
LENALIDOMIDE Aurovitas 15 mg HARD CAPSULES

How to use LENALIDOMIDE Aurovitas 15 mg HARD CAPSULES
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Lenalidomide Aurovitas 5 mg hard capsules EFG
Lenalidomide Aurovitas 10 mg hard capsules EFG
Lenalidomide Aurovitas 15 mg hard capsules EFG
Lenalidomide Aurovitas 20 mg hard capsules EFG
Lenalidomide Aurovitas 25 mg hard capsules EFG
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Lenalidomide Aurovitas and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you take Lenalidomide Aurovitas
- How to take Lenalidomide Aurovitas
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Lenalidomide Aurovitas
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Lenalidomide Aurovitas and what is it used for
What is Lenalidomide Aurovitas
Lenalidomide Aurovitas contains the active substance “lenalidomide”. This medicine belongs to a group of medicines that affect how the immune system works.
What Lenalidomide Aurovitas is used for
Lenalidomide is used in adults to:
- Multiple myeloma
- Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)
- Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
- Follicular lymphoma
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects a specific type of white blood cell called plasma cells. These cells accumulate in the bone marrow and multiply out of control. This can damage the bones and kidneys.
Multiple myeloma usually has no cure. However, the signs and symptoms can be greatly reduced or may disappear for a period of time. This is called “remission”.
Newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: in patients who have undergone a bone marrow transplant
Lenalidomide is used as maintenance treatment after recovery from a bone marrow transplant.
Newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: in patients who cannot be treated with a bone marrow transplant
Lenalidomide is taken with other medicines, including:
- a chemotherapy medicine called “bortezomib”
- an anti-inflammatory called “dexamethasone”
- a chemotherapy medicine called “melphalan” and
- an immunosuppressant called “prednisone”
You will take these medicines at the start of treatment and then continue to take lenalidomide alone.
If you are 75 years or older, or have moderate to severe kidney problems, your doctor will monitor you closely before starting treatment.
Multiple myeloma: in patients previously treated
Lenalidomide is taken with an anti-inflammatory called “dexamethasone”.
Lenalidomide may slow down the worsening of multiple myeloma symptoms. It has also been shown to delay the return of multiple myeloma after treatment.
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)
MDS are a group of many different blood and bone marrow disorders. The blood cells become abnormal and do not work properly. Patients may experience a range of signs and symptoms including low red blood cell count (anemia), the need for blood transfusions, and the risk of infection.
Lenalidomide is used to treat adult patients diagnosed with MDS, when all of the following apply:
- need regular blood transfusions to treat low red blood cell counts (“transfusion-dependent anemia”)
- have a bone marrow cell abnormality called “isolated deletion 5q cytogenetic abnormality”. This means that your body does not produce enough healthy blood cells.
- other treatments you have used before are not suitable or do not work well enough.
Lenalidomide may increase the number of healthy red blood cells your body produces by reducing the number of abnormal cells:
- this may reduce the number of blood transfusions needed. You may not need transfusions at all.
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
MCL is a cancer of the immune system (lymphatic tissue). It affects a type of white blood cell called “B lymphocytes” or B cells. MCL is a disease in which B cells grow out of control and accumulate in the lymphatic tissue, bone marrow, or blood.
Lenalidomide is used alone to treat adult patients who have previously been treated with other medicines.
Follicular lymphoma (FL)
FL is a slow-growing cancer that affects B lymphocytes. These are a type of white blood cell that helps the body fight infections. When a person has FL, they may have too many of these B lymphocytes in the blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen.
Lenalidomide is used with another medicine called “rituximab” to treat adult patients who have previously been treated for follicular lymphoma.
How Lenalidomide Aurovitas works
Lenalidomide works by affecting the body's immune system and directly attacking the cancer. It works in several ways:
- stops the growth of cancer cells.
- stops the growth of blood vessels in the cancer.
- stimulates part of the immune system to attack cancer cells.
2. What you need to know before you take Lenalidomide Aurovitas
You must read the package leaflet of all the medicines you are going to take in combination with lenalidomide before starting treatment with this medicine.
Do not take Lenalidomide Aurovitas
If any of these conditions apply to you, do not take lenalidomide. If in doubt, talk to your doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting Lenalidomide Aurovitas if:
- you have ever had blood clots; during treatment, you have a higher risk of getting blood clots in the veins and arteries.
- you have any signs of infection, such as cough or fever.
- you have or have previously had a viral infection, especially hepatitis B, varicella-zoster, or HIV. If in doubt, talk to your doctor. Treatment with lenalidomide may cause the virus to become active again in patients who carry the virus. This can lead to the return of the infection. Your doctor should check if you have ever had a hepatitis B infection.
- you have kidney problems; your doctor may adjust your dose of lenalidomide.
- you have had a heart attack, have ever had a blood clot, or if you smoke, have high blood pressure, or high cholesterol levels.
- you have had an allergic reaction while using thalidomide (another medicine used to treat multiple myeloma), such as a skin rash, itching, swelling, dizziness, or breathing problems.
- you have experienced in the past a combination of any of the following symptoms: widespread rash, skin redness, high body temperature, flu-like symptoms, elevated liver enzymes, blood abnormalities (eosinophilia), swollen lymph nodes (these are signs of a severe skin reaction called drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, also known as DRESS syndrome).
If any of the above conditions apply to you, inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting treatment.
At any time, during or after treatment, tell your doctor or nurse immediately if you:
- have blurred vision, loss of vision, or double vision, difficulty speaking, weakness in an arm or leg, a change in the way you walk or balance problems, numbness, decreased sensitivity, or loss of sensitivity, memory loss, or confusion. These may be symptoms of a serious and potentially life-threatening brain disease called progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). If you have any of these symptoms before starting treatment with lenalidomide, tell your doctor if you notice any change in these symptoms.
- have shortness of breath, tiredness, dizziness, chest pain, faster heartbeat, or swelling in the legs or ankles. These may be symptoms of a serious condition called pulmonary hypertension (see section 4).
Tests and examinations
Before starting treatment with lenalidomide and during treatment, you will have regular blood tests. This is because lenalidomide may cause a decrease in the blood cells that help fight infections (white blood cells) and those that help the blood to clot (platelets).
Your doctor will ask you to have a blood test:
- before treatment.
- every week, during the first 8 weeks of treatment.
- then, at least every month.
You may be evaluated for signs of heart and lung problems before and during treatment with lenalidomide.
For patients with MDS taking lenalidomide
If you have MDS, you may be more likely to develop a more advanced disease called acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Additionally, it is not known how lenalidomide affects the chances of developing AML. Your doctor may therefore have you undergo tests to detect signs that may predict a better chance of developing AML during treatment with lenalidomide.
For patients with MCL taking lenalidomide
Your doctor will ask you to have a blood test:
- before treatment
- every week, during the first 8 weeks (2 cycles) of treatment
- then, every 2 weeks in cycles 3 and 4 (see section 3 “Treatment cycle” for more information)
- after that, at the start of each cycle and
- at least once a month
For patients with FL taking lenalidomide
Your doctor will ask you to have a blood test:
- before treatment
- every week, during the first 3 weeks (1 cycle) of treatment
- then, every 2 weeks in cycles 2 to 4 (see section 3 “Treatment cycle” for more information)
- after that, at the start of each cycle and
- at least every month
Your doctor may check if you have a high total tumor burden in the body, including the bone marrow. This could lead to a condition in which the tumors break down and produce unusual levels of chemicals in the blood, which can cause kidney failure (this condition is called “tumor lysis syndrome”).
Your doctor may examine you to check for changes in your skin, such as red spots or skin rashes.
Your doctor may adjust your dose of lenalidomide or interrupt your treatment, depending on the results of your blood tests and your overall condition. If you are a newly diagnosed patient, your doctor may also evaluate your treatment based on your age and any other conditions you may have.
Blood donation
You must not donate blood during treatment or for at least 7 days after the end of treatment.
Children and adolescents
Elderly patients and patients with kidney problems
If you are 75 years or older, or have moderate to severe kidney problems, your doctor will monitor you closely before starting treatment.
Other medicines and Lenalidomide Aurovitas
Tell your doctor or nurse if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines. This is because lenalidomide may affect how other medicines work. Also, some medicines may affect how lenalidomide works.
In particular, tell your doctor or nurse if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- some medicines used to prevent pregnancy, such as oral contraceptives, as they may stop working.
- some medicines used for heart problems, such as digoxin.
- some medicines used to thin the blood, such as warfarin.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and contraception: information for women and men
Pregnancy
Women taking lenalidomide
- Do not take lenalidomide if you are pregnant, as it is expected to be harmful to the fetus.
- Do not become pregnant while taking lenalidomide. You must use effective contraception if there is a possibility that you may become pregnant (see “Contraception”).
- If you become pregnant during treatment with lenalidomide, stop treatment and tell your doctor immediately.
Men taking lenalidomide
- If your partner becomes pregnant while you are taking lenalidomide, tell your doctor immediately. It is recommended that your partner seeks medical advice.
- You must also use effective contraception (see “Contraception”).
Breastfeeding
Do not breastfeed while taking lenalidomide, as it is not known whether lenalidomide passes into breast milk.
Contraception
For women taking lenalidomide
Before starting treatment, ask your doctor if you are able to become pregnant, even if you think it is unlikely.
If you can become pregnant:
- you will have pregnancy tests under medical supervision (before each treatment, at least every 4 weeks during treatment, and for at least 4 weeks after the end of treatment) unless it has been confirmed that your fallopian tubes have been blocked (tubal ligation).
And
- you must use effective contraception from at least 4 weeks before starting treatment, during treatment, and for at least 4 weeks after the end of treatment. Your doctor will advise you on the most suitable contraceptive methods.
For men taking lenalidomide
Lenalidomide passes into human semen. If your partner is pregnant or may become pregnant and is not using any effective contraception, you must use condoms during treatment and for at least 7 days after the end of treatment, even if you have had a vasectomy. Do not donate semen or sperm during treatment or for at least 7 days after the end of treatment.
Driving and using machines
Do not drive or use machines if you feel dizzy, tired, drowsy, have vertigo, or blurred vision after taking lenalidomide.
Lenalidomide Aurovitas contains lactose
This medicine contains lactose. If your doctor has told you that you have an intolerance to some sugars, talk to your doctor before taking this medicine.
Lenalidomide Aurovitas contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per capsule; this is essentially “sodium-free”.
3. How to Take Lenalidomide Aurovitas
Lenalidomide should be administered by a healthcare professional with experience in the treatment of multiple myeloma, MDS, MCL, or FL.
- When lenalidomide is used to treat multiple myeloma in patients who cannot undergo a bone marrow transplant or have undergone other treatments before, it is taken with other medications (see section 1 "What Lenalidomide Aurovitas is used for").
- When lenalidomide is used to treat multiple myeloma in patients who have undergone a bone marrow transplant or to treat patients with MDS or MCL, it is taken alone.
- When lenalidomide is used to treat follicular lymphoma, it is taken with another medication called "rituximab".
Follow your doctor's instructions for taking this medication exactly. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
If you are taking lenalidomide with other medications, you should consult the package insert of those other medications for additional information on their use and effects.
Treatment Cycle
Lenalidomide is taken on certain days during a period of 3 weeks (21 days).
- A "treatment cycle" consists of 21 days.
- Depending on the day of the cycle, you will take one or more medications. However, on some days, you will not take any medication.
- After completing each 21-day cycle, you should start a new "cycle" for the next 21 days.
Or
Lenalidomide is taken on certain days during a period of 4 weeks (28 days).
- A "treatment cycle" consists of 28 days.
- Depending on the day of the cycle, you will take one or more medications. However, on some days, you will not take any medication.
- After completing each 28-day cycle, you should start a new "cycle" for the next 28 days.
How Much Lenalidomide Aurovitas to Take
Before starting treatment, your doctor will tell you:
- how much lenalidomide you should take.
- how much of the other medications you should take with lenalidomide, if applicable.
- which days of the treatment cycle you should take each medication.
How and When to Take Lenalidomide Aurovitas
- Swallow the capsules whole, preferably with water.
- Do not break, open, or chew the capsules. If the powder from a broken lenalidomide capsule comes into contact with the skin, wash the skin immediately and carefully with water and soap.
- Healthcare professionals, caregivers, and family members should wear disposable gloves when handling the blister or capsule. Afterwards, they should carefully remove the gloves to avoid skin exposure, place them in a sealable polyethylene plastic bag, and dispose of them according to local requirements. Then, they should wash their hands well with water and soap. Pregnant women or those who suspect they may be pregnant should not handle the blister or capsule.
- The capsules can be taken with or without food.
- You should take lenalidomide at approximately the same time on scheduled days.
Taking this Medication
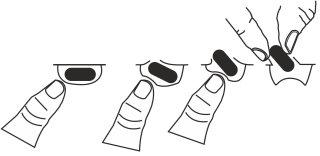
To remove the capsule from the blister:
- Press only one end of the capsule to release it through the foil.
- Do not press on the center of the capsule as it may break.
Duration of Treatment with Lenalidomide Aurovitas
Lenalidomide is taken in treatment cycles, each cycle lasting 21 or 28 days (see "Treatment Cycle" above). You should continue the treatment cycles until your doctor tells you to stop the treatment.
If you Take More Lenalidomide Aurovitas than you Should
If you take more lenalidomide than prescribed, inform your doctor immediately.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medication and the amount ingested.
If you Miss a Dose of Lenalidomide Aurovitas
If you forget to take lenalidomide at your usual time and:
- less than 12 hours have passed: take the capsule immediately.
- more than 12 hours have passed: do not take the capsule. Take the next capsule the next day at the usual time.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
If you experience any of the following serious side effects, stop treatment with lenalidomide and see a doctor immediately, as you may need urgent medical treatment:
- Hives, rash, swelling of the eyes, mouth, or face, difficulty breathing or itching, which can be symptoms of severe allergic reactions called angioedema and anaphylactic reaction.
- A severe allergic reaction that can start as a rash in one area but spreads, causing significant skin loss throughout the body (Stevens-Johnson syndrome and/or toxic epidermal necrolysis).
- Widespread rash, high body temperature, increased liver enzymes, blood abnormalities (eosinophilia), swollen lymph nodes, and effects on other parts of the body (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, also known as DRESS or drug hypersensitivity syndrome). See also section 2.
Consult your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following serious side effects:
- Fever, chills, sore throat, cough, mouth sores, or any other symptom of infection, including in the bloodstream (sepsis).
- Bleeding (bleeding) or bruising (bruising) not due to an injury.
- Chest pain (thoracic) or leg pain.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Bone pain, muscle pain, confusion, or fatigue, which can be due to high calcium levels in the blood.
Lenalidomide can reduce the number of white blood cells that fight infections and also the blood cells that help blood clot (platelets), which can cause bleeding disorders such as nosebleeds and bruising. Lenalidomide can also cause blood clots in the veins (thrombosis).
Other Side Effects
It is essential to note that a small number of patients may develop other types of cancer, and this risk may increase with lenalidomide treatment. Therefore, your doctor should carefully evaluate the benefits and risks when prescribing lenalidomide.
Very Common Side Effects(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- A decrease in the number of red blood cells, which can cause anemia leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Skin rash, itching.
- Muscle cramps, muscle weakness, muscle pain, muscle discomfort, bone pain, joint pain, back pain, pain in the limbs.
- Generalized swelling, including swelling of the arms and legs.
- Weakness, fatigue.
- Fever and flu-like symptoms, including fever, muscle pain, headache, ear pain, cough, and chills.
- Numbness, tingling, or a prickling sensation in the skin, pain in the hands or feet, dizziness, tremors.
- Decreased appetite, changes in taste.
- Increased pain, tumor size, or redness around the tumor.
- Weight loss.
- Constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, heartburn.
- Low levels of potassium, calcium, or sodium in the blood.
- Underactive thyroid function.
- Pain in the legs (which could be a symptom of thrombosis), chest pain, or difficulty breathing (which could be a symptom of blood clots in the lungs, called pulmonary embolism).
- Infections of all kinds, including sinusitis, pneumonia, and upper respiratory tract infections.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Blurred vision.
- Eye opacity (cataracts).
- Kidney problems, including kidney failure or inability to maintain normal kidney function.
- Abnormal liver test results.
- High liver test results.
- Changes in a blood protein that can cause swelling of the arteries (vasculitis).
- Increased blood sugar levels (diabetes).
- Decreased blood sugar levels.
- Headache.
- Nosebleeds.
- Dry skin.
- Depression, mood changes, difficulty sleeping.
- Cough.
- Low blood pressure.
- A vague feeling of discomfort in the body, feeling unwell.
- Painful inflammation of the mouth, dry mouth.
- Dehydration.
Common Side Effects(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia).
- Certain types of skin tumors.
- Bleeding from the gums, stomach, or intestines.
- Increased blood pressure, slow, fast, or irregular heartbeat.
- Increased levels of a substance released after normal or abnormal red blood cell destruction.
- Increased levels of a protein that indicates inflammation in the body.
- Darkening of skin color; change in skin color due to internal bleeding, usually caused by bruising; skin inflammation caused by blood accumulation; bruising.
- Increased uric acid levels in the blood.
- Skin rashes, redness of the skin, cracked skin, peeling or flaking skin, hives.
- Increased sweating, night sweats.
- Difficulty swallowing, sore throat, difficulty maintaining voice quality or changes in voice.
- Runny nose.
- Strong increase or decrease in urine output compared to usual or inability to control urination.
- Blood in the urine.
- Difficulty breathing, especially when lying down (which could be a symptom of heart failure).
- Difficulty having an erection.
- Stroke, fainting, vertigo (inner ear disorder that causes a spinning sensation), temporary loss of consciousness.
- Chest pain that spreads to the arms, neck, jaw, back, or stomach, feeling of sweating and shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, which can be symptoms of a heart attack (myocardial infarction).
- Muscle weakness, lack of energy.
- Neck pain, chest pain.
- Chills.
- Swollen joints.
- Slowed or blocked bile flow from the liver.
- Low phosphate or magnesium levels in the blood.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Liver damage.
- Balance disturbance, difficulty moving.
- Hearing loss, ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
- Nerve pain, abnormal and unpleasant sensation, especially when touched.
- Excess iron in the body.
- Thirst.
- Confusion.
- Toothache.
- Falling, which can cause injuries.
Uncommon Side Effects(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Bleeding in the skull.
- Circulatory problems.
- Loss of vision.
- Loss of sexual desire (libido).
- Excretion of large amounts of urine with bone pain and weakness, which can be symptoms of a kidney disorder (Fanconi syndrome).
- Yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, or eyes (jaundice), pale stools, dark urine, itching, skin rash, pain or swelling of the stomach; these can be symptoms of liver damage (liver failure).
- Stomach pain, abdominal swelling, or diarrhea, which can be symptoms of inflammation of the large intestine (colitis or typhlitis).
- Kidney cell damage (called tubular necrosis).
- Changes in skin color, sensitivity to sunlight.
- Tumor lysis syndrome - metabolic complications can occur during cancer treatment and sometimes even without treatment. These complications occur as a result of the breakdown products of dying cancer cells and can include: changes in blood biochemistry, high levels of potassium, phosphorus, uric acid, and low levels of calcium, which can cause changes in kidney function and heart rhythm, seizures, and sometimes death.
- Increased blood pressure in the blood vessels that supply the lungs (pulmonary hypertension).
Side Effects of Unknown Frequency(cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Sudden, mild, or severe pain in the upper abdomen and/or back that lasts for several days, possibly accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and rapid pulse. These symptoms can be due to pancreatitis.
- Wheezing or whistling when breathing, difficulty breathing, or dry cough, which can be symptoms caused by inflammation of lung tissue.
- Rare cases of muscle breakdown (pain, weakness, or swelling of the muscles) have been observed, which can lead to kidney problems (rhabdomyolysis), some of which occur when lenalidomide is administered with a statin (a type of cholesterol-lowering medication).
- A disease that affects the skin caused by inflammation of small blood vessels, accompanied by joint pain and fever (leukocytoclastic vasculitis).
- Rupture of the stomach or intestine wall. This can lead to a severe infection. Inform your doctor if you have severe stomach pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, blood in the stool, or changes in bowel habits.
- Viral infections, including herpes zoster (also known as shingles, a viral disease that causes a painful rash with blisters) and the recurrence of hepatitis B infection (which can cause yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, stomach pain on the right side, fever, and nausea or feeling sick).
- Rejection of solid organ transplants (such as kidney, heart).
Reporting Side Effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are possible side effects not listed in this package insert. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medicines Monitoring System: www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Lenalidomide Aurovitas
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date shown on the packaging and blister, after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Store below 30°C.
Medications should not be disposed of through wastewater or household waste. Deposit the packaging and medications you no longer need in the pharmacy's SIGRE collection point. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medications you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container contents and additional information
Composition ofLenalidomida Aurovitas
- The active ingredient is lenalidomide.
Each hard capsule contains 5 mg of lenalidomide.
Each hard capsule contains 10 mg of lenalidomide.
Each hard capsule contains 15 mg of lenalidomide.
Each hard capsule contains 20 mg of lenalidomide.
Each hard capsule contains 25 mg of lenalidomide.
- The other components are:
Capsule content:lactose, microcrystalline cellulose (grade 102), sodium croscarmellose, and magnesium stearate.
Capsule shell:titanium dioxide (E171), yellow iron oxide (E172) (only for 10 mg and 20 mg), carmine indigo (E132) (only for 10 mg), red iron oxide (E172) (only for 10 mg, 15 mg, and 20 mg), and gelatin.
Printing ink:Shellac lacquer, black iron oxide (E172), and potassium hydroxide.
Appearance of the product and container contents
Lenalidomida Aurovitas 5 mg hard capsules EFG[approximately 17.8 mm in size]
Hard gelatin capsule of size “2”, with the cap white opaque and the body white opaque, with “L5” printed on the cap with black ink, filled with a white or pale yellow powder.
Lenalidomida Aurovitas 10 mg hard capsules EFG[approximately 21.4 mm in size]
Hard gelatin capsule of size “0”, with the cap olive green opaque and the body orange opaque, with “L10” printed on the cap with black ink, filled with a white or pale yellow powder.
Lenalidomida Aurovitas 15 mg hard capsules EFG[approximately 21.4 mm in size]
Hard gelatin capsule of size “0”, with the cap dark orange opaque and the body dark orange opaque, with “L15” printed on the cap with black ink, filled with a white or pale yellow powder.
Lenalidomida Aurovitas 20 mg hard capsules EFG[approximately 21.4 mm in size]
Hard gelatin capsule of size “0”, with the cap orange opaque and the body orange opaque, with “L20” printed on the cap with black ink, filled with a white or pale yellow powder.
Lenalidomida Aurovitas 25 mg hard capsules EFG[approximately 21.4 mm in size]
Hard gelatin capsule of size “0”, with the cap white opaque and the body white opaque, with “L25” printed on the cap with black ink, filled with a white or pale yellow powder.
Container sizes:
Blister:7, 14, 21, 28, and 42 hard capsules.
Only some container sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Eugia Pharma (Malta) Limited
Vault 14, Level 2, Valletta Waterfront
Floriana, FRN 1914
Malta
Manufacturer
APL Swift Services (Malta) Limited
HF26, Hal Far Industrial Estate, Hal Far
Birzebbugia, BBG 3000
Malta
Or
Generis Farmacêutica, S.A.
Rua João de Deus, 19
2700-487 Amadora
Portugal
Or
Arrow Génériques
26 Avenue Tony Garnier
69007 Lyon
France
You can request more information about this medication by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Aurovitas Spain, S.A.U.
Avda. de Burgos, 16-D
28036 Madrid
Spain
This medication is authorized in the member states of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Germany: Lenalidomid PUREN 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg/15 mg/20 mg/25 mg hard capsules
Belgium: Lenalidomide AB 2.5 mg/5 mg/7.5 mg/10 mg/15 mg/20 mg/25 mg, capsules, hard capsules
Spain: Lenalidomida Aurovitas 5 mg/10 mg/15 mg/20 mg/25 mg hard capsules EFG
France: Lenalidomide Arrow 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg & 25 mg, capsules
Netherlands: Lenalidomide Eugia 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, hard capsules
Poland: Lenalidomide Eugia
Portugal: Lenalidomida Generis
Date of the last revision of this prospectus:July 2023
Detailed information about this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) (http://www.aemps.gob.es/).
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to LENALIDOMIDE Aurovitas 15 mg HARD CAPSULESDosage form: CAPSULE, 10 mgActive substance: lenalidomideManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 15 mgActive substance: lenalidomideManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 2.5 mgActive substance: lenalidomideManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for LENALIDOMIDE Aurovitas 15 mg HARD CAPSULES
Discuss questions about LENALIDOMIDE Aurovitas 15 mg HARD CAPSULES, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






