FOSTIPUR 150 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION


How to use FOSTIPUR 150 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Fostipur 150 IU Powder and Solvent for Solution for Injection
Urofollitropin
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Fostipur and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you start using Fostipur
- How to use Fostipur
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Fostipur
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Fostipur and what is it used for
- Fostipur is used to stimulate ovulation in women who do not ovulate and do not respond to other treatments (clomiphene citrate).
- In the induction of multifollicular development (and therefore multiple eggs) in women undergoing fertility treatments.
Urofollitropin is a highly purified human follicle-stimulating hormone, which belongs to a group of medicines called gonadotropins.
This medicine should be used under the supervision of your doctor.
2. What you need to know before you start using Fostipur
Before starting treatment, the fertility of the couple should be assessed.
Do not use Fostipur
- If you are allergic to urofollitropin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- Enlargement of the ovaries or ovarian cysts not caused by a hormonal disorder (polycystic ovary syndrome).
Bleeding of unknown origin.
- Ovarian, uterine, or breast cancer.
- Abnormal swelling (tumor) of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus (in the brain).
You should not use this medicine if you have conditions such as premature menopause, malformation of the sex organs, or tumors of the uterus that prevent a normal pregnancy.
Warnings and Precautions
Although there is no information on allergic reactions with Fostipur, you should inform your doctor if you have any allergic reactions to similar medicines.
This treatment increases the risk of developing a disease known as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) (see Possible side effects). If ovarian hyperstimulation occurs, you should stop treatment and avoid becoming pregnant. The first signs of ovarian hyperstimulation are pain in the lower abdominal region, as well as nausea, vomiting, and weight gain. If these symptoms appear, you should be examined by your doctor as soon as possible. In severe but rare cases, the ovaries may enlarge and fluid may accumulate in the abdomen or chest.
The medicine used to achieve the final release of mature eggs (which contains human chorionic gonadotropin, hCG) may increase the likelihood of OHSS. Therefore, it is not advisable to use hCG in cases where ovarian hyperstimulation is developing, and you should not have sexual intercourse, even using barrier contraceptive methods, for at least 4 days.
It should be noted that women with fertility problems have a higher rate of spontaneous abortions than the normal population.
The occurrence of multiple pregnancies and births in patients receiving ovulation induction treatment increases compared to natural conception. However, this risk can be reduced if the recommended dose is used.
There is a slight increase in the risk of ectopic pregnancy in women with damaged Fallopian tubes.
Multiple pregnancies and characteristics of parents undergoing fertility treatments (e.g., mother's age, sperm characteristics) may be associated with a higher risk of birth defects.
Treatment with Fostipur, like pregnancy itself, may increase the risk of thrombosis. Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in a blood vessel, most often in the veins of the legs or in the lungs.
Consult your doctor before starting treatment, especially:
This medicine is prepared from human urine. The risk of transmission of infection or disease to the body cannot be completely eliminated. However, this risk is limited by the virus elimination phases in the manufacturing process, particularly AIDS, Herpes virus, and Papillomavirus.
No cases of viral contamination have been reported.
Using Fostipur with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Fostipur should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Fostipur contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1mmol of sodium (23mg) per dose, i.e., it is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Fostipur
Dose and duration of treatment:
Follow the administration instructions for this medication exactly as indicated by your doctor. If in doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Women who do not ovulate and have irregular or incomplete menstrual periods:
If you have your menstrual period, treatment should be started within 7 days following the start of your menstrual period (the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle).
The dosage consists of 1 injection per day, under the skin (subcutaneously) or in the muscle (intramuscularly).
The common initial dose is 75 IU to 150 IU of FSH (Fostipur) per day. This dose may be increased, if necessary, by 37.5 to 75 IU at intervals of 7 days or, preferably, 14 days, to obtain an adequate response.
The maximum daily dose of FSH should not generally exceed 225 IU.
If your doctor does not find an adequate response after 4 weeks of treatment, this treatment cycle should be discontinued. For the next cycle, your doctor will indicate a treatment with a higher initial dose.
When a good response is obtained (satisfactory follicular growth), you will be administered only one injection of another medication (hCG), used to induce follicular maturation and ovulation release. This will take place 24-48 hours after the last injection of Fostipur. It is recommended to have sexual intercourse on the same day of hCG administration and the next day.
If an excessive ovarian response is obtained, treatment should be discontinued and hCG should not be administered (see Possible adverse effects). For the next cycle, your doctor will indicate a lower initial dose.
Women undergoing ovarian stimulation for multiple follicular development prior to in vitro fertilization or other assisted reproduction techniques:
Situation 1 – If you have your menstrual period.
Treatment should be started 2 or 3 days after the start of your menstrual period (the first 2 or 3 days of the menstrual cycle).
The dosage consists of 1 injection per day subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
A commonly used dose for superovulation consists of the administration of 150 to 225 IU of Fostipur per day. Treatment continues, with dose adjustment according to your response, until adequate follicular development is achieved. This is usually achieved by the 10th day of treatment (an average of 5 to 20 days) and is evaluated by blood sampling and/or ultrasound examinations.
The maximum dose is generally 450 IU/day.
Once follicular development is achieved, a single injection of a medication used to induce final follicular maturation will be administered; this medication contains up to 10,000 IU of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). It will be administered between 24-48 hours after the last injection of Fostipur.
Egg retrieval will be performed approximately 35 hours later.
Situation 2 - When a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist is used
Fostipur should be administered approximately 2 weeks after the start of this treatment. Both treatments are maintained until adequate follicular development is achieved. An injection of Fostipur will be administered per day, intramuscularly or subcutaneously. For example, after 2 weeks of treatment with a GnRH agonist, 150 to 225 IU of Fostipur will be administered for the first 7 days. The dose will then be adjusted according to the ovarian response.
Administration instructions:
Fostipur is administered by injection either under the skin (subcutaneously) or in the muscle (intramuscularly).
Each vial is for single use and the injection should be administered immediately after preparation.
After advising and practicing appropriately, your doctor may ask you to administer the Fostipur injection yourself.
First, your doctor should:
- Allow you to practice administering the subcutaneous injection yourself.
- Indicate the possible areas where you can administer the injection.
- Indicate how to carefully prepare the solution for injection.
- Explain how to prepare the correct dose to be administered.
Other types of presentations, different from ampoules, are designed for self-administration by patients.
Before you administer the Fostipur injection, carefully read the following instructions:
How to prepare and inject Fostipur, using 1 vial of powder
The solution should be prepared just before administering the injection. Each vial is for single use. The medication should be reconstituted under aseptic conditions.
Fostipur should only be reconstituted with the solvent provided in the package.
Prepare a clean surface and wash your hands before reconstituting the solution. It is essential that both your hands and the utensils you will use are as clean as possible.
Lay out the following materials on a clean surface:
- 2 pieces of alcohol-soaked cotton (not included in the box)
- 1 vial containing Fostipur powder
- 1 ampoule of solvent
- 1 syringe (not included in the box)
- 1 needle for preparing the injection (not included in the box)
- 1 fine needle for subcutaneous injection (not included in the box)
Reconstitution of the solution for injection, using 1 vial of powder
Prepare the solution for injection:
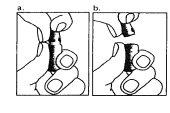
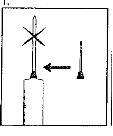
| 1. The neck of the ampoule is specifically designed to break more easily below the colored point. Gently shake the top part of the ampoule to dislodge any residual liquid in the tip. Hold the ampoule with the colored point facing outwards and break off the top part of the ampoule as shown in the image. Using a cloth or an ampoule breaker to hold the ampoule will help protect your fingers. Carefully place the open ampoule in a vertical position on the clean surface. |
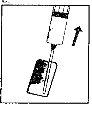
| 2. Remove the protective cap from the needle. Add the needle for reconstitution (large needle) to the syringe. With the syringe in one hand, take the open ampoule of solvent, insert the needle, and withdraw all the solvent into the syringe. Add the protective cap to the needle. Carefully place the syringe on the surface. |
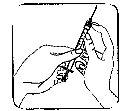
| 3. Remove the colored plastic cap from the powder vial by gently pushing upwards. Disinfect the top of the rubber stopper by rubbing it with an alcohol-soaked cotton swab and let it dry. |
| 4. Take the syringe, remove the protective cap from the needle, and slowly inject the solvent through the central top part of the rubber stopper of the powder vial. Press the plunger firmly downwards to expel all the solution over the powder. DO NOT SHAKE, but gently move the vial between your hands until the powder is completely dissolved, trying to avoid creating foam. |
| 5. Once the powder has dissolved (which usually occurs immediately), slowly withdraw the solution into the syringe.
|
Preparation of higher doses, using more than 1 vial of powder.
If your doctor has recommended higher doses, you can achieve this by using more than 1 vial of powder with a solvent ampoule.
When reconstituting more than 1 vial of Fostipur, at the end of phase 4 described above, introduce the reconstituted contents of the first vial back into the syringe and slowly inject it into a second vial. Repeat phases 2 to 4 for the second vial and subsequent ones, until the contents of the required number of vials are dissolved, equivalent to the prescribed dose (within the limit of the maximum total dose of 450 IU, corresponding to a maximum of 6 vials of Fostipur 75 IU or 3 vials of Fostipur 150 IU).
Your doctor may increase your dose by 37.5 IU, which represents half of a vial of Fostipur 75 IU.
To do this, you must reconstitute the contents of the 75 IU vial according to phases 2 to 3 described above and introduce half of this reconstituted solution (0.5 ml) into the syringe according to phase 4.
In this situation, you will have two preparations to inject: the first reconstituted preparation in 1 ml and the second containing 37.5 IU in 0.5 ml.
Both preparations should be injected with their own syringes according to the following phases.
The solution must be transparent and colorless.
Inject the medication subcutaneously:
|
|
|
|
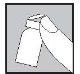
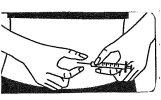
The injection site:
- Your doctor or nurse will have indicated where on your body you can inject the medication. The most common places are the thigh or the lower abdominal wall below the navel.
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol-soaked cotton swab.
Placing the needle:
|
|
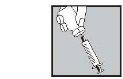
Injecting the solution:
- Inject it under the skin as you were taught. Do not inject it directly into a vein. Push the plunger slowly and steadily, so that the solution is injected correctly and the skin is not damaged.
Take all the time you need to inject the prescribed volume of the solution. As described in the preparation of the solution, depending on the dose prescribed by your doctor, you may not need to use the total volume of the solution.
Withdrawing the needle:
Quickly remove the syringe and press on the injection site with an alcohol-soaked cotton swab. A gentle massage at the site, while maintaining pressure, helps to disperse the Fostipur solution and alleviate discomfort.
Disposal of all used utensils:
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of according to local requirements (once the injection is finished, all needles and empty syringes should be discarded in an appropriate container).
If you use more Fostipur than you should
The effects of an overdose of Fostipur are unknown, although it is likely that an ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome could occur (see Possible adverse effects). If you administer more Fostipur than you should, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 915 620 420, indicating the medication and the amount ingested.
If you forget to use Fostipur
Take the next injection at the scheduled time. Do not take a double dose to make up for forgotten doses.
If you stop treatment with Fostipur
Do not stop treatment on your own initiative. Always consult your doctor if you are considering stopping the use of this medication. If you have any other doubts about the use of this medication, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible adverse effects
Like all medications, Fostipur can cause adverse effects, although not all people experience them.
The following adverse effects are important and will require immediate action if you experience them. You should discontinue the administration of Fostipur and immediately consult your doctor if you experience the following:
Frequent, may affect up to 1 in 10 people:
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (see section 2 for additional information).
The following adverse effects have also been reported:
Frequent, may affect up to 1 in 10 people:
- headache,
- feeling of swelling in the abdomen,
- constipation,
- pain at the injection site.
Uncommon, may affect up to 1 in 100 people:
- increased thyroid gland activity,
- mood changes,
- fatigue,
- dizziness,
- difficulty breathing (dyspnea),
- nasal bleeding,
- nausea, indigestion, abdominal pain,
- skin rash, itching,
- hot flashes,
- cystitis,
- breast enlargement, breast pain,
- difficulty stopping bleeding.
Redness, pain, and hematoma at the injection site may occur (frequency not established).
See section 2 for additional information on the risk of blood clots, ectopic pregnancy, multiple pregnancies, and miscarriages.
If you consider any of the adverse effects you are experiencing to be serious or if you notice any adverse effect not mentioned in this prospectus, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
Reporting adverse effects:
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect not listed in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es.
By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Fostipur
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Do not store above 25°C. Keep the vial and solvent ampoule in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
Do not use Fostipur after the expiration date shown on the package and vial.
Use immediately after reconstitution.
Do not use Fostipur if you notice that the solution is not transparent. After reconstitution, the solution should be transparent and colorless.
Medications should not be thrown away in drains or trash. Deposit the packaging and medications you no longer need in the SIGRE point of the pharmacy. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medications you no longer need. This way, you will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Composition of Fostipur
The active ingredient is urofolitropin. Each vial contains 150 IU of urofolitropin (follicle-stimulating hormone: FSH): 1 ml of reconstituted solution may contain 150 IU, 300 IU or 450 IU of urofolitropin, when 1, 2 or 3 vials, respectively, are reconstituted in 1 ml of solvent.
The specific activity in vivois equal to or greater than 5,000 IU of FSH per mg of protein.
The other components are:
Powder: lactose monohydrate.
Solvent: sodium chloride and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Product and Container Content
Fostipur is presented in powder and solvent for injectable solution.
Box with 1, 5 or 10 packs. Each pack contains: 1 vial with powder containing 150 IU of urofolitropin and 1 ampoule of solvent (1 ml).
The appearance of the powder is a hardened white to off-white mass and the solvent is transparent and colorless.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
IBSA Farmaceutici Italia srl
Via Martiri di Cefalonia 2
26900 Lodi (Italy)
Manufacturer
IBSA Farmaceutici Italia Srl., Via Martiri di Cefalonia, 2 - 26900 Lodi (Italy)
You can request more information about this medication by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Instituto Bioquimico Iberico IBSA S.L.
Avenida Diagonal 605,
Planta 8, Local 1,
08028 Barcelona (Spain)
This medication is authorized in the member states of the European Economic Area with the following names (concentrations and pharmaceutical forms are identical in all countries, only trade names differ)
Austria: Fostimon
Belgium: Fostimon
Cyprus: Fostimon
Denmark: Fostimon
Finland: Fostimon
France: Fostimon
Luxembourg: Fostimon
Ireland: Fostimon
Netherlands: Fostimon
Norway: Fostimon
Spain: Fostipur
Sweden: Fostimon
United Kingdom: Fostimon
Date of the last revision of this prospectus:February 2024
Detailed and updated information on this medication is available on the website of the
Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FOSTIPUR 150 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 75 IU per 1 ml of solution / 5000 IU of FSH per mgActive substance: urofollitropinManufacturer: Ibsa Farmaceutici Italia S.R.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 150 IU per 1 mL of reconstituted solutionActive substance: urofollitropinManufacturer: Ibsa Farmaceutici Italia S.R.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 225 IUActive substance: urofollitropinManufacturer: Ibsa Farmaceutici Italia S.R.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for FOSTIPUR 150 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about FOSTIPUR 150 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions