
JUNOD 60 mg Injectable Solution in Pre-filled Syringe
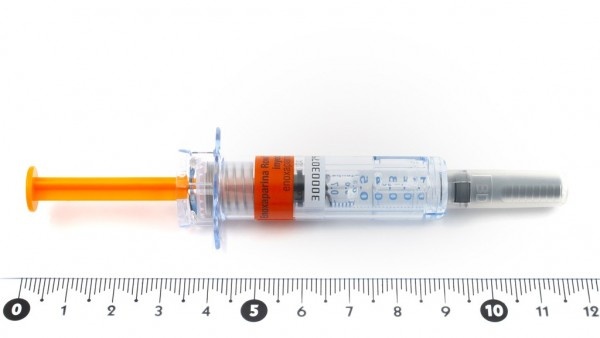

How to use JUNOD 60 mg Injectable Solution in Pre-filled Syringe
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Junod 60 mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
denosumab
This medicine is subject to additional monitoring, which will allow for quick identification of new safety information. You can help by reporting any side effects you may get. The last section of section 4 will tell you how to report side effects.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
- Your doctor will provide you with a patient reminder card, which contains important safety information that you should know before and during treatment with Junod.
Contents of the pack
- What is Junod and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Junod
- How to use Junod
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Junod
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Junod and what is it used for
What is Junod and how does it work
Junod contains denosumab, a protein (monoclonal antibody) that interferes with the action of another protein to treat bone loss and osteoporosis. Treatment with Junod strengthens bones and reduces the risk of fractures.
Bone is a living tissue that is constantly renewed. Estrogens contribute to the preservation of bone health.
In women, after menopause, estrogen levels decrease, which can cause bones to become thinner and more fragile. In the long run, this can lead to a disease called osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis can also occur in men due to various causes, including age and/or low levels of the male hormone, testosterone. It can also occur in patients undergoing treatment with glucocorticoids.
Many patients with osteoporosis do not have symptoms, although they still have a risk of fracturing bones, especially in the spine, hip, and wrists.
Surgical interventions or medications that stop the production of estrogen or testosterone, used to treat patients with prostate or breast cancer, can also cause bone loss. This makes bones weaker and more prone to fractures.
What is Junod used for
Junod is used to treat:
- postmenopausal osteoporosis in women and men at increased risk of fracture (bone break), reducing the risk of fractures of the hip, spine, and non-spinal locations.
- bone loss caused by reduced hormonal levels (testosterone) as a result of surgical intervention or treatment with medications in patients with prostate cancer.
- bone loss resulting from long-term treatment with glucocorticoids in patients at high risk of fracture.
2. What you need to know before you use Junod
Do not use Junod
- if you have low levels of calcium in the blood (hypocalcemia).
- if you are allergic to denosumab or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment with Junod.
During treatment with denosumab, you may develop a skin infection with symptoms such as an inflamed and reddened area on the skin, most frequently on the lower leg, which feels hot and sensitive to the touch (cellulitis), and may be accompanied by fever. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
In addition, you should take calcium and vitamin D supplements during treatment with Junod. Your doctor will discuss this with you.
Your blood calcium levels may decrease during treatment with denosumab. Inform your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms: muscle spasms, contractions, or cramps, and/or numbness or tingling in the fingers of the hands, feet, or around the mouth, and/or seizures, confusion, or loss of consciousness.
In rare cases, very low blood calcium levels have been reported, which have required hospitalization and, in some cases, have been life-threatening. Therefore, before each dose is administered and, in patients with a predisposition to hypocalcemia, within two weeks after the initial dose, your blood calcium levels will be checked (through a blood test).
Inform your doctor if you have or have had severe kidney problems, kidney failure, if you have needed to undergo dialysis, or if you are taking medications called glucocorticoids (such as prednisolone or dexamethasone), as they may increase the risk of low blood calcium levels if you do not take calcium supplements.
Problems in the mouth, teeth, or jaw
In patients receiving denosumab for osteoporosis, a rare side effect called osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) (damage to the jawbone) has been reported (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people). The risk of ONJ increases in patients treated for a long time (may affect up to 1 in 200 people if treated for 10 years). ONJ can also occur after stopping treatment. It is essential to try to prevent the development of ONJ, as it can be a painful condition that can be difficult to treat. To reduce the risk of developing ONJ, follow these precautions:
Before receiving treatment, inform your doctor or nurse (healthcare professional) if:
- you have any problems in your mouth or teeth, such as poor dental health, gum disease, or a planned tooth extraction.
- you do not receive regular dental check-ups or have not had a dental check-up for a long time.
- you are a smoker (as this may increase the risk of dental problems).
- you have been previously treated with a bisphosphonate (used to prevent or treat bone disorders).
- you are taking medications called corticosteroids (such as prednisolone or dexamethasone).
- you have cancer.
Your doctor may ask you to undergo a dental check-up before starting treatment with Junod.
While being treated, you should maintain good oral hygiene and undergo routine dental check-ups. If you use dental prosthetics, ensure they fit properly. If you are undergoing dental treatment or are going to undergo dental surgery (e.g., tooth extractions), inform your doctor about your dental treatment and inform your dentist that you are being treated with Junod.
Contact your doctor and dentist immediately if you experience any problems in your mouth or teeth, such as loose teeth, pain, or inflammation, or ulcers that do not heal or are suppurating, as these could be symptoms of ONJ.
Unusual fractures of the thigh
Some people have developed unusual fractures of the thigh while being treated with denosumab. Consult your doctor if you experience new or unusual pain in the hip, groin, or thigh.
Children and adolescents
Junod should not be used in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Other medicines and Junod
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
It is especially important that you inform your doctor if you are being treated with another medicine that contains denosumab. You should not use Junod with another medicine that contains denosumab.
Inform your doctor if you are taking medications called glucocorticoids (such as prednisolone or dexamethasone), see also the section "Warnings and precautions".
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Denosumab has not been tested in pregnant women. It is not recommended to use Junod during pregnancy. Women of childbearing age should use effective contraception during treatment with Junod and for at least 5 months after stopping treatment with Junod.
If you become pregnant during treatment with Junod or less than 5 months after stopping treatment with Junod, inform your doctor.
It is not known whether denosumab is excreted in breast milk. It is essential that you inform your doctor if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Your doctor will help you decide whether to stop breastfeeding or stop using Junod, considering the benefit of breastfeeding for the child and the benefit of Junod for you.
Driving and using machines
Junod has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Junod contains sorbitol, polysorbate 20, and sodium
This medicine contains 46 mg of sorbitol in each ml of solution.
This medicine contains 0.1 mg of polysorbate 20 in each ml of solution. Polysorbates may cause allergic reactions. Inform your doctor if you or your child have any known allergies.
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per ml; this is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Junod
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as prescribed by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
The recommended dose is a pre-filled syringe of 60 mg administered under the skin (subcutaneously) in a single injection once every 6 months.
The best places to inject are the top of the thighs and the abdomen. If the injection is given by a caregiver (the person taking care of you), they can also administer the injection in the outer aspect of the upper arm.
Consult your doctor for the date of the next possible injection.
Each pack of Junod contains a reminder card that can be detached from the carton and used to keep a record of the date of the next injection.
In addition, you should take calcium and vitamin D supplements during treatment with Junod. Your doctor will discuss this with you.
Your doctor may decide whether it is better for you or a caregiver to administer the Junod injection. Your doctor or healthcare professional will show you or your caregiver how to use Junod. If you want to obtain instructions on how to inject Junod, read the last section of this leaflet.
Do not shake.
If you miss a dose of Junod
If you miss a dose of Junod, the injection should be administered as soon as possible. Subsequently, injections should be scheduled every 6 months from the date of the last injection.
If you stop treatment with Junod
To get the most benefit from your treatment and reduce the risk of fractures, it is essential that you use Junod for the entire period prescribed by your doctor. Do not stop treatment without talking to your doctor first.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Patients treated with denosumab may develop skin infections (mainly cellulitis) with a frequency of up to 1 in 100 people. Inform your doctor immediatelyif you experience any of these symptoms during treatment with Junod: an inflamed and reddened area on the skin, usually on the lower leg, which feels hot and sensitive to the touch, and may be accompanied by fever.
Rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people), patients receiving denosumab may develop pain in the mouth and/or jaw, inflammation, or ulcers that do not heal in the mouth or jaw, suppurating, numbness, or a feeling of heaviness in the jaw, or tooth mobility. These could be symptoms of bone damage in the jaw (osteonecrosis). Inform your doctor and dentist immediatelyif you experience such symptoms while being treated with Junod or after stopping treatment.
Rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people), patients receiving denosumab may have low blood calcium levels (hypocalcemia); very low blood calcium levels may require hospitalization and, in some cases, may be life-threatening. Symptoms include muscle spasms, contractions, or cramps, and/or numbness or tingling in the fingers of the hands, feet, or around the mouth, and/or seizures, confusion, or loss of consciousness. If you experience any of these, inform your doctor immediately. Low blood calcium levels can also cause a change in heart rhythm called QT prolongation, which can be seen on an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people), unusual fractures of the thigh may occur in patients receiving denosumab. Consult your doctorif you experience new or unusual pain in the hip, groin, or thigh, as this may be an early indication of a possible fracture of the thigh.
Rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people), allergic reactions may occur in patients receiving denosumab. Symptoms include swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat, or other parts of the body; rash, itching, or hives on the skin; wheezing or difficulty breathing.
Inform your doctorif you experience such symptoms while being treated with Junod.
Very common side effects (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- bone, joint, and/or muscle pain, which can be severe,
- pain in the legs or arms (pain in the extremities).
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- painful urination, frequent urination, presence of blood in the urine, urinary incontinence,
- upper respiratory tract infection,
- pain, numbness, or tingling that extends to the lower leg (sciatica),
- constipation,
- abdominal discomfort,
- skin rash,
- skin condition with itching, redness, and/or dryness (eczema),
- hair loss (alopecia).
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- fever, vomiting, and abdominal pain or discomfort (diverticulitis),
- ear infection,
- skin rash or mouth ulcers (drug-induced lichenoid eruptions).
Rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- allergic reaction that can damage blood vessels, mainly in the skin (e.g., purple or reddish-brown spots, hives, or skin ulcers) (hypersensitivity vasculitis).
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- consult your doctor if you have ear pain, your ear is suppurating, and/or you have an ear infection. These could be symptoms of damage to the bones in the ear.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly via the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Junod
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton after "EXP". The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Do not use this medicine if you notice that the solution contains particles, or if it is cloudy or discolored.
Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C). Do not freeze.
Keep the pre-filled syringe in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
Once removed from the refrigerator, Junod can be stored at room temperature (up to 25°C) for a maximum of 30 days in the original package and outer packaging to protect it from light. It must be used within 30 days.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Junod
- The active ingredient is denosumab. Each ml of the pre-filled syringe contains 60 mg of denosumab.
- The other components are glacial acetic acid, sodium hydroxide, sorbitol (E420), polysorbate 20 (E432), and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Product and Container Contents
Junod is a clear, colorless to slightly yellowish injectable solution supplied in a pre-filled syringe ready for use.
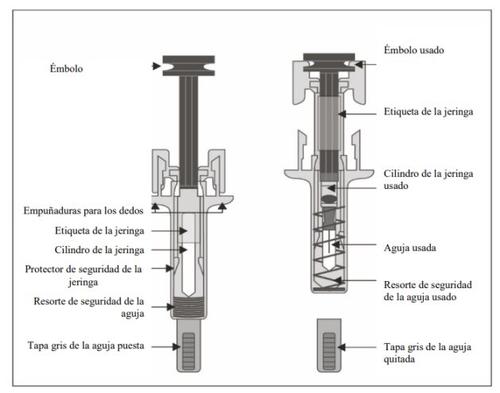
One ml of Junod is presented in a single glass pre-filled syringe (Type I glass) with a FluroTec® plunger stopper, fitted with a needle (27 G × 12.7 mm), and a rigid needle shield (rigid elastomer + polypropylene).
The container contains a pre-filled syringe with a safety protector.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Gedeon Richter Plc.
Gyömroi út 19-21.
1103 Budapest Hungary
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter Plc.
Gyömroi út 19-21.
1103 Budapest Hungary
Chemical Works of Gedeon Richter Plc.
(Gedeon Richter Plc.)
Richter Gedeon utca 20. Debrecen
4031
Hungary
Date of the Last Revision of this Leaflet:
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information about this product is also available by scanning the QR code included below or on the outer packaging with your mobile device. The same information is also available on the following URL: www.junodinfo.com
QR code must be included
Detailed information about this medication is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency: https://www.ema.europa.eu, and on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Guide to the Parts
Important
Before using the pre-filled Junod syringe with the automatic needle protector, read all this important information to the end.Follow the instructions carefully when using the syringe.
- It is essential that you do not attempt to administer the injection to yourself unless you have received training from your doctor or healthcare professional.
- Junod is presented as an injection that passes through the tissue under the skin (subcutaneous injection).
- Do notremove the gray needle cap from the pre-filled syringe until you are ready to inject.
- Do notuse the pre-filled syringe if it has been dropped onto a hard surface. Use a new pre-filled syringe and contact your doctor or healthcare professional.
- Do notattempt to activate the pre-filled syringe before injection.
- Do notattempt to remove the safety protector from the pre-filled syringe.
Contact your doctor or healthcare professional if you have any questions.
Step 1: Preparation
- Open the container that contains the pre-filled syringe and gather the necessary materials for your injection: alcohol wipes, a cotton ball or gauze, a plaster, and a container for disposing of sharp objects (not included).
For a more comfortable injection, leave the pre-filled syringe at room temperature for about 15-30 minutes before injecting. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
On a clean and well-lit work surface, place the new pre-filled syringe and the other materials.
- Do notattempt to heat the pre-filled syringe using a heat source such as hot water or a microwave.
- Do notleave the pre-filled syringe exposed to direct sunlight.
- Do notshake the pre-filled syringe.
Keep the pre-filled syringe out of sight and reach of children.
- Hold the safety protector to remove the syringe from the container.
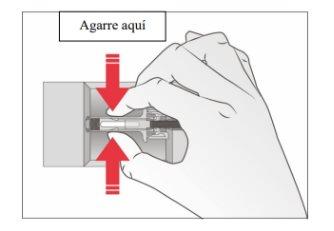
For safety reasons:
- Do nothold the plunger.
- Do nothold the gray needle cap.
- Examine the medication and the pre-filled syringe.
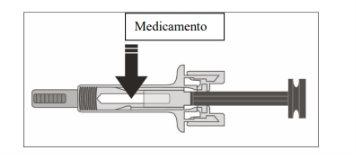
Do notuse the pre-filled syringe if:
- The medication is cloudy or if there are particles in it. It should be a clear, colorless to slightly yellowish solution.
- Any part appears cracked or broken.
- The gray needle cap is missing or not properly secured.
- The expiration date printed on the label has passed the last day of the indicated month.
In all cases, consult with your doctor or healthcare professional.
Step 2: Prepare Yourself
- Wash your hands carefully. Prepare and clean the injection site.
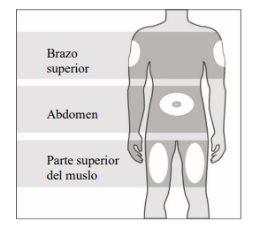
You can use:
- Upper thigh.
- Abdomen, except for an area of 5 cm around the navel.
- Outer area of the upper arm (only if someone is administering the injection to you).
Clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe. Let the skin dry.
- Do nottouch the injection site before injecting.
- Do notinject into areas where the skin is sensitive, bruised, red, or with hardening.
Avoid injecting into areas with scars or stretch marks.
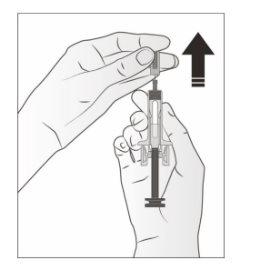
- Carefully pull the gray needle cap straight off and away from your body.
- Pinch the injection site to create a firm surface.
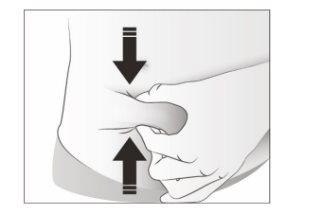
It is essential to maintain the pinched skin when injecting.
Step 3: Inject
- Hold the pinch. INSERT the needle at an angle of 45 to 90 degrees into the skin.
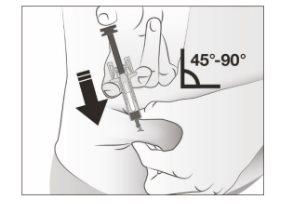
- Do nottouch the clean area of the skin.
- Pushthe plunger with slow and constant pressure until you feel or hear a "click". Push completely down until you hear the "click".
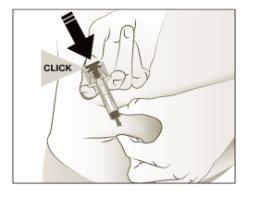
Note:It is essential to push down until you hear the "click" to administer the full dose.
- Releaseyour thumb. Then, separatethe syringe from the skin.
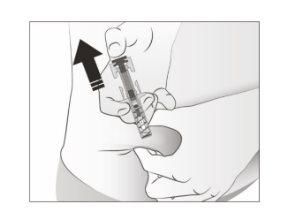
After releasing the plunger, the safety protector of the pre-filled syringe will safely cover the injection needle.
Do notput the gray needle cap back on the used pre-filled syringe.
Step 4: Final
- Dispose of the used pre-filled syringe and other materials in a container for disposing of sharp objects.
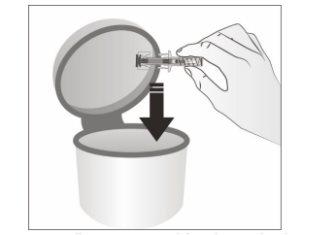
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
Keep the syringe and the container for disposing of sharp objects out of sight and reach of children.
- Do notreuse the pre-filled syringe.
- Do notrecycle the pre-filled syringes or throw them away.
- Examine the injection site.
If there is bleeding, press a cotton ball or gauze onto the injection site. Do notrub the injection site. Apply a plaster if necessary.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to JUNOD 60 mg Injectable Solution in Pre-filled SyringeDosage form: INJECTABLE, 120 mgActive substance: denosumabManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 120 mgActive substance: denosumabManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 60 mgActive substance: denosumabManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for JUNOD 60 mg Injectable Solution in Pre-filled Syringe
Discuss questions about JUNOD 60 mg Injectable Solution in Pre-filled Syringe, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions












