
AMINOPLASMAL PAED 10% SOLUTION FOR INFUSION

How to use AMINOPLASMAL PAED 10% SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Aminoplasmal Paed 10% Solution for Infusion
For use in children (0-11 years)
Amino Acids
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child starts using this medicine, because it contains important information for them.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child only. Do not give it to others, even if they have the same symptoms as your child, as it may harm them.
- If your child experiences any side effects, consult your doctor or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What Aminoplasmal Paed 10% is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before your child starts using Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
- How to use Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What Aminoplasmal Paed 10% is and what it is used for
Aminoplasmal Paed 10% is a solution that is given to your child through a small tube with a cannula placed in a vein (intravenous infusion).
The solution contains amino acids, which are essential for growth and recovery of the body.
The solution is adapted to meet the specific needs of newborns, premature and full-term infants, and children.
Your child will receive this medicine if they cannot eat normally and cannot be fed through a tube placed in the stomach. They may also receive other nutrients such as glucose solutions or fat emulsions in combination with Aminoplasmal Paed 10%.
2. What you need to know before your child starts using Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
Do not use Aminoplasmal Paed 10% if your child
- is allergic to the active substances or to any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- has a congenital error of amino acid and/or protein metabolism
- has a severe circulatory disorder (i.e., potentially life-threatening (circulatory shock) has insufficient oxygen supply (hypoxia)
- has acidic substances accumulating in the blood (metabolic acidosis)
- has severe liver disease (severe liver failure);
- has severe kidney disease (severe kidney failure) that is not adequately treated with a hemodialysis machine or similar treatments;
- has severe heart failure with significant impairment of blood circulation (decompensated heart failure);
- has fluid accumulation in the lungs (acute pulmonary edema)
Warnings and precautions
When used in children from premature birth to 2 years, the solution (in the bags and administration equipment) should be protected from light exposure until the end of administration. Exposure of parenteral nutrition solutions containing Aminoplasmal Paed 10% to ambient light, especially after mixing with trace elements or vitamins, generates peroxides and other degradation products that can be reduced by protecting the product from light exposure.
Consult your doctor or nurse before using Aminoplasmal Paed 10% if your child
- has a protein and amino acid metabolism disorder caused by a disease other than those mentioned above (see section "Do not use Aminoplasmal Paed 10% if your child...");
- has impaired liver or kidney function;
- has impaired heart function;
- has abnormally high blood serum concentration (elevated serum osmolality)
If your child's water or salt balance is disturbed, this disorder must be corrected before the child receives this medicine. Some examples of this disorder are simultaneous lack of water and salt (hypotonic dehydration) or lack of sodium (hyponatremia) or potassium (hypokalemia).
Both before and while children are receiving this solution, the doctor will check the levels of salts and sugar in the blood, water balance, and acid-base balance. They will also monitor blood proteins and liver and kidney function. To this end, blood and urine samples will be taken for analysis.
Amino acid solutions are only one component of parenteral nutrition. Children will normally receive Aminoplasmal Paed 10% as part of intravenous feeding, which also includes non-protein energy supplements (carbohydrate solutions, fat emulsions), essential fatty acids, electrolytes, vitamins, fluids, and trace elements.
Using Aminoplasmal Paed 10% with other medicines
Tell your doctor or nurse if your child is taking, has recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Aminoplasmal Paed 10% is only intended for use in children (under 12 years of age).
Driving and using machines
Not applicable.
3. How to use Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
Aminoplasmal Paed 10% is administered by healthcare professionals.
In children, the doctor will adjust the dose according to the child's age, developmental stage, and disease.
The amount administered will be approximately:
Preterm newborns: 40 ml per kg of body weight per day
Full-term newborns (0 to 27 days): 30 ml per kg of body weight per day
Infants (28 days to 23 months): 25 ml per kg of body weight per day
Children (2 to 11 years): 20 ml per kg of body weight per day
For children in critical condition, the amount administered may be higher (up to 30 ml per kilogram of body weight per day).
Patients with renal or hepatic disease
The doses will be adjusted according to the individual needs of the child if they have liver or kidney disease.
Duration of treatment
This medicine may be used as long as the child requires intravenous feeding.
Method of administration
This medicine will be administered to your child through a small tube inserted into a vein (intravenous infusion).
When used in children from premature birth to 2 years, the solution (in the bags and administration equipment) should be protected from light exposure until the end of administration (see section 2).
If your child receives more Aminoplasmal Paed 10% than they should
This is unlikely to happen, as the doctor will determine the daily doses for your child.
However, if your child receives an overdose or the infusion rate of the solution is too fast, your child may feel nauseous, vomit, and have chills or headache.
Additionally, the blood may contain too many acidic substances (metabolic acidosis) or too much ammonia (hyperammonemia), and your child may suffer from loss of amino acids in the urine.
Your child may also have too much fluid in their body (hyperhydration), the electrolyte balance of your child's body may be disturbed (electrolyte imbalance), and your child may have fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema). If this happens, the infusion will be stopped and restarted at a lower infusion rate shortly after.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
These side effects are not specifically related to Aminoplasmal Paed 10%, but can occur with any type of intravenous feeding, especially at the start.
The following side effects may be serious. If your child experiences any of the following side effects, tell your doctor immediately, who will stop administering this medicine to your child:
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data)
? Allergic reactions.
Other side effects
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
? Vomiting, nausea.
Reporting of side effects
If your child experiences any side effects, consult your doctor or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) Yellow Card Scheme at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
When used in children from premature birth to 2 years, the solution (in the bags and administration equipment) should be protected from light exposure until the end of administration (see section 2).
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and carton. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
No special storage conditions are required.
Do not freeze.
After infusion, the remaining solution must never be stored for later use.
6. Contents of the pack and further information
Composition of Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
The active substances are amino acids.
This medicine contains:
Amino Acids | per 1ml | per 100ml | per 250ml |
Isoleucine | 5.10 mg | 0.51 g | 1.28 g |
Leucine | 7.60 mg | 0.76 g | 1.90 g |
Lysine monohydrate (equivalent to lysine) | 9.88 mg (8.80 mg) | 0.99 g (0.88 g) | 2.47 g (2.20 g) |
Methionine | 2.00 mg | 0.20 g | 0.50 g |
Phenylalanine | 3.10 mg | 0.31 g | 0.78 g |
Threonine | 5.10 mg | 0.51 g | 1.28 g |
Tryptophan | 4.00 mg | 0.40 g | 1.00 g |
Valine | 6.10 mg | 0.61 g | 1.53 g |
Arginine | 9.10 mg | 0.91 g | 2.28 g |
Histidine | 4.60 mg | 0.46 g | 1.15 g |
Alanine | 15.90 mg | 1.59 g | 3.98 g |
Glycine | 2.00 mg | 0.20 g | 0.50 g |
Aspartic acid | 6.60 mg | 0.66 g | 1.65 g |
Glutamic acid | 9.30 mg | 0.93 g | 2.33 g |
Proline | 6.10 mg | 0.61 g | 1.53 g |
Serine | 2.00 mg | 0.20 g | 0.50 g |
N-acetyltyrosine (equivalent to tyrosine) | 1.30 mg (1.06 mg) | 0.13 g (0.11 g) | 0.33 g (0.27 g) |
Acetylcysteine (equivalent to cysteine) | 0.700 mg (0.520 mg) | 0.070 g (0.052 g) | 0.175 g (0.13 g) |
Taurine | 0.300 mg | 0.030 g | 0.075 g |
per 1ml | per 100ml | per 250ml | |
Total amino acids | 0.1 g | 10 g | 25 g |
Total nitrogen | 0.0152 g | 1.52 g | 3.8 g |
Energy [kJ/l (kcal/l)] | 1,700 (406) |
Theoretical osmolality [mOsm/l] | 790 |
Acidity (titration to pH 7.4) [mmol NaOH/l] | 23 |
pH | approximately 6.1 |
The other components are citric acid monohydrate (for pH adjustment) and water for injections.
Appearance of the product and pack contents
Aminoplasmal Paed 10% is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution.
It is supplied in flexible bags containing 100 ml or 250 ml of amino acid solution. The bags are made of a multilayer sheet. The inner layer in contact with the solution is made of polypropylene.
The packaging does not contain PVC, DEHP, or latex.
The bag is packaged in a protective wrapper. An oxygen absorber and oxygen indicator have been placed between the bag and the wrapper; the oxygen indicator is a thermoformed blister and contains sodium resorufin, an oxygen-sensitive dye; the oxygen absorber packet is made of an inert material and contains iron hydroxide.
The different pack sizes are presented in boxes of 12 bags. Pack sizes: 12 x 100 ml and 12 x 250 ml
Only some pack sizes may be marketed
Marketing authorisation holder and manufacturer
- Braun Melsungen AG
Carl-Braun-Straße 1
34212 Melsungen, Germany
Postal address:
34209 Melsungen, Germany
Phone: +49/5661/71-0
Fax: +49/5661/71-4567
This medicine is authorised in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria Aminoplasmal Paed 10% Infusionslösung
Czech Republic Amiped
Denmark Amiped
Germany Aminoplasmal Paed 10% Infusionslösung
Greece Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
Italy Amiped
Luxembourg Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
Netherlands Aminoplasmal Paed 100mg/ml, oplossing voor infusie
Norway Amiped
Poland Aminoplasmal Paed 10%
Portugal Aminoplasmal Paed 100mg/ml, Solucao para perfusao
Slovak Republic Amiped 10% infuzny roztok
Slovenia Aminoplasmal Paed 100mg/ml, raztopina za infundiranje
Spain Aminoplasmal Paed 10 % solucion para perfusion
United Kingdom Aminoplasmal Paediatric 10% solution for infusion
Date of last revision of this leaflet:January 2020.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Dosage
Method of administration
Intravenous route.
Only for central venous infusion.
When used in children from premature birth to 2 years, the solution (in the bags and administration equipment) should be protected from light exposure until the end of administration. During the preparation of the mixtures, the light protection wrapper may not be suitable. However, attention should be paid to reducing exposure to light during the preparation of the mixtures to a minimum.
Pediatric population
The doses for the indicated groups are average guidance values. The exact dose must be adjusted individually according to the child's age, developmental stage, and predominant disease.
Administration should be started below the target infusion rate and increased to the same during the first hour.
The parenteral amino acid supply considered adequate for most pediatric patients:
Daily dose for preterm newborns:
1.5-4.0 g of amino acids/kg of body weight = 15-40 ml/kg of body weight
Daily dose for full-term newborns (0 to 27 days):
1.5-3.0 g/kg of body weight = 15-30 ml/kg of body weight
Daily dose for infants (28 days to 23 months):
1.0-2.5 g/kg of body weight = 10-25 ml/kg of body weight
Daily dose for children (2 to 11 years):
1.0-2.0 g/kg of body weight = 10-20 ml/kg of body weight
Special warnings and precautions for use:
Exposure of intravenous parenteral nutrition solutions to ambient light, especially after mixing with trace elements and/or vitamins, may have adverse effects on the clinical outcome of newborns due to the generation of peroxides and other degradation products. When used in children from premature birth to 2 years, Aminoplasmal Paed 10% should be protected from ambient light until the end of administration.
Special Precautions for Disposal and Other Handling
Use sterile administration equipment for the administration of Aminoplasmal Paed 10%.
Before opening the protective wrapper, check the color of the oxygen indicator (see Figure A). Do not use if the oxygen indicator has turned pink. Use only if the oxygen indicator is yellow.
If, in the context of total parenteral nutrition, it is necessary to add other nutrients, such as carbohydrates, lipids, vitamins, electrolytes, and trace elements, to this medication, the mixture must be prepared under strict aseptic conditions. Mix well after adding any additive. Aminoplasmal Paed 10% can only be mixed with other nutrients whose compatibility has been documented. The manufacturer can provide, upon request, the compatibility data of different additives and the corresponding validity period of such mixtures.
When used in children from premature birth to 2 years of age, parenteral nutrition solutions containing Aminoplasmal Paed 10% should be protected from light exposure until administration is completed. Exposure of such solutions to ambient light, especially after mixing with trace elements and/or vitamins, generates peroxides and other degradation products that can be reduced by protecting the product from light exposure.
Special Precautions for Storage
The product should not be used if the solution is not transparent, colorless to light yellow, free of particles, or if the bag or its closure is damaged.
The containers are valid for single use. Discard the wrapper, oxygen indicator, oxygen absorber, container, and remaining contents after use.
During Preparation of Mixtures
During the preparation of mixtures, the light-protective wrapper may not be suitable. Nevertheless, attention should be paid to minimizing exposure to light during the preparation of mixtures.
Validity Period After Mixing Additives
From a microbiological point of view, mixtures should be administered immediately after preparation. If not administered immediately, the storage conditions and times of the mixtures before use are the responsibility of the user and should not normally exceed 24 hours at a temperature of 2°C to 8°C, unless the mixture was prepared in controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
To view the complete information for this medication, consult the Technical Data Sheet or Summary of Product Characteristics.
Aminoplasmal Paed 10%: Handling
Figure A:Bag and Wrapper
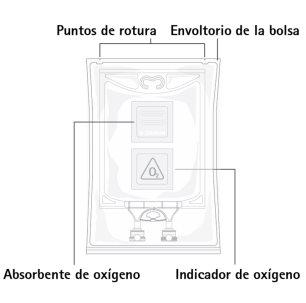
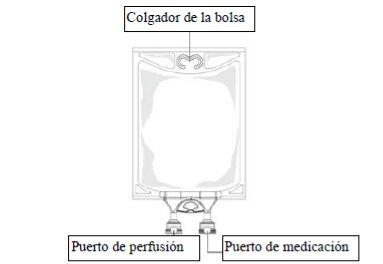
Figure B:Bag
To Open:
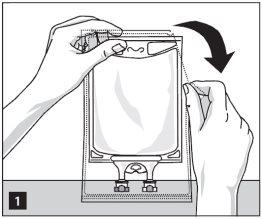
Remove the bag from its protective wrapper from the break points at the top and extract the container of the solution (figure 1). Discard the wrapper, absorber, and oxygen indicator.
Check for leaks. Discard the product if the bag has leaks, as sterility may have been compromised.
To Add Medication:
Mixtures must be prepared following strict aseptic techniques.
Compatible supplementary medications can be added through the medication port (transparent color).
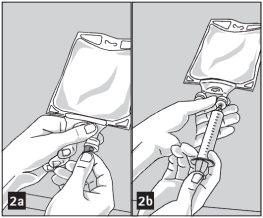
- Prepare the medication port (transparent color) by removing the aluminum foil (figure 2a). Note that the area under the foil of the medication port is sterile.
- Puncture the resealable medication port and inject the additive(s) (figure 2b).
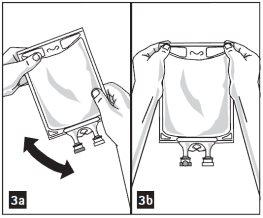
- Mix the solution and medication completely (figure 3a).
- The medication port can be cleaned with a disinfectant (e.g., isopropanol) before being punctured again.
- Visually inspect the mixture for particles (figure 3b).
During Preparation of Mixtures
During the preparation of mixtures, the light-protective wrapper may not be suitable. Nevertheless, attention should be paid to minimizing exposure to light during the preparation of mixtures.
Preparation for Administration:
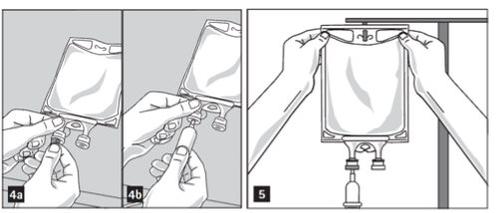
- Remove the aluminum foil from the perfusion port (green color) at the bottom of the container (figure 4a) and connect the administration equipment (figure 4b): use an air-free perfusion set or close the air intake of a set that has one. Follow the instructions for use of the perfusion equipment. Note that the area under the foil of the perfusion port is sterile.
- Hang the bag on an IV pole (figure 5).
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to AMINOPLASMAL PAED 10% SOLUTION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 g/L Total Amino AcidsActive substance: amino acidsManufacturer: B. Braun Melsungen AgPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 g/L Total Amino AcidsActive substance: amino acidsManufacturer: B. Braun Melsungen AgPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 150 g/l total amino acidsActive substance: amino acidsManufacturer: B. Braun Melsungen AgPrescription required
Online doctors for AMINOPLASMAL PAED 10% SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about AMINOPLASMAL PAED 10% SOLUTION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















