
BONDRONAT 6 mg CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION

Ask a doctor about a prescription for BONDRONAT 6 mg CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION

How to use BONDRONAT 6 mg CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Bondronat 6 mg Concentrate for Solution for Infusion
ibandronic acid
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4
Contents of the pack:
- What is Bondronat and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you are given Bondronat
- How Bondronat is given
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Bondronat
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Bondronat and what is it used for
Bondronat contains the active substance ibandronic acid. This belongs to a group of medicines called bisphosphonates.
Bondronat is used in adults and you have been prescribed Bondronat if you have breast cancer that has spread to the bones (called ‘bone metastases’)
- It helps to prevent your bones from breaking (fractures)
- It helps to prevent other bone problems that may need surgery or radiotherapy
You may also be given Bondronat if you have a high level of calcium in your blood due to a tumor.
Bondronat works by reducing the amount of calcium that is lost from your bones. This helps to prevent your bones from becoming weaker.
2. What you need to know before you are given Bondronat
Do not receive Bondronat:
- if you are allergic to ibandronic acid or any of the other ingredients of this medicine listed in section 6
- if you have or have had low levels of calcium in your blood
Do not receive this medicine if any of the above applies to you. If you are not sure, consult your doctor or pharmacist before receiving Bondronat.
Warnings and precautions
A very rare side effect called osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) (bone damage in the jaw) has been reported in patients treated with Bondronat for cancer-related disorders. ONJ can also occur after stopping treatment.
It is important to try to prevent the development of ONJ as it is a painful condition that can be difficult to treat. To reduce the risk of developing osteonecrosis of the jaw, certain precautions should be taken.
Before you receive treatment, tell your doctor/nurse (healthcare professional) if:
- you have dental problems or are planning to undergo dental surgery
- you do not receive regular dental check-ups or have not had a dental check-up for a long time
- you are a smoker (as this can increase the risk of dental problems)
- you have been previously treated with a bisphosphonate (used to treat or prevent bone disorders)
- you are taking medicines called corticosteroids (such as prednisolone or dexamethasone)
- you have cancer
Your doctor may ask you to have a dental check-up before starting treatment with Bondronat.
While you are being treated, you should maintain good oral hygiene (including regular tooth brushing) and have regular dental check-ups. If you wear dentures, you should ensure they fit properly. If you are undergoing dental treatment or are going to have dental surgery (e.g. tooth extraction), inform your doctor about your dental treatment and inform your dentist that you are being treated with Bondronat.
Contact your doctor and dentist immediately if you experience any problems with your mouth or teeth, such as tooth loss, pain, or swelling, or difficulty healing of ulcers or discharge, as these can be signs of osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before taking Bondronat:
- if you are allergic to any other bisphosphonate
- if you have high or low levels of vitamin D, calcium, or any other mineral
- if you have kidney problems
- if you have heart problems and your doctor has recommended that you limit your daily fluid intake
Severe, sometimes fatal allergic reactions have been reported in patients treated with intravenous ibandronic acid.
You should immediately inform your doctor or nurse if you experience any of the following symptoms, such as shortness of breath/difficulty breathing, feeling of throat tightness, swelling of the tongue, dizziness, feeling of loss of consciousness, redness or swelling of the face, body rash, nausea, and vomiting (see section 4).
Children and adolescents
Bondronat should not be used in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Using Bondronat with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using or have recently used or might use any other medicines. This is because Bondronat may affect the way other medicines work. Also, other medicines may affect the way Bondronat works.
In particular, tell your doctor or pharmacistif you are receiving a type of injected antibiotic called ‘aminoglycoside’ such as gentamicin. This is because both aminoglycosides and Bondronat can lower the level of calcium in your blood.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Do not receive Bondronat if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or if you are breastfeeding.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
You can drive and use machines as Bondronat is not expected to have a significant effect on your ability to drive and use machines. Consult your doctor first if you want to drive, use machines, or tools.
Bondronat contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per vial, i.e. it is essentially ‘sodium-free’
3. How Bondronat is given
Administration of this medicine
- Bondronat is usually given by a doctor or other healthcare professional with experience in the treatment of cancer.
- It is given by infusion into a vein
Your doctor may perform regular blood tests while you are receiving Bondronat. This is to check that you are receiving the correct amount of this medicine.
Dose that you will receive
Your doctor will decide the dose of Bondronat that you will be given, depending on your illness. If you have breast cancer that has spread to the bones, the recommended dose is 3 vials (6 mg) every 3-4 weeks, given by infusion into a vein over at least 15 minutes.
If you have a high level of calcium in your blood due to a tumor, the recommended dose is a single dose of 2 mg or 4 mg, depending on the severity of your illness. The medicine should be given by infusion into a vein over 2 hours. A further dose may be considered if you do not respond or if your illness returns.
If you have kidney problems, your doctor will adjust the dose and duration of the infusion.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Tell your doctor or nurse immediately if you notice any of the following serious side effects, as you may need urgent medical treatment:
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- persistent eye pain and inflammation
- new pain, weakness, or discomfort in the thigh, hip, or groin. These can be early symptoms of a possible unusual fracture of the thigh bone
Very rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
pain or sensation of pain in the mouth or jaw. These can be early symptoms of serious jaw problems [necrosis (death of bone tissue) of the jawbone]
- Tell your doctor if you have ear pain, discharge from the ear, or an ear infection. These could be symptoms of damage to the bones of the ear.
- itching, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat, with difficulty breathing. You may be having a severe allergic reaction to the medicine (see section 2)
- severe skin reactions
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from the available data)
- asthma attack
Other possible side effects
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- flu-like symptoms, including fever, chills, and shaking, feeling unwell, fatigue, bone, muscle, and joint pain. These symptoms usually disappear within a couple of hours or days.
Talk to your nurse or doctor if any effect becomes troublesome or lasts more than a couple of days
- increased body temperature
- stomach and abdominal pain, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (intestinal losses)
- decrease in calcium or phosphorus levels in the blood
- changes in blood test results such as Gamma GT or creatinine
- a heart rhythm problem called ‘bundle branch block’
- muscle or bone pain
- headache, feeling dizzy or weak
- thirst, sore throat, changes in taste
- swelling of the legs or feet
- pain in the joints, arthritis, or other joint problems
- problems with the parathyroid gland
- bruising
- infections
- a problem in your eyes called ‘cataracts’
- skin changes
- dental changes
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- shaking or shivering
- excessive decrease in body temperature (‘hypothermia’)
- a condition that affects the blood vessels in the brain called “cerebrovascular disorder” (stroke or cerebral hemorrhage)
- cardiovascular changes (including palpitations, heart attack, hypertension, varicose veins)
- changes in blood cells (‘anemia’)
- increase in alkaline phosphatase level in the blood
- fluid accumulation and swelling (‘lymphedema’)
- fluid in the lungs
- stomach problems such as ‘gastroenteritis’ or ‘gastritis’
- gallstones
- inability to urinate (urine), cystitis (inflammation of the bladder)
- migraine
- nerve pain, nerve root injury
- deafness
- increased sensitivity to stimuli of sound, taste, touch, or changes in smell
- difficulty swallowing
- mouth ulcers, swollen lips (‘cheilitis’), mouth sores
- itching or tingling around the mouth
- pain in the pelvis, discharge, itching, or pain in the vagina
- skin growth called ‘benign skin neoplasia’
- memory loss
- sleep changes, anxiety, mood changes, or emotional instability
- skin rash
- hair loss
- pain or injury at the injection site
- weight loss
- kidney cyst (fluid-filled sac in the kidney)
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly via the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Bondronat
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and label after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month shown
- After dilution, the infusion solution is stable for 24 hours between 2°C and 8°C (in a refrigerator)
- Do not use this medicine if you notice that the solution is not clear or contains particles
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Bondronat Composition
- The active ingredient is ibandronic acid. A vial with 6 ml of concentrate for solution for infusion contains 6 mg of ibandronic acid (as sodium monohydrate)
- The other components are: sodium chloride, acetic acid, sodium acetate, water for injectable preparations.
Product Appearance and Container Contents
Bondronat is a colorless and transparent solution. Bondronat is presented in containers containing 1, 5, and 10 vials (6 ml type I glass vial with a bromobutyl rubber stopper). Not all containers may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
Atnahs Pharma Netherlands B.V.
Strawinskylaan 3127
1077 ZX Amsterdam
Netherlands
Manufacturer
Waymade PLC
Sovereign House,
Miles Gray Road,
Basildon, Essex,
SS14 3FR
United Kingdom
Waymade PLC
Josselin Road
Burnt Mills Industrial Estate
Basildon,
SS13 1QF
United Kingdom
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: MM/YYYY
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency website http://www.ema.europa.eu.
___________________________________________________________________________
The following information is intended only for healthcare professionals
Dosage: Prevention of Bone Events in Patients with Breast Cancer and
Bone Metastases
The recommended dose for the prevention of bone events in patients with breast cancer and bone metastases is 6 mg by intravenous route every 3-4 weeks. The dose should be infused over at least 15 minutes.
Patients with renal impairment.
No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild renal impairment (CLcr = 50 and <80 ml min).< p>
Patients with moderate renal impairment (CLcr = 30 and <50 ml min) or severe renal impairment (clcr < 30 min), who also have breast cancer and bone metastatic disease are being treated for the prevention of events, should follow following dosage recommendations:< p>
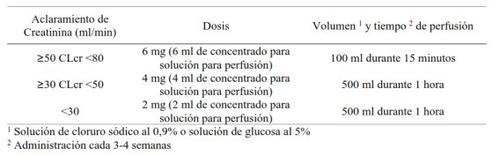
A perfusion time of 15 minutes has not been studied in patients with cancer with a CLcr <50 ml min.< p>
Dosage: Treatment of Tumor-Induced Hypercalcemia
Bondronat is administered in a hospital setting. The dose will be determined by the doctor, taking into account the following factors:
Before treatment with Bondronat, the patient should be adequately rehydrated with 9 mg/ml of sodium chloride (at 0.9%). Both the severity of hypercalcemia and the type of tumor should be taken into account. In most patients with severe hypercalcemia (albumin-corrected serum calcium ≥ 3 mmol/l or ≥ 12 mg/dl), 4 mg is an adequate single dose. In patients with moderate hypercalcemia (albumin-corrected serum calcium <3 mmol l or < 12 mg dl), 2 is an effective dose. the maximum dose used in clinical trials was 6 mg, but this does not provide any additional benefit terms of efficacy.< p>
- Note: albumin-corrected serum calcium concentrations are calculated as follows:
Albumin-corrected serum calcium (mmol/l) Albumin-corrected serum calcium (mg/dl) | = serum calcium (mmol/l) - [0.02 x albumin (g/l)] + 0.8 Or = serum calcium (mg/dl) + 0.8 x [4 - albumin (g/dl)] |
To convert the albumin-corrected serum calcium value from mmol/l to mg/dl, multiply by 4.
In most cases, an elevated serum calcium level can be reduced to normal levels within 7 days. The median time to relapse (new increase above 3 mmol/l of albumin-corrected serum calcium) was 18-19 days for the 2 mg and 4 mg doses. The median time to relapse was 26 days with the 6 mg dose.
Method and Route of Administration
Bondronat concentrate for solution for infusion should be administered as an intravenous infusion.
To do this, the contents of the vial should be used as follows:
- Prevention of bone events in patients with breast cancer and bone metastases - add to 100 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution or 100 ml of 5% dextrose solution and infuse over at least 15 minutes. See the dosage section above for patients with renal impairment.
- Treatment of tumor-induced hypercalcemia - add to 500 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution or 500 ml of 5% dextrose solution and infuse over 2 hours.
Note:
To avoid possible incompatibilities, Bondronat concentrate for solution for infusion should only be mixed with isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose solution. It should not be mixed with solutions containing calcium.
The diluted solutions are for single use. Only clear and particle-free solutions should be administered.
It is recommended that the product be used immediately once it has been diluted (see point 5 of this leaflet: Conservation of Bondronat.
Bondronat concentrate for solution for infusion should be administered by intravenous infusion. Care should be taken not to administer Bondronat concentrate for solution for infusion by intra-arterial or venous extravasation, as it could cause tissue damage.
Frequency of Administration
For the treatment of tumor-induced hypercalcemia, Bondronat concentrate for solution for infusion is generally administered as a single infusion.
For the prevention of bone events in patients with breast cancer and bone metastases, the infusion of Bondronat is repeated at intervals of 3-4 weeks.
Duration of Treatment
A limited number of patients (50 patients) received a second infusion for hypercalcemia. In case of recurrent hypercalcemia or insufficient efficacy, the possibility of repeating the treatment may be considered.
For patients with breast cancer and bone metastases, Bondronat infusions should be administered every 3-4 weeks. In clinical trials, treatment was maintained for up to 96 weeks.
Overdose:
So far, there is no experience with acute intoxication with Bondronat concentrate for solution for infusion. Considering that in preclinical studies at high doses, it was observed that both the kidney and liver are target organs in terms of toxicity, renal and hepatic function should be monitored.
A clinically relevant hypocalcemia (very low serum calcium levels) should be corrected by intravenous administration of calcium gluconate.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to BONDRONAT 6 mg CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTIONDosage form: TABLET, 150 mgActive substance: ibandronic acidManufacturer: Especialidades Farmaceuticas Centrum S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 2 mgActive substance: ibandronic acidManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 6 mgActive substance: ibandronic acidManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription required
Alternatives to BONDRONAT 6 mg CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to BONDRONAT 6 mg CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION in Poland
Alternative to BONDRONAT 6 mg CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION in Ukraine
Online doctors for BONDRONAT 6 mg CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for BONDRONAT 6 mg CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION – subject to medical assessment and local rules.











