
ADENOSINE KABI 3 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE

How to use ADENOSINE KABI 3 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Adenosine Kabi 3 mg/ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
Adenosine
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What Adenosine Kabi is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Adenosine Kabi
- How to use Adenosine Kabi
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Adenosine Kabi
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Adenosine Kabi is and what it is used for
Adenosine Kabi contains a medicine called adenosine which belongs to a group of medicines called anti-arrhythmics.
Adenosine Kabi reduces the electrical impulses between the upper and lower chambers of the heart. This slows down the fast or irregular heartbeats called “arrhythmias”.
Adenosine Kabi is used in adults:
- To make a diagnosis. This medicine helps your doctor find out what kind of arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat) you have.
- To get your heart back to a normal beat if you have a type of arrhythmia called “paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia” or “Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome”
2. What you need to know before you use Adenosine Kabi
Do not use Adenosine Kabi if
- you are allergic to adenosine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). The signs of an allergic reaction include: rash, problems swallowing or breathing, swelling of the lips, face, throat or tongue
- you have problems with your heartbeat and you do not have a pacemaker (second or third degree atrioventricular block, sinus node dysfunction).
- you have very low blood pressure (severe hypotension)
- you have asthma or other severe breathing problems
- you have a type of heart failure where your heart does not pump enough blood
- you have been told you have “long QT syndrome” which is a heart problem that occurs rarely and can cause a fast heartbeat and fainting
- you have unstable angina (a disease where your heart does not get enough blood and oxygen) that is not properly controlled with medical treatment
- you are taking dipyridamole (a medicine used to thin the blood).
Do not use this medicine if any of the above applies to you. If you are not sure, consult your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before you are given Adenosine Kabi.
Warnings and precautions
Tell your doctor or nurse before using Adenosine Kabi if you have:
- low blood volume (hypovolemia) and it is not properly corrected with medicines.
- narrowing of the main artery that supplies blood to the heart (left main coronary artery stenosis)
- you have been told you have a heart problem where the electrical impulses in parts of your heart take longer than normal to discharge and recharge (prolonged QT interval)
- narrowing of the main arteries in the neck (carotid artery). This means that not enough blood gets to the brain (cerebrovascular insufficiency).
- a heart disease caused by narrowing of the heart valves (valvular stenosis).
- a short circuit in the heart. This means that blood passes directly from the left side to the right side of the heart.
- problems with a part of your nervous system called the “autonomic nervous system”.
- Inflammation of the membrane that surrounds your heart (pericarditis) or fluid accumulation around your heart (pericardial effusion).
- you have had severe heart failure
- if you have had a heart attack or if you have had a heart transplant in the last year.
- any minor heart problems (first degree atrioventricular block or bundle branch block). These conditions may get worse temporarily when you are given adenosine.
- a rare heartbeat, for example, your heartbeat is very fast or irregular (atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter) and in particular if you have a condition where your heart has abnormal electrical activity (“accessory conduction pathway”).
- breathing difficulties (bronchospasm).
- you have ever had seizures.
Treatment with adenosine should be stopped if you get a very slow heartbeat (severe bradycardia), breathing problems, a life-threatening heart problem (asystole), severe chest pain (angina) or very low blood pressure (severe hypotension).
If you are not sure if any of the above applies to you, consult your doctor or nurse before you are given Adenosine Kabi.
Using Adenosine Kabi with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription.
This is because adenosine can affect how some medicines work. Also, some of these medicines can change the effect of adenosine.
In particular, tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- Dipyridamole(a medicine used to thin the blood). Tell your doctor that you are taking dipyridamole. Your doctor will decide whether you should take Adenosine Kabi or not, or may tell you to stop taking dipyridamole 24 hours before you are given Adenosine Kabi, or may need to give you a lower dose of Adenosine Kabi.
- Aminophyllineor theophylline(medicines used to help you breathe). Your doctor may tell you to stop taking them 24 hours before you are given Adenosine Kabi.
- Caffeine(sometimes found in headache medicines)
Using Adenosine Kabi with food and drink
You should avoid food and drink that contains caffeine, such as tea, coffee, chocolate and cola, for at least 12 hours before you are given Adenosine Kabi.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding and fertility
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine if:
- you are pregnant, might be pregnant or think you may be pregnant. You should not be given Adenosine Kabi unless it is clearly necessary.
- you are breastfeeding. You should not be given Adenosine Kabi if you are breastfeeding.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Adenosine Kabi contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per ml, which is essentially “sodium-free”.
3. How to use Adenosine Kabi
How Adenosine Kabi is given to you
Adenosine Kabi is a hospital medicine.
It will be given to you by a doctor or nurse through a vein.
Your heart and blood pressure will be closely monitored.
How much Adenosine Kabi is given to you
If you are not sure why you are being given Adenosine Kabi or have questions about the amount you are being given, ask your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Adults
- The first dose is 3 mg given over 2 seconds. It is given by rapid injection into a vein
- If the first dose does not get your heartbeat back to normal, you will be given a second dose. The second dose is 6 mg given by rapid injection.
- If the second dose does not get your heartbeat back to normal, you will be given a third dose. The third dose is 12 mg given by rapid injection.
- You should not be given more doses after the 12 mg dose.
Children
These pre-filled syringes are not suitable for the administration of small volumes needed for children.
Elderly
See the dosage recommendation for adults.
If you have been given too much Adenosine Kabi
As this medicine is given by a doctor or nurse, it is unlikely that you will be given too much. Your doctor will carefully calculate how much Adenosine Kabi you should be given.
If you are given too much medicine, you may get the following effects:
- Very low blood pressure (severe hypotension).
- Slow heartbeat (bradycardia).
- A heart problem (asystole).
Your doctor will continuously monitor your heart during the procedure.
As the time that adenosine stays in the blood is very short, any side effects due to an overdose of Adenosine Kabi would stop quickly when the injection is stopped. Sometimes you may need an injection of a medicine called aminophylline or theophylline to prevent any possible side effects.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
While you are being given Adenosine Kabi, you may get the following side effects.
If any of the following side effects get worse, tell your doctor or nurse immediately and they will decide whether you should continue with the injection or not.
Side effects usually go away after a few seconds or minutes after the injection has finished, but you should tell your doctor or nurse if you get any of them.
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Redness of the skin with a feeling of heat (flushing)
- Slow heartbeat (bradycardia)
- Extra or skipped heartbeats
- A heart problem called atrioventricular block where the heart starts beating slowly
- Severe heart problems that can cause death (asystole) or irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath or need to breathe deeply (dyspnoea)
- Chest pain or pressure in the chest
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Feeling dizzy.
- Feeling sick.
- Headache
- Unusual sensations in the skin, such as burning
- Feeling nervous.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Blurred vision
- Feeling your heartbeat or feeling that it is going too fast (palpitations)
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Breathing more quickly or deeply than normal (hyperventilation)
- Feeling of pressure in the head or heaviness in the arms
- General discomfort, feeling weak or pain.
- Sweating
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Severe shortness of breath or breathing problems.
- Redness, pain or swelling at the injection site
- Feeling uncomfortable during the injection
- Worsening of high blood pressure in the brain (intracranial hypertension)
- Fast, irregular or very slow heartbeats
- Severe slow heartbeat (severe bradycardia)
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Loss of consciousness, fainting
- Seizures
- Vomiting
- Low blood pressure
- Your heart not working properly to get blood around your body (cardiac arrest). This can be fatal.
- Your lungs not working
- Shortness of breath (respiratory arrest)
- Allergic reaction (including swelling of the face and throat, and skin reactions such as blisters or rash)
- Spasm of the heart artery that can cause a heart attack
- Heart attack (myocardial infarction/ST elevation) especially in patients with narrowing of the heart arteries
- Infarct/small infarct as a consequence of the haemodynamic effects of adenosine, including hypotension
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly via the Spanish Medicines Agency’s website: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Adenosine Kabi
Your doctor, nurse or pharmacist will keep this medicine in a safe place where children cannot see or reach it.
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the packaging. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Do not refrigerate.
The medicine is for single use and should be used immediately after opening. Any remaining amount in the pre-filled syringe should be discarded.
Adenosine Kabi should not be used if, before administration, your doctor or nurse notices particles in the solution or any change in the colour of the solution.
The pre-filled syringe should be thrown away if the appearance of the medicine has changed.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Your doctor or nurse will dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Composition of Adenosine Kabi
- The active ingredient is adenosine. Each single-dose prefilled syringe of 1 ml contains 3 mg of adenosine. Each single-dose prefilled syringe of 2 ml contains 6 mg of adenosine. Each single-dose prefilled syringe of 4 ml contains 12 mg of adenosine.
- The other components are sodium chloride and water for injectable preparations.
Product Appearance and Container Content
Adenosine Kabi is a clear and colorless injectable solution.
Adenosine Kabi is supplied in containers that contain 1, 6, or 10 prefilled syringes
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder:
Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.
C/ Marina, 16-18, 08005 Barcelona
Spain
Manufacturer:
Fresenius Kabi Austria GmbH
Hafnerstrasse 36, 8055 Graz
8055 Graz
Austria
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Medicinal Product Name
Member State
Belgium Adenosine Fresenius Kabi 3 mg/ml, solution for injection in a prefilled syringe
Denmark Adenosine Fresenius Kabi
Italy Adenosine Kabi
Ireland Adenosine 3 mg/ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
Netherlands Adenosine Fresenius Kabi 3 mg/ml, solution for injection in a prefilled syringe
Poland Adenosine Kabi
Portugal Adenosine Kabi
Spain Adenosine Kabi 3mg/ml injectable solution in prefilled syringe
United Kingdom Adenosine 3 mg/ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
(Northern Ireland)
Date of the last revision of this leaflet: February 2024
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals
Adenosine Kabi 3 mg/ml solution for injection in prefilled syringe
For more details on this medicinal product, consult the summary of product characteristics
Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
1 ml of solution contains 3 mg of adenosine.
Each single-dose prefilled syringe of 1 ml contains 3 mg of adenosine.
Each single-dose prefilled syringe of 2 ml contains 6 mg of adenosine.
Each single-dose prefilled syringe of 4 ml contains 12 mg of adenosine
To consult the complete list of excipients, see section 6.1.
Pharmaceutical Form
Solution for injection in prefilled syringe
Therapeutic Indications
Rapid conversion to normal sinus rhythm of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardias, including those associated with anomalous conduction pathways (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome).
Diagnostic Indications
Aid in the diagnosis of supraventricular tachycardias with wide or narrow complexes. Although Adenosine Kabi does not reverse atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, or ventricular tachycardia to sinus rhythm, the slowing of AV conduction facilitates the diagnosis of atrial activity.
Sensitization in endocavitary electrophysiological investigations.
Posology and Method of Administration
Adenosine Kabi is for hospital use only, with monitoring and cardiorespiratory resuscitation equipment available for immediate use if necessary.
Adenosine Kabi should only be used in facilities with cardiac monitoring. Patients who, after a certain dose, present with a high-degree atrioventricular block should not be given additional doses.
Posology
Adults:
Initial dose: 3 mg administered as a rapid intravenous bolus (2-second injection)
Second dose: if the first dose does not stop the supraventricular tachycardia within 1 or 2 minutes, 6 mg should be administered as a rapid intravenous bolus.
Third dose: if the second dose does not stop the supraventricular tachycardia within 1 or 2 minutes, 12 mg should be administered as a rapid intravenous bolus.
Doses higher than or in addition to those recommended are not advised.
Pediatric Population
These prefilled syringes are not suitable for pediatric use.
Elderly
See recommended posology in adults.
Diagnostic Dose
The ascending posology indicated above may be administered until sufficient diagnostic information is obtained.
Method of Administration
Adenosine should be administered by rapid intravenous (IV) bolus injection directly into a vein or through an intravenous catheter. If administered through an intravenous catheter, the injection should be made as proximal as possible, followed by a rapid flush with physiological serum. If administered through a peripheral vein, a larger diameter cannula should be used.
Pharmaceutical Data
List of Excipients
Sodium chloride.
Water for injectable preparations.
Incompatibilities
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product should not be mixed with others.
Shelf Life
36 months
The medicinal product should be used immediately after opening
Special Precautions for Storage
Do not refrigerate.
Nature and Content of Container
1 ml plastic prefilled syringe containing 1 ml (3 mg/1 ml) with a halobutyl protective cap.
Packages with:
1 prefilled syringe
6 prefilled syringes
10 prefilled syringes
2 ml plastic prefilled syringe containing 2 ml (6 mg/2 ml) with a halobutyl protective cap.
Packages with:
1 prefilled syringe
6 prefilled syringes
10 prefilled syringes
4 ml plastic prefilled syringe containing 4 ml (12 mg/4 ml) with a halobutyl protective cap.
Packages with:
1 prefilled syringe
6 prefilled syringes
10 prefilled syringes
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Special Precautions for Disposal
Do not use if particles or a change in the color of the solution are observed.
Disposal of the unused medicinal product and all materials that have come into contact with it should be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
Instructions for Use of the Prefilled Syringe:
When using the 5 ml plastic prefilled syringe containing 4 ml (12 mg of adenosine / 4 ml) to administer only a 6 mg dose, 2 ml should be discarded from the syringe before administering the remaining 2 ml to the patient.
Use an aseptic technique
- Remove the protector
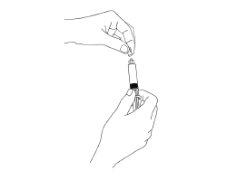
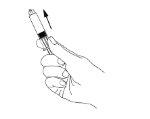
- Hold the plunger and press the syringe cylinder forward to overcome any resistance it may present
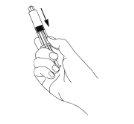
- Slide the cylinder down to eliminate all the air inside the syringe
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ADENOSINE KABI 3 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGEDosage form: INJECTABLE, 6 mg adenosine/2 mlActive substance: adenosineManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 30 mg adenosine/10mlActive substance: adenosineManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 30 mg injectable 10 mlActive substance: adenosineManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for ADENOSINE KABI 3 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Discuss questions about ADENOSINE KABI 3 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions











