color, or contains particles.
STEP 2: Attach a New Needle
- Do notreuse needles. Always use a new sterile needle for each injection. This will help prevent needle blockage, contamination, and infection.
- Always use needles compatible with your Suliqua pen.
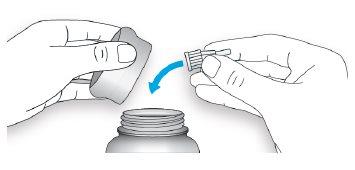
- Take a new needle and remove the protective seal.
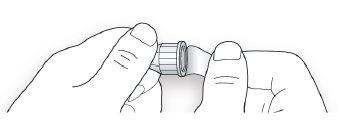
- Hold the needle straight and screw it onto the pen until it is fixed. Do not overtighten.
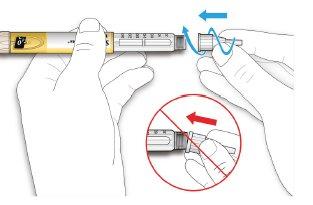
- Remove the outer needle cap. Save it for later.
- Remove the inner needle cap and discard it.
If you try to put it back on, you may accidentally prick yourself with the needle.
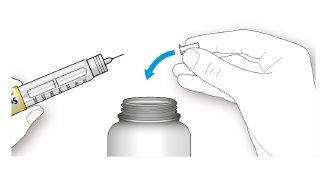
Handling Needles
- Be careful when handling needles to avoid puncture injuries and cross-infection.
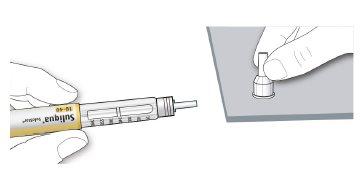
STEP 3: Perform a Safety Test
Always perform a safety test before each injection to:
- Check that your pen and needle are working correctly.
- Make sure you receive the correct dose.
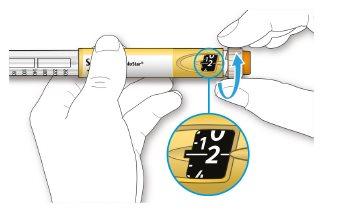
- Select 2 dose steps by turning the dose selector until the dose marker is at the 2 mark.
- Press the injection button all the way down.
- If medication comes out of the needle tip, your pen is working correctly and the dose selector will return to "0".
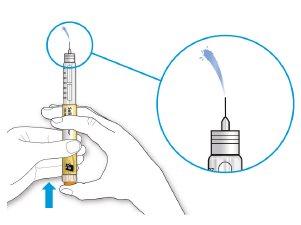
Doctor with a needle inserted, enlarged detail showing the expulsion of the medication and blue arrow indicating direction">
If no liquid comes out:
- It is possible that you need to repeat this step up to 3 times, before you see the medication come out.
- If the medication does not come out after the third time, it is possible that the needle is blocked. If this happens:
- change the needle (see STEP 6 and STEP 2),
- then repeat the safety test (STEP 3).
- Do notuse your pen if the medication still does not come out of the needle tip. Use a new pen.
- Do notuse a syringe to extract the medication from your pen.
If you see air bubbles
- You may see air bubbles in the medication. This is normal, they will not harm you.
STEP 4: Select the dose
- Use this pen only to inject a single daily dose of 10 to 40 dose steps.
- Do notselect a dose or press the injection button while the needle is not in place, as you could damage your pen.
- Make sure the needle is in place and the dose is set to “0”.

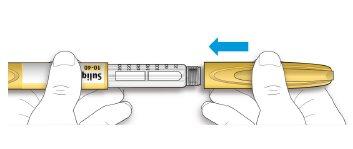
- Turn the dose selector until the dose marker is aligned with your dose.
- If you exceed your dose, you can turn it back.
- If there are not enough dose steps left in your pen to administer your dose, the dose selector will stop at the number of dose steps left.
- If you cannot select your full prescribed dose, use a new pen or inject the remaining dose steps and use a new pen to complete your dose. Only in this case, it would be appropriate to inject a partial dose of less than 10 dose steps. Always use another Suliqua (10-40) SoloStar pen to complete your dose and not another pen.
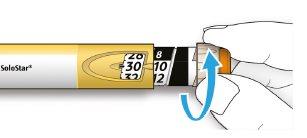
How to read the dose window
The even numbers are displayed in line with the dose indicator and the odd numbers are displayed as a line between the even numbers.

29 units selected
- Do notuse this pen if your single daily dose is less than 10 dose steps, which appears as white numbers on a black background.
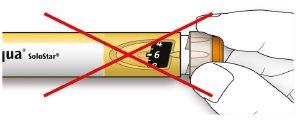
Medication units in your pen
- Your pen contains a total of 300 dose steps. You can select your dose in 1 dose step increments.
- Do notuse this pen if you need a single daily dose of less than 10 dose steps or more than 40 dose steps. Consult your doctor to determine which pen is suitable for your needs.
- Each pen contains more than one dose.
STEP 5: Inject the dose
- If you have trouble pressing the injection button, do notforce it, as you could break your pen.
- Change the needle (see STEP 6Remove the needle and STEP 2Put on a new needle) and then perform the safety test.
- If you still have trouble pressing the injection button, use a new pen.
- Do notuse a syringe to extract the medication from your pen.
- Choose an injection site as shown in the previous drawing.
- Push the needle into your skin, just as your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse has taught you.
- Do not press the injection button yet.
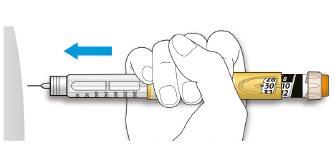
- Place your thumb on the injection button. Press it all the way down and hold it.
- Do notpress the button at an angle: your thumb could block the dose selector and prevent it from turning.
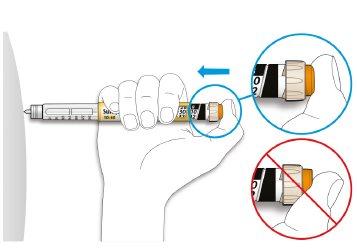
- Hold the injection button down and when you see “0” in the dose window, count slowly to 10.
- This will ensure that you receive your full dose.
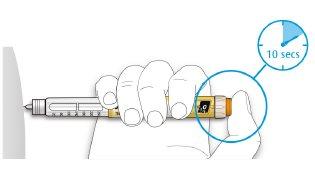
- After holding it down and counting slowly to 10, release the injection button. Then, remove the needle from your skin.
STEP 6: Remove the needle
- Be careful when handling needles to avoid puncture injuries and cross-infection.
- Do notput the inner needle cap back on.
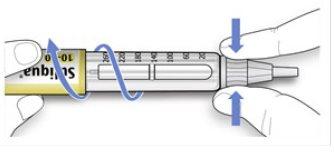
AHold the wider part of the outer needle cap. Keep the needle straight and direct it towards the outer needle cap. Then press firmly.
- The needle may puncture the cap if it is placed at an angle.
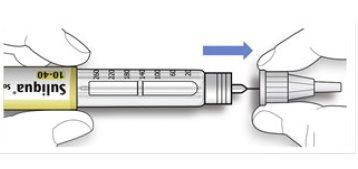
- Hold and twist the wider part of the outer needle cap. Turn the pen several times with your other hand to remove the needle.
- Try again if the needle does not come out the first time.
- Discard the used needle in a puncture-resistant container (see “Disposing of your pen” at the end of these Instructions for Use).
- Put the pen cap back on.
- Do not put the pen back in the refrigerator.
How to store your pen
Before first use
- Store new pens in the refrigerator, between 2°C and 8°C.
- Do notfreeze.
After first use
- Store your pen at room temperature, below 25 ºC.
- Do notput your pen back in the refrigerator.
- Do notstore your pen with the needle attached.
- Store your pen with the cap on.
- Only use your pen for 28 daysafter first use.
How to care for your pen
Treat your pen with care
- If you think your pen may be damaged, do nottry to repair it. Use a new one.
Protect your pen from dust and dirt
- You can clean the outside of your pen with a damp cloth (only with water). Do notget your pen wet, wash it, or lubricate it, as this could damage it.
Disposing of your pen
- Remove the needle before disposing of your pen.
- Dispose of your used pen as instructed by your healthcare professional or local authorities.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to SULIQUA 100 units/mL + 50 micrograms/mL pre-filled pen solution for injectionDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 U/ml + 33 micrograms/mlActive substance: insulin glargine and lixisenatideManufacturer: Sanofi Winthrop IndustriePrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 U/mlActive substance: insulin glargineManufacturer: Eli Lilly Nederland B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, UnknownActive substance: insulin glargineManufacturer: Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for SULIQUA 100 units/mL + 50 micrograms/mL pre-filled pen solution for injection
Discuss questions about SULIQUA 100 units/mL + 50 micrograms/mL pre-filled pen solution for injection, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















