ASPAVELI 1080 MG SOLUTION FOR INFUSION

How to use ASPAVELI 1080 MG SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
ASPAVELI 1 080 mg solution for infusion
pegcetacoplan
This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring, which will allow for quicker identification of new safety information. You can help by reporting any side effects you may get. The last section of the leaflet includes information on how to report side effects.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is ASPAVELI and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use ASPAVELI
- How to use ASPAVELI
- Possible side effects
- Storage of ASPAVELI
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is ASPAVELI and what is it used for
What is ASPAVELI
ASPAVELI is a medicine that contains the active substance pegcetacoplan. Pegcetacoplan has been designed to bind to complement protein C3, which is part of the body's defense system known as the "complement system". Pegcetacoplan prevents the immune system from destroying red blood cells.
What ASPAVELI is used for
ASPAVELI is used to treat adult patients with a disease called paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) who have anemia as a result of this disease.
In patients with PNH, the "complement system" is overactive and attacks their red blood cells, which can cause low blood counts (anemia), fatigue, difficulty functioning, pain, abdominal pain, dark urine, shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, erectile dysfunction, and blood clots. By binding to complement protein C3 and blocking it, this medicine can prevent the complement system from attacking red blood cells, thereby controlling the symptoms of the disease. It has been shown that this medicine increases the number of red blood cells (reduces anemia), which can improve these symptoms.
2. What you need to know before you use ASPAVELI
Do not use ASPAVELI
- if you are allergic to pegcetacoplan or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have an infection caused by so-called encapsulated bacteria.
- if you are not vaccinated against Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting treatment with ASPAVELI.
Symptoms of infection
Before starting treatment with ASPAVELI, inform your doctor if you have any infection.
Since the medicine targets the complement system, which is part of the body's defenses against infections, the use of this medicine increases the risk of developing infections, including those caused by encapsulated bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae. These are serious infections that affect the nose, throat, and lungs or the tissue covering the brain and can spread throughout the blood and body.
Consult your doctor before starting treatment with ASPAVELI to ensure you receive vaccinations against Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzaeif you have not received them before. If you have already received these vaccinations in the past, you may still need additional vaccinations before starting treatment with this medicine. These vaccinations should be given at least 2 weeks before starting treatment. If you cannot be vaccinated 2 weeks in advance, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection for 2 weeks after vaccination. After vaccination, your doctor may monitor you more closely to detect symptoms of infection.
Symptoms of infection
If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should inform your doctor immediately:
- headache and fever
- fever and rash
- fever with or without chills or shivering
- shortness of breath
- rapid heartbeat
- sweaty skin
- headache with stiff neck or back
- headache with nausea (feeling sick) or vomiting
- eyes sensitive to light
- muscle pain with flu-like symptoms
- confusion
- severe pain or discomfort
Make sure you are up to date with your vaccinations. You should also be aware that vaccinations reduce the risk of developing serious infections, but do not prevent all serious infections. In accordance with national recommendations, your doctor may consider that you need additional measures, such as antibacterial medications, to prevent infections.
Allergic reactions
In some patients, allergic reactions may occur. In the event of a severe allergic reaction, discontinue the ASPAVELI infusion and seek immediate medical attention. A severe allergic reaction may manifest as difficulty breathing, chest pain or tightness, and/or a feeling of dizziness or fainting, intense skin itching or hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and/or throat, which can cause difficulty swallowing or fainting.
Reactions at the injection site
Reactions at the injection site have been observed with the use of ASPAVELI. Before self-administration, you should receive proper training on the correct injection technique.
Laboratory tests
During treatment with ASPAVELI, your doctor will perform regular checks, including blood tests for lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels and kidney function tests, and may adjust the dose if necessary.
Effects on laboratory tests
The use of silica reagents in coagulation tests should be avoided, as it may cause artificial prolongation of the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT).
Children and adolescents
Do not give this medicine to children under 18 years of age, as there is no data available on its safety and efficacy in this age group.
Other medicines and ASPAVELI
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Women of childbearing age
The effects of the medicine on the fetus are not known. Effective contraceptive methods should be used during treatment and for up to 8 weeks after treatment in women who can become pregnant. Consult your doctor before using this medicine.
Pregnancy/breastfeeding
ASPAVELI should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, consult your doctor before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
The medicine has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
ASPAVELI contains sorbitol
Sorbitol is a source of fructose. If your doctor has told you that you have an intolerance to some sugars, or you have been diagnosed with hereditary fructose intolerance (HFI), a rare genetic disorder in which the patient cannot break down fructose, consult your doctor before taking this medicine.
ASPAVELI contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per dose, which is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use ASPAVELI
Follow your doctor's administration instructions for this medication exactly. If in doubt, consult your doctor again.
At least 2 weeks before starting treatment with this medication, your doctor will review your medical history and may administer one or more vaccines to you. If you cannot be vaccinated at least 2 weeks before starting treatment with ASPAVELI, to reduce the risk of infection, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics for 2 weeks after vaccination.
Dose
The recommended initial dose for adults with PNH is 1080 mg twice a week. You should take the dose twice a week, on Day 1 and Day 4 of each treatment week.
If you are replacing another type of PNH medication, called a C5 inhibitor, with ASPAVELI, you should take ASPAVELI in addition to your current dose of the C5 inhibitor as prescribed for 4 weeks. After 4 weeks, you should stop taking the C5 inhibitor.
The dose or dosing interval should not be modified without consulting your doctor. Your doctor may adjust your dose to 1080 mg every three days (e.g., Day 1, Day 4, Day 7, Day 10, Day 13, and so on) if necessary. If you think you have missed a dose, speak with your doctor as soon as possible.
Form and route of administration
ASPAVELI is intended to be administered subcutaneously by infusion using an infusion pump. The first doses of the medication will be administered by a healthcare professional in a clinic or treatment center. If the treatment works well, your doctor may discuss the possibility of administering the medication at home. If this is appropriate, a healthcare professional will teach you or a caregiver how to administer the infusion.
Infusion rate(s)
The usual infusion time is about 30 minutes if two infusion sites are used or about 60 minutes if one site is used. The infusion should be started without delay (and completed within 2 hours of preparing the syringe) after loading this medication into the syringe.
Instructions for use
Step 1 | Prepare for infusion Before starting:
C1 Transfer needle OR C2 Needle-free transfer device to extract the product from the vial
|
|
Thoroughly clean the work surface with an alcohol wipe. | ||
Wash your hands well with soap and water. Dry your hands. | ||
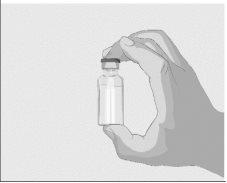
Step 2 | Check the vial and liquid Remove the vial from the box. Carefully examine the liquid in the vial. ASPAVELI is a clear, colorless to slightly yellowish liquid. Check for particles or color changes (Figure 2). Do not use the vial if:
| Figure 2
|
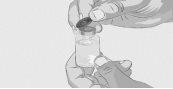
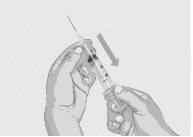
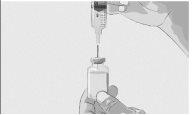
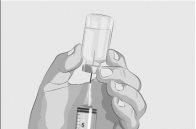
Step 3 | Prepare and fill the syringe Remove the protective cap from the vial to expose the central part of the gray rubber stopper (Figure 3). Discard the protective cap. Clean the stopper with a new alcohol wipe and let it dry. Option 1: If using a needle-free transfer device (such as a vial adapter), follow the manufacturer's instructions for the device. OR Option 2: If transferring with a transfer needle and syringe, follow these instructions:
| Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 7
|
Step 4 | Prepare the syringe infusion pump system and tubes Gather the pump components and follow the manufacturer's instructions for the device to prepare the pump and tubes. | |
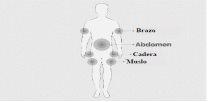
Step 5 | Prepare the infusion site(s)
| Figure 8
Figure 9
Figure 10
|
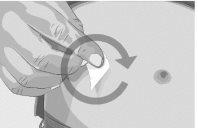
Step 6 | Insert and secure the infusion needle(s)
| Figure 11
Figure 12
|
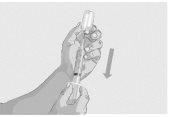
Step 7 | Start the infusion Follow the manufacturer's instructions for the device to start the infusion. Start the infusion without delay after drawing the solution into the syringe. | |
Step 8 | Complete the infusion Follow the manufacturer's instructions for the device to complete the infusion. | |
Step 9 | Record the infusion Record your treatment as instructed by your healthcare professional. | |
Step 10 | Dispose
| Figure 13
|
If you missed using ASPAVELI
If you miss a dose, you should receive it as soon as possible; then receive the next dose at the scheduled time.
If you interrupt treatment with ASPAVELI
PNH is a lifelong disease, so it is expected that you will use this medication for a long time. If you want to stop using the medication, consult your doctor first. If you interrupt treatment suddenly, you may be at risk of worsening symptoms.
If your doctor decides to interrupt treatment with this medication, follow their instructions on how to interrupt it. Your doctor will closely monitor you for at least 8 weeks after interrupting treatment to detect any signs of red blood cell destruction (hemolysis) due to PNH. Symptoms or problems that may occur due to red blood cell destruction include:
- fatigue
- shortness of breath
- blood in the urine
- abdominal pain
- decreased red blood cell count
- blood clots (thrombosis)
- difficulty swallowing
- erectile dysfunction in men
Contact your doctor if you experience any of these signs and symptoms.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone may experience them.
Your doctor will discuss the possible side effects and explain the risks and benefits of ASPAVELI before treatment.
The most serious side effect is a severe infection.
If you experience any symptoms of infection (see section 2 "Symptoms of infection"), you should inform your doctor immediately.
In case of doubt about the following side effects, ask your doctor to explain them.
Very common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Injection site reactions: these include redness (erythema), swelling, itching (pruritus), bruising, and pain. These reactions usually resolve within a few days
- Nasal, throat, or respiratory tract infection (upper respiratory tract infection)
- Diarrhea
- Red blood cell destruction (hemolysis)
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Fever or elevated temperature (pyrexia)
- Cough
- Urinary tract infection
- Complications related to mandatory vaccinations
- Pain in the arms and legs (pain in the extremities)
- Dizziness
- Joint pain (arthralgia)
- Back pain
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Injection site reaction, such as redness or skin hardening
- Ear, mouth, or skin infection
- Sore throat
- Low platelet count in the blood (thrombocytopenia), which can make you bleed or bruise more easily than normal
- Nausea (vomiting)
- Low potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia)
- Nosebleeds (epistaxis)
- Redness of the skin (erythema)
- Muscle pain (myalgia)
- Gastrointestinal infection, which can cause mild to severe symptoms of nausea, vomiting, cramps, diarrhea (gastrointestinal infection)
- Elevated liver tests
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
- Low white blood cell count (neutropenia)
- Kidney function impairment
- Discolored urine
- High blood pressure
- Muscle spasms
- Stuffy nose (nasal congestion)
- Rash
- Blood infection (sepsis)
- Viral infection
- Fungal infection
- Respiratory tract infection
- Eye infection
- COVID-19
- Bacterial infection
- Vaginal infection
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Cervical inflammation
- Groin infection
- Nasal abscess
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- Esophageal yeast infection
- Anal abscess
- Hives
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of ASPAVELI
- Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medication after the expiration date stated on the box after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
- Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C).
- Keep the vial in the original box to protect it from light.
- Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medication. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and additional information
Composition of ASPAVELI
The active ingredient is pegcetacoplan 1080 mg (54 mg/ml in a 20 ml vial).
The other ingredients are sorbitol (E 420) (see section 2 "ASPAVELI contains sorbitol"), glacial acetic acid, sodium acetate trihydrate (see section 2 "ASPAVELI contains sodium"), sodium hydroxide (see section 2 "ASPAVELI contains sodium"), and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the product and package contents
ASPAVELI is a clear, colorless to slightly yellowish solution for subcutaneous infusion (54 mg/ml in each 20 ml vial). Turbid or particulate solutions or those with color changes should not be used.
Package sizes
ASPAVELI is available in a pack of 1 vial or a multipack of 1 x 8 vials.
Note that the package does not contain alcohol swabs, needles, or other supplies or equipment.
Not all package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB (publ)
SE-112 76 Stockholm
Sweden
Manufacturer
Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB (publ)
Norra Stationsgatan 93
113 64 Stockholm
Sweden
Date of last revision of this leaflet: 05/2024.
Other sources of information
Detailed information on this medication is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu. There are also links to other websites on rare diseases and orphan medicines.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ASPAVELI 1080 MG SOLUTION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE INFUSION, 300 mgActive substance: eculizumabManufacturer: Amgen Technology (Ireland) Unlimited CompanyPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 300 mgActive substance: eculizumabManufacturer: Samsung Bioepis Nl B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 200 mgActive substance: iptacopanManufacturer: Novartis Europharm LimitedPrescription required
Online doctors for ASPAVELI 1080 MG SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about ASPAVELI 1080 MG SOLUTION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions