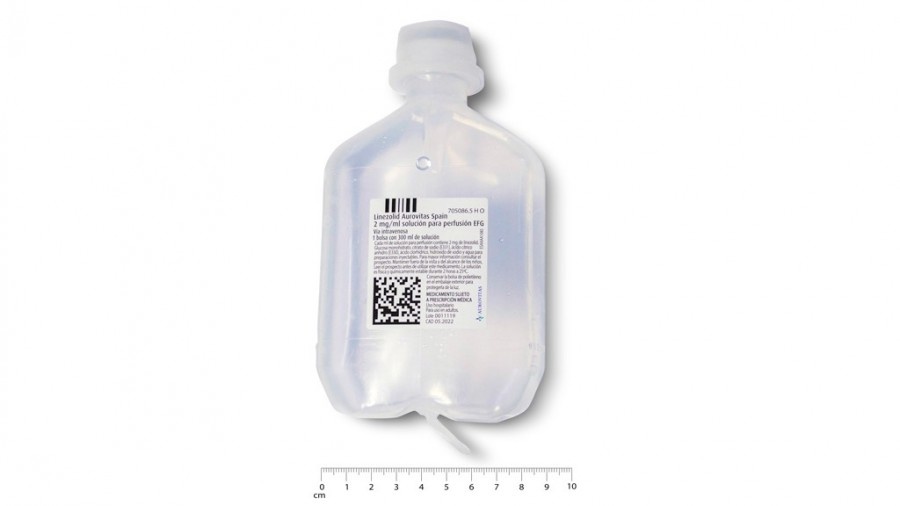
LINEZOLID KABI 2 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSION


How to use LINEZOLID KABI 2 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml solution for infusion EFG
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start takingthis medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What is Linezolid Kabi and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Linezolid Kabi
- How to use Linezolid Kabi
- Possible side effects
- Storing Linezolid Kabi
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Linezolid Kabi and what is it used for
Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml is an antibiotic of the oxazolidinone group that works by slowing the growth of certain types of bacteria (germs) that cause infections.
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections and do not work for viral infections such as the flu or the common cold.
It is essential that you follow the dosage, administration interval, and treatment duration instructions indicated by your doctor.
Do not store or reuse this medication. If you have any leftover antibiotic after finishing the treatment, return it to the pharmacy for proper disposal. Do not throw away medications down the drain or in the trash.
It is used for the treatment of pneumonia and certain skin or subcutaneous tissue infections. Your doctor will decide if Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml is suitable for treating your infection.
2. What you need to know before you use Linezolid Kabi
Do not use Linezolid Kabi
- if you are allergic to linezolid or any of the other components of this medication (listed in section 6).
- if you are taking or have taken in the last 2 weeks any medication belonging to the class of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs, e.g., phenelzine, isocarboxazid, selegiline, moclobemide). You may have been prescribed these medications to treat depression or Parkinson's disease.
- if you are breastfeeding. The reason is that linezolid passes into breast milk and may affect the baby.
Warnings and Precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting to use Linezolid Kabi.
Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml may not be suitable for you if you answer "yes" to any of the following questions. In this case, inform your doctor, who will need to examine your overall health and blood pressure before and during treatment or decide if there is another treatment better for you.
Ask your doctor if you are unsure if these categories apply to you.
- Do you have high blood pressure, regardless of whether you are taking medications for it?
- Have you been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism?
- Do you have a tumor of the adrenal glands (pheochromocytoma) or carcinoid syndrome (caused by tumors of the hormonal system with symptoms of diarrhea, skin flushing, and wheezing)?
- Do you suffer from bipolar disorder, schizoaffective disorders, mental confusion, or other mental problems?
- Do you have a history of hyponatremia (low sodium levels in the blood) or take medications that reduce sodium levels in the blood, such as certain diuretics, e.g., hydrochlorothiazide?
- Do you take opioids?
The use of certain medications, including antidepressants and opioids, along with linezolid, may cause adverse reactions, such as changes in blood pressure, temperature, or heart rate.
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medication.
Tell your doctor if you are taking or have taken in the last 2 weeksthe following medications, as Linezolid Kabi should not be taken if you are already taking these medications or have taken them recently (see also section 2, "Do not use Linezolid Kabi"):
- medications that can inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAOIs, e.g., phenelzine, isocarboxazid, selegiline, moclobemide). You may have been prescribed these medications to treat depression or Parkinson's disease.
Also, inform your doctor if you are taking any of the following medications. Your doctor may still decide to prescribe Linezolid Kabi, but needs to examine your overall health and blood pressure before and during treatment. In other cases, your doctor may decide to prescribe another treatment that is better for you.
- nasal decongestants or anti-cold medications containing pseudoephedrine or phenylpropanolamine.
- certain medications for treating asthma, such as salbutamol, terbutaline, fenoterol.
- certain antidepressants, such as tricyclics or SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors). There are many of these, such as amitriptyline, citalopram, clomipramine, dosulepin, doxepin, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, imipramine, lofepramine, paroxetine, sertraline.
- medications for treating migraines, such as sumatriptan and zolmitriptan.
- medications for treating severe and sudden allergic reactions, such as adrenaline (epinephrine).
- medications that increase blood pressure, such as noradrenaline (norepinephrine), dopamine, and dobutamine.
- opioids (e.g., pethidine) used to treat moderate to severe pain.
- medications for treating anxiety disorders, such as buspirone.
- medications that prevent blood clotting, such as warfarin.
- an antibiotic called rifampicin.
Using Linezolid Kabi with food and drinks
- You can use Linezolid Kabi before, during, or after meals.
- Avoid taking large amounts of mature cheese, yeast extracts, or soy extracts (such as soy sauce) and alcoholic beverages, especially draft beer and wine. The reason is that linezolid may react with a substance called tyramine that is present in some foods. This interaction can cause an increase in your blood pressure.
- If you develop a throbbing headache after eating or drinking, inform your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
The effects of Linezolid Kabi on pregnant women are not known. Therefore, it should not be used during pregnancy, unless advised by your doctor. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
You should not breastfeed if you are using Linezolid Kabi, as it passes into breast milk and may affect the baby.
Driving and using machines
Linezolid Kabi may cause dizziness or vision problems. If this happens, do not drive or use machines. Remember that if you feel unwell, your ability to drive or use machines may be impaired.
Linezolid Kabi contains glucose
This medication contains glucose.
Patients with diabetes mellitus should note that this medication contains 45.7 mg of glucose per ml of solution (13.7 g in a bag).
Linezolid Kabi contains sodium
Patients on low-sodium diets should note that each 1 ml of Linezolid Kabi contains 0.38 mg of sodium (the main component of table/cooking salt) (114 mg of sodium in a bag). The sodium in a bag is equivalent to 5.7% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake for an adult.
3. How to use Linezolid Kabi
Follow exactly the administration instructions of this medication indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Adults
This medication will be administered to you by a doctor or another healthcare professional through a drip (by infusion into a vein).
The recommended dose for adults (18 years or older) is 300 ml (600 mg of linezolid) twice a day, administered directly into the bloodstream (intravenously) through a drip over a period of 30 to 120 minutes.
If you are on dialysis, you will be administered Linezolid Kabi after each dialysis session.
A normal treatment period usually lasts from 10 to 14 days, but can be up to 28 days. The safety and efficacy of this medication for periods longer than 28 days have not been established. Your doctor will decide the duration of treatment.
During treatment with Linezolid Kabi, your doctor should perform periodic blood tests to monitor your blood count.
Your doctor should monitor your vision if you use Linezolid Kabi for more than 28 days.
Use in children and adolescents
Linezolid Kabi is not normally used in children and adolescents (under 18 years of age).
If you use more Linezolid Kabi than you should
If you think you may have been given more Linezolid Kabi than you should, inform your doctor or nurse.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medication and the amount ingested.
If you forget to use Linezolid Kabi
Since this medication is administered under close supervision, it is very unlikely that a dose will be missed. If you think a dose of the treatment has been missed, inform your doctor or nurse. Do not take a double dose to make up for missed doses.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, Linezolid Kabi can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist immediatelyif you experience any of these side effects during treatment with Linezolid Kabi:
The most serious side effects (whose frequency is between parentheses) of Linezolid Kabi are:
- Severe skin reactions (uncommon), swelling, particularly around the face and neck (uncommon), wheezing, and/or difficulty breathing (rare). This may be a sign of an allergic reaction, and it may be necessary to discontinue treatment with Linezolid Kabi. Skin reactions such as a purple elevated rash due to inflammation of blood vessels (rare), skin with red blisters and peeling (dermatitis) (uncommon), skin rash (common), itching (common).
- Vision problems (uncommon) such as blurred vision (uncommon), changes in color perception (not known), difficulty seeing details (not known), or narrowing of the visual field (rare).
- Severe diarrhea, with bloody and/or mucous stools (antibiotic-associated colitis, including pseudomembranous colitis), which can rarely lead to potentially life-threatening complications (uncommon).
- Repeated nausea or vomiting, abdominal pain, or rapid breathing (rare).
- Seizures or convulsions have been reported (uncommon).
- Serotonin syndrome (not known) should inform your doctor if you experience agitation, confusion, delirium, rigidity, tremors, uncoordination, convulsions, rapid heartbeat, severe respiratory problems, and diarrhea (suggestive of serotonin syndrome) while taking antidepressants such as SSRIs or opioids (see section 2).
- Unexplained bleeding or bruising, which may be due to an alteration in the number of certain blood cells that can affect blood clotting or produce anemia (common).
- Changes in the number of certain blood cells that can affect the ability to fight infections (uncommon). Some signs of infection include: fever (common), sore throat (uncommon), mouth ulcers (uncommon), and fatigue (uncommon).
- Rhabdomyolysis (rarely): signs and symptoms include muscle pain, sensitivity, or weakness without explanation, and/or dark urine. These can be signs of a serious condition called rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown), which can cause kidney damage. Pancreatitis (uncommon).
- Seizures (uncommon).
- Transient ischemic attacks (temporary alteration of blood flow to the brain that causes short-term symptoms such as vision loss, weakness in arms and legs, difficulty speaking, and loss of consciousness) (uncommon).
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus) (uncommon).
Numbness, tingling, or blurred vision are other side effects reported by patients treated with Linezolid Kabi for more than 28 days. If you experience vision difficulties, consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Other side effects include:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Fungal infections, especially vaginal or oral
- Headache
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting
- Changes in some blood test results, including protein, salt, or enzyme tests that measure kidney or liver function or blood glucose concentration
- Difficulty sleeping
- Increased blood pressure
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Dizziness
- Abdominal pain, localized or generalized
- Constipation
- Indigestion
- Localized pain
- Decreased platelet count
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Vaginal or genital inflammation in women
- Tingling or numbness sensations
- Swollen, painful, or discolored tongue
- Dry mouth
- Pain at the injection site (vein) or around it
- Venous inflammation (including where the vein is placed for infusion)
- Frequent need to urinate
- Chills
- Feeling of thirst
- Increased sweating
- Hyponatremia (low sodium levels in the blood)
- Kidney failure
- Abdominal swelling
- Pain at the injection site
- Increased creatinine
- Stomach pain
- Changes in heart rhythm (e.g., increased heart rate)
- Decrease in blood cell count
- Weakness and/or sensory changes
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people)
- Change in tooth surface color, which can be removed with a professional dental cleaning (tartrectomy)
The following side effects have also been reported (frequency not known: cannot be estimated from available data)
- Alopecia (hair loss)
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medication Surveillance System for Human Use: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Linezolid Kabi
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Freeflex Bag: Do not use this medication after the expiration date shown on the bag, outer bag, and outer packaging after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the indicated month.
The healthcare professional will ensure that Linezolid Kabi is not used after the "Use by" date printed on the bag and that it will be administered as soon as the seal is broken. They will also visually inspect the solution before use and only administer the solution if it is transparent and particle-free. Store the outer bag in the original packaging to protect it from light until preparation.
KabiPac Vial: Do not use this medication after the expiration date shown on the vial and outer packaging after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the indicated month.
Hospital staff will ensure that Linezolid Kabi is not used after the "Use by" date printed on the vial and that it will be administered as soon as it is removed from the outer packaging. They will also visually inspect the solution before use and only administer the solution if it is transparent and particle-free. They will also ensure that the solution is stored correctly in its outer packaging to protect it from light and keep it out of sight and reach of children until needed.
After opening
Physical and chemical stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 2-8°C.
From a microbiological point of view, unless the opening method excludes the risk of microbial contamination, the product must be used immediately. If not used immediately, the storage time and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medications you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Linezolid Kabi
- The active ingredient is linezolid. Each 1 ml of solution contains 2 mg of linezolid.
- The other components are glucose monohydrate (a type of sugar), sodium citrate, citric acid, hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide, and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of Linezolid Kabi and Container Contents
Freeflex Bag:
Linezolid Kabi is presented as a clear, practically particle-free, colorless or yellowish solution in single-unit perfusion bags containing 300 ml (600 mg of linezolid) of solution.
The bags are supplied in boxes of 10, 30, or 50 bags.
KabiPac Vial:
Linezolid Kabi is presented as a clear, practically particle-free, colorless or yellowish or slightly brown solution in single-unit perfusion vials containing 300 ml (600 mg of linezolid) of solution.
The vials are supplied in boxes of 10, 30, or 50 vials.
Only some pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.
Marina 16-18,
08005 Barcelona
Spain
Manufacturer
Fresenius Kabi Norge AS
Svinesundsveien 80,
NO-1788 Halden
Norway
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Member State | Medicinal Product Name |
Austria | Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml Infusionslösung |
Belgium | Linezolid Fresenius Kabi 2 mg/ml, oplossing voor infusie |
Bulgaria | Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml ?????????? ??????? |
Croatia | Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml otopina za infuziju |
Czech Republic | Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml |
Denmark | Linezolid Fresenius Kabi |
Estonia | Linezolid Fresenius Kabi |
France | Linezolide Kabi 2 mg/ml, solution pour perfusion |
Germany | Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml Infusionslösung |
Hungary | Linezolid Fresenius Kabi, 2 mg/ml oldatos infúzió |
Ireland | Linezolid 2 mg/ml solution for infusion |
Italy | Linezolid Kabi |
Luxembourg | Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml Infusionslösung |
Netherlands | Linezolid Fresenius Kabi 2 mg/ml, oplossing voor infusie |
Poland | Linezolid Kabi |
Portugal | Linezolida Kabi |
Romania | Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml solutie perfuzabila |
Slovakia | Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml |
Slovenia | Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml raztopina za infundiranje |
Spain | Linezolid Kabi 400 mg/250 ml solution for perfusion |
United Kingdom | Linezolid 2 mg/ml solution for infusion |
Greece | Linezolid Kabi |
Norway | Linezolid Fresenius Kabi |
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet:
Detailed and up-to-date information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml solution for infusion
IMPORTANT: Consult the summary of product characteristics before prescribing.
Linezolid lacks activity against infections caused by Gram-negative microorganisms. Specific treatment against this type of microorganism will be initiated at the same time if the presence of a Gram-negative microorganism is documented or suspected.
Description of Freeflex bags:
Freeflex perfusion bags, made of polyolefin, multilayer, latex-free, single-use, ready-to-use, sealed inside an aluminum laminated outer bag. The bag contains 300 ml of solution and is packaged in a box. Each box contains 10, 30, or 50 perfusion bags.
Linezolid Kabi contains linezolid 2 mg/ml in an isotonic solution, clear, practically particle-free, colorless to yellowish. The other ingredients are: glucose monohydrate, sodium citrate, citric acid, hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide, and water for injectable preparations.
Description of KabiPac vials:
KabiPac vials, made of polyethylene, single-use, ready-to-use, closed with a stopper that contains a rubber disk that allows the insertion of the needle. The vial contains 300 ml of solution and is packaged in a box. Each box contains 10, 30, or 50 perfusion vials.
Linezolid Kabi contains linezolid 2 mg/ml in an isotonic solution, clear, particle-free, colorless to yellowish or slightly brown. The other ingredients are: glucose monohydrate, sodium citrate, citric acid, hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide, and water for injectable preparations.
Posology and Method of Administration
Linezolid should only be initiated in a hospital setting and after consultation with a relevant specialist such as a microbiologist or an infectious disease specialist. Patients who initiate treatment with the parenteral formulation may switch to any of the oral formulations when clinically indicated. In this case, no dose adjustment is required, as the oral bioavailability of linezolid is approximately 100%.
The solution for infusion should be administered over a period of 30 to 120 minutes.
The recommended dose of linezolid should be administered intravenously (IV) twice a day.
Recommended Doses and Duration of Treatment in Adults:
The duration of treatment depends on the pathogen, the site of infection, and its severity, and the patient's clinical response.
The following recommendations on the duration of treatment are a reflection of those used in clinical trials. It is possible that for some types of infection, shorter therapeutic guidelines may be adequate, although they have not been evaluated in clinical trials.
The maximum duration of treatment is 28 days. The safety and efficacy of linezolid administered for periods longer than 28 days have not been established.
No increase in the recommended dose or duration of treatment is necessary for infections associated with concurrent bacteremia.
The posological recommendations are as follows:
Infections | Posology | Duration of Treatment |
Nosocomial pneumonia | 600 mg twice a day | 10-14 consecutive days |
Community-acquired pneumonia | ||
Complicated skin and soft tissue infections | 600 mg twice a day |
Pediatric Population
The safety and efficacy of linezolid have not been established in children under 18 years of age. The currently available data are described in sections 4.8, 5.1, and 5.2 of the summary of product characteristics, however, no posological recommendation can be made.
Elderly:No dose adjustments are required.
Renal Impairment:No dose adjustment is required.
Severe renal impairment (i.e., creatinine clearance [ClCr] <30 ml min)< p>
No dose adjustments are required. Since the clinical importance of greater exposure (up to 10 times) to the two main metabolites of linezolid in patients with severe renal impairment is unknown, linezolid should be used with caution in these patients and only when the expected benefits outweigh the theoretical risk.
Since approximately 30% of the linezolid dose is eliminated during the 3 hours of hemodialysis, linezolid should only be administered after dialysis in this type of patient. The main metabolites of linezolid are partially eliminated during hemodialysis, although their concentrations remain considerably higher after dialysis than those observed in patients with normal renal function or mild to moderate renal impairment.
Therefore, linezolid should be used with special caution in patients with severe renal impairment undergoing dialysis and only when the expected benefits outweigh the theoretical risk.
So far, there is no experience with the administration of linezolid to patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) or alternative treatments for renal failure (other than hemodialysis).
Hepatic Impairment:Patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A or B): No dose adjustment is required.
Severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C): As linezolid is metabolized by a non-enzymatic process, it is not expected that hepatic function impairment will significantly alter its metabolism, and therefore, no dose adjustments are recommended. However, there are not enough clinical data, and it is recommended to use linezolid in these patients only when the expected benefit is considered superior to the theoretical risk (see sections 4.4 and 5.2 of the summary of product characteristics).
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to linezolid or to any of the excipients.
Linezolid should not be used in patients who are taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors A or B (such as phenelzine, isocarboxazid, selegiline, moclobemide) or in the two weeks following the use of these medications. Unless there are facilities for strict surveillance and control of blood pressure, linezolid should not be administered to patients with the following underlying diseases or under the following concomitant treatments:
- Patients with untreated hypertension, pheochromocytoma, carcinoid syndrome, thyrotoxicosis, bipolar disorder, schizoaffective disorders, acute confusion states.
- Patients taking any of the following medications: serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, 5-HT1 receptor agonists (triptans), direct or indirect sympathomimetics (including adrenergic bronchodilators, pseudoephedrine, and phenylpropanolamine), vasopressors (such as epinephrine and norepinephrine), dopaminergics (such as dopamine and dobutamine), pethidine, or buspirone.
Breastfeeding should be interrupted before and during treatment (see section 4.6 of the summary of product characteristics).
Special Warnings and Precautions for Use
Myelosuppression
Cases of myelosuppression (including anemia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, and thrombocytopenia) have been reported in patients treated with linezolid. In patients who were followed up, it has been seen that after discontinuing treatment, the affected hematological parameters have increased towards pre-treatment levels. The risk of these effects appears to be associated with the duration of treatment. Elderly patients treated with linezolid may be at greater risk of experiencing blood dyscrasias than younger patients. Thrombocytopenia may occur more frequently in patients with severe renal impairment, with or without dialysis, and in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment. Therefore, it is recommended to perform close monitoring of the hemogram in patients who: have pre-existing anemia, granulocytopenia, or thrombocytopenia; receive concomitant medication that may decrease hemoglobin levels and hematocrit or reduce platelet count or affect platelet function; have severe renal impairment or moderate to severe hepatic impairment; or receive more than 10-14 days of treatment.
Linezolid should only be administered to these patients if close monitoring of hemoglobin levels, blood count, and platelets is possible.
If significant myelosuppression occurs during treatment with linezolid, treatment should be discontinued, unless it is considered absolutely necessary to continue, in which case, exhaustive monitoring of hematological parameters should be performed and appropriate therapeutic measures should be implemented.
Additionally, a complete blood count (including hemoglobin, platelets, absolute leukocyte count, and formula) is recommended weekly for patients receiving linezolid, regardless of their baseline hemogram.
In compassionate use studies, a higher incidence of severe anemia was reported in patients who were being treated with linezolid for periods longer than the recommended maximum treatment duration of 28 days. These patients required blood transfusions more frequently. Cases of anemia that required blood transfusion have also been reported during post-marketing experience, with a higher number of cases in patients who received linezolid for more than 28 days.
Cases of sideroblastic anemia have been reported during post-marketing experience. In the cases where the time of onset is known, most patients were treated for more than 28 days. Most patients recovered fully or partially after discontinuing treatment with linezolid, with or without treatment for anemia.
Mortality Imbalance in a Clinical Trial in Patients with Gram-Positive Catheter-Related Vascular Infections
In an open study in severely ill patients with catheter-related vascular infections, an excess of mortality was observed in patients treated with linezolid compared to those treated with vancomycin/dicloxacillin/oxacillin [78/363 (21.5%) versus 58/363 (16.0%)]. The main factor that influenced the mortality rate was the baseline status of Gram-positive infection. Mortality rates were similar in patients with infections caused exclusively by Gram-positive microorganisms (odds ratio 0.96; 95% CI: 0.58-1.59), but were significantly higher (p = 0.0162) in the linezolid arm for patients infected with any other microorganism or in whom no baseline microorganism was isolated (odds ratio 2.48; 95% CI: 1.38-4.46). The greatest imbalance occurred during treatment and within 7 days after discontinuation of the study drug. In the linezolid arm, there were more patients who acquired Gram-negative infections during the study and who died from Gram-negative infections and polymicrobial infections. Therefore, linezolid should only be used in patients with complicated skin and soft tissue infections in whom a Gram-negative co-infection is suspected or confirmed, if no alternative treatments are available. In these circumstances, concomitant treatment against Gram-negative microorganisms should be initiated.
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea and Colitis
With the use of almost all antibiotics, including linezolid, cases of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and colitis, including pseudomembranous colitis and Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea, have been reported, whose severity can range from mild diarrhea to life-threatening colitis. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who develop severe diarrhea during or after treatment with linezolid. If antibiotic-associated diarrhea or colitis is suspected or confirmed, treatment with the antibacterial agent, including linezolid, should be discontinued, and appropriate therapeutic measures should be initiated immediately. In this situation, medications that inhibit peristalsis are contraindicated.
Lactic Acidosis
Cases of lactic acidosis have been reported with the use of linezolid. Patients who develop signs or symptoms of metabolic acidosis, including recurrent nausea or vomiting, abdominal pain, low bicarbonate levels, or hyperventilation while being treated with linezolid should receive immediate medical attention. If lactic acidosis occurs, the benefits of continuing treatment with linezolid should be weighed against the potential risks.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Linezolid inhibits mitochondrial protein synthesis. As a result of this inhibition, adverse events such as lactic acidosis, anemia, and neuropathy (optic and peripheral) may occur; these events are more frequent when the duration of treatment is longer than 28 days.
Serotonin Syndrome
Spontaneous reports of serotonin syndrome associated with the concomitant administration of linezolid and serotonergic agents, including antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and opioids, have been communicated. Therefore, the concomitant administration of linezolid and serotonergic agents is contraindicated (see section 4.3 of the summary of product characteristics), unless the administration of linezolid and serotonergic agents is absolutely necessary. In these cases, patients should be closely monitored for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, such as cognitive dysfunction, hyperpyrexia, hyperreflexia, and incoordination. If signs or symptoms appear, it should be considered to discontinue one or both agents; if treatment with the serotonergic agent is discontinued, symptoms may disappear.
Rhabdomyolysis
Cases of rhabdomyolysis have been reported with the use of linezolid. Linezolid should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors to rhabdomyolysis. If signs or symptoms of rhabdomyolysis are observed, treatment with linezolid should be discontinued, and appropriate treatment should be initiated.
Hyponatremia and SIADH
Hyponatremia and/or syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) have been observed in some patients treated with linezolid. It is recommended to monitor sodium levels regularly.
Carefully monitor serum sodium levels in patients at risk of hyponatremia, such as elderly patients or patients taking medications that may reduce sodium levels in the blood (e.g., thiazide diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide).
Optic and Peripheral Neuropathy
Cases of peripheral neuropathy, as well as optic neuropathy and optic neuritis, which can progress to vision loss, have been reported in patients treated with linezolid; these cases have occurred primarily in patients treated for periods longer than the recommended maximum duration of 28 days.
Patients should be advised to report symptoms of visual impairment, such as changes in visual acuity, changes in color vision, blurred vision, or defects in the visual field. In such cases, it is recommended to evaluate visual function as soon as possible and consult an ophthalmologist if necessary. Visual function should be regularly monitored in any patient treated with linezolid for a period longer than the recommended 28 days.
Continuation of treatment with linezolid in patients who have experienced optic or peripheral neuropathy should be weighed against the potential risks.
There may be a higher risk of neuropathies when linezolid is used in patients who are currently taking or have recently taken antimycobacterial medication for the treatment of tuberculosis.
Seizures
Seizures have been reported in patients treated with linezolid. In most of these cases, a history of seizures or risk factors for seizures was reported. Patients should be advised to inform their doctor if they have a history of seizures.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Linezolid is a reversible and non-selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase (MAOI); however, it does not exert any antidepressant effect at the doses used for antibacterial treatment. There are limited data on pharmacological interaction and safety studies of linezolid in patients receiving linezolid and presenting underlying conditions and/or receiving concomitant treatment with drugs that increase this risk. Therefore, it is not recommended to use linezolid in these circumstances unless close observation and monitoring of the patient are possible.
Use with Foods Rich in Tyramine
Patients should be warned not to consume large amounts of foods rich in tyramine.
Superinfection
The effects of treatment with linezolid on normal flora have not been evaluated in clinical trials.
Occasionally, the use of antibacterial agents may produce an overgrowth of non-susceptible microorganisms. Approximately 3% of patients who received linezolid at the recommended doses during clinical trials presented treatment-associated candidiasis. In cases of superinfection during treatment, adequate measures should be taken.
Special Populations
Linezolid should be used with special caution in patients with severe renal impairment and only if the expected benefit is considered to outweigh the potential risk (see sections 4.2 and 5.2).
It is recommended that linezolid be administered to patients with severe hepatic impairment only if the expected benefit is considered to outweigh the potential risk.
Effects on Fertility
In studies conducted in adult male rats with exposure levels to linezolid similar to those expected in humans, a reversible decrease in fertility and abnormal sperm morphology were observed. The potential effects of linezolid on the human male reproductive system are unknown.
Clinical Trials
The safety and efficacy of linezolid have not been established when administered for periods longer than 28 days.
Controlled clinical trials did not include patients with diabetic foot lesions, decubitus ulcers, ischemic lesions, severe burns, or gangrene. Consequently, there is limited experience with the use of linezolid in the treatment of these conditions.
Excipients
Glucose
This medicinal product contains 45.7 mg of glucose per ml of solution (13.7 g/300 ml), which should be taken into account in the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus or other conditions associated with glucose intolerance.
Sodium
This medicinal product contains 0.38 mg of sodium per ml of solution (114 mg/300 ml), equivalent to 0.02 of the maximum daily recommended intake (DRI) of 2 g of sodium per WHO for an adult, which should be taken into account in the treatment of patients on low-sodium diets.
Linezolid solution for infusion may be prepared for administration with solutions containing sodium (see sections 4.2, 6.2, and 6.6) and this should be considered in relation to the total sodium from all sources administered to the patient.
Interactions
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Linezolid is a reversible non-selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase (MAOI). Data from pharmacological interaction and safety studies of linezolid administered to patients undergoing concomitant treatment with risk of MAO inhibition are very limited. Therefore, it is not recommended to use linezolid in these circumstances unless close observation and control of the patient are possible.
Potential Interactions that Produce Increased Blood Pressure
Linezolid increased the hypertensive effect produced by pseudoephedrine and phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride in healthy normotensive volunteers. The simultaneous administration of linezolid with pseudoephedrine or phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride produced mean increases in systolic blood pressure of the order of 30-40 mmHg, compared to the 11-15 mmHg produced by linezolid alone, the 14-18 mmHg produced by pseudoephedrine or phenylpropanolamine alone, and the 8-11 mmHg produced by placebo. No similar studies have been conducted in hypertensive patients. It is recommended that if linezolid is administered with vasopressor agents (including dopaminergic agents), the doses of these agents should be carefully titrated to achieve the desired response.
Potential Serotoninergic Interactions
In healthy volunteers, the potential pharmacological interaction of linezolid with dextromethorphan was studied. Two doses of 20 mg of dextromethorphan were administered with a difference of 4 hours, with or without linezolid. In healthy subjects who received linezolid and dextromethorphan, no effects of the serotoninergic syndrome (confusion, delirium, restlessness, tremor, flushing, diaphoresis, hyperpyrexia) were observed.
During post-marketing experience: a case of a patient experiencing symptoms similar to those of the serotoninergic syndrome during the intake of linezolid and dextromethorphan was reported, which resolved with the interruption of both treatments.
Cases of serotoninergic syndrome have been reported during the clinical use of linezolid in combination with serotoninergic agents, including antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and opioids. Therefore, as concomitant administration is contraindicated (see section 4.3 of the technical sheet), the management of patients for whom treatment with linezolid and serotoninergic agents is absolutely necessary.
Use with Foods Rich in Tyramine
No significant pressor response was observed in subjects who received linezolid and less than 100 mg of tyramine. This suggests that it is only necessary to avoid the intake of excessive amounts of foods or beverages with high tyramine content (e.g., mature cheese, yeast extracts, non-distilled alcoholic beverages, and fermented soy products such as soy sauce).
Medications that are Metabolized through Cytochrome P450
Linezolid is not metabolized to a detectable extent by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system nor does it inhibit any of the human cytochrome P450 isoforms that are clinically significant (1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4). Similarly, linezolid does not induce cytochrome P450 isoenzymes in rats. Therefore, no cytochrome P450-induced pharmacological interactions with linezolid are expected.
Rifampicin
The effect of rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics of linezolid has been studied in sixteen healthy adult males who were administered 600 mg of linezolid twice daily for 2.5 days, with or without 600 mg of rifampicin once daily for 8 days. Rifampicin decreased the Cmax and AUC of linezolid by a mean of 21% [90% CI, 15, 27] and a mean of 32% [90% CI, 27, 37], respectively. The mechanism of this interaction and its clinical relevance are unknown.
Warfarin
The simultaneous administration of warfarin and linezolid (at steady state) produced a reduction of 10% of the maximum mean INR (International Normalized Ratio) and a decrease of 5% of the AUC of INR. Data from patients who have received warfarin and linezolid are insufficient to evaluate the clinical relevance, if any, of these findings.
Fertility, Pregnancy, and Lactation
Pregnancy
Data on the use of linezolid in pregnant women are limited. Animal studies have shown reproductive toxicity. There is a potential risk in humans.
Linezolid should not be used during pregnancy, unless it is clearly necessary, i.e., only if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Breastfeeding
Animal data suggest that linezolid and its metabolites may pass into breast milk; therefore, breastfeeding should be interrupted before and during the entire treatment.
Fertility
In animal studies, linezolid caused a reduction in fertility.
Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
Patients should be warned that they may experience dizziness or symptoms of visual impairment while receiving linezolid, and they should be advised not to drive or operate machinery if any of these symptoms occur.
Adverse Reactions
The following table lists all adverse drug reactions with a frequency based on all causality data from clinical trials in which a total of more than 2,000 adult patients received the recommended doses of linezolid for up to a maximum of 28 days.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were diarrhea (8.9%), nausea (6.9%), vomiting (4.3%), and headache (4.2%).
The most frequently reported adverse reactions related to the drug that led to discontinuation of treatment were headache, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Approximately 3% of patients discontinued treatment due to a drug-related adverse reaction.
Additional adverse reactions reported during post-marketing experience are included in the table in the category of "Unknown frequency" since the frequency cannot be estimated from the available data.
The following adverse reactions have been observed and reported during treatment with linezolid with the following frequencies: Very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100 to <1>
System Organ Classification | Common (≥1/100 to <1> | Uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1> | Rare (≥1/10,000 to <1> | Unknown frequency (cannot be estimated from the available data) |
Infections and Infestations | candidiasis, oral candidiasis, vaginal candidiasis, fungal infections | antibiotic-associated colitis, including pseudomembranous colitis*, vaginitis | ||
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | thrombocytopenia*, anemia*† | pancytopenia*, leucopenia*, neutropenia, eosinophilia | sideroblastic anemia* | myelosuppression*, |
Immune System Disorders | anaphylaxis | |||
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | hyponatremia | lactic acidosis* | ||
Psychiatric Disorders | insomnia | |||
Nervous System Disorders | headache, altered taste (metallic taste), dizziness, | seizures*, peripheral neuropathy, hypoaesthesia, paresthesia | serotoninergic syndrome** | |
Eye Disorders | optic neuropathy*, blurred vision* | changes in the visual field* | optic neuritis*, vision loss*, changes in visual acuity*, changes in color vision*, | |
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders | tinnitus | |||
Cardiac Disorders | arrhythmia (tachycardia) | |||
Vascular Disorders | hypertension | transient ischemic attacks, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis | ||
Gastrointestinal Disorders | diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain localized or generalized, constipation, dyspepsia | pancreatitis, gastritis, abdominal distension, dry mouth, glossitis, soft stools, stomatitis, changes in tongue color | discoloration of the dental surface | |
Hepatobiliary Disorders | abnormal liver function tests, AST, ALT, and alkaline phosphatase elevated. | total bilirubin elevated | ||
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | pruritus, rash | angioedema, urticaria, bullous dermatitis, dermatitis, diaphoresis | toxic epidermal necrolysis#, Stevens-Johnson syndrome#, hypersensitivity vasculitis | alopecia. |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | rhabdomyolysis* | |||
Renal and Urinary Disorders | increased BUN | renal failure, polyuria, increased creatinine | ||
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders | vulvovaginal disorders | |||
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | fever, localized pain | chills, fatigue, pain at the injection site, increased thirst. | ||
Investigations | Biochemistry Increased LDH, creatine kinase, lipase, amylase, or non-fasting glucose. Decreased total proteins, albumin, sodium, or calcium. Increased or decreased potassium or bicarbonate. | Biochemistry Increased sodium or calcium. Decreased non-fasting glucose. Increased or decreased chloride. | ||
Hematology Neutrophilia or eosinophilia. Decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, or red blood cell count. Increased or decreased platelet count or white blood cell count. | Hematology Increased reticulocyte count. Neutropenia. |
- See section Warnings and Precautions
** See section Contraindications and Interaction with Other Medicinal Products and Other Forms of Interaction
# Estimated frequency of adverse drug reactions using "The Rule of Three".
† See below
The following adverse reactions to linezolid were considered serious in rare cases: localized abdominal pain, transient ischemic attacks, and hypertension.
† In controlled clinical trials in which linezolid was administered for periods of up to 28 days, anemia was reported in 2% of patients. In a compassionate use program for patients with life-threatening infections and underlying comorbidities, the percentage of patients who developed anemia when receiving linezolid ≤ 28 days was 2.5% (33/1326) compared to 12.3% (53/430) when treated for > 28 days. The proportion of cases of anemia related to the medication that required blood transfusion was 9% (3/33) in patients treated ≤ 28 days and 15% (8/53) in those treated for more than 28 days.
Pediatric Population
Safety data from clinical trials based on more than 500 pediatric patients (from birth to 17 years) do not indicate that the safety profile of linezolid for pediatric patients differs from that of adults.
Reporting of Suspected Adverse Reactions
It is important to report any suspected adverse reactions to the medicinal product after authorization. This allows for continuous monitoring of the benefit-risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are invited to report any suspected adverse reactions to the Spanish Medicines Surveillance System for Human Use https://www.notificaram.es.
Overdose
No specific antidotes are known.
No cases of overdose have been reported. However, the following information may be useful:
Supportive measures should be instituted, and glomerular filtration should be maintained. Approximately 30% of the linezolid dose is eliminated during 3 hours of hemodialysis, although there are no data on the elimination of linezolid by peritoneal dialysis or hemoperfusion.
Instructions for Use and Handling
For single use. Freeflex bag: Remove the outer packaging only at the time of use, checking for minor leaks by firmly pressing the
Bag. In case of leaks, it should not be used because it may have lost its sterility. The solution will be inspected visually before use and only transparent and particle-free solutions should be used. Do not use these bags in serial connections. Any remaining solution must be discarded. Do not reconnect partially used bags.
KabiPac Vial:
Remove the vial from the outer packaging only at the time of use. The solution will be inspected visually before use and only transparent and particle-free solutions should be used. Do not use these vials in serial connections. Any remaining solution must be discarded. It does not require any special requirements for disposal. Any remaining solution must be discarded according to local requirements. Do not reconnect partially used vials.
Linezolid Kabi 2 mg/ml solution for infusion is compatible with the following solutions:
- glucose 50 mg/ml (5%) for intravenous infusion,
- sodium chloride 0.9% for intravenous infusion,
- Ringer's lactate solution for injectable preparations (Hartmann's solution for infusion).
Incompatibilities
No additives should be added to this solution. If linezolid is administered with other drugs simultaneously, each one should be administered separately according to their instructions for use. Similarly, if the same intravenous line is used for the sequential intravenous infusion of several drugs, it should be flushed before and after the administration of linezolid with a compatible solution.
It is known that Linezolid Kabi solution for infusion is not physically compatible with the following compounds: amphotericin B, chlorpromazine hydrochloride, diazepam, pentamidine isethionate, erythromycin lactobionate, sodium phenytoin, and sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim. Additionally, it is not chemically compatible with sodium ceftriaxone.
Shelf Life
Physical and chemical stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 2-8°C and 25°C.
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately, unless the opening/reconstitution/dilution method avoids the risk of microbial contamination.
If it is not used immediately, the storage times in use and the conditions before use are the responsibility of the user.
Special Precautions for Storage
Freeflex Bag: Store the outer bag in the original packaging to protect it from light until preparation.
KabiPac Vial: Store the vial in the outer packaging until it is ready for use to protect it from light.
- Country of registration
- Availability in pharmacies
Supply issue reported
Data from the Spanish Agency of Medicines (AEMPS) indicates a supply issue affecting this medicine.<br><br>Availability may be limited in some pharmacies.<br><br>For updates or alternatives, consult your pharmacist. - Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to LINEZOLID KABI 2 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: TABLET, 600 mgActive substance: linezolidManufacturer: Medochemie LimitedPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 2 mg/mlActive substance: linezolidManufacturer: Altan Pharmaceuticals SaPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 2 mg/mlActive substance: linezolidManufacturer: Eugia Pharma (Malta) LimitedPrescription required
Online doctors for LINEZOLID KABI 2 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about LINEZOLID KABI 2 mg/ml SOLUTION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions