
Trifas 10

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Trifas 10

How to use Trifas 10
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Trifas 10;5 mg/ml, solution for injection
Torasemidum
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed to you by a doctor. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet:
- 1. What is Trifas 10 and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Trifas 10
- 3. How to use Trifas 10
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Trifas 10
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Trifas 10 and what is it used for
Trifas 10 contains the active substance torasemide and belongs to a group of medicines called loop diuretics.
Torasemide has a diuretic effect and also lowers blood pressure.
Trifas 10 is used in adults to treat:
- fluid retention in tissues (edema) and/or
- fluid retention in body cavities (effusions) that may occur in connection with heart function disorders, if intravenous treatment is necessary (e.g. pulmonary edema caused by sudden heart failure).
2. Important information before using Trifas 10
When not to use Trifas 10
- if the patient is allergic to:
- the active substance torasemide;
- substances with a similar chemical structure (sulfonylurea derivatives);
- any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has renal failure (with anuria);
- if the patient has severe liver dysfunction with impaired consciousness (hepatic coma or pre-coma);
- if the patient has low blood pressure (hypotension);
- if the patient has decreased blood volume (hypovolemia);
- if the patient has low sodium and potassium levels in the blood (hyponatremia, hypokalemia);
- if the patient has significant urinary retention disorders (e.g. due to prostate hypertrophy);
- if the patient is breastfeeding.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to take Trifas 10, the patient should discuss it with their doctor or pharmacist.
Due to insufficiently documented results, Trifas 10 should not be used in:
- gout,
- severe heart rhythm disorders, when heartbeats are slowed down (atrioventricular block II or III),
- acid-base balance disorders,
- patients taking lithium salts (medicines used to treat mood and depression disorders);
- patients taking certain antibiotics for infection treatment, such as aminoglycosides, cephalosporins;
- patients with blood morphology disorders, e.g. thrombocytopenia or anemia in patients without renal function disorders;
- patients with renal function disorders caused by nephrotoxic compounds.
Children and adolescents
Trifas 10 should not be used in children and adolescents under 18 years of age, due to the lack of data on the use of torasemide in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Impact on doping tests
The use of Trifas 10 may result in positive doping test results.
It is difficult to predict the effects of using Trifas 10 as a doping agent; the risk to health cannot be ruled out.
Trifas 10 and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
- The use of Trifas 10 may affect the action of the following medicines
- Blood pressure lowering medicines, especially ACE inhibitors: the administration of ACE inhibitors at the same time or immediately after torasemide treatment may cause a sudden drop in blood pressure.
- Theophylline (a medicine used to treat asthma): Trifas 10 may increase the effect of theophylline.
- Muscle relaxants: increased muscle relaxant effect.
- Antidiabetic medicines: Trifas 10 may reduce the effect of antidiabetic medicines.
- Painkillers and rheumatic medicines - in the case of high doses of salicylates, torasemide may enhance their toxic effect on the central nervous system.
- Medicines used to treat circulation disorders (epinephrine and norepinephrine). Trifas 10 may reduce the effect of these medicines.
- The following medicines have an effect on Trifas 10
- Probenecid (a medicine used to treat gout): Probenecid may inhibit the diuretic and antihypertensive effect of Trifas 10.
- Certain anti-inflammatory medicines (e.g. indomethacin, acetylsalicylic acid): these medicines may inhibit the diuretic and antihypertensive effect of Trifas 10.
- During treatment with high doses (see section 3), Trifas 10 may lead to an increase in the following side effects
- Hearing and kidney damage caused by aminoglycoside antibiotics (e.g. kanamycin, gentamicin, tobramycin) used to treat infections.
- Hearing and kidney damage caused by cisplatin (used to treat tumors).
- Kidney damage caused by cephalosporins (a group of antibiotics) used to treat infections.
- Other interactions between Trifas 10 and other medicines
- The decrease in potassium levels caused by Trifas 10 may increase the side effects of concurrently used digitalis glycosides (used to treat heart failure).
- Laxatives may increase the potassium loss caused by Trifas 10.
- Adrenal cortex hormones (mineralo- and glucocorticoids, e.g. cortisone), used concurrently with Trifas 10, may increase the potassium loss caused by it.
- Concomitant treatment with Trifas 10 and lithium salts (used to treat mood swings and depression) may increase the lithium level in the blood and thus enhance the cardiotoxic and nephrotoxic effects of lithium salts.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
Trifas 10 should only be used during pregnancy if it is absolutely necessary. Only the smallest dose should be used.
There is a lack of sufficient clinical data on the effect of Trifas 10 on the unborn child.
Breastfeeding
It is not known whether the active substance of Trifas 10 passes into breast milk. Therefore, Trifas 10 should not be used during breastfeeding. If the use of the medicine during breastfeeding is necessary, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Driving and using machines
Trifas 10 may affect reaction time. Trifas 10 may impair the ability to actively participate in road traffic, operate machines or work without safe support for the feet.
This applies in particular to:
- the initial treatment period,
- the period after dose increase,
- the period after replacing another medicine,
- the period of starting concurrent treatment with another product.
Alcohol may enhance this effect.
During treatment with Trifas 10, the patient should not consume alcohol.
3. How to use Trifas 10
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubts, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
Dosage
The dosage should be determined based on the severity of renal function disorders.
The recommended initial dose is 2 ml of Trifas 10 per day (corresponding to 10 mg of torasemide).
If the therapeutic effect is not satisfactory, the dose can be increased to 4 ml of Trifas 10 (corresponding to 20 mg of torasemide) per day. If this does not produce the desired effect, short-term treatment for no more than 3 days can be used, consisting of administering 8 ml of Trifas 10 (corresponding to 40 mg of torasemide) per day.
In the case of acute pulmonary edema, treatment should be started with an intravenous dose of 4 ml of Trifas 10 (corresponding to 20 mg of torasemide). Then, depending on the clinical picture, the dose can be repeated every 30 minutes. A dose greater than 20 ml of Trifas 10 (corresponding to 100 mg of torasemide) should not be used per day.
Patients with liver failure
Treatment should be carried out with special caution, due to the possibility of increased torasemide levels in the blood
Elderly patients
No dose adjustment is required in elderly patients.
Method of administration
The solution is administered by slow intravenous injection.
Only clear solution should be injected!
Do not administer intrarterially!
Trifas 10 should not be used in injections and infusions together with other medicines.
Handling of one-point-cut (OPC) ampoules
Note: It is not necessary to file the ampoule!
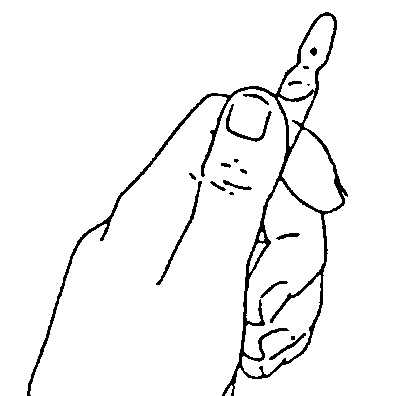
The ampoule should be held with the colored end up
The end of the ampoule should be
broken off.
Treatment duration
The duration of treatment with Trifas 10 is decided by the attending physician. Trifas 10 should not be administered intravenously for more than 1 week.
In the case of continued treatment, it is recommended to change the intravenous form of the medicine to an oral form as soon as possible.
During treatment, the doctor should closely monitor the patient.
Using a higher dose of Trifas 10 than recommended
Using a higher dose of Trifas 10 than recommended may cause:
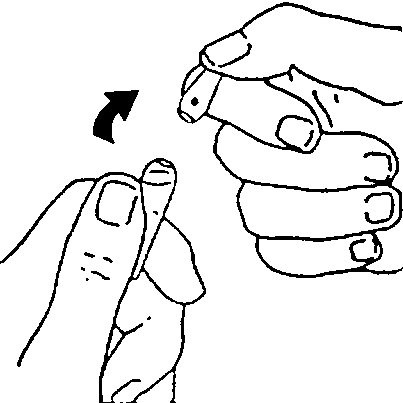
The ampoule should be held with the colored end up
By shaking or tapping the ampoule, the solution should be made to flow from the end of the ampoule to its base
- increased, potentially life-threatening diuresis with fluid and electrolyte loss,
- disturbances of consciousness,
- confusional state,
- drop in blood pressure,
- circulatory collapse,
- gastrointestinal disorders. The patient should immediatelycontact their doctor, who will recommend the appropriate course of action.
In case of questions or doubts, the patient should contact their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Trifas 10 can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Acid-base balance disorders (metabolic alkalosis)
- Muscle cramps (especially at the beginning of treatment)
- Increased levels of uric acid, glucose and lipids in the blood (triglycerides, cholesterol)
- Potassium deficiency (hypokalemia) when using a low-potassium diet, vomiting, diarrhea, abuse of laxatives, in patients with chronic liver function disorders)
- Depending on the dose used and the duration of treatment, disorders of water and electrolyte balance may occur, in particular decreased blood volume (hypovolemia), potassium and sodium loss (hypokalemia and/or hyponatremia)
- Gastrointestinal disorders (e.g. loss of appetite, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation), especially at the beginning of treatment
- Increased activity of certain liver enzymes (gamma-GT) in the blood
- Headache and dizziness, feeling of fatigue, weakness (especially at the beginning of treatment)
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Increased levels of urea and creatinine (muscle protein) and urea in the blood. In patients with urinary retention disorders (e.g. due to prostate hypertrophy), urinary retention may occur. In such cases, urination is impaired or impossible.
- Dryness in the mouth,
- Feeling of numbness and cold in the limbs (paresthesia)
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Decreased number of red and white blood cells (erythrocytes and lymphocytes) and platelets
- Allergic reactions, e.g. itching, rash, hypersensitivity to light, severe allergic skin reactions. In the case of intravenous administration, it is impossible to rule out the occurrence of acute, potentially life-threatening anaphylactic reactions
- Blood clots in blood vessels (thromboembolic complications)
- Confusional states
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Disorders of coronary or cerebral circulation (including myocardial ischemia and cerebral ischemia). These conditions may lead to arrhythmias, feeling of pressure in the chest (angina pectoris), acute myocardial infarction or, for example, sudden loss of consciousness (syncope).
- Pancreatitis.
- Visual disturbances.
- Tinnitus.
- Hearing loss.
If any of the above side effects occur, the patient should inform their doctor immediately. The doctor will assess the severity of the symptoms and decide what tests should be performed.
In the case of sudden and severe side effects, the patient should immediatelyconsult their doctor. This is very important, as some side effects may potentially be life-threatening. The doctor will decide what tests should be performed and whether treatment should be continued.
If an allergic reaction occurs (e.g. severe allergic skin reaction), Trifas 10 should not be used again.
Procedure in case of an allergic reaction
Severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock) may occur, which require appropriate action. The patient should be laid on a flat surface with their legs raised, the airway should be cleared, oxygen therapy should be initiated, an intravenous line should be inserted, and epinephrine (adrenaline), glucocorticoids, and fluids should be administered as needed.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including those not listed in the leaflet, the patient should inform their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309,
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Trifas 10
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature below 30°C.
Only clear solution should be injected. The solution for injection should be used immediately after opening. The remainder should be discarded.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and ampoules.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the given month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Trifas 10 contains
The active substance of Trifas 10 is torasemide.
Each 2 ml ampoule of solution for injection contains 10.631 mg of torasemide sodium salt, corresponding to 10 mg of torasemide.
Other ingredients of the medicine are: sodium hydroxide, trometamol, Macrogol 400, water for injections.
The pH of Trifas 10 is between 8.5 and 9.5.
What Trifas 10 looks like and contents of the pack
Trifas 10 ampoules contain a clear and colorless solution.
The pack contains 5 ampoules of 2 ml.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Menarini International Operations Luxembourg S.A.
1, Avenue de la Gare,
L-1611 Luxembourg, Luxembourg
Manufacturer
- A. Menarini Manufacturing Logistics and Services S.r.I. Via Sette Santi 3, 50131 Florence, Italy
For more detailed information, the patient should contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Berlin-Chemie/Menarini Polska Sp. z o.o.
Tel: (22) 566 2100
Fax: (22) 566 2101
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 05/2023
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterA.Menarini Manufacturing Logistics and Services S.r.l.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Trifas 10Dosage form: Tablets, 5 mgActive substance: torasemideManufacturer: Polfarmex S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 10 mgActive substance: torasemideManufacturer: Polfarmex S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 20 mgActive substance: torasemideManufacturer: Polfarmex S.A.Prescription required
Alternatives to Trifas 10 in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Trifas 10 in Spain
Alternative to Trifas 10 in Ukraine
Online doctors for Trifas 10
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Trifas 10 – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










