
SIALANAR 320 micrograms/ml ORAL SOLUTION

How to use SIALANAR 320 micrograms/ml ORAL SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Sialanar 320 micrograms/ml oral solution
Glycopyrronium
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child starts taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as your child's.
- If your child experiences any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What Sialanar is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you give Sialanar
- How to use Sialanar
- Possible side effects
- Storing Sialanar
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Sialanar is and what it is used for
Sialanar is a medicine that contains the active substance glycopyrronium.
Glycopyrronium belongs to a group of medicines known as quaternary ammonium anticholinergics, which are agents that block or reduce transmission between nerve cells.
This reduced transmission can deactivate the cells that produce saliva.
Sialanar is used to treat excessive saliva production (sialorrhoea) in adolescents and children aged 3 years and older.
Sialorrhoea (drooling or excessive salivation) is a frequent symptom of many diseases that affect the nerves and muscles. It is mainly caused by poor control of the facial muscles. Acute sialorrhoea may be associated with inflammation, dental infections, or mouth infections.
Sialanar acts on the salivary glands to reduce saliva production.
2. What you need to know before you give Sialanar
Do not give Sialanar if your child:
- is allergic to glycopyrronium or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- is pregnant or breastfeeding
- has glaucoma (increased pressure in the eye)
- is unable to empty the bladder completely (urinary retention)
- has severe kidney problems
- has a stomach obstruction (pyloric stenosis) or intestinal obstruction that causes vomiting
- has diarrhea (liquid and frequent stools)
- has ulcerative colitis (inflammation of the intestine)
- has stomach pain and bloating (paralytic ileus)
- has myasthenia gravis (muscle weakness and fatigue)
- is taking one of the following medicines (see section "Other medicines and Sialanar"):
oral solid dose of potassium chloride;
anticholinergic medicines.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before using Sialanar if your child has:
- heart disease, heart failure, irregular heartbeats, or high blood pressure
- gastrointestinal disorders (constipation; chronic heartburn and indigestion)
- high temperature (fever)
- inability to sweat normally
- kidney problems or difficulty passing urine
- abnormal blood-brain barrier (the layer of cells that surrounds the brain)
If you are not sure if any of the above situations apply to your child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before giving Sialanar.
Avoid exposing your child to high temperatures or very hot environments (hot weather, high ambient temperature) to avoid overheating and the possibility of heat syncope. Consult your child's doctor in case of hot weather to see if the dose of Sialanar should be reduced.
Reduced salivation may increase the risk of dental diseases, so your child's teeth should be brushed daily and regular dental health checks should be performed.
Children with kidney problems may receive a lower dose.
Check your child's pulse if they seem unwell. Inform the doctor in case of very low or very high heart rate.
Children under 3 years
This medicine is formulated as an oral formulation and a dose for use specifically in adolescents and children aged 3 years and older.
Sialanar is not recommended for children under 3 years.
Other medicines and Sialanar
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if your child is taking, has recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
In particular, taking Sialanar with the following medicines may affect how Sialanar or the mentioned medicines work or may increase the risk of side effects:
- oral solid dose of potassium chloride(see section "Do not give Sialanar if your child")
- anticholinergic medicines(see section "Do not give Sialanar if your child")
- anti-emetic medicinesused to treat nausea or vomiting, such as domperidone and metoclopramide
- topiramateused to treat epilepsy
- antihistaminesused to treat some allergies
- neuroleptics/antipsychotics(clozapine, haloperidol, phenothiazine), used to treat some mental illnesses
- skeletal muscle relaxants(botulinum toxin)
- antidepressants(tricyclic antidepressants)
- opioidsused to treat severe pain
- corticosteroidsused to treat inflammatory diseases
Consult your doctor or pharmacist for more information about the medicines to avoid while taking Sialanar.
Long-term safety
The long-term efficacy and safety of Sialanar have not been studied beyond 24 weeks of use. Continued use of Sialanar should be consulted with your child's doctor every 3 months to check that Sialanar is still suitable for your child.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
This medicine is intended for use in children and adolescents. Sialanar should not be given if the patient is pregnant (or could be pregnant) or breastfeeding (see section 2 "Do not give"). Consult your child's doctor if the use of contraceptives is necessary.
Driving and using machines
Sialanar may affect vision and coordination. This may affect the performance of hazardous tasks such as driving, cycling, or using machines. After taking Sialanar, the patient should not drive a vehicle, cycle, or operate a machine until they have fully recovered from the effect on their vision and coordination. Consult your doctor if you need more information.
Sialanar contains sodium and benzoic acid salt (E211)
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per maximum dose, i.e., it is essentially "sodium-free". This medicine contains 2.3 mg of benzoic acid salt (E211) per ml.
3. How to use Sialanar
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. If you are not sure, ask your doctor.
Children aged 3 years and older and adolescents under 18 years:
Your doctor will decide the correct dose of Sialanar. The initial dose will be calculated according to your child's weight. Your child's doctor will decide on dose increases, using the following table as a guide, and will depend on both the effect of Sialanar and the side effects your child experiences (for this reason, the following table shows several dose levels). Section 4 includes possible side effects related to the use of Sialanar. These should be discussed with your child's doctor at all medical visits, including those for dose increases and decreases, and at any other time you consider it necessary.
Your child should be monitored at regular intervals (at least every 3 months) to check that Sialanar is still the right treatment for them.
Weight | Dose level 1 | Dose level 2 | Dose level 3 | Dose level 4 | Dose level 5 |
kg | ml | ml | ml | ml | ml |
13-17 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 3.0 |
18-22 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 3.2 | 4.0 |
23-27 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
28-32 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 3.6 | 4.8 | 6.0 |
33-37 | 1.4 | 2.8 | 4.2 | 5.6 | 6.0 |
38-42 | 1.6 | 3.2 | 4.8 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
43-47 | 1.8 | 3.6 | 5.4 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
≥48 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
Give the prescribed dose to your child three times a day.
The dose should be given 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after meals.
It is important that the dose is given at the same time in relation to meals. Do not give with foods high in fat.
Method of administration
Sialanar should be given by mouth.
Instructions for use
Using the oral syringe
Remove the child-resistant cap from the bottle.
Insert the syringe adapter into the neck of the bottle (the pharmacist may have already done this).
Insert the end of the oral syringe into the syringe adapter and make sure it is securely attached.

Hold the oral syringe and tilt the bottle downwards. Carefully press the plunger down to the correct level (see tables for correct dose). Check that it is at the correct level. The maximum volume of the highest dose is 6 ml.
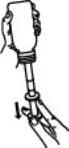
Tilt the bottle upwards.
Remove the oral syringe by holding the bottle and carefully turning the oral syringe.

Place the oral syringe inside your child's mouth and slowly press the plunger to carefully release the medicine.
After use, leave the syringe adapter in the neck of the bottle.
Replace the cap.
The oral syringe should be washed with hot water and allowed to dry after each use (i.e., three times a day).
If the medicine is given to your child through a feeding tube, wash the tube with 10 ml of water after administering the medicine.
If you give too much Sialanar to your child
It is important to make sure that the correct dose is given each time, to avoid the harmful effects that have been seen with Sialanar in case of dose errors or overdoses.
Check that the correct level has been reached in the syringe before giving Sialanar.
Consult a doctor immediately if too much Sialanar has been given to your child, even if your child seems to be well.
If you forget to give Sialanar
Give the next dose when it is due. Do not give a double dose to make up for the forgotten dose.
If you stop giving Sialanar to your child
No withdrawal effects are expected if Sialanar is stopped. Your child's doctor may decide to interrupt treatment with Sialanar if the side effects cannot be resolved by reducing the dose.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If any of the following serious side effects occur, stop using the medicine and consult a doctor urgently.
- Constipation (difficulty passing stools) – very common
- Difficulty passing urine (urinary retention) – very common
- Pneumonia (severe lung infection) – common
- Allergic reaction (rash, itching, red blistering skin rash, difficulty breathing or swallowing, dizziness) – frequency not known
The following side effects may be a sign of a serious allergic reaction. If they occur, take your child to the nearest emergency department and bring the medicine with you.
- Swelling mainly of the tongue, lips, face, or throat (signs of angioedema) – frequency not known
Other side effects are:
Very common side effects(may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Redness of the skin
- Nasal congestion
- Difficulty emptying the bladder completely
- Reduced secretions in the chest
- Irritability
Common side effects(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- Pneumonia (severe lung infection)
- Urinary tract infection
- Drowsiness
- Agitation
- Fever
- Nosebleeds
- Rash
Uncommon side effects(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Bad breath
- Fungal infection of the throat (candidiasis)
- Abnormal contractions of the digestive tract when food is ingested
- Disorder of the muscles and nerves of the intestine that causes obstruction or blockage
- Dilated pupils
- Involuntary eye movements
- Headache
- Dehydration
- Thirst in hot weather
Other side effects that occur with anticholinergics but whose frequency with glycopyrronium is not known
- Allergic reaction (rash, itching, red blistering skin rash, difficulty breathing or swallowing, dizziness)
- Severe allergic reaction (angioedema); signs include swelling mainly of the tongue, lips, face, or throat
- Irritability; attention deficit; frustration; mood changes; temper outbursts or explosive behavior; excessive sensitivity; seriousness or sadness; frequent episodes of crying; fear
- Insomnia (difficulty sleeping)
- Increased pressure in the eyes (which can cause glaucoma); photophobia (sensitivity to light); dry eyes
- Low heart rate followed by high heart rate, palpitations, and irregular heartbeats
- Sinus inflammation and swelling
- Nausea
- Dry skin
- Reduced sweating ability, which can cause fever and heat stroke
- Urgent need to urinate
Sometimes, side effects can be difficult to detect in patients with neurological problems who cannot easily express how they feel.
If you think a problematic side effect is occurring after increasing the dose, the dose should be reduced to the previously used dose and you should contact your doctor.
Tell your doctor if you notice any change in behavior or any other change in your child.
Reporting side effects
If your child experiences any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. Even if it is possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storing Sialanar
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Do not store above 25°C.
This medicine should be used within 2 months of opening the bottle.
Sialanar should not be used if the packaging is opened or damaged.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Packaging Contents and Additional Information
Sialanar Composition
The active ingredient is glycopyrronium.
Each ml of solution contains 400 micrograms of glycopyrronium bromide equivalent to 320 micrograms of glycopyrronium.
The other ingredients are sodium benzoate (E211), see section 2 (Sialanar contains sodium and benzoic acid salt), raspberry flavor (contains propylene glycol E1520), sucralose (E955), citric acid (E330), and purified water.
Appearance of Sialanar and Packaging Contents
Sialanar oral solution is a clear, colorless liquid. It is supplied in a 60 ml or 250 ml amber glass bottle in a cardboard box. Each box contains a bottle, an 8 ml oral syringe, and a syringe adapter. Only certain pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Proveca Pharma Ltd Marine House Clanwilliam Place Dublin 2
Ireland
Manufacturer
BCM Ltd
Nottingham
NG90 2PR
United Kingdom
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: month/YYYY
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency website:
http://www.ema.europa.eu.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to SIALANAR 320 micrograms/ml ORAL SOLUTIONDosage form: TABLET, 40 mgActive substance: otilonium bromideManufacturer: Laboratorios Cinfa S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 40 mgActive substance: otilonium bromideManufacturer: Neuraxpharm Spain S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 40 mgActive substance: otilonium bromideManufacturer: Laboratorios Menarini S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for SIALANAR 320 micrograms/ml ORAL SOLUTION
Discuss questions about SIALANAR 320 micrograms/ml ORAL SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















