BUVIDAL 160 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use BUVIDAL 160 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Buvidal 8 mg prolonged-release solution for injection
Buvidal 16 mg prolonged-release solution for injection
Buvidal 24 mg prolonged-release solution for injection
Buvidal 32 mg prolonged-release solution for injection
Buvidal 64 mg prolonged-release solution for injection
Buvidal 96 mg prolonged-release solution for injection
Buvidal 128 mg prolonged-release solution for injection
Buvidal 160 mg prolonged-release solution for injection
buprenorphine
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack and other information
- What is Buvidal and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you are given Buvidal
- How Buvidal is given
- Possible side effects
- Storing Buvidal
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Buvidal and what is it used for
Buvidal contains the active substance buprenorphine, which is a type of opioid medicine. It is used to treat opioid dependence in patients who are also receiving medical, social, and psychological support.
Buvidal is indicated in adults and adolescents aged 16 years and older.
2. What you need to know before you are given Buvidal
Do not use Buvidal
- if you are allergic to buprenorphine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- if you have severe breathing problems
- if you have severe liver problems
- if you have alcohol intoxication or have tremors, sweating, anxiety, confusion or hallucinations caused by alcohol
Warnings and precautions
Tell your doctor before using Buvidal if you have:
- asthma or other breathing problems
- any liver disease such as hepatitis
- severe kidney problems
- certain heart rhythm problems (long QT syndrome or prolonged QT interval)
- low blood pressure
- have recently had a head injury or a brain disease
- urinary retention (especially associated with an enlarged prostate in men)
- thyroid problems
- a corticosteroid deficiency (e.g. Addison's disease)
- gallbladder problems
- depression or other illnesses that are treated with antidepressants. Using these medicines with Buvidal may cause serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening disease (see "Other medicines and Buvidal").
- if you have ever had an allergic reaction to latex
Important things to consider
- Breathing problems:Some people have died due to very slow or shallow breathing caused by taking buprenorphine with other central nervous system depressants (substances that slow down some brain activities), such as benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other opioids.
- Drowsiness:This medicine can cause drowsiness, especially when used with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants (substances that slow down some brain activities), such as benzodiazepines, other anxiety-reducing medicines that cause drowsiness, pregabalin, or gabapentin.
- Dependence:This medicine can cause dependence.
- Liver damage:Liver damage can occur with buprenorphine, especially when used improperly. This can also occur due to viral infections (chronic hepatitis C), alcohol abuse, anorexia (eating disorder), or use of other medicines that can damage the liver. Your doctor may ask you to have blood tests done regularly to check the condition of your liver. Tell your doctor if you have liver problems before starting treatment with Buvidal.
- Withdrawal symptoms: This medicine can cause withdrawal symptoms if you take it less than 6 hours after taking a short-acting opioid (e.g. morphine, heroin) or less than 24 hours after taking a long-acting opioid, such as methadone.
- Blood pressure:This medicine can cause a sudden drop in your blood pressure, which can cause dizziness if you get up too quickly when sitting or lying down.
- Diagnosis of unrelated medical conditions:This medicine can mask pain, which can make it difficult to diagnose some diseases. Do not forget to tell your doctor that you are taking this medicine.
- Sleep-related breathing disorders:Buvidal can cause sleep-related breathing disorders such as sleep apnea (pauses in breathing during sleep) and sleep-related hypoxemia (low oxygen levels in the blood). Symptoms may include pauses in breathing during sleep, nighttime awakenings due to difficulty breathing, difficulty staying asleep, or excessive daytime sleepiness. Contact your doctor if you or someone else notices these symptoms. Your doctor may consider a dose reduction.
Tolerance, dependence, and addiction
This medicine contains buprenorphine, an opioid substance. Repeated use of opioids can reduce the effectiveness of the medicine (your body gets used to the medicine, this is what is known as tolerance). Repeated use of buprenorphine can also cause dependence, abuse, and addiction, which can lead to a potentially life-threatening overdose.
Dependence or addiction can make you feel like you no longer have control over the amount of medicine you need to use or how often you need to use it.
The risk of becoming dependent or addicted varies from person to person. You may be at higher risk of becoming dependent or addicted to buprenorphine if:
- You or a family member have a history of alcohol, prescription medicine, or illegal substance abuse ("addiction").
- You are a smoker.
- You have ever had problems with your mood (depression, anxiety, or personality disorder) or have received treatment from a psychiatrist for other mental illnesses.
If you notice any of the following signs while taking buprenorphine, it could be a sign that you have become dependent or addicted:
- You need to use the medicine for longer than recommended by your doctor.
- You need to use more doses than recommended.
- You are using the medicine for reasons other than those prescribed, for example, "to calm down" or "to help you sleep".
- You have made repeated attempts to stop or control the use of the medicine without success.
- You do not feel well when you stop using the medicine and feel better when you start using it again ("withdrawal symptoms").
If you notice any of these signs, talk to your doctor to address the most suitable treatment strategy for you, including when it is appropriate to stop using it and how to do it safely (see section 3 "If you stop treatment with Buvidal").
Children and adolescents
Buvidal should not be used in children under 16 years of age. Your doctor will monitor you more closely if you are an adolescent (16 to 17 years old).
Other medicines and Buvidal
Tell your doctor if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Some medicines can increase the adverse effects of Buvidal and can cause very serious reactions.
It is especially important that you tell your doctor if you are taking:
- benzodiazepines(used to treat anxiety or sleep disorders). Taking very high doses of a benzodiazepine with Buvidal can cause death because both medicines can make breathing very slow and shallow (respiratory depression). If you need a benzodiazepine, your doctor will prescribe the correct dose.
- gabapentinoids (gabapentin or pregabalin)(used to treat epilepsy or neuropathic pain). Taking very high doses of a gabapentinoid can cause death because both medicines can make breathing very slow and shallow (respiratory depression). You should take the dose that your doctor has prescribed.
- alcohol or medicines that contain alcohol. Alcohol can worsen the sedative effect of this medicine.
- other medicines that can make you feel drowsyused to treat diseases such as anxiety, insomnia, seizures (fits), and pain. These medicines, when taken with Buvidal, can slow down some brain activities, and reduce your alertness and ability to drive and use machines correctly. Examples of medicines that can make you feel drowsy or less alert include:
- other opioids such as methadone, certain painkillers, and cough medicines. These medicines can also increase the risk of opioid overdose
- antidepressants (used to treat depression)
- sedating antihistamines (used to treat allergic reactions)
- barbiturates (used to induce sleep or sedation)
- certain anxiolytics (used to treat anxiety disorders)
- antipsychotics (used to treat psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia)
- clonidine (used to treat high blood pressure)
- opioid painkillers.These medicines may not work properly if taken with Buvidal and can increase the risk of overdose.
- naltrexone and nalmefene(used to treat addiction disorders) because they can also prevent Buvidal from working properly. You should not take them at the same time as this medicine.
- certain antiretrovirals(used to treat HIV infection) such as ritonavir, nelfinavir, indinavir, because they can increase the effects of this medicine.
- certain antifungal medicines(used to treat fungal infections) such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, because they can increase the effects of this medicine.
- macrolide antibiotics(used to treat bacterial infections) such as clarithromycin and erythromycin, because they can increase the effects of this medicine.
- certain antiepileptic medicines(used to treat epilepsy) such as phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and phenytoin, because they can reduce the effect of Buvidal.
- rifampicin(used to treat tuberculosis). Rifampicin can reduce the effect of Buvidal.
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors(used to treat depression) such as phenelzine, isocarboxazid, iproniazid, and tranylcypromine, because they can increase the effects of this medicine.
- antidepressantssuch as moclobemide, tranylcypromine, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, doxepin, or trimipramine. These medicines can interact with Buvidal and you may experience symptoms such as involuntary muscle contractions, including muscles that control eye movement, agitation, hallucinations, coma, excessive sweating, tremors, exaggerated reflexes, increased muscle tension, body temperature above 38°C. Contact your doctor if you experience these symptoms.
- medicines used to treat allergies and to treat nausea and vomiting during travel(antihistamines or antiemetics).
- muscle relaxants
- medicines for the treatment of Parkinson's disease
Using Buvidal with alcohol
Do not drink alcohol while using Buvidal (see section 2 Warnings and Precautions). Drinking alcohol with this medicine can increase drowsiness and can increase the risk of breathing problems.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before using this medicine. The risks of using Buvidal in pregnant women are not known. Your doctor will help you decide if you should continue taking the medicine during pregnancy.
Taking this medicine during pregnancy can cause withdrawal symptoms, including breathing problems in your newborn baby. This can happen several hours to several days after birth.
Ask your doctor before using Buvidal during breastfeeding, as this medicine is excreted in breast milk.
Driving and using machines
Buvidal may cause drowsiness and dizziness. This is more likely at the start of treatment and when the dose is being changed. These effects can be worsened if you drink alcohol or take other sedative medicines. Do not drive, use tools or machines, or perform hazardous activities until you know how this medicine affects you.
Buvidal contains alcohol
Buvidal 8 mg, 16 mg, 24 mg, and 32 mg contain 95.7 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per ml (10% w/w).
The amount in one dose of this medicine is equivalent to less than 2 ml of beer or 1 ml of wine.
The small amount of alcohol in this medicine does not have any noticeable effect.
3. How Buvidal is given
Buvidal should only be given by healthcare professionals.
Buvidal 8 mg, 16 mg, 24 mg, and 32 mg are given weekly. Buvidal 64 mg, 96 mg, 128 mg, and 160 mg are given monthly.
Your doctor will decide which dose is best for you. During treatment, your doctor may adjust your dose, depending on how well the medicine is working.
Starting treatment
The first dose of Buvidal will be given to you when you show clear signs of withdrawal. If you are dependent on short-acting opioids (e.g. morphine or heroin), the first dose of Buvidal will be given to you at least 6 hours after your last opioid use.
If you are dependent on long-acting opioids (e.g. methadone), your methadone dose will be reduced to below 30 mg per day before starting Buvidal. The first dose of Buvidal will be given to you at least 24 hours after you last took methadone.
If you are not taking buprenorphine (the same active substance as Buvidal) sublingually (under the tongue), the recommended starting dose is 16 mg, with one or two additional doses of 8 mg of Buvidal given with at least one day in between during the first week of treatment. This means that the target dose during the first week of treatment is 24 mg or 32 mg.
If you have not taken buprenorphine before, you will receive a sublingual dose of 4 mg of buprenorphine and will be observed for one hour before the first dose of Buvidal.
Monthly treatment with Buvidal can be used if it is suitable for you, once you have been stabilized with Buvidal on weekly treatment (four weeks of treatment or more, when practical).
If you are already taking buprenorphine sublingually, you can start receiving Buvidal the day after your last treatment. Your doctor will prescribe the correct starting dose of Buvidal for you, depending on the dose of buprenorphine sublingually you are currently taking.
Continuing treatment and dose adjustment
During continued treatment with Buvidal, your doctor may increase or decrease your dose according to your needs. You may be switched from weekly to monthly treatment and from monthly to weekly treatment. Your doctor will tell you the correct dose for you.
During continued treatment, you may receive an additional dose of 8 mg of Buvidal between weekly or monthly treatments if your doctor considers it suitable for you.
The maximum weekly dose if you are receiving weekly treatment with Buvidal is 32 mg with an additional dose of 8 mg. The maximum monthly dose if you are receiving monthly treatment with Buvidal is 160 mg.
Method of administration
Buvidal is given as a single injection under the skin (subcutaneously) in any of the allowed injection sites: buttocks, thighs, abdomen, or arms. You can receive multiple injections in the same area, but the exact injection site should be varied for each weekly and monthly injection, with a minimum of 8 weeks in between.
If you use more Buvidal than you should
If you have received more buprenorphine than you should, contact your doctor immediately, as this can cause your breathing to become very slow and shallow, which can be life-threatening.
If you use too much buprenorphine, you should seek medical attention immediately, as an overdose can cause serious and potentially life-threatening breathing problems. Symptoms of overdose may include slower and weaker breathing than normal, more drowsiness than usual, nausea, vomiting, and/or difficulty speaking. You may also have a decrease in pupil size. If you feel faint, it can be a sign of low blood pressure.
If you miss a dose of Buvidal
It is very important that you attend all appointments to receive Buvidal. If you miss an appointment, ask your doctor when you can schedule the next dose.
If you stop treatment with Buvidal
Do not stop treatment without consulting the doctor who is treating you. Stopping treatment can cause withdrawal symptoms.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Inform your doctor immediately or receive urgent medical attentionif you experience adverse effects, such as:
- sudden wheezing, difficulty breathing, swelling of eyelids, face, tongue, lips, throat, or hands; rash or itching, especially all over the body. These could be signs of a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.
- if you start breathing more slowly or weakly than usual (respiratory depression).
- if you experience a feeling of fainting, as this may be a sign of low blood pressure.
Also, inform your doctor immediately if you experience adverse effects such as:
- severe fatigue, loss of appetite, or if the skin or eyes appear yellow. These may be symptoms of liver damage.
Other adverse effects:
Very common adverse effects (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- insomnia (difficulty sleeping)
- headache
- nausea (feeling of dizziness)
- sweating, withdrawal syndrome, pain
Common adverse effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- infection, flu, sore throat, and difficulty swallowing, nasal discharge
- inflamed glands (lymph nodes)
- hypersensitivity
- decreased appetite
- anxiety, agitation, depression, hostility, nervousness, abnormal thoughts, paranoia
- drowsiness, dizziness, migraines, burning or tingling in hands and feet, fainting, tremors, increased muscle tension, speech disorders
- tearful eyes, abnormal increase or decrease in pupil size (the dark part of the eye)
- palpitations
- low blood pressure
- cough, shortness of breath, yawning, asthma, bronchitis
- constipation, vomiting (nausea), stomach pain, flatulence (gas), indigestion, dry mouth, diarrhea
- rash, itching, hives
- joint pain, back pain, muscle pain, muscle spasms, neck pain, bone pain
- painful menstruation
- reactions at the injection site, e.g., pain, itching, redness of the skin, swelling, and hardening of the skin, swelling of the ankles, feet, or fingers, weakness, general malaise, fever, chills, neonatal withdrawal syndrome, chest pain
- abnormal liver test results
Uncommon adverse effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- skin infection at the injection site
- feeling of dizziness or vertigo
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from available data):
- hallucinations, feeling of happiness and excitement (euphoria)
- abnormal redness of the skin
- pain or difficulty urinating
- reactions at the injection site, such as open sores, inflamed areas with accumulated pus, and cell or tissue death at the injection site.
Reporting Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, even if it is a possible adverse effect that does not appear in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Buvidal
Buvidal should only be administered by healthcare professionals. Patients are not allowed to take the product home or self-administer it.
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the carton or the label on the syringe after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Do not use this medicine if you notice that it contains visible particles or is cloudy.
Buvidal is for single use only. All used syringes must be discarded.
Medicines should not be thrown away via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Buvidal
- The active ingredient is buprenorphine
- The other components are soy phosphatidylcholine, glycerol dioleate, anhydrous ethanol (see section 2 Buvidal contains alcohol) (only in the weekly formulation) and N-methylpyrrolidone (only in the monthly formulation).
The following syringes are available:
Weekly injection:
8 mg: Pre-filled syringe with 8 mg of buprenorphine in 0.16 ml of solution
16 mg: Pre-filled syringe with 16 mg of buprenorphine in 0.32 ml of solution
24 mg: Pre-filled syringe with 24 mg of buprenorphine in 0.48 ml of solution
32 mg: Pre-filled syringe with 32 mg of buprenorphine in 0.64 ml of solution
Monthly injection:
64 mg: Pre-filled syringe with 64 mg of buprenorphine in 0.18 ml of solution
96 mg: Pre-filled syringe with 96 mg of buprenorphine in 0.27 ml of solution
128 mg: Pre-filled syringe with 128 mg of buprenorphine in 0.36 ml of solution
160 mg: Pre-filled syringe with 160 mg of buprenorphine in 0.45 ml of solution
Appearance of Buvidal and Package Contents
Buvidal is a prolonged-release injectable solution. Each pre-filled syringe contains a clear yellowish liquid.
The following package sizes are available:
Pre-filled syringes containing 8 mg, 16 mg, 24 mg, 32 mg, 64 mg, 96 mg, 128 mg, and 160 mg of injectable solution.
Each package contains 1 pre-filled syringe with a plug, needle, needle protector, safety device, and 1 plunger rod.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Camurus AB
Rydbergs torg 4
SE-224 84 Lund
Sweden
Manufacturer
Rechon Life Science AB
Soldattorpsvägen 5
216 13
Limhamn
Sweden
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: 07/03/2025.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu.
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Instructions for Use for Healthcare Professionals
Contents:
- Important Information
- Safety Syringe Parts
- Administration
- Disposal of the Syringe
- Important Information
- The administration should be done in subcutaneous tissue. ONLY.
- Do not use if the safety syringe is broken or the package is damaged.
- The needle protector of the safety syringe may contain latex rubber that can cause allergic reactions in people with latex sensitivity.
- Handle the safety syringe with care to avoid needle sticks. The safety syringe includes a needle protection safety device that will be activated at the end of the injection. The needle protector will help prevent needle stick injuries.
- Do not remove the safety protector from the syringe until you are ready to inject.
- Once removed, never attempt to put the needle protector back on.
- Discard the used safety syringe immediately after use. Do not reuse the safety syringe.
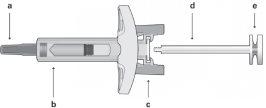
- Safety Syringe PartsBefore Administration
|
| |
Figure 1 | Safety Syringe: Before Use
| Safety Syringe: After Use (With the needle protection mechanism activated) |
Note that the smaller injection volume is barely visible in the viewing window, as the safety device spring is "covering" a part of the glass cylinder near the needle.
- DO NOT TOUCH THE SYRINGE PROTECTOR WINGS UNTIL YOU ARE READY TO INJECT. TOUCHING THEM MAY ACTIVATE THE SYRINGE PROTECTOR TOO EARLY.
- DO NOT USE THE PRODUCT IF IT HAS FALLEN ON A HARD SURFACE OR IS DAMAGED. USE A NEW PRODUCT FOR THE INJECTION.
- Administration
- Remove the syringe from the carton: hold the syringe by the protector body.
- Holding the syringe firmly by the inspection window, insert the plunger rod into the plunger stop by gently turning the plunger rod clockwise until it is secured (see Figure 2).
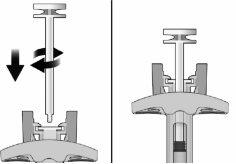
Figure 2 | Before | After |
- Inspect the safety syringe carefully:
- Do not use the safety syringe after the expiration date that appears on the carton or the label on the syringe.
- A small air bubble may be visible, which is normal.
- The liquid should be clear. Do not use the safety syringe if the liquid contains particles or is cloudy.
- Choose the injection site. The injection site should be rotated between buttocks, thighs, abdomen, or arms (see Figure 3), waiting at least 8 weeks before re-injecting at a previously used site. Injections in the waist or less than 5 cm from the navel should be avoided.
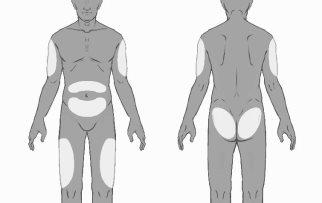
Figure 3
- Put on gloves and clean the injection site with circular movements using a swab with alcohol (not included in the package). Do not touch the cleaned area again before injection.
- Holding the safety syringe by the syringe protector body, as shown (see Figure 4), carefully pull the needle protector straight out. Discard the needle protector immediately (do not attempt to put the needle protector back on). There may be a drop of liquid on the tip of the needle. This is normal.
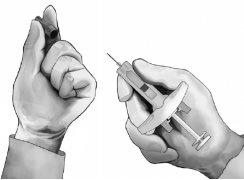
Figure 4
- Pinch the skin at the injection site between the thumb and index finger, as shown (see Figure 5).
- Holding the safety syringe as shown, insert the needle at a 90-degree angle, approximately (see Figure 5). Push the needle until it is fully inserted.
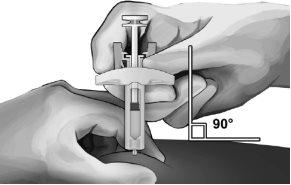
Figure 5
- Holding the syringe as shown (see Figure 6), slowly press the plunger until the head clicks between the syringe protector wings and the entire solution has been injected.

Figure 6
- Gently withdraw the needle from the skin. It is recommended to keep the plunger fully pressed while carefully withdrawing the needle from the injection site (see Figure 7).
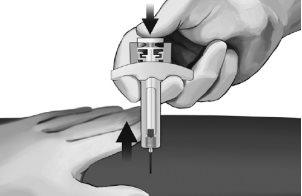
Figure 7
- As soon as the needle is withdrawn from the skin, slowly remove your thumb from the plunger and let the syringe protector automatically cover the exposed needle (see Figure 8). There may be a small amount of blood at the injection site; if necessary, clean with a cotton ball or swab.
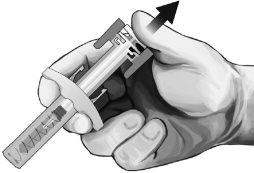
Figure 8
- Disposal of the Syringe
- The disposal of unused medicine and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to BUVIDAL 160 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 128 mg/0.36 mlActive substance: buprenorphineManufacturer: Camurus AbPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50 mg/mLActive substance: buprenorphineManufacturer: Camurus AbPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50 mg/mLActive substance: buprenorphineManufacturer: Camurus AbPrescription required
Online doctors for BUVIDAL 160 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about BUVIDAL 160 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions