
SODIUM CHLORIDE FRESENIUS KABI 5.84% INJECTABLE SOLUTION


How to use SODIUM CHLORIDE FRESENIUS KABI 5.84% INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USERSodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi 5.84% solution for injection
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine.
|
In this leaflet:
- What Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi is and what it is used for
- Before you use Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi
- How to use Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi
- Further information
1. What Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi is and what it is used for
Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi is a solution for injection, which belongs to the group of medicines called electrolyte solutions.
Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi is indicated for the treatment of severe hyponatremia (low sodium levels in the blood) of various causes.
2. Before you use Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi
Do not use Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi:
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi.
- if you have edema (excessive fluid accumulation)
- if you have eclampsia (seizures not attributed to any other cause during pregnancy)
- if you have hypernatremia (high sodium levels in the blood)
Be cautious when using Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi:
Sodium chloride should be used with extreme caution in patients with heart failure, severe renal insufficiency (significant reduction in kidney function), liver cirrhosis (chronic progressive liver disease), and in those receiving corticosteroids or corticotropin (medicines used as anti-inflammatory agents). It should also be used with caution in elderly patients and those recovering from surgery.
Excess chloride in the body can cause a loss of bicarbonate, resulting in a decrease in pH. Excessive intravenous administration of sodium chloride can also lead to low potassium levels in the blood.
The coexistence of insufficient blood oxygenation and low sodium levels in the blood can cause brain damage, even in the absence of any correction of the low sodium levels in the blood.
It should be administered with caution in patients with high blood pressure.
If administered continuously in the same injection site, it can cause pain, infection, and phlebitis (inflammation of the vein wall).
Consult your doctor, even if any of the above circumstances have occurred to you in the past.
Use of other medicines:
Before mixing with other medicines, check the compatibility tables, consider the pH, and monitor the ions.
The concomitant administration of sodium chloride and corticosteroids or corticotropin (medicines used as anti-inflammatory agents) can lead to excessive fluid accumulation due to the sodium content.
The interaction between sodium and lithium (a medicine used to treat certain psychiatric disorders) is clinically significant. Excess sodium can prevent the establishment of adequate lithium levels, and conversely, a deficiency of sodium chloride can lead to an increase in lithium levels to toxic values.
Note that these instructions may also apply to medicines that have been used before or may be used after.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using or have recently used any other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before using any medicine.
The safety of its use during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been established. Therefore, it should only be used when clearly necessary and when the benefits justify the potential risks to the fetus or infant.
Driving and using machines:
This is not applicable due to the characteristics of its use.
3. How to use Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi:
Follow exactly the administration instructions of Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi as indicated by your doctor. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have any doubts.
The doses will be adapted to the patient's needs according to medical criteria based on age, weight, clinical status, fluid balance, ions, and acid-base balance.
Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi is administered intravenously, intramuscularly, or subcutaneously.
It is not necessary to sterilize the ampoule before opening. No cutting element is required to open the ampoule. Once the ampoule is opened, the nozzle fits perfectly onto the cone of the syringe (Luer cone), so it is not necessary to use a needle.
To open, separate one ampoule from the rest, twist one ampoule around itself against the rest of the ampoules on the strip without touching the head and neck of the ampoules (1). Shake the ampoule with a single movement as shown in the drawing to eliminate any liquid that may be in the stopper (2). To open the ampoule, twist the body and head of the ampoule in opposite directions until it breaks at the neck (3). Connect the Luer or Luer-lock syringe as shown in the drawing (4).
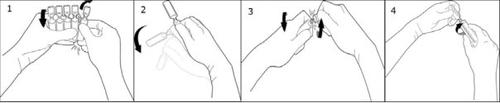
The solution does not contain any preservative or bactericide, so opened and unused ampoules must be discarded immediately.
If you use more Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi than you should:
Accidental overdose can lead to the symptoms described for excess sodium in the blood, and the measures to be taken will be those corresponding to the reduction of high sodium levels in the blood.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount used. It is recommended to take the packaging and leaflet to the healthcare professional.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi can cause side effects.
Since sodium chloride is part of the normal composition of the internal medium, adverse reactions would be related to its concentration, which is higher than that of blood serum.
The adverse effects described have been due to excessive or too rapid administration. There are two forms of toxicity: the first is high sodium levels in the blood, and the second is an excess of sodium and water that can lead to excessive fluid accumulation, affecting the brain, lungs, or peripheral circulation. The symptoms of excess sodium are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, thirst, reduced tear and saliva production, excessive sweating, fever, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, kidney failure, excessive fluid accumulation in different areas of the body and in the lungs, respiratory arrest, headache, dizziness, restlessness, weakness, muscle tremors and stiffness, seizures, coma, and death. However, most of the hypernatremias described have been as a result of the use of oral sodium chloride solutions and not due to the intravenous use of solutions with a sodium concentration higher than that of blood serum.
The administration of significant amounts of chloride can lead to a decrease in the body's pH as a consequence of the decrease in bicarbonate concentration.
If you experience any of the side effects, or if you notice any side effects not mentioned in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
5. Storage of Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
No special storage conditions are required.
Do not use Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi after the expiration date stated on the packaging after EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Do not use this medicine if you notice that the solution is not transparent, colorless, and free of particles.
Once the packaging is opened, the product must be used immediately.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine. This will help protect the environment.
6. Further information
Composition of Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi
- The active substance is: sodium chloride. Each ml of solution contains 58.4 mg of sodium chloride (ionic content: Na+ = Cl- = 1 mEq/ml).
Other ingredients are: water for injection and hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide.
Appearance and packaging of the product
Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi is a transparent and colorless solution, free or practically free of particles.
Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi is available in the following formats:
Box of 20 ampoules of 10 ml
Box of 50 ampoules of 10 ml
Box of 20 ampoules of 20 ml
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Fresenius Kabi España S.A.U. Marina 16-18
08005 – Barcelona
This leaflet was approved in October 2019
Detailed and updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gov.es/
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Solution for infusion for intravenous administration.
The ampoule of Sodium Chloride Fresenius Kabi should be diluted in a minimum volume of 50 ml of an infusion solution.
Use only if the solution is transparent and free of visible particles. If not all of the contents are used, discard the remainder.
In severe acute hyponatremia, rates of 1 mmol/l/hour are recommended to prevent neurological damage.
If the hyponatremia is chronic, furosemide or an osmotic diuretic should be associated with hypertonic saline solution.
Correction of hyponatremia should not be excessively rapid to avoid demyelinating lesions. Some authors recommend not exceeding a correction of 10 mEq/l in the first 24 hours and 21 mEq/l in the first 48 hours. In general, serum sodium levels should be monitored to stop replacement when normal values are reached.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to SODIUM CHLORIDE FRESENIUS KABI 5.84% INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, -Active substance: potassium acetateManufacturer: B Braun Medical S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE INFUSION, 100 mlActive substance: sodium bicarbonateManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.840 g sodium bicarbonate/10 mlActive substance: sodium bicarbonateManufacturer: Laboratorios Grifols S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for SODIUM CHLORIDE FRESENIUS KABI 5.84% INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about SODIUM CHLORIDE FRESENIUS KABI 5.84% INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















