SIGNIFOR 0.6 mg INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use SIGNIFOR 0.6 mg INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Signifor0.3mg solution for injection
Signifor 0.6mgsolution for injection
Signifor 0.9mgsolution for injection
pasireotide
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Signifor and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Signifor
- How to use Signifor
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Signifor
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Signifor and what is it used for
Signifor is a medicine that contains the active substance pasireotide. It is used to treat Cushing's disease in adult patients for whom surgery is not an option or for whom surgery has failed.
Cushing's disease is caused by an increase in the size of the pituitary gland (a gland located at the base of the brain) called a pituitary adenoma. This causes the body to produce more of a hormone called adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which in turn causes an increase in the production of another hormone called cortisol.
The human body naturally produces a substance called somatostatin, which blocks the production of certain hormones, including ACTH. Pasireotide works in a very similar way to somatostatin. Signifor is therefore able to block the production of ACTH, helping to control the overproduction of cortisol and improve the symptoms of Cushing's disease.
If you have any questions about how Signifor works or why you have been prescribed this medicine, ask your doctor.
2. What you need to know before you use Signifor
Do not use Signifor:
- if you are allergic to pasireotide or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have severe liver problems.
Warnings and precautions
Tell your doctor before you start using Signifor if you have or have ever had:
- problems with blood sugar levels, either too high (as in hyperglycemia/diabetes) or too low (hypoglycemia);
- heart problems such as a recent heart attack, congestive heart failure (a type of heart disease where the heart cannot pump enough blood through the body) or sudden, severe chest pain (usually felt as pressure, heaviness, tightness, or pain in the chest);
- a heart rhythm disorder, such as an irregular heartbeat or an abnormal electrical signal called "prolonged QT interval" or "QT prolongation";
- low levels of potassium or magnesium in the blood;
- gallstones.
During your treatment with Signifor
- Signifor controls the overproduction of cortisol. The control may be too strong and may cause signs or symptoms associated with a lack of cortisol, such as extreme weakness, tiredness, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, or low blood pressure. If this happens, tell your doctor immediately.
- Signifor may cause an increase in blood sugar levels. Your doctor may check your blood sugar levels and start treatment or adjust your antidiabetic medication.
- Signifor may slow your heart rate. Your doctor may check your heart rate using a machine that measures the electrical activity of the heart (an "ECG" or electrocardiogram). If you are using a medicine to treat a heart problem, your doctor may also need to adjust the dose.
- your doctor may also periodically check your gallbladder, liver enzymes, and pituitary hormones, as they may be affected by this medicine.
Children and adolescents
Do not give this medicine to children and adolescents under 18 years of age because there is no data available for this age group.
Other medicines and Signifor
Signifor may affect the way other medicines work. If you are using other medicines at the same time as Signifor (including non-prescription medicines), your doctor may need to check your heart more carefully or change the dose of Signifor or the other medicines. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines. In particular, tell your doctor if you are using:
- medicines to treat irregular heartbeats, such as those containing disopyramide, procainamide, quinidine, sotalol, dofetilide, ibutilide, amiodarone, or dronedarone;
- medicines to treat bacterial infections (by mouth: clarithromycin, moxifloxacin; by injection: erythromycin, pentamidine);
- medicines to treat fungal infections (ketoconazole, except in shampoo);
- medicines to treat certain psychiatric disorders (chlorpromazine, thioridazine, fluphenazine, pimozide, haloperidol, tiapride, amisulpride, sertindole, methadone);
- medicines to treat hay fever and other allergies (terfenadine, astemizole, mizolastine);
- medicines used to prevent or treat malaria (chloroquine, halofantrine, lumefantrine);
- medicines to control blood pressure, such as:
- beta blockers (metoprolol, carteolol, propranolol, sotalol)
- calcium channel blockers (bepridil, verapamil, diltiazem)
- cholinesterase inhibitors (rivastigmine, physostigmine);
- medicines to control the balance of electrolytes (potassium, magnesium) in the body.
It is particularly important to tell your doctor if you are using:
- cyclosporin (used in organ transplantation to reduce the activity of the immune system);
- medicines to treat high or low blood sugar levels, such as:
- insulin;
- metformin, liraglutide, vildagliptin, nateglinide (antidiabetic medicines).
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
- You should not use Signifor during pregnancy unless clearly necessary. If you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant, you should tell your doctor, who will decide with you whether you can use Signifor during your pregnancy.
- You should not breastfeed while using Signifor. It is not known whether Signifor passes into breast milk.
- If you are a sexually active woman, you should use an effective method of contraception during treatment. Ask your doctor about the need for contraception before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Signifor may have a minor effect on your ability to drive and use machines, as some of the side effects you may experience while using Signifor, such as dizziness, headache, and tiredness, may reduce your ability to drive and use machines safely.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Signifor
Signifor contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per dose; this is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Signifor
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as told by your doctor. If you are not sure, ask your doctor or pharmacist again. This medicine comes in an ampoule, which is a small glass container.
How much Signifor to use
The recommended dose is one ampoule of Signifor 0.6 mg twice a day. Using Signifor at the same time each day will help you remember when to use your medicine. After starting treatment, your doctor may decide to increase the dose to one ampoule of Signifor 0.9 mg twice a day.
If side effects occur, your doctor may temporarily reduce the dose by 0.3 mg per injection.
If you have liver disease before starting treatment with Signifor, your doctor may decide to start treatment with a dose of one ampoule of Signifor 0.3 mg twice a day.
Ampoules of Signifor of different strengths (0.3 mg, 0.6 mg, and 0.9 mg) are available to administer the specific dose prescribed by your doctor.
Your doctor will regularly check how you respond to treatment with Signifor and decide what dose is best for you.
How to use Signifor
Your doctor or nurse will teach you how to inject Signifor yourself. You should also read the instructions at the end of this leaflet. If you have any questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Signifor should be administered subcutaneously. This means it is injected with a short needle into the fatty tissue just under the skin. The thighs and abdomen are suitable areas for subcutaneous injection. Using a different site from the previous injection for each injection will help avoid pain and skin irritation. You should also avoid injecting into areas that are painful or where the skin is irritated.
Do not use Signifor if you notice that the solution is not clear or contains particles. The solution should be free of particles, clear, and colorless.
How long to use Signifor
You should continue to use Signifor for as long as your doctor tells you.
If you use more Signifor than you should
If you have accidentally used more Signifor than your doctor prescribed, contact your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse immediately.
If you forget to use Signifor
Do not inject a double dose of Signifor to make up for forgotten doses. If you forget to inject a dose of Signifor, simply inject the next dose at the scheduled time.
If you stop using Signifor
If you stop using Signifor, your cortisol levels may increase again and your symptoms may return. Therefore, do not stop using Signifor unless your doctor tells you to.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects can be serious. Tell your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Change in blood sugar levels. You may notice excessive thirst, urination, increased appetite with weight loss, tiredness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain.
- Gallstones or associated complications. You may experience fever, chills, yellowing of the skin/eyes, sudden back pain or pain in the right side of the abdomen.
- Extreme tiredness.
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Low cortisol levels. You may experience extreme weakness, tiredness, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, and low blood pressure.
- Slow heart rate.
- Low blood pressure. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded, or faint when standing up.
- Problems with bile flow (cholestasis). You may experience yellowing of the skin, dark urine, pale stools, and itching.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis).
Other side effects of Signifor may include:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Pain at the injection site
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Prolonged QT interval (an abnormal electrical signal in your heart that can be seen on tests)
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Hair loss
- Itching (pruritus)
- Muscle pain (myalgia)
- Joint pain (arthralgia)
- Abnormal liver function test results
- Abnormal pancreas function test results
- Abnormal blood coagulation properties
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Low red blood cell count (anemia)
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- High levels of ketone bodies (a group of substances produced in the liver) in the urine or blood (diabetic ketoacidosis) as a complication of high blood sugar levels. You may experience fruity breath, breathing problems, and confusion.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly via the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Signifor
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the ampoule label and carton after "EXP"/"CAD". The expiry date is the last day of the month shown.
- Store in the original package to protect from light.
- Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Signifor
- The active ingredient is pasireotide.
Signifor 0.3 mg: A 1 ml solution ampoule contains 0.3 mg of pasireotide (as pasireotide diaspartate).
Signifor 0.6 mg: A 1 ml solution ampoule contains 0.6 mg of pasireotide (as pasireotide diaspartate).
Signifor 0.9 mg: A 1 ml solution ampoule contains 0.9 mg of pasireotide (as pasireotide diaspartate).
- The other components are mannitol, tartaric acid, sodium hydroxide, and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of Signifor and Container Contents
Signifor injectable solution is a clear and colorless solution in an ampoule. Each ampoule contains 1 ml of injectable solution.
Signifor is available in packs containing 6 ampoules or in multipacks containing 18 (3 packs of 6), 30 (5 packs of 6), or 60 (10 packs of 6) ampoules.
In your country, only some doses and pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Recordati Rare Diseases
Immeuble Le Wilson
70 avenue du Général de Gaulle
92800 Puteaux
France
Manufacturer
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Roonstrasse 25
D-90429 Nürnberg
Germany
Recordati Rare Diseases
Immeuble Le Wilson
70 avenue du Général de Gaulle
92800 Puteaux
France
Recordati Rare Diseases
Eco River Parc
30 rue des Peupliers
92000 Nanterre
France
You can request more information about this medicinal product by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien Recordati Tel: +32 2 46101 36 | Lietuva Recordati AB. Tel: +46 8 545 80 230 Švedija |
??????? Recordati Rare Diseases Tel: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 ??????? | Luxembourg/Luxemburg Recordati Tel: +32 2 46101 36 Belgique/Belgien |
Ceská republika Recordati Rare Diseases Tel: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 Francie | Magyarország Recordati Rare Diseases Tel: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 Franciaország |
Danmark Recordati AB. Tlf: +46 8 545 80 230 Sverige | Malta Recordati Rare Diseases Tel: +33 1 47 73 64 58 Franza |
Deutschland Recordati Rare Diseases Germany GmbH Tel: +49 731 140 554 0 | Nederland Recordati Tel: +32 2 46101 36 België |
Eesti Recordati AB. Tel: +46 8 545 80 230 Rootsi | Norge Recordati AB. Tlf: +46 8 545 80 230 Sverige |
Ελλ?δα Recordati Hellas Τηλ: +30 210 6773822 | Österreich Recordati Rare Diseases Germany GmbH Tel: +49 731 140 554 0 Deutschland |
España Recordati Rare Diseases Spain S.L.U. Tel: +34 91 659 28 90 | Polska Recordati Rare Diseases Tel: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 Francja |
France Recordati Rare Diseases Tél: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 | Portugal Jaba Recordati S.A. Tel: +351 21 432 95 00 |
Hrvatska Recordati Rare Diseases Tél: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 Francuska | România Recordati Rare Diseases Tel: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 Franta |
Ireland Recordati Rare Diseases Tél: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 France | Slovenija Recordati Rare Diseases Tel: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 Francija |
Ísland Recordati AB. Simi: +46 8 545 80 230 Svíþjóð | Slovenská republika Recordati Rare Diseases Tel: +33 (0)1 47 73 64 58 Francúzsko |
Italia Recordati Rare Diseases Italy Srl Tel: +39 02 487 87 173 | Suomi/Finland Recordati AB. Puh/Tel: +46 8 545 80 230 Sverige |
Κ?προς Recordati Rare Diseases Τηλ: +33 1 47 73 64 58 Γαλλ?α | Sverige Recordati AB. Tel: +46 8 545 80 230 |
Latvija Recordati AB. Tel: +46 8 545 80 230 Zviedrija | United Kingdom Recordati Rare Diseases UK Ltd. Tel: +44 (0)1491 414333 |
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet:
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu. There are also links to other websites on rare diseases and orphan medicines.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF SIGNIFOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
This medicinal product comes in an ampoule, i.e., a small glass container. Signifor must be administered using disposable syringes and needles for injection.
Your doctor or nurse will have given you instructions on how to use Signifor ampoules. However, before using the ampoule, read the following information carefully. If you are unsure about how to administer the injection yourself or if you have any doubts, contact your doctor or nurse for help.
The injection can be prepared using either two different needles for withdrawing and injecting the solution or a short fine needle for injection for these two steps. Based on local clinical practice, your doctor or nurse will inform you about which method to use. Please follow their instructions.
Store the Signifor ampoules according to the storage conditions indicated on the carton.
Important Safety Information
Caution: Keep ampoules out of the reach of children.
What You Need
To inject yourself, you will need:
- A Signifor ampoule
- An alcohol swab or similar
- A sterile syringe
- A sterile long thick needle with a blunt tip for withdrawing the solution (your doctor or nurse will inform you if you need it)
- A sterile short fine needle
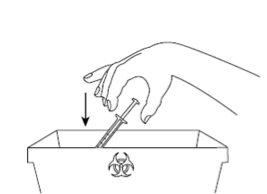
- A needle container or another rigid closed container for disposal
Injection Site
The injection site is the place on your body where the injection will be administered. Signifor is administered subcutaneously. This means it is injected using a short needle into the fatty tissue just under the skin. The thighs and abdomen are suitable areas for subcutaneous injection. Using a different site from the previous injection will avoid pain and irritation. You should also avoid injecting into areas that are painful or where the skin is irritated.
Preparation
When you are ready to administer the injection yourself, carefully follow the following steps:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with water and soap.
- Use disposable syringes and needles each time you administer an injection. Use syringes and needles only once. Nevershare needles or syringes.
- Remove the ampoule from the carton.
- Inspect the ampoule. DO NOT USE IT if it is broken or if the liquid appears cloudy or contains particles. In all these cases, return the complete package to the pharmacy.
To reduce local discomfort, it is recommended that the solution be kept at room temperature before administration.
The ampoules should be opened just before administration, and any unused portion should be discarded.
Check the Expiration Date and Dose
Check the expiration date on the ampoule label (after "EXP") and check that the ampoule contains the dose prescribed by your doctor.
DO NOT USE IT if the medicinal product has expired or if the dose is not correct. In both cases, return the complete package to the pharmacy.
How to Inject Signifor
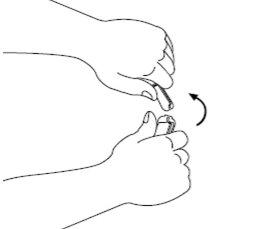
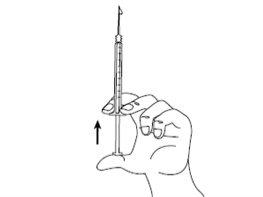
| Step 1: Signifor injectable solution is contained in a breakable ampoule. The colored dot on the top indicates the position of the break point on the neck of the ampoule. Gently tap the ampoule with your finger to ensure that there is no liquid in the top when you open it. |
| Step 2: Recommended procedure: Hold the ampoule vertically with the colored dot facing away. Hold the base of the ampoule in one hand. Keeping your thumbs together above and below the neck, break the top of the ampoule at the break point. Once the ampoule is open, place it vertically on a clean and flat surface. |
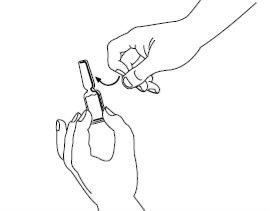
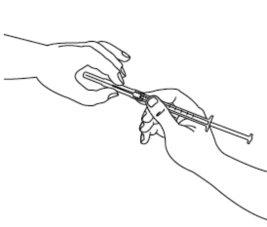
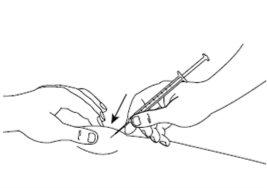
| Step 3: Take the sterile syringe and insert the needle. If you have been instructed to use two needles, you must use the long thick needle with a blunt tip for this step. Before proceeding with step 4, clean the injection site with a cotton swab. |
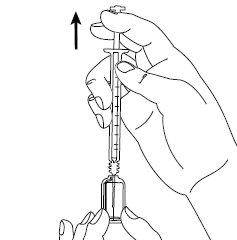
| Step 4: Remove the needle cover. Insert the needle into the ampoule and pull the plunger to withdraw the complete contents of the ampoule into the syringe. If you have been instructed to use two needles, you must now replace the long needle with the short needle. |
| Step 5: Hold the syringe in one hand between two fingers, placing your thumb on the bottom of the plunger. Gently tap the syringe with your fingers to eliminate air bubbles. Make sure there are no air bubbles in the syringe by pressing the plunger until the first drop appears at the tip of the needle. Do not let the needle touch anything. You are now ready for the injection. |
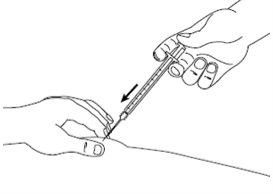
| Step 6: Gently pinch the skin at the injection site and, keeping the needle at an angle of approximately 45 degrees (as shown in the figure), insert it into the injection site. Gently pull the plunger to check that you have not punctured a blood vessel. If you see blood in the syringe, first remove the needle from the skin, and then replace the short needle with a new one and insert it into a different injection site. |
| Step 7: With the skin still pinched, slowly press the plunger to the end, injecting the entire solution. Keep the plunger pressed and the syringe in place for 5 seconds. |
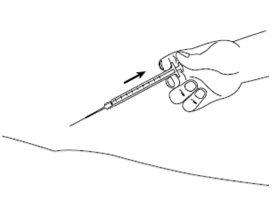
| Step 8: Slowly release the skin fold and gently remove the needle. Put the needle cover back on. |
| Step 9: Immediately dispose of the used syringe and needle in a needle container or another rigid closed container for disposal. The disposal of unused medicinal product and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations. |
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to SIGNIFOR 0.6 mg INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.3 mgActive substance: pasireotideManufacturer: Recordati Rare DiseasesPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.3 mgActive substance: pasireotideManufacturer: Recordati Rare DiseasesPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.9 mgActive substance: pasireotideManufacturer: Recordati Rare DiseasesPrescription required
Online doctors for SIGNIFOR 0.6 mg INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about SIGNIFOR 0.6 mg INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions