
FREEFLEX 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE

How to use FREEFLEX 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
sodium chloride
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9% and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you start using Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
- How to use Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9% and what is it used for
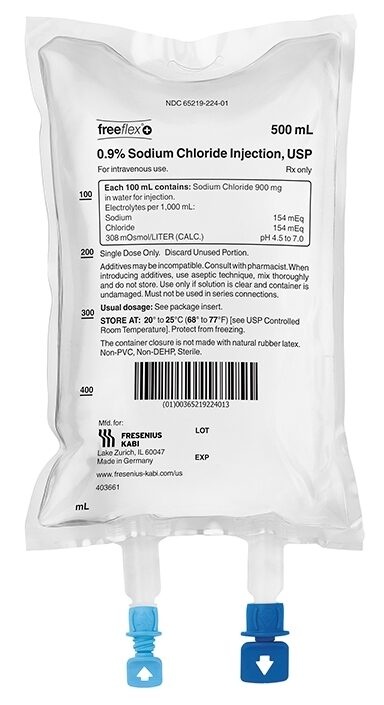
Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9% is a solution for intravenous infusion presented in freeflex bags of 50 ml, 100 ml, 250 ml, 500 ml, and 1000 ml, with an overpouch for intravascular administration of water, sodium, and chlorides.
It is indicated for:
- Ionic rebalancing by providing chlorides and sodium
- Extracellular dehydration
- Hypovolemia
2. What you need to know before you start using Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
Do not use Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
If you are allergic to the active substance or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
If you suffer from acidosis, hyperchloremia, hypokalemia, renal and/or cardiac insufficiency, hypernatremia, hyperhydration, edema in general, hypertension, liver insufficiency, or if you are undergoing prolonged treatment with corticosteroids or ACTH.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting to use Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%.
Other medicines and Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
No interactions with other preparations have been observed.
Pregnancy and lactation
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
No studies have been conducted in this population group. Given the characteristics of the preparation, the benefit/risk ratio will be assessed.
3. How to use Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
Follow exactly the administration instructions of this medicine indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
The recommended dose should be adapted according to the patient's weight and dehydration status.
If you use more Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9% than you should
Given the nature of its components, no intoxications have been described.
Excessive dosing may lead to hypernatremia with dehydration of internal organs and hyperchloremic acidosis.
Hypertension. Acute edema.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult the Toxicology Information Service. Telephone (91) 562 04 20.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
No side effects have been described, but if any adverse reaction attributable to the medicine occurs, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any type of side effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible side effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use website: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging after CAD. The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
6. Contents of the pack and further information
Composition of Freeflex Sodium Chloride 0.9%
- The active substance is sodium chloride. Each 100 ml of solution contains 0.9 g of sodium chloride.
- The only excipient is water for injectable preparations.
Electrolyte composition | mmol/l | meq/l |
Sodium ion | 154 | 154 |
Chloride ion | 154 | 154 |
Theoretical osmolality: 308 mosmol/l
Appearance of the product and contents of the pack
Intravenous infusion solution in freeflex bags of 50 ml, 100 ml, 250 ml, 500 ml, and 1000 ml, with an overpouch.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder:
Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.
C/ Marina 16-18,
08005-Barcelona
Manufacturer:
Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbH
Werk Friedberg Freseniusstraβe 1
D-61169 Friedberg
Fresenius Kabi France, S.A.
6, Rue du Rempart, B.P. 611
(Louviers) F-27400 France
HP Halden Pharma AS
Svinesundsveien 80
1788 Halden
Norway
Fresenius Kabi India PVT. LTD.
A-3 MIDC, Ranajangoan Ganpati, ‘tal. Shirur.
412220 Maharashtra
India
Date of last revision of this leaflet: March 2023.
Detailed and updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE CORRECT ADMINISTRATION OF THE PREPARATION
Visual inspection
- Do not remove the freeflex from its overpouch until immediately before use.
- Check the composition, batch number, and expiry date.
- Inspect the set by checking the integrity of the primary packaging. Do not use if this packaging is not intact.
Removal of the overpouch
Some freeflex bags have an overpouch as protection during storage. The overpouch, with a "peel" opening system, can be removed as follows:
- Locate the tabs at the end where the ports of the bag are.
- Separate the two halves of the overpouch, leaving the bag on a clean surface.
Preparation for administration
The freeflex bags are designed for air-free administration. If you need to use an infusion set with air entry, make sure it is always closed.
- Squeeze the freeflex to ensure it does not leak and examine the solution to observe the presence of visible particles or precipitates. DO NOT ADMINISTER IF THE SOLUTION IS NOT TRANSPARENT AND/OR THE PACKAGING IS NOT INTACT.
- Using an aseptic technique, prepare the infusion set with the flow regulator closed.
- Identify the administration port (blue) in the shape of an arrow indicating the exit from the bag.
- Remove the protective cap from the administration port of the freeflex, holding the lower wings firmly with one hand and breaking the cap in the shape of an arrow by means of a sustained twisting action.
- Hold the base of the administration port, placing your fingers behind the protector, and push the spike of the administration set firmly into the port. You should feel a slight resistance when the port membrane breaks. To prevent leaks, insert the spike to the bottom of the administration port.
- Suspend the bag on the hanger and purge the administration set according to the manufacturer's instructions. Perform the venipuncture and immediately connect the administration set to the intravenous cannula. Adjust the flow regulator to achieve the desired drip rate.
- The freeflex bags are calibrated to indicate the approximate volume that has been infused. The scale should be read by stretching the bag and reading the volume on the upper surface of the liquid. For a more accurate measurement of the fluid volume, an administration set with a measuring chamber should be used.
To add medication
The freeflex bags have a medication addition port that is independent and has a self-closing cap. Since the port is protected by a hermetically sealed cap, it is not necessary to disinfect the medication addition site before its first use.
Additions using syringes
- Identify the medication addition port (white) in the shape of an arrow indicating an entry flow into the bag.
- Using an aseptic technique, prepare a syringe with the medication, using a 20-22 G needle.
- Remove the protective cap from the medication addition port of the bag, holding the lower wings firmly with one hand and breaking the cap in the shape of an arrow by means of a sustained twisting action.
- Hold the medication addition port, placing your fingers behind the protector, and insert the needle completely, so that it pierces the outer cap and the inner membrane. Its rigid construction prevents the needle from penetrating the sides of the port.
- Add the medication and withdraw the needle. To prevent any aerosol formation, a sterile swab should be kept around the cap.
The following maximum addition volumes are recommended:
Freeflex bag size (ml) Maximum recommended addition (ml)
- 50
- 50
- 100
- 150
- 250
NOTE: Additives may be incompatible, so expert advice should be sought before adding medication to freeflex. If the doctor decides to add medication, an aseptic technique should be used. It is recommended that the medication be added only under the supervision of a pharmacist. Do not store solutions to which medication has been added.
- Shake and squeeze the freeflex to ensure a complete mix of the medication. With dense medications such as potassium chloride, it is advisable to squeeze both ports while the bag is in a vertical position and invert the bag several times.
- If necessary, a protective cap can be placed over the medication addition port to prevent subsequent additions.
Additions using reconstitution devices
- Identify the medication addition port (white) in the shape of an arrow indicating an entry flow into the bag.
- Remove the protective cap from the medication addition port of the bag, holding the lower wings firmly with one hand and breaking the cap in the shape of an arrow by means of a sustained twisting action.
- Using an aseptic technique, remove the reconstitution device from its packaging and push the narrow end over the medication addition port of the freeflex, so that the wings of the port fit into the grooves of the reconstitution device. Stop when the upper surface of the wings reaches the first stop of the groove. In this position, the upper part of the needle of the reconstitution device is between the cap and the inner membrane, so that fluid cannot escape from the freeflex.
- Using an aseptic technique, prepare the vial of the medication and connect it to the open end of the reconstitution device.
- Connect the medication to the intravenous solution by turning the reconstitution device so that the wings of the port fit into the inner groove and pushing the vial and the reconstitution device until the upper surface of the wings reaches the second stop.
- With the vial inverted, squeeze and release the freeflex several times to transfer solution to the medication vial. Shake to dissolve the medication. Note:If the medication is a liquid, this step 6 can be omitted.
- Invert the freeflex so that the vial is above the bag and transfer the medication to the bag by squeezing and releasing the bag several times, so that the sterile air pushes the liquid out of the vial.
- If the solubility of the medication is low, it may be necessary to repeat steps 6 and 7.
- When the transfer is complete, remove the reconstitution device from the freeflex and discard the vial and the reconstitution device in a safe place. The reconstitution device is designed for single use and should not be used for subsequent additions to this or another freeflex.
NOTE: Additives may be incompatible, so expert advice should be sought before adding medication to freeflex. If the doctor decides to add medication, an aseptic technique should be used. It is recommended that the medication be added only under the supervision of a pharmacist. Do not store solutions to which medication has been added.
- Shake and squeeze the freeflex to ensure a complete mix of the medication. With dense medications such as potassium chloride, it is advisable to squeeze both ports while the bag is in a vertical position and invert the bag several times.
- If necessary, a protective cap can be placed over the medication addition port to prevent subsequent additions.
Warnings:
- Do not vent
- Do not administer if the solution is not transparent and the freeflexis not intact
- If adverse reactions occur, stop the infusion
- It is recommended that infusion sets be changed at least every 24 hours
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FREEFLEX 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDEDosage form: INJECTABLE INFUSION, 100 mlActive substance: Solutions affecting the electrolyte balanceManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE INFUSION, 900 mg sodium chloride / 100 mlActive substance: Solutions affecting the electrolyte balanceManufacturer: B Braun Medical S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 900 mgActive substance: Solutions affecting the electrolyte balanceManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for FREEFLEX 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE
Discuss questions about FREEFLEX 0.9% SODIUM CHLORIDE, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















