
PHOXILIUM 1.2 mmol/L PHOSPHATE SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS/HEMOFILTRATION


How to use PHOXILIUM 1.2 mmol/L PHOSPHATE SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS/HEMOFILTRATION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
PHOXILIUM® 1.2 mmol/l of phosphate
Solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration
Calcium chloride dihydrate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, potassium chloride, disodium phosphate dihydrate
Read this package leaflet carefully before starting to use this medicine, as it contains important information for you.
- Keep this package leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- If you experience side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this package leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the package leaflet
- What Phoxilium is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before receiving Phoxilium
- How to use Phoxilium
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Phoxilium
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What Phoxilium is and what it is used for
Phoxilium, which belongs to the group of hemofiltration solutions, contains calcium chloride dihydrate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, potassium chloride, and disodium phosphate dihydrate.
Phoxilium is used in hospitals in intensive care treatments to correct chemical imbalances in the blood caused by kidney injury.
The goal of these treatments, which include renal replacement therapy, is to remove waste products from the blood that accumulate when the kidneys are not functioning properly.
Phoxilium solutionis used especially in the treatment of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury who also have:
- a normal potassium concentration in the blood (normal kalemia), or
- a normal or low phosphate concentration in the blood (normal or low phosphatemia).
This medicine may also be used in cases of poisoning with medications, dialyzable or filterable substances.
2. What you need to know before using Phoxilium
Do not use Phoxilium in the following three cases:
- high potassium concentration in the blood (hyperkalemia)
- high bicarbonate concentration in the blood (metabolic alkalosis)
- high phosphate concentration in the blood (hyperphosphatemia)
Do not subject the patient to hemodialysis or hemofiltration in the following three cases:
as follows:
- If hemofiltration cannot correct the symptoms caused by a high concentration of urea in the blood (uremic symptoms)due to a kidney injury with significant hypercatabolism (an abnormal increase in the degradation process of substances).
If the blood pressure in the vascular access is insufficient.
If the blood coagulation capacity is reduced (systemic anticoagulation) and there is a high risk of bleeding.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting to use Phoxilium.
Your blood condition will be checked before and during treatment. The acid-base balance and the concentration of salts in the blood (electrolytes) will be monitored, including all inputs (intravenous perfusion) and outputs (diuresis) of fluids, even those not directly related to the treatment.
Using Phoxilium with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or may need to use any other medicine. You must do this because the concentration of some medicines may affect the treatment with Phoxilium. Your doctor will decide if it is necessary to modify the dose of the medicines you are using.
In particular, talk to your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- Phosphate supplements (e.g., nutritional liquids), as they may increase the risk of high phosphate concentration in the blood (hyperphosphatemia).
- Vitamin D and medicines containing calcium chloride or calcium gluconate, as they may increase the risk of high calcium concentration in the blood (hypercalcemia).
- Sodium bicarbonate, as it may cause an increased risk of excess bases in the blood (metabolic alkalosis).
- Citrate used as an anticoagulant, as it may reduce calcium levels in the plasma.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
There are no documented clinical data on the use of this medicine during pregnancy and breastfeeding. This medicine should only be administered to pregnant and breastfeeding women if it is clearly necessary.
Fertility:
No effect on fertility is expected, as calcium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, chloride, hydrogen phosphate, and bicarbonate are normal components of the body.
Driving and using machines
Phoxilium does not affect the ability to drive vehicles or operate machinery.
3. How to use Phoxilium
Phoxilium is a hospital product that should only be administered by medical professionals. The volume of Phoxilium used and, therefore, the dose will depend on your conditions. The dose volume will be determined by the doctor responsible for the treatment.
Phoxilium can be administered directly into the bloodstream (intravenously)using a TCRR device or through hemodialysis, a technique in which the solution circulates on one side of the dialysis membrane while the blood circulates on the other.
Follow the administration instructions of the medicine contained in this package leaflet or as indicated by your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. In case of doubt, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
To obtain instructions for use, see the section "This information is intended only for healthcare professionals".
If you use more Phoxilium than you should
Phoxilium is a hospital product that is administered only by medical professionals; furthermore, exhaustive control of fluid balance and blood tests is carried out.
Therefore, it is unlikely that you will use more Phoxilium than you should.
In the unlikely event of an overdose, the doctor will take the necessary corrective measures and adjust the dose.
Overdose may result in fluid overload, reduced bicarbonate concentration in the plasma (metabolic acidosis), and/or high phosphate concentration (hyperphosphatemia) if the patient has kidney damage. It could have serious consequences, such as congestive heart failure or changes in blood tests.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
It is possible that the patient may experience the three side effects related to the use of Phoxiliumdescribed below:
- Abnormally high or low water volume in the body (hyper or hypovolemia)
- Variations in salt levels in the blood (electrolyte imbalances, such as hyperphosphatemia)
- Increased bicarbonate concentration in plasma (metabolic alkalosis) or reduced bicarbonate concentration in plasma (metabolic acidosis).
There are also some side effectsthat may be due to dialysis treatments, such as:
- Nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, and low blood pressure (hypotension).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this package leaflet.
You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Phoxilium
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the label and carton. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Store at a temperature between 4°C and 30°C. Do not refrigerate or freeze.
The physical and chemical stability of the reconstituted solution has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 22°C. If the solution is not used immediately, the storage conditions and time will be the responsibility of the user; in any case, this time should not exceed 24 hours, including the duration of the treatment.
Do not use this medicine if the solution is cloudy or if the packaging is damaged.
All seals must be intact.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
PHOXILIUM IS POLYOLEFIN WITH LUER CONNECTOR AND VALVE; 2016-07
Phoxilium Composition
The following are the active principles before and after the mixture (reconstitution) of the solution.
The active principles before mixing are:
1,000 ml of solution from the small compartment (A)contain:
Calcium chloride, 2 H2O 3.68 g
Magnesium chloride, 6 H2O 2.44 g
1,000 ml of solution from the large compartment (B)contain:
Sodium chloride 6.44 g
Sodium bicarbonate 2.92 g
Potassium chloride 0.314 g
Disodium phosphate, 2 H2O 0.225 g
The active principles after mixing are:
The solutions from compartments A (250 ml) and B (4,750 ml) are mixed to produce a reconstituted solution (5,000 ml) with the following composition:
mmol/l
Calcium, Ca2+ 1.25
Magnesium, Mg2+ 0.6
Sodium, Na+ 140
Chloride, Cl- 115.9
Hydrogen phosphate, HPO42- 1.2
Bicarbonate, HCO3- 30
Potassium, K+ 4
Theoretical osmolality: 293 mOsm/l
Other components are:
- Carbon dioxide (for pH adjustment) E290
- Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment) E507
- Water for injectable preparations
Product Appearance and Container Content
Phoxilium is a solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration presented in a bag consisting of two compartments. The final reconstituted solution is obtained after breaking the seal and mixing both solutions. The reconstituted solution is transparent and colorless. Each bag (A+B) contains 5,000 ml of hemodialysis and hemofiltration solution. The bag is wrapped in transparent film.
Each box contains two bags and a leaflet.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer:
Vantive Belgium SRL
Boulevard d'Angleterre 2
1420 Braine-l'Alleud
Belgium
Manufacturer:
Bieffe Medital S.p.A.
Via Stelvio 94
23035 Sondalo (SO)
ITALY
Or
Vantive Manufacturing Limited
Moneen Road
Castlebar, County Mayo, F23 XR63
Ireland
For further information on this medicinal product, please refer to the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Health, S.L.
Polígono Industrial Sector 14
C/ Pouet de Camilo, 2
46394 Ribarroja del Turia (Valencia)
Spain
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain
Estonia, Finland, France, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg
Malta, Norway, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland), Romania, and Sweden: Phoxilium
Hungary: Phoxil
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:
10/2018
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended exclusively for healthcare professionals
Phoxilium 1.2 mmol/l of phosphate
Solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration
Precautions
Follow the instructions for use and handlingof Phoxilium accurately.
The solutions from the two compartments mustbe mixed before use.
The use of a contaminated solution can cause sepsis and shock.
To increase patient comfort, Phoxilium can be heated to 37°C. Preheating before use of the solution should be done before reconstitution using only dry heat. The solutions should not be heated in water or in a microwave oven. Before administration, visually check that Phoxilium does not contain particles or has lost its original color. Do not administer the solution unless it is transparent and the seal is intact.
The concentration of inorganic phosphate should be determined periodically. Inorganic phosphate should be replaced in cases where the blood phosphate level is low.
The addition of sodium bicarbonate replacement may increase the risk of metabolic alkalosis.
In case of fluid imbalance, the clinical situation should be closely monitored and fluid balance restored:
- In case of hypervolemia, the prescribed net ultrafiltration rate for the TCRR device can be increased and/or the administration rate of solutions other than rehydration fluids and/or dialysis fluid can be reduced.
- In case of hypovolemia, the prescribed net ultrafiltration rate for the TCRR device can be reduced and/or the administration rate of solutions other than rehydration fluids and/or dialysis fluid can be increased.
Warnings:
Phoxilium should not be used in patients with hyperkalemia. Potassium concentration in serum should be monitored before and during hemofiltration and/or hemodialysis.
Phoxilium is a solution containing potassium, which can cause transient hyperkalemia once treatment is started. In such cases, reduce the perfusion rate and ensure that the necessary potassium concentration is achieved. If hyperkalemia does not resolve, discontinue treatment immediately.
If hyperkalemia occurs when using Phoxilium as dialysis fluid, it may be necessary to administer a potassium-free dialysis fluid to increase the rate of potassium elimination.
Since Phoxilium is a solution containing phosphate, it can cause temporary hyperphosphatemia once treatment is started. In such cases, reduce the perfusion rate until the desired phosphate concentration is achieved. If hyperphosphatemia does not resolve, administration should be discontinued immediately.
Electrolytes and acid-base parameters in blood should be periodically monitored in patients treated with Phoxilium. Phoxilium contains hydrogen phosphate, a weak acid that can affect the patient's acid-base balance. If metabolic acidosis occurs or worsens during treatment with Phoxilium, it may be necessary to reduce the perfusion rate or discontinue administration.
Phoxilium does not contain glucose, so its administration can cause hypoglycemia. Blood glucose levels should be regularly monitored in diabetic patients (including careful consideration in patients taking insulin or other hypoglycemic medications), but also considered in non-diabetic patients due to the risk of asymptomatic hypoglycemia during the procedure. If hypoglycemia occurs, consider using a glucose-containing solution. Other corrective measures may be necessary to maintain the desired glycemic control.
Posology:
The volume and rate at which Phoxilium is administered depend on the concentration of phosphate and other electrolytes in the blood, acid-base balance, fluid balance, and the patient's overall clinical condition. The volume of the replacement solution and/or dialysis fluid to be administered will also depend on the intensity (dose) of the desired treatment. The administration schedule (dose, perfusion rate, and cumulative volume) of Phoxilium should only be determined by a physician with experience in intensive medicine and TCRR (continuous renal replacement therapy).
Therefore, the dose volume will be determined and prescribed by the responsible physician.
The flow rate of the replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration therapies is:
Adults: 500-3,000 ml/h
The flow rate of the dialysis fluid in hemodialysis and continuous hemodiafiltration therapies is:
Adults: 500-2,500 ml/h
The total combined flow rate commonly used for TCRR (dialysis fluid and replacement solutions) in adults is approximately 2,000 to 2,500 ml/h, which corresponds to a daily fluid volume of approximately 48 to 60 liters.
Pediatric Population:
In the case of children, from neonates to adolescents up to 18 years, the flow rate range when used as a replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration and as a dialysis solution (dialysis fluid) in continuous hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration is 1,000 to 4,000 ml/h/1.73 m2.
In adolescents (12 to 18 years), when the calculated pediatric dose exceeds the maximum dose for adults, the recommended dose for adults should be used.
Instructions for Use and Handling
The solution from the small compartment A is added to the solution from the large compartment B after breaking the seal and immediately before use. The reconstituted solution should be transparent and colorless.
Aseptic technique should be used during handling and administration to the patient.
Use only if the packaging is intact, the seals are intact, the peelable seal is not broken, and the solution is transparent. Squeeze the bag to ensure there are no leaks. If a leak is found, discard the solution immediately as its sterility cannot be guaranteed.
The large compartment B has an injection port for adding other medications that may be necessary once the solution is reconstituted.It is the physician's responsibility to judge the compatibility of the added medication with the Phoxilium solution by checking for any change in color and/or precipitation, insoluble complexes, or crystals. Before adding a medication, check that it is soluble and stable in this medication and that the pH range of Phoxilium is suitable (the pH range of the reconstituted solution is 7.0-8.5). Additives may not be compatible. The instructions for use of the medication to be added should be consulted.
Remove any liquid from the injection port, hold the bag in a vertical position with the bottom facing down
add the medication through the injection port and mix thoroughly. The introduction and mixing of additives should always be done before connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit. The solution should be administered immediately.
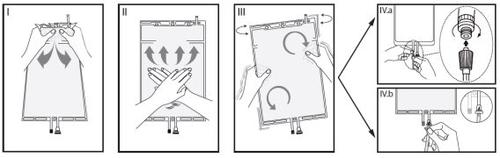
IRemove the bag's packaging immediately before use and discard the other packaging materials
Break the seal by holding the small compartment between the two hands and squeezing until the wall separating the two compartments opens (see figure I below).
IIPress the large compartment with both hands until the wall between the two compartments is fully open (see figure II below).
IIIEnsure that the solutions are thoroughly mixed by gently shaking the bag. The solution is now ready for use and the bag can be hung on the equipment (see figure III below).
IVThe dialysis or replacement fluid line can be connected to either of the two access connectors.
IV.aIf the Luer connector is used, remove the cap with a twisting and pulling motion and connect the male Luer connector of the dialysis or replacement line to the female Luer receptor of the bag with a pushing and twisting motion. Ensure that the connection is secure and tightened. The connection will open. Check that the fluid flows freely. (see figure IV.a below)
If the dialysis or replacement line is disconnected from the Luer connector, the connector will close and the flow of the solution will stop. The Luer port is a needle-free port that can be cleaned.
IV.bIf the injection port is used, first remove the cap by lifting it. The injection port is a port that can be disinfected with a swab. Then insert the spike through the rubber wall. Check that the fluid flows freely (see figure IV.b below)
The reconstituted solution should be used immediately. If not used immediately, note that the reconstituted solution should be used within 24 hours after adding solution A to solution B, including the duration of treatment.
The reconstituted solution is for single use. Discard any remaining solution immediately after use.
The disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have come into contact with them should be done in accordance with local regulations.
PHOXILIUM IS PVC WITH LUER CONNECTOR AND VALVE; 2016-07
Phoxilium Composition
The following are the active principles before and after the mixture (reconstitution) of the solution.
The active principles before mixing are:
1,000 ml of solution from the small compartment (A)contain:
Calcium chloride, 2 H2O 3.68 g
Magnesium chloride, 6 H2O 2.44 g
1,000 ml of solution from the large compartment (B)contain:
Sodium chloride 6.44 g
Sodium bicarbonate 2.92 g
Potassium chloride 0.314 g
Disodium phosphate, 2 H2O 0.225 g
The active principles after mixing are:
The solutions from compartments A (250 ml) and B (4,750 ml) are mixed to produce a reconstituted solution (5,000 ml) with the following composition:
mmol/l
Calcium, Ca2+ 1.25
Magnesium, Mg2+ 0.6
Sodium, Na+ 140
Chloride, Cl- 115.9
Hydrogen phosphate, HPO42- 1.2
Bicarbonate, HCO3- 30
Potassium, K+ 4
Theoretical osmolality: 293 mOsm/l
Other components are:
Carbon dioxide (for pH adjustment) E290
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment) E507
Water for injectable preparations
Product Appearance and Container Content
Phoxilium is a solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration presented in a bag consisting of two compartments. The final reconstituted solution is obtained after breaking the breakable valve and mixing both solutions. The reconstituted solution is transparent and colorless. Each bag (A+B) contains 5,000 ml of hemodialysis and hemofiltration solution. The bag is wrapped in transparent film.
Each box contains two bags and a leaflet.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer:
Vantive Belgium SRL
Boulevard d'Angleterre 2
1420 Braine-l'Alleud
Belgium
Manufacturer:
Bieffe Medital S.p.A.
Via Stelvio 94
23035 Sondalo (SO)
ITALY
Or
Vantive Manufacturing Limited
Moneen Road
Castlebar, County Mayo, F23 XR63
Ireland
For further information on this medicinal product, please refer to the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Health, S.L.
Polígono Industrial Sector 14
C/ Pouet de Camilo, 2
46394 Ribarroja del Turia (Valencia)
Spain
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain
Estonia, Finland, France, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg
Malta, Norway, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland), Romania, and Sweden: Phoxilium
Hungary: Phoxil
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:
10/2018
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended exclusively for healthcare professionals
Phoxilium 1.2 mmol/l of phosphate
Solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration
Precautions
Follow the instructions for use and handlingof Phoxilium accurately.
The solutions from the two compartments mustbe mixed before use.
The use of a contaminated solution can cause sepsis and shock.
To increase patient comfort, Phoxilium can be heated to 37°C. Preheating before use of the solution should be done before reconstitution using only dry heat. The solutions should not be heated in water or in a microwave oven. Before administration, visually check that Phoxilium does not contain particles or has lost its original color. Do not administer the solution unless it is transparent and the seal is intact.
The concentration of inorganic phosphate should be determined periodically. Inorganic phosphate should be replaced in cases where the blood phosphate level is low.
The addition of sodium bicarbonate replacement may increase the risk of metabolic alkalosis.
In case of fluid imbalance, the clinical situation should be closely monitored and fluid balance restored:
- In case of hypervolemia, the prescribed net ultrafiltration rate for the TCRR device can be increased and/or the administration rate of solutions other than rehydration fluids and/or dialysis fluid can be reduced.
- In case of hypovolemia, the prescribed net ultrafiltration rate for the TCRR device can be reduced and/or the administration rate of solutions other than rehydration fluids and/or dialysis fluid can be increased.
Warnings:
Phoxilium should not be used in patients with hyperkalemia. Potassium concentration in serum should be monitored before and during hemofiltration and/or hemodialysis.
Phoxilium is a solution containing potassium, which can cause transient hyperkalemia once treatment is started. In such cases, reduce the perfusion rate and ensure that the necessary potassium concentration is achieved. If hyperkalemia does not resolve, discontinue treatment immediately.
If hyperkalemia occurs when using Phoxilium as dialysis fluid, it may be necessary to administer a potassium-free dialysis fluid to increase the rate of potassium elimination.
Since Phoxilium is a solution containing phosphate, it can cause temporary hyperphosphatemia once treatment is started. In such cases, reduce the perfusion rate until the desired phosphate concentration is achieved. If hyperphosphatemia does not resolve, administration should be discontinued immediately.
Electrolytes and acid-base parameters in blood should be periodically monitored in patients treated with Phoxilium. Phoxilium contains hydrogen phosphate, a weak acid that can affect the patient's acid-base balance. If metabolic acidosis occurs or worsens during treatment with Phoxilium, it may be necessary to reduce the perfusion rate or discontinue administration.
Phoxilium does not contain glucose, so its administration can cause hypoglycemia. Blood glucose levels should be regularly monitored in diabetic patients (including careful consideration in patients taking insulin or other hypoglycemic medications), but also considered in non-diabetic patients due to the risk of asymptomatic hypoglycemia during the procedure. If hypoglycemia occurs, consider using a glucose-containing solution. Other corrective measures may be necessary to maintain the desired glycemic control.
Hemofiltration and/or hemodialysis.
Phoxilium is a solution that contains potassium, so it may cause transient hyperkalemia once treatment is started. In such a case, reduce the perfusion rate and ensure that the necessary potassium concentration has been reached. If hyperkalemia does not subside, discontinue treatment immediately.
If hyperkalemia occurs when using Phoxilium as a dialysis fluid, it may be necessary to administer a potassium-free dialysis fluid to increase the rate of potassium elimination.
Since Phoxilium is a solution that contains phosphate, it may cause temporary hyperphosphatemia once treatment is started. In such a case, the perfusion rate should be reduced until the desired phosphate concentration is reached. If hyperphosphatemia does not subside, administration should be discontinued immediately.
The electrolytes and acid-base parameters in the blood should be periodically monitored in patients treated with Phoxilium. Phoxilium contains hydrogen phosphate, a weak acid that can affect the patient's acid-base balance. If metabolic acidosis appears or worsens during treatment with Phoxilium, it may be necessary to reduce the perfusion rate or discontinue administration.
Phoxilium does not contain glucose, so its administration may cause hypoglycemia. Blood glucose levels should be regularly monitored in diabetic patients (including careful consideration in patients taking insulin or other hypoglycemic medications), but also in non-diabetic patients, due to the risk of asymptomatic hypoglycemia during the procedure. If hypoglycemia occurs, the use of a glucose solution should be considered. Other corrective measures may be necessary to maintain the desired glycemic control.
Dosage:
The volume and rate at which Phoxilium is administered depend on the concentration of phosphate and other electrolytes in the blood, acid-base balance, fluid balance, and the patient's overall clinical condition. The volume of the substitution solution and/or dialysis fluid to be administered will also depend on the desired treatment intensity (dose). The administration schedule (dose, perfusion rate, and cumulative volume) of Phoxilium should only be determined by a physician with experience in intensive medicine and CRRT (continuous renal replacement therapy).
Therefore, the dose volume will be determined and prescribed by the responsible physician.
The flow rate of the substitution solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration therapies is:
Adults: 500-3,000 ml/h
The flow rate of the dialysis fluid in hemodialysis and continuous hemodiafiltration therapies is:
Adults: 500-2,500 ml/h
The combined total flow rate commonly used for CRRT (dialysis fluid and substitution solutions) in adults is approximately 2,000 to 2,500 ml/h, which corresponds to an approximate daily fluid volume of 48 to 60 liters.
Pediatric population:
In the case of children, from neonates to adolescents up to 18 years, the flow rate range when used as a substitution solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration and as a dialysis solution (dialysis fluid) in continuous hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration is 1,000 to 4,000 ml/h/1.73 m2.
In adolescents (12 to 18 years), when the calculated pediatric dose exceeds the maximum dose for adults, the recommended dose for adults should be used.
Instructions for use and handling
The solution from the small compartment A is added to the solution from the large compartment B after breaking the breakable vial and immediately before use. The reconstituted solution should be transparent and colorless.
Aseptic technique should be used during handling and administration to the patient.
Use only if the packaging is intact, the seals are intact, the breakable vial is not broken, and the solution is transparent. Squeeze the bag firmly to ensure there are no leaks. If any leak is found, discard the solution immediately as its sterility cannot be guaranteed.
The large compartment B has an injection access to add other medications that may be necessary once the solution is reconstituted. It is the physician's responsibility to assess the compatibility of the added medication with the Phoxilium solution by checking for any change in color and/or precipitation, insoluble complexes, or crystals. Before adding a medication, verify that it is soluble and stable in this medication and that the pH range of Phoxilium is suitable (the pH range of the reconstituted solution is 7.0-8.5). Additives may not be compatible. The instructions for use of the medication to be added should be consulted.
Remove any liquid from the injection access, hold the bag in a vertical position downwards, add the medication through the injection access, and mix thoroughly. The mixing of additives should always be done before connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit. The solution should be administered immediately.
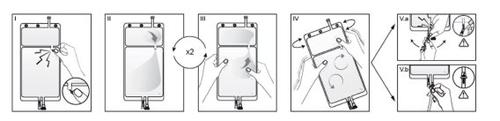
IRemove the bag packaging immediately before use and discard the other packaging materials. Open the closure by breaking the vial located between the two compartments of the bag. The vial remains in the bag (see figure I below).
II.Ensure that all the liquid from the small compartment A passes into the large compartment B (see figure II below).
III.Clarify the small compartment A twice by forcing the mixed solution back into this small compartment A and then again into the large compartment B (see figure III below).
IV.Once the small compartment A is empty, shake the large compartment B to mix its contents completely. The solution is now ready for use and the bag can be hung on the equipment (see figure IV below).
V.The dialysis fluid or substitution line can be connected to either of the two access connectors.
V.a.If the luer access is used, remove the plug using aseptic technique and connect the luer male connector of the dialysis fluid or substitution line to the luer female receptor of the bag; do it firmly. With both hands, break the blue breakable vial at the base and move it back and forth. Do not use tools. Check that the breakable vial is completely separated and that the liquid circulates freely. The breakable vial will remain in the luer port during treatment (see figure V.a below).
V.b.If the injection access is used, first remove the plug by lifting it. The injection port is a port that can be disinfected with a swab. Then insert the spike through the rubber wall. Check that the liquid circulates freely (see figure V.b below).
The reconstituted solution should be used immediately. If it is not used immediately, note that the reconstituted solution should be used within 24 hours after adding solution A to solution B, including the duration of treatment.
The reconstituted solution is for single use. Discard any remaining solution immediately after use.
The disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
PHOXILIUM IS PVC CONNECTOR LUER WITH VALVE; 2016-07
Phoxilium composition
The following are the active principles before and after mixing (reconstitution) of the solution.
The active principles before mixing are:
1,000 ml of solution from the small compartment (A)contain:
Calcium chloride, 2 H2O 3.68 g
Magnesium chloride, 6 H2O 2.44 g
1,000 ml of solution from the large compartment (B)contain:
Sodium chloride 6.44 g
Sodium bicarbonate 2.92 g
Potassium chloride 0.314 g
Disodium phosphate, 2 H2O 0.225 g
The active principles after mixing are:
The solutions from compartments A (250 ml) and B (4,750 ml) are mixed to produce a reconstituted solution (5,000 ml) with the following composition:
mmol/l
Calcium, Ca2+ 1.25
Magnesium, Mg2+ 0.6
Sodium, Na+ 140
Chloride, Cl- 115.9
Hydrogen phosphate, HPO42- 1.2
Bicarbonate, HCO3- 30
Potassium, K+ 4
Theoretical osmolality: 293 mOsm/l
Other components are:
Carbon dioxide (for pH adjustment) E290
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment) E507
Water for injectable preparations
Product appearance and packaging content
Phoxilium is a solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration presented in a bag consisting of two compartments. The final reconstituted solution is obtained after breaking the breakable vial and mixing both solutions. The reconstituted solution is transparent and colorless. Each bag (A+B) contains 5,000 ml of hemodialysis and hemofiltration solution. The bag is wrapped in transparent film.
Each box contains two bags and a leaflet.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer:
Vantive Belgium SRL
Boulevard d'Angleterre 2
1420 Braine-l'Alleud
Belgium
Manufacturer:
Bieffe Medital S.p.A.
Via Stelvio 94,
23035 Sondalo (SO)
ITALY
Or
Vantive Manufacturing Limited
Moneen Road,
Castlebar, County Mayo, F23 XR63
Ireland
For further information about this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Health, S.L.
Polígono Industrial Sector 14.
C/ Pouet de Camilo, 2
46394 Ribarroja del Turia (Valencia)
Spain
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Estonia, Finland, France, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Norway, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland), Romania, and Sweden: Phoxilium
Hungary: Phoxil
Date of last revision of this leaflet:
10/2018
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals
Phoxilium®1.2 mmol/l of phosphate
Solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration
Precautions
Follow the instructions for use and handlingof Phoxilium accurately.
The solutions from the compartments mustbe mixed before use.
The use of a contaminated solution can cause sepsis and shock.
To increase patient comfort, Phoxilium can be warmed up to 37°C. Pre-warming of the solution should be done before reconstitution using only dry heat. The solutions should not be heated in water or in a microwave oven. Before administration, it should be visually checked that Phoxilium does not contain particles or has lost its original color. Do not administer the solution unless it is transparent and the seal is intact.
The concentration of inorganic phosphate should be determined periodically. Inorganic phosphate should be replaced in cases where the blood phosphate level is low.
The addition of sodium bicarbonate replacement may increase the risk of metabolic alkalosis.
In case of fluid imbalance, the clinical situation should be closely monitored and fluid balance should be restored:
- In case of hypervolemia, the prescribed net ultrafiltration rate for the CRRT device can be increased and/or the administration rate of solutions other than rehydration fluids and/or dialysis fluid can be reduced.
- In case of hypovolemia, the prescribed net ultrafiltration rate for the CRRT device can be reduced and/or the administration rate of solutions other than rehydration fluids and/or dialysis fluid can be increased.
Warnings:
Phoxilium should not be used in patients with hyperkalemia. Potassium concentration in the serum should be monitored before and during hemofiltration and/or hemodialysis.
Phoxilium is a solution that contains potassium, so it may cause transient hyperkalemia once treatment is started. In such a case, reduce the perfusion rate and ensure that the necessary potassium concentration has been reached. If hyperkalemia does not subside, discontinue treatment immediately.
If hyperkalemia occurs when using Phoxilium as a dialysis fluid, it may be necessary to administer a potassium-free dialysis fluid to increase the rate of potassium elimination.
Since Phoxilium is a solution that contains phosphate, it may cause temporary hyperphosphatemia once treatment is started. In such a case, the perfusion rate should be reduced until the desired phosphate concentration is reached. If hyperphosphatemia does not subside, administration should be discontinued immediately.
The electrolytes and acid-base parameters in the blood should be periodically monitored in patients treated with Phoxilium. Phoxilium contains hydrogen phosphate, a weak acid that can affect the patient's acid-base balance. If metabolic acidosis appears or worsens during treatment with Phoxilium, it may be necessary to reduce the perfusion rate or discontinue administration.
Phoxilium does not contain glucose, so its administration may cause hypoglycemia. Blood glucose levels should be regularly monitored in diabetic patients (including careful consideration in patients taking insulin or other hypoglycemic medications), but also in non-diabetic patients, due to the risk of asymptomatic hypoglycemia during the procedure. If hypoglycemia occurs, the use of a glucose solution should be considered. Other corrective measures may be necessary to maintain the desired glycemic control.
Dosage:
The volume and rate at which Phoxilium is administered depend on the concentration of phosphate and other electrolytes in the blood, acid-base balance, fluid balance, and the patient's overall clinical condition. The volume of the substitution solution and/or dialysis fluid to be administered will also depend on the desired treatment intensity (dose). The administration schedule (dose, perfusion rate, and cumulative volume) of Phoxilium should only be determined by a physician with experience in intensive medicine and CRRT (continuous renal replacement therapy).
Therefore, the dose volume will be determined and prescribed by the responsible physician.
The flow rate of the substitution solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration therapies is:
Adults: 500-3,000 ml/h
The flow rate of the dialysis fluid in hemodialysis and continuous hemodiafiltration therapies is:
Adults: 500-2,500 ml/h
The combined total flow rate commonly used for CRRT (dialysis fluid and substitution solutions) in adults is approximately 2,000 to 2,500 ml/h, which corresponds to an approximate daily fluid volume of 48 to 60 liters.
Pediatric population:
In the case of children, from neonates to adolescents up to 18 years, the flow rate range when used as a substitution solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration and as a dialysis solution (dialysis fluid) in continuous hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration is 1,000 to 4,000 ml/h/1.73 m2.
In adolescents (12 to 18 years), when the calculated pediatric dose exceeds the maximum dose for adults, the recommended dose for adults should be used.
Instructions for use and handling
The solution from the small compartment A is added to the solution from the large compartment B after breaking the breakable vial and immediately before use. The reconstituted solution should be transparent and colorless.
Aseptic technique should be used throughout the administration process to the patient.
Use only if the packaging is intact, the seals are intact, the breakable vial is not broken, and the solution is transparent. Squeeze the bag firmly to ensure there are no leaks. If any leak is found, discard the solution immediately as its sterility cannot be guaranteed.
The large compartment B has an injection access to add other medications that may be necessary once the solution is reconstituted.It is the physician's responsibility to assess the compatibility of the added medication with the Phoxilium solution by checking for any change in color and/or precipitation, insoluble complexes, or crystals. Before adding a medication, verify that it is soluble and stable in this medication and that the pH range of Phoxilium is suitable (the pH range of the reconstituted solution is 7.0-8.5). Additives may not be compatible. The instructions for use of the medication to be added should be consulted.
Remove any liquid from the injection access, hold the bag in a vertical position downwards, add the medication through the injection access, and mix thoroughly. The mixing of additives should always be done before connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit. The solution should be administered immediately.
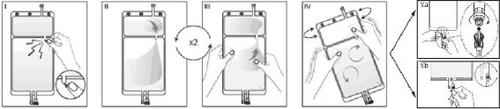
IRemove the bag packaging immediately before use and discard the other packaging materials. Open the closure by breaking the vial located between the two compartments of the bag.
... (rest of the translation remains the same)
closing by breaking the stem located between the two compartments of
the bag. The stem remains in the bag (see figure I below).
II.Make sure all the liquid from the small compartment A passes to the large compartment
B (see figure II below).
IIIClarify the small compartment A twice by forcing the mixed solution back to this small compartment A and then again to the large compartment B (see figure III below).
IVOnce the small compartment A is empty, shake the large compartment B so that its
contents are completely mixed. The solution is now ready for use and the bag can
be hung on the equipment (see figure IV below).
VThe dialysis or substitution line can be connected to either of the two access connectors.
V.aIf the luer access is used, remove the cap with a twisting and pulling motion and connect the male luer connector of the dialysis or substitution line to the female luer receptor of the bag with a pushing and twisting motion. Make sure the connection is secure and tight. The connection will open. Check that the liquid circulates freely (see figure V.a below).
If the dialysis or substitution line is disconnected from the luer connector, the connector will close and
the flow of the solution will stop. The luer port is a needle-free port that can be
cleaned.
V.bIf the injection access is used, first remove the cap by lifting it. The injection port is a port that can be disinfected with a swab. Then insert the spike through the rubber wall. Check that the liquid circulates freely (see figure V.b below).
The reconstituted solution must be used immediately. If it is not used immediately, note that the reconstituted solution must be used within 24 hours after adding solution A to solution B, including the duration of treatment.
The reconstituted solution is for single use. Discard any remaining solution immediately after use.
The disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to PHOXILIUM 1.2 mmol/L PHOSPHATE SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS/HEMOFILTRATIONDosage form: HEMOFILTRATION, 2 mmol potassium/lActive substance: HemofiltratesManufacturer: Nikkiso BelgiumPrescription requiredDosage form: HEMOFILTRATION, 4 mmol potassium/lActive substance: HemofiltratesManufacturer: Nikkiso BelgiumPrescription requiredDosage form: HEMOFILTRATION, -Active substance: HemofiltratesManufacturer: Nikkiso BelgiumPrescription required
Online doctors for PHOXILIUM 1.2 mmol/L PHOSPHATE SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS/HEMOFILTRATION
Discuss questions about PHOXILIUM 1.2 mmol/L PHOSPHATE SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS/HEMOFILTRATION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















