
PALIPERIDONA STADA 150 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
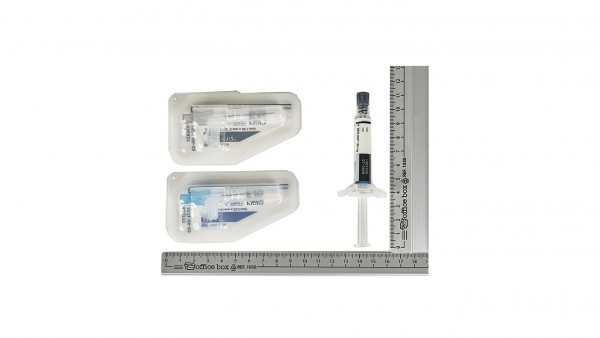

How to use PALIPERIDONA STADA 150 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Paliperidona Stada 50 mg prolonged-release injectable suspension
in a pre-filled syringeEFG
Paliperidona Stada 75 mg prolonged-release injectable suspension
in a pre-filled syringeEFG
Paliperidona Stada 100 mg prolonged-release injectable suspension
in a pre-filled syringeEFG
Paliperidona Stada 150 mg prolonged-release injectable suspension
in a pre-filled syringeEFG
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Paliperidona Stada and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Paliperidona Stada
- How to use Paliperidona Stada
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Paliperidona Stada
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Paliperidona Stada and what is it used for
Paliperidona Stada contains the active substance paliperidone, which belongs to a class of medicines called antipsychotics, and is used as maintenance treatment for symptoms of schizophrenia in adult patients who have been stabilized with paliperidone or risperidone.
If you have previously responded to paliperidone or risperidone and have mild or moderate symptoms, your doctor may start treatment with paliperidone without prior stabilization with paliperidone or risperidone.
Schizophrenia is a disorder with "positive" and "negative" symptoms. Positive means an excess of symptoms that are not normally present. For example, a person with schizophrenia may hear voices or see things that do not exist (called hallucinations), have false beliefs (called delusions), or have an abnormal distrust of others. Negative refers to the lack of behaviors or feelings that are normally present. For example, a person with schizophrenia may withdraw into themselves and not respond to any emotional stimulus or may have problems speaking in a clear and logical way. People with this disorder may also feel depressed, anxious, guilty, or tense.
Paliperidona can help alleviate the symptoms of your illness and prevent them from coming back.
2. What you need to know before you use Paliperidona Stada
Do not use Paliperidona Stada
- if you are allergic to paliperidone or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- if you are allergic to any other antipsychotic medicine, including risperidone.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting treatment with paliperidone.
This medicine has not been studied in elderly patients with dementia. However, elderly patients with dementia who are being treated with other similar medicines may have an increased risk of stroke or death (see section 4, Possible side effects).
All medicines can cause side effects, and some of the side effects of this medicine may worsen the symptoms of other illnesses. For this reason, it is important that you discuss with your doctor any of the following illnesses, which may worsen during treatment with this medicine:
- if you have Parkinson's disease
- if you have ever been diagnosed with a disease whose symptoms include high temperature and muscle stiffness (also known as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome)
- if you have ever experienced abnormal movements of the tongue or face (Tardive Dyskinesia)
- if you have had low white blood cell counts in the past (which may or may not have been caused by other medicines)
- if you are diabetic or have a tendency to diabetes
- if you have had breast cancer or a tumor in the pituitary gland of the brain
- if you have heart disease or are being treated for heart diseases that may make you more prone to low blood pressure
- if you have low blood pressure when standing up or getting up suddenly
- if you have epilepsy
- if you have kidney problems
- if you have liver problems
- if you have a prolonged and/or painful erection
- if you have difficulty controlling body temperature or are overheated
- if you have an abnormally high level of the hormone prolactin in your blood or if you have a tumor that may be dependent on prolactin
- if you or someone in your family has a history of blood clots, as antipsychotics have been associated with the formation of blood clots.
If you have any of these illnesses, please consult your doctor, as it may be necessary to adjust your dose or keep you under observation for a while.
- Because it has been very rarely observed in patients treated with this medicine that there is a dangerously low number of a type of white blood cells necessary to fight infections in the blood, your doctor may check the number of white blood cells in your blood.
- Even if you have previously tolerated oral paliperidone or risperidone, allergic reactions rarely occur after receiving paliperidone injections. Seek medical help immediately if you experience a skin rash, swelling of the throat, itching, or breathing problems, as these can be signs of a severe allergic reaction.
- This medicine may cause you to gain weight. Significant weight gain can negatively affect your health. Your doctor will regularly monitor your weight.
- In patients treated with this medicine, diabetes mellitus or worsening of pre-existing diabetes mellitus has been observed, and your doctor should check for signs of high blood sugar. In patients with pre-existing diabetes mellitus, blood sugar should be regularly monitored.
- Since this medicine can reduce the impulse to vomit, there is a possibility that it may mask the body's normal response to the ingestion of toxic substances or other illnesses.
- During eye surgery for cataracts, the pupil (the black circle in the middle of the eye) may not increase in size as needed. Additionally, the iris (the colored part of the eye) may become flaccid during surgery, which can cause damage to the eye. If you are planning to have eye surgery, make sure to inform your ophthalmologist that you are using this medicine.
Children and adolescents
Do not use this medicine in children under 18 years of age.
Other medicines and Paliperidona Stada
Tell your doctor if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
- Taking this medicine with carbamazepine(an antiepileptic and mood stabilizer) may require a change in your dose of this medicine.
- Since this medicine acts mainly on the brain, interaction with other medicines that also act on it may cause an exaggeration of side effects, such as drowsiness or other effects on the brain, such as other psychiatric medicines, opioids, antihistamines, and sleeping medicines.
- Since this medicine can lower blood pressure, you should be careful if you use this medicine with other medicines that lower blood pressure.
- This medicine may reduce the effect of medicines for Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome (e.g., levodopa).
- This medicine may cause an abnormality in the electrocardiogram (ECG) that shows that it is necessary to have a prolonged period for an electrical impulse to travel through a certain part of the heart (known as "prolongation of the QT interval"). Other medicines that have this effect include some medicines used to treat heart rhythm or to treat infectionsand other antipsychotics.
- If you are prone to developing seizures, this medicine may increase your chances of experiencing them. Other medicines that have this effect include some medicines used to treat depression or to treat infectionsand other antipsychotics.
- Paliperidona should be used with caution with medicines that increase the activity of the central nervous system (psychostimulants such as methylphenidate).
Using Paliperidona Stada with alcohol
Alcohol should be avoided.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
Do not use this medicine during pregnancy unless you have discussed it with your doctor. The following symptoms may occur in newborn babies of mothers who have been treated with paliperidone in the last trimester of pregnancy (the last three months of pregnancy): shaking, stiffness, and/or muscle weakness, drowsiness, agitation, breathing problems, and difficulty feeding. If your baby develops any of these symptoms, you should contact your doctor.
Breastfeeding
This medicine may pass from mother to child through breast milk and may harm the baby. Therefore, you should not breastfeed while using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
During treatment with this medicine, dizziness, extreme fatigue, and vision problems (see section 4) may occur. This should be taken into account when requiring maximum attention, e.g., when driving or operating machinery.
Paliperidona Stada contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per dose; it is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Paliperidona Stada
Your doctor or another healthcare professional will administer this medicine to you. Your doctor will tell you when you should receive the next injection. It is important that you do not miss any of the scheduled doses. If you cannot attend your appointment with the doctor, make sure to call them immediately to schedule another appointment as soon as possible.
Dose and method of administration
You will receive the first injection (150 mg) and the second injection (100 mg) of this medicine in the upper arm approximately one week apart. From then on, you will receive an injection (of 25 mg to 150 mg) in the upper arm or buttocks once a month.
If your doctor is switching you from risperidone long-acting injection to this medicine, you will receive the first injection of this medicine (of 25 mg to 150 mg) in the upper arm or buttocks at the next scheduled injection. From then on, you will receive an injection (of 25 mg to 150 mg) in the upper arm or buttocks once a month.
Depending on your symptoms, the doctor may increase or decrease the amount of medicine you receive at a dose level at the time of the scheduled monthly injection.
Patient with kidney problems
Your doctor may adjust the dose of this medicine according to your kidney function. If you have mild kidney problems, your doctor may give you a lower dose. You should not use this medicine if you have moderate or severe kidney problems.
Elderly patients
Your doctor may reduce the dose of this medicine if your kidney function is decreased.
If you receive more Paliperidona Stada than you should
You will receive this medicine under medical supervision; it is therefore unlikely that you will receive an excessive dose.
Patient who have received an overdose of paliperidone may experience the following symptoms: drowsiness or sedation, rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, abnormal electrocardiogram (heart tracing), or slow or abnormal movements of the face, body, arms, or legs.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, contact your doctor or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount ingested.
If you stop treatment with Paliperidona Stada
If you stop receiving your injections, the effects of the medicine will be lost. You should not stop using this medicine unless your doctor tells you to, as your symptoms may come back.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Report immediately to your doctor if:
- you have blood clots in the veins, especially in the legs (symptoms include swelling, pain, and redness of the leg), which can circulate through the blood vessels to the lungs, causing chest pain and difficulty breathing. If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical advice immediately.
- you have dementia and experience a sudden change in your mental state or sudden weakness or numbness of the face, arms, or legs, especially on one side, or have difficulty speaking even for a short period. These may be signs of a stroke.
- you have fever, muscle stiffness, sweating, or a decrease in the level of consciousness (a condition known as "Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome"). You may need immediate medical treatment.
- you are a man and experience a prolonged or painful erection. This is known as priapism. You may need immediate medical treatment.
- you experience involuntary rhythmic movements of the tongue, mouth, and face. It may be necessary to withdraw paliperidone.
- you have a severe allergic reaction characterized by fever, swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue, difficulty breathing, itching, rash, and sometimes a drop in blood pressure (anaphylactic reaction). Even if you have previously tolerated oral risperidone or paliperidone, in rare cases, allergic reactions have appeared after receiving paliperidone injections.
- you are scheduled to undergo eye surgery, make sure to tell your ophthalmologist that you are taking this medicine. During eye surgery for cataracts, it is possible that the iris (the colored part of the eye) may become flaccid during surgery (known as "floppy iris syndrome"), which can cause eye damage.
- you have a dangerously low number of a type of white blood cell necessary to fight blood infections.
The following adverse effects may appear:
Very common:may affect more than 1 in 10 people
- difficulty staying or falling asleep.
Common:may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- common cold symptoms, urinary tract infection, feeling like you have the flu
- Paliperidone may increase the levels of a hormone called "prolactin" that is detected in blood tests (which may or may not cause symptoms). When symptoms of increased prolactin appear, they may include (in men) breast swelling, difficulty having or maintaining erections, or other sexual dysfunctions; (in women) breast discomfort, milk secretion from the breasts, loss of menstrual periods, or other problems with the cycle
- increased blood sugar, weight gain, weight loss, decreased appetite
- irritability, depression, anxiety
- parkinsonism: this disease may include slow or altered movement, feeling of stiffness or tightness of the muscles (making jerky movements), and sometimes a feeling of "freezing" of movement that then restarts. Other signs of parkinsonism include walking slowly, dragging feet, tremors while resting, increased saliva and/or drooling, and loss of facial expressiveness
- restlessness, feeling drowsy or less attentive
- distonia: it is a disorder that involves slow or continuous involuntary contraction of the muscles. Although any part of the body can be affected (and can cause abnormal postures), distonia often affects the muscles of the face, including abnormal movements of the eyes, mouth, tongue, or jaw
- dizziness
- diskinesia: this disorder involves involuntary muscle movements and may include repetitive, spasmodic, or twisting movements, or spasms
- tremors (agitation)
- headache
- rapid heartbeat
- increased blood pressure
- cough, nasal congestion
- abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, constipation, diarrhea, indigestion, toothache
- increased liver transaminases in blood
- bone or muscle pain, back pain, joint pain
- absence of menstruation
- fever, weakness, fatigue (tiredness)
- a reaction at the injection site, including itching, pain, or swelling
Uncommon:may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- pneumonia, chest infection (bronchitis), respiratory tract infection, sinus infection, bladder infection, ear infection, fungal nail infection, tonsillitis, skin infection
- decrease in the number of white blood cells, decrease in a type of white blood cell that helps fight infections, anemia
- allergic reaction
- diabetes or worsening of diabetes, increased insulin (a hormone that controls blood sugar levels) in blood
- increased appetite
- loss of appetite that causes malnutrition and weight loss
- increased triglycerides in blood (a type of fat), increased cholesterol in blood
- sleep disorder, euphoria (mania), decreased sexual desire, nervousness, nightmares
- late diskinesia (spasms or uncontrolled spasmodic movements of the face, tongue, or other parts of the body). Report to your doctor immediately if you experience involuntary rhythmic movements of the tongue, mouth, or face. It may be necessary to withdraw this medicine.
- fainting, restlessness that causes movement of body parts, dizziness when standing up, altered attention, speech problems, loss or alteration of taste, decreased skin sensitivity to pain or touch, tingling, pinching, or numbness of the skin
- blurred vision, eye infection or "pink eye", dry eyes
- feeling that everything is spinning (vertigo), ringing in the ears, ear pain
- disruption of conduction between the upper and lower parts of the heart, anomaly in the electrical activity of the heart, prolonged QT interval in the heart, rapid heartbeat when standing up, slow heartbeat, anomalies in the electrical tracing of the heart (electrocardiogram or ECG), feeling of fluttering or pounding in the chest (palpitations)
- decreased blood pressure, low blood pressure when standing up (therefore, some people taking this medicine may feel weak, dizzy, or may faint when getting up or sitting up suddenly)
- difficulty breathing, sore throat, nasal bleeding
- abdominal discomfort, stomach or intestine infection, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth
- excess gas or flatulence
- increased GGT (a liver enzyme called gamma-glutamyltransferase) in blood, increased liver enzymes in blood
- hives (or "urticaria"), itching, rash, hair loss, eczema, dry skin, redness of the skin, acne, abscess under the skin
- increased CPK (creatine phosphokinase) in blood, an enzyme that is sometimes released with muscle breakdown
- muscle spasms, joint stiffness, muscle weakness
- urinary incontinence, frequent urination, pain when urinating
- erectile dysfunction, ejaculation disorder, absence of menstrual periods or other problems with the cycle (women), breast development in men, sexual dysfunction, breast pain, milk secretion from the breasts
- swelling of the face, mouth, eyes, or lips, swelling of the body, arms, or legs
- increased body temperature
- change in gait
- chest pain, chest discomfort, feeling of discomfort
- skin hardening
- falls
Rare:may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- eye infection
- skin inflammation caused by mites, scaly and itchy skin or scalp
- increased eosinophils (a type of white blood cell) in blood
- decrease in platelets (blood cells that help stop bleeding)
- head agitation
- inadequate secretion of the hormone that controls urine volume
- sugar in the urine
- complications of uncontrolled diabetes that can be fatal
- decreased blood sugar
- excessive water intake
- lack of movement or response while awake (catatonia)
- confusion
- sleepwalking
- absence of emotions
- inability to achieve orgasm
- neuroleptic malignant syndrome (confusion, decreased or lost consciousness, high fever, and severe muscle stiffness), problems in the blood vessels of the brain, including sudden loss of blood flow to the brain (stroke or "mini" stroke), unresponsiveness to stimuli, loss of consciousness, decreased level of consciousness, seizures (epileptic crises), balance disorder
- abnormal coordination
- glaucoma (increased pressure in the eyeball)
- eye movement problems, eye rotation, hypersensitivity of the eyes to light, increased tearing, redness of the eyes
- atrial fibrillation (abnormal heart rhythm), irregular heartbeat
- blood clots in the lungs, which cause chest pain and difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
- blood clots in the veins, especially in the legs (symptoms include swelling, pain, and redness of the leg). If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
- flushing
- difficulty breathing during sleep (sleep apnea)
- pulmonary congestion, respiratory tract congestion
- crackling sounds in the lungs, wheezing
- pancreatitis, tongue swelling, fecal incontinence, very hard stools
- intestinal obstruction
- chapped lips
- drug-related skin rash, skin thickening, dandruff
- muscle fiber breakdown and muscle pain (rhabdomyolysis)
- joint swelling
- inability to urinate
- breast discomfort, breast gland growth, breast growth
- vaginal discharge
- priapism (a prolonged erection of the penis that may require surgical treatment)
- very low body temperature, chills, feeling of thirst
- withdrawal symptoms from the medicine
- pus accumulation due to infection at the injection site, deep skin infection, cyst at the injection site, bruising at the injection site.
Frequency not known:cannot be estimated from the available data
- dangerously low number of a type of white blood cell necessary to fight infections
- severe allergic reaction characterized by fever, swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue, difficulty breathing, itching, rash, and sometimes a drop in blood pressure
- dangerously excessive water intake
- sleep-related eating disorder
- diabetic coma due to uncontrolled diabetes
- decrease in oxygen in parts of the body (due to decreased blood flow)
- rapid, shallow breathing, pneumonia caused by aspiration of food, voice disorder
- absence of intestinal movement that causes obstruction
- yellow color of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- severe or potentially fatal rash with blisters and peeling of the skin that can start in the mouth, nose, eyes, and genitals and spread to other areas of the body (Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis)
- severe allergic reaction with swelling that can affect the throat, causing difficulty breathing
- skin discoloration
- posture abnormality
- newborn babies, from mothers who have been treated with paliperidone during pregnancy, may experience adverse effects from the medicine and/or withdrawal symptoms, such as irritability, weak or sustained muscle contractions, restlessness, drowsiness, breathing problems, or difficulty feeding
- decreased body temperature
- dead skin cells at the injection site and ulcer at the injection site
Reporting of adverse effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible adverse effect that is not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Conservation of Paliperidona Stada
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the box and on the pre-filled syringe after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
This medicine does not require special storage conditions.
Medicines should not be thrown down the drain or into the trash. Deposit the containers and medicines that you no longer need in the SIGRE point of the pharmacy. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the containers and medicines that you no longer need. This way, you will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Composition of Paliperidona Stada
The active ingredient is paliperidone.
Each Paliperidona Stada 50 mg pre-filled syringe contains paliperidone palmitate equivalent to 50 mg.
Each Paliperidona Stada 75 mg pre-filled syringe contains paliperidone palmitate equivalent to 75 mg.
Each Paliperidona Stada 100 mg pre-filled syringe contains paliperidone palmitate equivalent to 100 mg.
Each Paliperidona Stada 150 mg pre-filled syringe contains paliperidone palmitate equivalent to 150 mg.
The other components are:
Polysorbate 20 (E 432)
Macrogol
Citric acid monohydrate (E 330)
Sodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous (E 339)
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate
Sodium hydroxide (E 542) (for pH adjustment)
Water for injectable preparations
Appearance of the Product and Container Content
Paliperidona Stada is a white to off-white prolonged-release injectable suspension in a pre-filled syringe.
Pre-filled syringe made of cyclic olefin copolymer with a plunger-type stopper, rear stopper, and a needle shield (bromobutyl rubber).
Each pack contains 1 pre-filled syringe and 2 needles.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
Laboratorio STADA, S.L.
Frederic Mompou, 5
08960 Sant Just Desvern (Barcelona)
Spain
Manufacturer
STADA Arzneimittel AG
Stadastraße, 2-18
61118 Bad Vilbel
Germany
or
STADA Arzneimittel GmbH
Muthgasse 36/2
1190 Wien
Austria
or
Centrafarm Services B.V.
Van de Reijtstraat 31-E
4814 NE Breda
Netherlands
Date of the Last Revision of this Leaflet: March 2024.
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es.
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals and should be read in conjunction with the complete prescribing information (Summary of Product Characteristics).
The injectable suspension is for single use. It should be visually examined for any foreign particles before administration. Do not use the product if the syringe is not visually free of foreign particles.
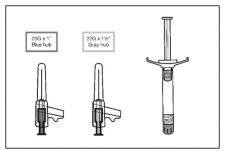
The pack contains a pre-filled syringe and 2 safety needles (one 22-gauge 1½-inch [38 mm x 0.7 mm] needle and one 23-gauge 1-inch [25 mm x 0.6 mm] needle) for intramuscular injection.
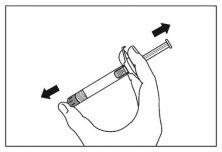
- Shake the syringe vigorously for at least 10 seconds to ensure a homogeneous suspension.
- Select the appropriate needle.
The first initiation dose of Paliperidona Stada (150 mg) is administered on Day 1 in the DELTOID muscle using the needle for DELTOID injection. The second initiation dose of Paliperidona Stada (100 mg) is also administered in the DELTOID muscle one week later (Day 8) using the needle for DELTOID injection.
If a patient is switched from prolonged-release injectable risperidone to Paliperidona Stada, the first injection of Paliperidona Stada (dose range 25 mg to 150 mg) can be administered in the DELTOID muscle or GLUTEAL muscle, using the appropriate needle for the injection site, at the time of the next scheduled injection.
Subsequent monthly maintenance injections can be administered in either the DELTOID or GLUTEAL muscle using the appropriate needle for the injection site.
In the case of DELTOID injection, if the patient weighs <90 kg, use the 23-gauge 1-inch (25 mm x 0.6 mm) needle (needle with blue hub); if patient weighs ≥ 90 22-gauge 1½-inch (38 0.7 gray hub).< p>
In the case of GLUTEAL injection, use the 22-gauge 1½-inch (38 mm x 0.7 mm) needle (needle with gray hub).
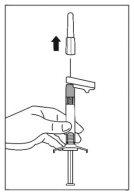
- While holding the syringe in a vertical position, remove the rubber needle shield with a gentle twisting motion.
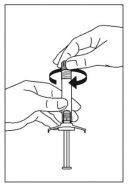
- Open the safety needle blister pack halfway. Hold the needle cover using the plastic of the pack. Add the safety needle to the Luer-type connection of the syringe with a gentle twisting motion in a clockwise direction.
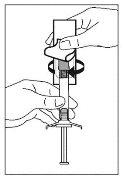
- Pull the sheath straight off to separate it from the needle. Do not twist the sheath, as the needle may become loose from the syringe.
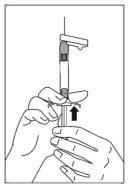
- Hold the syringe with the needle in a vertical position to proceed with air elimination. Eliminate air from the syringe by carefully pushing the plunger forward.
- Inject the entire contents slowly, deeply into the selected deltoid or gluteal muscle of the patient. Do not administer intravascularly or subcutaneously.
- Once the injection is complete, use your thumb or another finger (8a, 8b) or a flat surface (8c) to activate the needle protection system. The system is fully activated when a "click" is heard. Dispose of the syringe with the needle properly.
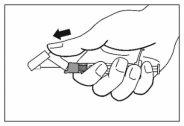
8a
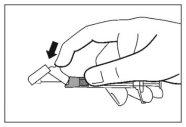
8b
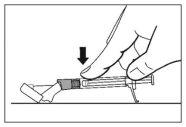
8c
Disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have come into contact with them should be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price262.27 EUR
- Availability in pharmacies
Supply issue reported
Data from the Spanish Agency of Medicines (AEMPS) indicates a supply issue affecting this medicine.<br><br>Availability may be limited in some pharmacies.<br><br>For updates or alternatives, consult your pharmacist. - Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to PALIPERIDONA STADA 150 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGEDosage form: INJECTABLE, 150 mg + 100 mgActive substance: paliperidoneManufacturer: Teva Pharma S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50 mgActive substance: paliperidoneManufacturer: Teva Pharma S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1000 mgActive substance: paliperidoneManufacturer: Janssen-Cilag International N.VPrescription required
Online doctors for PALIPERIDONA STADA 150 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Discuss questions about PALIPERIDONA STADA 150 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SUSPENSION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions











