
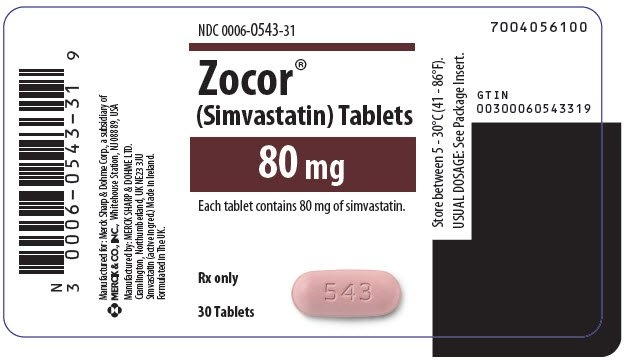
Zocor 80

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Zocor 80

How to use Zocor 80
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
ZOCOR 10, 10 mg, film-coated tablets
ZOCOR 20, 20 mg, film-coated tablets
ZOCOR 40, 40 mg, film-coated tablets
ZOCOR 80, 80 mg, film-coated tablets
Simvastatin
You should carefully read the contents of this leaflet before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Zocor and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Zocor
- 3. How to take Zocor
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Zocor
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Zocor and what is it used for
Zocor contains the active substance simvastatin. Zocor is a medicine used to lower the level of cholesterol in the blood, "bad" cholesterol (LDL cholesterol) and fatty substances called triglycerides. Additionally, Zocor increases the level of "good" cholesterol (HDL cholesterol). Zocor belongs to a group of medicines called statins.
Cholesterol is one of several fatty substances found in the blood. Total cholesterol is mainly made up of LDL cholesterol and HDL cholesterol.
LDL cholesterol is often called "bad" cholesterol because it can build up on the walls of arteries, forming plaques. Eventually, these plaques can cause the arteries to narrow, restricting or blocking the flow of blood to vital organs such as the heart and brain. Restricted blood flow can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
HDL cholesterol is often called "good" cholesterol because it helps prevent the buildup of bad cholesterol in the arteries and protects against heart disease.
Triglycerides are another type of fat found in the blood that can increase the risk of developing heart disease.
While taking this medicine, you should follow a cholesterol-lowering diet.
Zocor is used as a supplement to a cholesterol-lowering diet, in the case of:
- high cholesterol levels in the blood (primary hypercholesterolemia) or high levels of fats in the blood (mixed hyperlipidemia);
- a hereditary disorder (homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia) that causes high cholesterol levels in the blood. Other treatments may also be used;
- ischemic heart disease (coronary heart disease) or a high risk of developing ischemic heart disease (due to diabetes, a history of stroke or other blood vessel diseases). Zocor may prolong life by reducing the risk of heart disease, regardless of cholesterol levels in the blood.
In most people, there are no direct symptoms of high cholesterol. Your doctor may assess your cholesterol level by ordering a simple blood test. You should regularly attend check-ups, monitor your cholesterol level, and discuss your treatment goals with your doctor.
2. Important information before taking Zocor
When not to take Zocor
If you are unsure whether you are taking any of the above medicines, consult your doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Tell your doctor:
- about all your illnesses, including allergies,
- about consuming large amounts of alcohol,
- about any history of liver disease. Taking Zocor may not be suitable.
- about any planned surgery. It may be necessary to stop taking Zocor for a short time.
or eye muscle weakness (a disease that causes muscle weakness in the eyes), as statins can sometimes exacerbate the condition or lead to muscle weakness (see section 4).
Your doctor should perform a blood test before starting Zocor and during treatment if you have any liver problems. The purpose of the test is to assess liver function.
Your doctor may also perform blood tests to assess liver function after starting Zocor.
During therapy, your doctor will closely monitor your health if you have diabetes or are at risk of developing diabetes. The risk of developing diabetes exists in people who have high blood sugar and fat levels, are overweight, and have high blood pressure.
Tell your doctor about any serious lung diseases.
You should contact your doctor immediately if you experience unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness. In rare cases, muscle problems can be serious, including muscle breakdown leading to
kidney damage, and in very rare cases, death.
The risk of muscle damage is higher when taking higher doses of Zocor, particularly the 80 mg dose. The risk of muscle breakdown is also higher in some patients. Tell your doctor if:
- you consume large amounts of alcohol,
- you have kidney problems,
- you have thyroid problems,
- you are 65 years of age or older,
- you are female,
- you have ever had muscle problems while taking cholesterol-lowering medicines called "statins" or fibrates,
- you or a close relative have had a hereditary muscle disorder.
Your doctor or pharmacist should also be informed if muscle weakness persists. To diagnose and treat this condition, additional tests and medications may be necessary.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of Zocor have been studied in boys aged 10-17 years and girls who have started menstruation (menstruation) at least one year earlier (see section 3: How to take Zocor). No studies have been conducted in children under the age of 10. For more information, consult your doctor.
Zocor and other medicines
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you are currently taking or plan to take, including those that are available without a prescription. Taking Zocor with any of the following medicines can increase the risk of muscle problems (some of which are listed above in the "When not to take Zocor" section).
- If it is necessary to take fusidic acid orally for the treatment of a bacterial infection, it will be necessary to temporarily stop taking this medicine. Your doctor will inform you when it is safe to restart Zocor.
Taking Zocor with fusidic acid can rarely lead to muscle weakness, tenderness, or pain (rhabdomyolysis).
Additional information on rhabdomyolysis can be found in section 4.
- cyclosporine (often used in organ transplant patients),
- danazol (a synthetic hormone used to treat endometriosis, a disease in which the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus),
- medicines containing the following active substances: itraconazole, ketoconazole, fluconazole, posaconazole, or voriconazole (used to treat fungal infections),
- fibrates containing the following active substances: gemfibrozil and bezafibrate (used to lower cholesterol),
- erythromycin, clarithromycin, or telithromycin (used to treat bacterial infections),
- HIV protease inhibitors, such as indinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir (used to treat AIDS),
- antiviral medicines used to treat hepatitis C, such as boceprevir, telaprevir, elbasvir, or grazoprevir (used to treat hepatitis C),
- nefazodone (used to treat depression),
- medicines containing the active substance cobicistat,
- amiodarone (used to treat heart rhythm disorders),
- verapamil, diltiazem, or amlodipine (used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain related to heart disease, or other heart diseases),
- lomitapide (used to treat a rare genetic cholesterol disorder),
- daptomycin (an antibiotic used to treat complicated skin and soft tissue infections and bacteremia). It is possible that muscle-related side effects may be greater when this medicine is taken with simvastatin (e.g., Zocor). Your doctor may decide to stop Zocor for a while,
- colchicine (used to treat gout),
- tikagrelor (an antiplatelet medicine).
You should also tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you have taken recently, including those available without a prescription. In particular, you should tell your doctor about medicines containing any of the following active substances:
- medicines that prevent blood clots, such as warfarin, phenprocoumon, or acenocoumarol (anticoagulant medicines),
- fenofibrate (also used to lower cholesterol),
- niacin (also used to lower cholesterol),
- rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis).
You should also inform any doctor who prescribes a new medicine that you are taking Zocor.
Zocor with food and drink
Grapefruit juice contains one or more compounds that affect the action of some medicines in the body, including Zocor. You should avoid drinking grapefruit juice.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Do not take Zocor if you are pregnant, planning to have a baby, or think you may be pregnant. If you become pregnant while taking Zocor, stop treatment and consult your doctor. Do not take Zocor while breastfeeding, as it is not known whether the medicine is excreted in breast milk.
Before taking any medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Driving and using machines
Zocor does not affect the ability to drive or use machines. However, you should consider that some people may experience dizziness after taking Zocor.
Zocor contains lactose
Zocor tablets contain a sugar called lactose. If you have been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, consult your doctor before taking the medicine.
3. How to take Zocor
Your doctor will determine the dose of Zocor suitable for you, depending on your current treatment and individual risk.
This medicine should always be taken as directed by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
While taking Zocor, you should follow a cholesterol-lowering diet.
Dosage:
The recommended dose is 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, or 80 mg of simvastatin, taken orally, once a day.
Adults:
The initial dose is 10 mg, 20 mg, or in some cases 40 mg per day. Your doctor may adjust the dose after at least 4 weeks of treatment to a maximum of 80 mg per day. Do not take more than 80 mg per day.
Your doctor may recommend lower doses, especially if you are taking certain medicines listed above or have kidney problems.
A dose of 80 mg is recommended only for adult patients with very high cholesterol levels in the blood and a high risk of heart disease, who have not achieved the target cholesterol level with a lower dose.
Use in children and adolescents:
For children (aged 10-17 years), the recommended initial dose is 10 mg once daily in the evening. The maximum recommended dose is 40 mg per day.
Method of administration:
Zocor should be taken in the evening. The medicine can be taken with or without food. Zocor should be taken continuously until your doctor advises you to stop.
If your doctor has prescribed Zocor with another cholesterol-lowering medicine containing a bile acid sequestrant, take Zocor at least 2 hours before or 4 hours after taking the bile acid sequestrant.
Taking a higher dose of Zocor than recommended
- Consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Missing a dose of Zocor
- Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose. Take the next dose of Zocor at the usual time the next day.
Stopping Zocor treatment
- Consult your doctor or pharmacist, as your cholesterol level may rise again.
If you have any further questions about taking this medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Zocor can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following terms are used to describe how often side effects are reported:
- rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people).
- very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people).
- frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data).
If you experience any of the following serious side effects, stop taking the medicine and immediately consult your doctor or go to the emergency department of your nearest hospital.
The following serious side effects have been reported rarely:
- muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness. In rare cases, these problems can be serious and include muscle breakdown leading to kidney damage; very rare cases of death have been reported.
- allergic reactions (hypersensitivity) in the form of: o swelling of the face, tongue, and throat that can cause breathing difficulties (angioedema), o severe muscle pain, usually in the shoulder and hip area, o rash with muscle weakness in the arms and neck, o joint pain or inflammation (polymyalgia rheumatica), o blood vessel inflammation (vasculitis), o unusual bruising, skin rashes, and swelling (dermatomyositis), o hives, sun sensitivity, fever, o shortness of breath (dyspnea) and malaise, o symptoms of lupus-like disease (including rash, joint pain, and changes in blood cells),
- liver inflammation with symptoms of yellowing of the skin and eyes, itching, dark urine, or pale stools, fatigue, or weakness, loss of appetite, liver failure (very rare),
- pancreatitis, often with severe abdominal pain.
The following very rare serious side effects have been reported:
- a severe allergic reaction that causes breathing difficulties or dizziness (anaphylaxis),
- a rash that can occur on the skin or mouth ulcers (drug-induced pemphigoid),
- muscle damage,
- gynecomastia (breast enlargement in men).
The following side effects have also been reported rarely:
- decreased red blood cell count (anemia),
- numbness or weakness in the hands and feet,
- headache, tingling, dizziness,
- blurred vision; vision disturbances,
- gastrointestinal problems (abdominal pain, constipation, bloating, indigestion, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting),
- rash, itching, hair loss,
- weakness,
- sleep disturbances (very rare),
- poor memory (very rare), memory loss, confusion.
The following side effects have also been reported, but their frequency cannot be estimated from the available data (frequency not known):
- erectile dysfunction,
- depression,
- lung inflammation causing breathing problems, including persistent cough and (or) shortness of breath or fever,
- tendon problems, sometimes complicated by tendon rupture,
- myasthenia gravis (a disease that causes general muscle weakness, including in some cases muscles used for breathing),
- eye muscle weakness (a disease that causes muscle weakness in the eyes).
You should consult your doctor if you experience weakness in your arms or legs that worsens after periods of activity, double vision, or drooping eyelids, difficulty swallowing, or shortness of breath.
Additional possible side effects reported during the use of some statins:
- sleep disturbances, including nightmares,
- sexual problems,
- diabetes. The development of diabetes is more likely in people with high blood sugar and fat levels, who are overweight, and have high blood pressure. Your doctor will monitor your health during treatment with this medicine,
- muscle pain, tenderness, or persistent weakness, which may not resolve after stopping Zocor (frequency not known).
Laboratory test results
Increased muscle enzyme activity (creatine kinase) in the blood and abnormal liver function test results have been observed.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl .
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Zocor
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
The medicine should be stored at a temperature below 30°C.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton after: EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Zocor contains
- The active substance is simvastatin. Zocor 10 mg film-coated tablets contain 10 mg of simvastatin. Zocor 20 mg film-coated tablets contain 20 mg of simvastatin. Zocor 40 mg film-coated tablets contain 40 mg of simvastatin. Zocor 80 mg film-coated tablets contain 80 mg of simvastatin.
- The other ingredients are: Tablet core:butylhydroxyanisole, ascorbic acid, citric acid monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, magnesium stearate, lactose monohydrate. Coating: hypromellose, hydroxypropylcellulose, titanium dioxide, talc, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow (in Zocor 10 mg and Zocor 20 mg tablets).
What Zocor looks like and contents of the pack
Available packs:
- Zocor 10, Zocor 40, Zocor 80 - PVC/PE/PVDC/Al foil blisters in a cardboard box containing 28 film-coated tablets.
- Zocor 20 - PVC/PE/PVDC/Al foil blisters in a cardboard box containing 28 or 60 film-coated tablets.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Organon Polska Sp. z o.o.
Marszałkowska Street 126/134
00-008 Warsaw
Tel.: +48 22 105 50 01
[email protected]
Manufacturer/Importer
Merck Sharp & Dohme B.V.
Waarderweg 39
2031 BN Haarlem
Netherlands
Organon Heist bv
Industriepark 30
2220 Heist-op-den-Berg
Belgium
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 07/2023
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterMerck Sharp & Dohme B.V. Merck Sharp & Dohme B.V. Organon Heist bv
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Zocor 80Dosage form: Tablets, 10 mgActive substance: simvastatinPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 20 mgActive substance: simvastatinPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 40 mgActive substance: simvastatinPrescription required
Alternatives to Zocor 80 in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Zocor 80 in Spain
Alternative to Zocor 80 in Ukraine
Online doctors for Zocor 80
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Zocor 80 – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










