
DROSURE 0.03 mg/3 mg FILM-COATED TABLETS

How to use DROSURE 0.03 mg/3 mg FILM-COATED TABLETS
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Leaflet: information for the user
Drosure 0.03 mg/3 mg film-coated tablets EFG
etinilestradiol/drospirenona
Read this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only, and you should not pass it on to others, even if they have the same symptoms as you, as it may harm them.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Important things to know about combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs):
- They are one of the most reliable reversible contraceptive methods if used correctly.
- They slightly increase the risk of having a blood clot in the veins and arteries, especially in the first year or when restarting a combined hormonal contraceptive after a break of 4 weeks or more.
- Be alert and talk to your doctor if you think you may have symptoms of a blood clot (see section 2 “Blood clots”).
Contents of the pack
- What Drosure is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you start using Drosure
- How to take Drosure
- Possible side effects
- Storing Drosure
- Package contents and further information
1. What Drosure is and what it is used for
- Drosure is a contraceptive and is used to prevent pregnancy.
- Each tablet contains a small amount of two different female hormones, called etinilestradiol and drospirenona.
- Contraceptives that contain two hormones are called “combined” contraceptives.
2. What you need to know before starting to use Drosure
General considerations
Before starting to use Drosure, you should read the information about blood clots in section 2. It is particularly important that you read the symptoms of a blood clot (see section 2 "Blood clots").
Before starting to take Drosure, your doctor will ask you some questions about your personal and family medical history. Your doctor will also measure your blood pressure and, depending on your personal situation, may carry out some other tests.
This prospectus describes several situations in which you should interrupt the use of Drosure, or in which the effect of Drosure may decrease. In such situations, you should not have sexual intercourse or should take additional non-hormonal contraceptive precautions, for example, use a condom or another barrier method. Do not use the rhythm or temperature method. These methods may not be reliable since Drosure alters the monthly changes in body temperature and cervical mucus.
Drosure, like other hormonal contraceptives, does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) or any other sexually transmitted disease.
Do not take Drosure
You should not use Drosure if you have any of the conditions listed below. Inform your doctor if you have any of the conditions listed below. Your doctor will discuss with you what other form of contraception would be more suitable.
- If you have (or have ever had) a blood clot in a blood vessel in your legs (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), in your lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE), or in other organs.
- If you know you have a disorder that affects blood clotting: for example, protein C deficiency, protein S deficiency, antithrombin III deficiency, factor V Leiden, or antiphospholipid antibodies.
- If you need an operation or if you spend a lot of time immobile (see section "Blood clots").
- If you have ever had a heart attack or a stroke.
- If you have (or have ever had) angina pectoris (a condition that causes severe chest pain and may be the first sign of a heart attack) or a transient ischemic attack (TIA, temporary stroke symptoms).
- If you have any of the following diseases that may increase your risk of forming a clot in the arteries:
- Severe diabetes with blood vessel damage.
- Very high blood pressure.
- Very high levels of fat in the blood (cholesterol or triglycerides).
- A condition called hyperhomocysteinemia.
- If you have (or have ever had) a type of migraine called "migraine with aura".
- If you have (or have ever had) inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
- If you have (or have ever had) a liver disease and your liver function has not yet returned to normal.
- If your kidneys do not work well (renal insufficiency).
- If you have (or have ever had) a tumor in the liver.
- If you have (or have ever had), or if you suspect you have breast cancer or cancer of the genital organs.
- If you have vaginal bleeding, whose cause is unknown.
- If you are allergic to ethinylestradiol or drospirenone, or to any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6). This may cause itching, rash, or inflammation.
- Do not take Drosure if you have hepatitis C and are taking medicines that contain ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir and dasabuvir, glecaprevir/pibrentasvir, or sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir (see also section "Other medicines and Drosure").
Additional information on additional populations
Children and adolescents
Drosure is not indicated for use in women who have not yet had their first menstrual period.
Women of advanced age
Drosure is not indicated for use after menopause.
Women with liver insufficiency
Do not take Drosure if you are suffering from liver disease. See sections "Do not take Drosure" and "Warnings and precautions".
Women with renal insufficiency
Do not take Drosure if you are suffering from kidney malfunction or acute kidney failure. See sections "Do not take Drosure" and "Warnings and precautions".
Warnings and precautions
When should you consult your doctor?
Seek urgent medical attention
- If you notice possible signs of a blood clot that may mean you are suffering from a blood clot in your leg (i.e., deep vein thrombosis), a blood clot in your lung (i.e., pulmonary embolism), a heart attack, or a stroke (see section "Blood clot" below).
To obtain a description of the symptoms of these serious side effects, see "How to recognize a blood clot".
Tell your doctor if you suffer from any of the following conditions
If the condition develops or worsens while you are using Drosure, you should inform your doctor. In some situations, you will need to be particularly careful while using Drosure or any other combined contraceptive, and it may be necessary for your doctor to examine you periodically.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Drosure:
- If a close relative has or has had breast cancer.
- If you have any liver disease (such as a blockage of the bile ducts that can cause jaundice or symptoms of itching) or gallbladder disease (such as gallstones).
- If you have other kidney problems and are taking medicines that increase potassium levels in the blood.
- If you have diabetes.
- If you have depression. Some women who use hormonal contraceptives like Drosure have reported depression or a depressed mood. Depression can be serious and sometimes can induce suicidal thoughts. If you experience mood changes and depressive symptoms, contact your doctor for additional medical advice as soon as possible.
- If you have Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis (chronic inflammatory bowel disease).
- If you have systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, a disease that affects your natural defense system).
- If you have hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS, a blood clotting disorder that causes kidney failure).
- If you have sickle cell anemia (an inherited disease of red blood cells).
- If you have high levels of fat in the blood (hypertriglyceridemia) or a known family history of this condition. Hypertriglyceridemia has been associated with an increased risk of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
- If you need an operation or spend a lot of time immobile (see section 2 "Blood clots").
- If you have just given birth, you are at a higher risk of blood clots. You should ask your doctor when you can start taking Drosure after childbirth.
- If you have inflammation of the veins that are under the skin (superficial thrombophlebitis).
- If you have varicose veins.
- If you have epilepsy (see "Other medicines and Drosure").
- If you have a disease that first appeared during pregnancy or during previous use of sex hormones (e.g., hearing loss, a blood disease called porphyria, blistering skin rash during pregnancy (herpes gestationalis), a nervous system disease in which involuntary movements appear (Sydenham's chorea).
- If you have high blood pressure during treatment and it is not controlled with medication.
- If you have or have had chloasma (a skin discoloration, especially on the face or neck, known as "pregnancy patches"). In this case, you should avoid direct exposure to the sun or ultraviolet rays.
- Consult your doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of angioedema, such as swelling of the face, tongue, and/or throat, difficulty swallowing, or urticaria potentially with difficulty breathing. Medicines that contain estrogens may cause or worsen the symptoms of hereditary and acquired angioedema.
BLOOD CLOTS
The use of a combined hormonal contraceptive like Drosure increases your risk of having a blood clotcompared to not using it. In rare cases, a blood clot can block blood vessels and cause serious problems.
Blood clots can form:
- In the veins (this is called "venous thrombosis", "venous thromboembolism", or VTE).
- In the arteries (this is called "arterial thrombosis", "arterial thromboembolism", or ATE).
Recovery from blood clots is not always complete. In rare cases, there can be serious long-term effects or, very rarely, they can be fatal.
It is important to remember that the overall risk of a harmful blood clot due to Drosure is small.
HOW TO RECOGNIZE A BLOOD CLOT
Seek urgent medical attention if you notice any of the following signs or symptoms
Are you experiencing any of these signs? | What might you be suffering from? |
| Deep vein thrombosis |
If you are unsure, consult your doctor, as some of these symptoms, such as coughing or shortness of breath, can be confused with a milder condition such as a respiratory infection (e.g., a "common cold") | Pulmonary embolism |
Symptoms that occur more frequently in one eye:
| Retinal vein thrombosis (blood clot in the eye) |
| Heart attack |
Sometimes the symptoms of a stroke can be brief, with almost immediate and complete recovery, but you should still seek urgent medical attention as you may be at risk of having another stroke. | Stroke |
| Blood clots that block other blood vessels |
BLOOD CLOTS IN A VEIN
What can happen if a blood clot forms in a vein?
- The use of combined hormonal contraceptives has been associated with an increased risk of blood clots in the veins (venous thrombosis). However, these side effects are rare. They occur more frequently in the first year of use of a combined hormonal contraceptive.
- If a blood clot forms in a vein in the leg or foot, it can cause deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- If a blood clot moves from the leg and lodges in the lung, it can cause a pulmonary embolism.
- In very rare cases, a clot can form in a vein in another organ, such as the eye (retinal vein thrombosis).
When is the risk of a blood clot in a vein higher?
The risk of having a blood clot in a vein is higher during the first year that you take a combined hormonal contraceptive for the first time. The risk may also be higher if you start taking a combined hormonal contraceptive (the same medicine or a different one) after an interruption of 4 weeks or more.
After the first year, the risk decreases, but it is always slightly higher than if you were not taking a combined hormonal contraceptive.
When you stop taking Drosure, your risk of having a blood clot returns to normal within a few weeks.
What is the risk of having a blood clot?
The risk depends on your natural risk of VTE and the type of combined hormonal contraceptive you are taking.
The overall risk of having a blood clot in the leg or lung (DVT or PE) with Drosure is small.
- Out of 10,000 women who do not use a combined hormonal contraceptive and are not pregnant, about 2 will have a blood clot in a year.
- Out of 10,000 women who use a combined hormonal contraceptive that contains levonorgestrel, norethisterone, or norgestimate, about 5-7 will have a blood clot in a year.
- Out of 10,000 women who use a combined hormonal contraceptive that contains drospirenone, such as Drosure, about 9-12 will have a blood clot in a year.
- The risk of having a blood clot will depend on your personal history (see "Factors that increase your risk of a blood clot" below).
Risk of having a blood clot in a year | |
Women who do not usea combined hormonal pill/patch/ring and who are not pregnant. | About 2 out of 10,000 women |
Women who use a combined hormonal pill that contains levonorgestrel, norethisterone, or norgestimate | About 5-7 out of 10,000 women |
Women who use Drosure | About 9-12 out of 10,000 women |
Factors that increase your risk of a blood clot in a vein
The risk of having a blood clot with Drosure is small, but some conditions increase the risk. Your risk is higher:
- If you are overweight (body mass index or BMI over 30 kg/m2).
- If any of your close relatives have had a blood clot in the leg, lung, or other organ at a young age (i.e., before the age of about 50). In this case, you may have a hereditary blood clotting disorder.
- If you need an operation or spend a lot of time immobile due to an injury or illness or if you have your leg in a cast. You may need to stop using Drosure several weeks before surgery or while you have reduced mobility. If you need to stop using Drosure, ask your doctor when you can start using it again.
- As you get older (especially above about 35 years).
- If you have given birth within the past few weeks.
The risk of having a blood clot increases with the number of conditions you have.
Long-distance flights (more than 4 hours) may temporarily increase the risk of a blood clot, especially if you have any of the other risk factors listed.
It is important to inform your doctor if you suffer from any of the above conditions, even if you are not sure. Your doctor may decide that you should stop using Drosure.
If any of the above conditions change while you are using Drosure, for example, a close relative experiences a thrombosis without a known cause or you gain a lot of weight, inform your doctor.
BLOOD CLOTS IN AN ARTERY
What can happen if a blood clot forms in an artery?
Like a blood clot in a vein, a clot in an artery can cause serious problems. For example, it can cause a heart attack or a stroke.
Factors that increase your risk of a blood clot in an artery
It is important to note that the risk of a heart attack or stroke due to Drosure is very small, but it can increase:
- With age (above about 35 years).
- If you smoke. When using a combined hormonal contraceptive like Drosure, you are advised to stop smoking. If you are unable to stop smoking and are over 35 years old, your doctor may advise you to use a different type of contraceptive.
- If you are overweight.
- If you have high blood pressure.
- If any of your close relatives have had a heart attack or stroke at a young age (less than about 50 years). In this case, you may also be at higher risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
- If you or any of your close relatives have a high level of fat in the blood (cholesterol or triglycerides).
- If you have migraines, especially migraines with aura.
- If you have a heart problem (valve disorder, heart rhythm disturbance called atrial fibrillation).
- If you have diabetes.
If you have more than one of these conditions or if any of them are particularly severe, the risk of having a blood clot may be increased further.
If any of the above conditions change while you are using Drosure, for example, you start smoking, a close relative experiences a thrombosis without a known cause, or you gain a lot of weight, inform your doctor.
Drosure and cancer
Breast cancer has been slightly more common in women who use combined contraceptives, but it is not known if this is due to the treatment. For example, it may be that more tumors are detected in women who take combined contraceptives because they are examined by a doctor more frequently. The incidence of breast tumors decreases gradually after stopping combined hormonal contraceptives. It is important to have regular check-ups with your doctor.
3. Cómo tomar Drosure
Siga exactamente las instrucciones de administración de este medicamento indicadas por su médico o farmacéutico. En caso de duda, consulte de nuevo a su médico o farmacéutico.
Tome un comprimido de Drosure cada día con algo de agua si fuera necesario. Puede tomar los comprimidos con o sin comida, pero todos los días aproximadamente a la misma hora.
Un envase contiene 21 comprimidos. Al lado de cada comprimido está impreso el día de la semana en el que debe ser tomado. Por ejemplo, si empieza un miércoles, tome un comprimido con “MIE” al lado. Siga la dirección de la flecha del envase hasta que haya tomado los 21 comprimidos.
Después no debe tomar ningún comprimido durante 7 días. A lo largo de estos 7 días en los que no se toman comprimidos (periodo llamado semana de descanso), debería tener lugar la menstruación. La menstruación, que también puede denominarse hemorragia por privación, comienza el 2º o 3º día de la semana de descanso.
Al 8º día de tomar el último comprimido de Drosure (es decir, después del periodo de descanso de 7 días), debe comenzar con el siguiente envase, aunque no haya finalizado el sangrado. Esto quiere decir que usted debería comenzar cada envase el mismo día de la semana y que la menstruación debe tener lugar durante los mismos días cada mes.
Si usted usa Drosure de este modo, también está protegida frente al embarazo durante los 7 días en los que no toma ningún comprimido.
Cuando puede empezar con el primer envase
- Si usted no ha usado ningún anticonceptivo hormonal en el mes anterior
Comience a tomar Drosure el primer día del ciclo (es decir, el primer día de su periodo). Si comienza Drosure el primer día de su periodo, estará protegida inmediatamente frente a un embarazo. También puede empezar los días 2-5 del ciclo, pero debe utilizar métodos anticonceptivos adicionales (por ejemplo, un preservativo) durante los primeros 7 días.
- Cambio desde otro anticonceptivo hormonal combinado, anillo anticonceptivo combinado vaginal o parche
Usted puede comenzar a tomar Drosure preferentemente el día después de tomar el último comprimido activo (el último comprimido que contiene principios activos) de su anticonceptivo anterior, pero a más tardar al día siguiente de la semana de descanso de su anticonceptivo anterior (o después de tomar el último comprimido inactivo de su anticonceptivo anterior). Cuando cambie desde un anillo anticonceptivo combinado vaginal o parche, siga las recomendaciones de su médico.
- Cambio desde un método basado exclusivamente en progestágenos (píldora de progestágenos solos, inyección, implante o sistema de liberación intrauterino de progestágenos SLI)
Puede cambiar desde la píldora de progestágenos solos cualquier día (si se trata de un implante o un SLI, el mismo día de su retirada; si se trata de un inyectable, cuando corresponda la siguiente inyección), pero en todos los casos utilice medidas anticonceptivas adicionales (por ejemplo, un preservativo) durante los 7 primeros días de toma de comprimidos.
- Tras un aborto
Siga las recomendaciones de su médico.
- Tras tener un niño.
Puede comenzar a tomar Drosure entre 21 y 28 días después de tener un niño. Si usted comienza más tarde, utilice uno de los denominados métodos de barrera (por ejemplo, un preservativo) durante los 7 primeros días del uso de Drosure.
Si, tras tener un niño, usted ya ha tenido relaciones sexuales antes de comenzar a tomar Drosure (de nuevo), debe estar segura de no estar embarazada o esperar a su siguiente periodo menstrual.
- Si usted está en periodo de lactancia y quiere empezar a tomar Drosure (de nuevo) después de tener un niño
Lea la sección “Lactancia”.
Pregunte a su médico si no está segura de cuando empezar.
Si toma más Drosure del que debe
No se han comunicado casos en los que la ingestión de una sobredosis de Drosure haya causado daños graves.
Si usted toma muchos comprimidos a la vez puede encontrarse mal o tener vómitos o hemorragia vaginal.
Esta hemorragia puede aparecer incluso en chicas que aún no han tenido su primer periodo menstrual, si accidentalmente han tomado este medicamento.
Si usted ha tomado demasiados comprimidos de Drosure, o descubre que un niño los ha tomado, consulte inmediatamente con su médico o farmacéutico.
En caso de sobredosis o ingestión accidental, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico o llame al Servicio de Información Toxicológica, teléfono 91 562 04 20 indicando el medicamento y la cantidad utilizada.
Si olvidó tomar Drosure
- Si usted se retrasa menos de 12 horasen la toma de algún comprimido, la protección frente al embarazo no disminuye. Tome el comprimido tan pronto como se acuerde y los comprimidos siguientes a la hora habitual.
- Si usted se retrasa más de 12 horasen la toma de algún comprimido, la protección frente al embarazo puede reducirse. Cuantos más comprimidos haya olvidado, mayor es el riesgo de quedarse embarazada.
El riesgo de una protección incompleta frente al embarazo es máximo si usted olvida tomar el comprimido al principio o al final del envase. Por tanto, debe seguir las siguientes recomendaciones (ver también el diagrama más abajo):
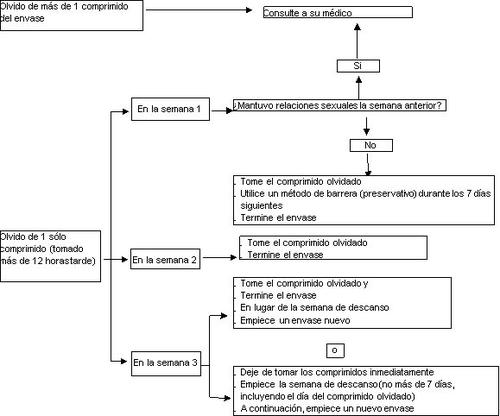
- Olvido de más de un comprimido del envase
Consulte con su médico.
- Olvido de un comprimido en la semana 1
Tome el comprimido olvidado tan pronto como se acuerde, aunque esto signifique que tenga que tomar dos comprimidos a la vez. Siga tomando los comprimidos a la hora habitual y utilice precauciones adicionales, por ejemplo, preservativo, durante los 7 días siguientes. Si usted ha mantenido relaciones sexuales en la semana previa al olvido del comprimido, puede estar embarazada. En ese caso, consulte a su médico.
- Olvido de un comprimido en la semana 2
Tome el comprimido olvidado tan pronto como se acuerde, aunque esto signifique que tenga que tomar dos comprimidos a la vez. Siga tomando los comprimidos a la hora habitual. La protección anticonceptiva no disminuye y usted no necesita tomar precauciones adicionales.
- Olvido de un comprimido en la semana 3
Puede elegir entre dos posibilidades:
- Tome el comprimido olvidado tan pronto como se acuerde, aunque esto signifique que tenga que tomar dos comprimidos a la vez. Siga tomando los comprimidos a la hora habitual. En lugar de iniciar el periodo de descanso, comience a tomar el siguiente envase.
Probablemente tendrá la regla al final del segundo envase, aunque también puede presentar sangrado leve o parecido a la regla durante la toma del segundo envase.
- También puede interrumpir la toma de comprimidos y pasar directamente al periodo de descanso de 7 días (anotando el día en el que olvidó tomar el comprimido). Si quiere comenzar un nuevo envase en el día en que siempre empieza, su periodo de descanso deberá durar menos de 7 días.
Si usted sigue una de estas dos recomendaciones, permanecerá protegida frente al embarazo.
- Si usted ha olvidado tomar algún comprimido y no tiene sangrado durante el primer periodo de descanso, puede estar embarazada. Contacte con su médico antes de seguir con el siguiente envase.
El siguiente esquema le indica cómo actuar en el caso de que se le haya olvidado algún comprimido:
Qué debe hacer en caso de vómitos o diarrea intensa
Si usted tiene vómitos en las 3-4 horas siguientes a la toma de un comprimido o padece diarrea intensa, hay un riesgo de que los principios activos del anticonceptivo no sean absorbidos totalmente por el organismo. La situación es casi equivalente al olvido de un comprimido. Tras los vómitos o la diarrea, tome un comprimido de un envase de reserva lo antes posible. Si es posible, tómelo dentro de las 12 horasposteriores a la hora habitual en que toma su anticonceptivo. Si esto no es posible o han transcurrido más de 12 horas, siga los consejos del apartado “Si olvidó tomar Drosure”.
Retraso de su período: qué debe saber
Aunque no es recomendable, puede retrasar su período si comienza a tomar un nuevo envase de Drosure en lugar de continuar con la semana de descanso y lo termina. Usted puede experimentar el uso del segundo envase un sangrado leve o parecido a la regla. Tras la semana de descanso habitual de 7 días, empieceel siguiente envase.
Usted debería pedir consejo a su médico antes de decidir retrasar su periodo menstrual.
Cambio del primer día de su período: qué debe saber
Si usted toma los comprimidos según las instrucciones, su período comenzará durante la semana de descanso. Si usted tiene que cambiar ese día, reduzca el número de días de descanso (¡pero nunca los aumente- 7 como máximo!). Por ejemplo, si sus días de descanso comienzan habitualmente los viernes y quiere cambiar a los martes (3 días antes), comience un nuevo envase 3 días antes de lo habitual. Si usted hace que el período de descanso sea muy corto (por ejemplo, 3 días o menos), puede que no se produzca sangrado durante estos días. Entonces usted puede experimentar un sangrado leve o parecido a la regla.
Si no está segura de cómo proceder, consulte a su médico.
Si interrumpe el tratamiento con Drosure
Usted puede dejar de tomar Drosure cuando desee. Si no quiere quedarse embarazada, consulte con su médico sobre otros métodos de control de la natalidad eficaces. Si quiere quedarse embarazada, deje de tomar Drosure y espere hasta su periodo antes de intentar quedarse embarazada. Así podrá calcular la fecha estimada del parto más fácilmente.
Si tiene cualquier duda sobre el uso de este medicamento, pregunte a su médico o farmacéutico.
4. Posibles efectos adversos
Al igual que todos los medicamentos, este medicamento puede producir efectos adversos, aunque no todas las personas los sufran. Si sufre cualquier efecto adverso, especialmente si es grave y persistente, o tiene algún cambio de salud que cree que puede deberse a Drosure, consulte a su médico.
Todas las mujeres que toman anticonceptivos hormonales combinados corren mayor riesgo de presentar coágulos de sangre en las venas (tromboembolismo venoso (TEV)) o coágulos de sangre en las arterias (tromboembolismo arterial (TEA)). Para obtener información más detallada sobre los diferentes riesgos de tomar anticonceptivos hormonales combinados, ver sección 2 “Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a usar Drosure”.
Contacte inmediatamente con su médico si experimenta alguno de los siguientes síntomas de angioedema: hinchazón de la cara, lengua y/o garganta y/o dificultad para tragar o urticaria potencialmente con dificultad para respirar (ver también la sección “Advertencias y precauciones”).
El siguiente listado de efectos adversos se ha relacionado con el uso de Drosure:
Efectos adversosfrecuentes(pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 10 personas):
- Estado de ánimo depresivo
- Dolor de cabeza
- Migraña
- Náuseas
- Trastornos menstruales, hemorragia intermenstrual, dolor en las mamas, sensibilidad en las mamas
- Secreción vaginal espesa blanquecina e infección vaginal por hongos.
Efectos adversos poco frecuentes(pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 100 personas):
- Aumento del tamaño de las mamas, cambios en el interés por el sexo
- Tensión arterial alta, tensión arterial baja
- Vómitos, diarrea
- Acné, erupción cutánea, picor intenso, pérdida de cabello (alopecia)
- Infección de la vagina
- Retención de líquidos y aumento o disminución del peso corporal.
Efectos adversos raros(pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 1000 personas):
- Reacciones alérgicas (hipersensibilidad), asma
- Problemas auditivos
- Trastornos cutáneos como eritema nudoso (caracterizado por nódulos dolorosos en la piel de color rojizo) o eritema multiforme (caracterizado por erupción con rojeces en forma de diana o úlceras)
- Secreción mamaria
- Coágulos de sangre perjudiciales en una vena o arteria, por ejemplo:
- En una pierna o pie (es decir, TVP)
- En un pulmón (es decir, PE)
- Ataque al corazón
- Ictus
- Ictus leve o síntomas temporales similares a los de un ictus, lo que se llama accidente isquémico transitorio (AIT)
- Coágulos de sangre en el hígado, estómago/intestino, riñones u ojo.
La probabilidad de tener un coágulo sanguíneo puede ser mayor si tiene otras afecciones que aumenten este riesgo (consulte la sección 2 para obtener más información sobre las afecciones que aumentan el riesgo de coágulos de sangre y los síntomas de un coágulo de sangre).
Comunicación de efectos adversos
Si experimenta cualquier tipo de efecto adverso, consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero, incluso si se trata de posibles efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. También puede comunicarlos directamente a través del Sistema Español de Farmacovigilancia de medicamentos de Uso Humano: https://www.notificaram.es. Mediante la comunicación de efectos adversos usted puede contribuir a proporcionar más información sobre la seguridad de este medicamento.
5. Storage of Drosure
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store below 30°C.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the packaging after "CAD". The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine in the pharmacy's SIGRE collection point. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Drosure
The active ingredients are 0.03 mg of ethinylestradiol and 3 mg of drospirenone.
The other ingredients are:
Core of the tablet: lactose monohydrate, corn starch, pregelatinized corn starch, povidone, polysorbate 80, magnesium stearate.
Coating: partially hydrolyzed polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide (E171), macrogol, talc, yellow iron oxide (E172).
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
Film-coated tablets, round, yellow, approximately 5.7 mm in diameter.
Drosure is available in packs of 1, 2, 3, 6, and 13 units (blisters), each containing 21 tablets.
Only some pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Laboratorios Effik, S.A.
C/ San Rafael, 3
28108 Alcobendas, Madrid
Spain
Manufacturer
Laboratorios León Farma, S.A.
C/ La Vallina, s/n,
Navatejera Industrial Estate,
Villaquilambre
24193 León, Spain
This medicine isauthorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Bulgaria: Jangee 0.03 mg/3mg ????????? ????????
Greece: Estrofix 0.03 mg/3 mg επικαλυμμ?νο με λεπτ? υμ?νιο δισκ?ο
Spain: Drosure 0.03 mg/3 mg film-coated tablets EFG
Ireland: Ethinylestradiol/Drospirenone Leon Farma 0.03 mg/3 mg film-coated tablets
Portugal: Drospirenone + Etinilestradiol Generis 3 mg + 0.03 mg film-coated tablets
Date of the Last Revision of this Leaflet: November 2022
Updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DROSURE 0.03 mg/3 mg FILM-COATED TABLETSDosage form: TABLET, 3 mg/0.03 mgActive substance: drospirenone and ethinylestradiolManufacturer: Laboratorios Cinfa S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 3 mg/0.03 mgActive substance: drospirenone and ethinylestradiolManufacturer: Laboratorios Cinfa S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 3 mg/0.02 mgActive substance: drospirenone and ethinylestradiolManufacturer: Laboratorios Cinfa S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for DROSURE 0.03 mg/3 mg FILM-COATED TABLETS
Discuss questions about DROSURE 0.03 mg/3 mg FILM-COATED TABLETS, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






