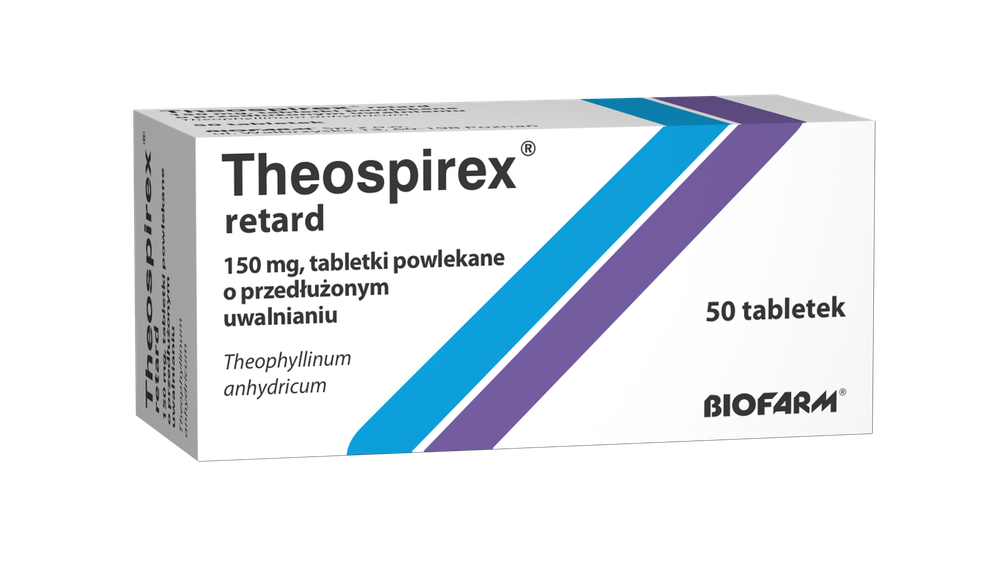
Theospirex retard

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Theospirex retard

How to use Theospirex retard
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Theospirex retard
150 mg, prolonged-release coated tablets
Anhydrous theophylline
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What Theospirex retard is and what it is used for
- 2. Important information before taking Theospirex retard
- 3. How to take Theospirex retard
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Theospirex retard
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What Theospirex retard is and what it is used for
Theospirex retard is a medicine that contains theophylline in the form of prolonged-release coated tablets.
The medicine has a bronchodilator effect on the smooth muscles of the bronchi, bronchioles, and blood vessels, and inhibits the release of mediators from cells involved in inflammatory reactions.
The medicine also has a positive effect on the strength and duration of cardiac muscle contraction, increases urine excretion, and reduces edema.
Indication:
- Prevention of bronchospasm in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Warning!
Medicines containing theophylline with prolonged release are not intended for the emergency treatment of acute asthma attacks or breathing disorders caused by acute bronchospasm.
Theophylline should not be used as a first-line treatment for asthma in children.
2. Important information before taking Theospirex retard
When not to take Theospirex retard
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Theospirex retard, you should discuss it with your doctor:
The medicine should be used with caution during vaccination and in the elderly.
The medicine should not be used in acute asthma attacks and status asthmaticus.
Fever reduces the rate of theophylline elimination from the body. In the case of acute illness with fever, it may be necessary to reduce the dose to avoid toxicity.
Children and adolescents
Theospirex retard should not be used in children under 6 years old.
Other pharmaceutical forms of the medicine are available, which are more suitable for children under 6 years old.
Detailed information on the use of this medicine in children and adolescents is presented in section 3. "How to take Theospirex retard".
Theospirex retard and other medicines
You should tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or plan to take.
In particular, you should inform about the use of any of the following medicines, as Theospirex retard may change their effect and increase the risk of side effects:
- Theospirex retard should not be used concomitantly with other xanthine and its derivative preparations.
- Ephedrine. Theophylline enhances the effect of ephedrine.
- Theophylline enhances the effect of sympathomimetics (such as salbutamol, formoterol) used in the treatment of bronchospastic conditions, caffeine, and similar substances.
- Theophylline increases the renal excretion of lithium salts (used in the treatment of mania or depression), reduces its absorption, and concentration in the blood.
- Glycosides of foxglove (cardiac stimulants). Through its positive effect on the strength and duration of cardiac muscle contraction, theophylline may enhance the effect of glycosides and lead to conduction disorders in the heart muscle.
- Theophylline may weaken the effect of beta-adrenergic blockers (medicines used, among others, in the treatment of hypertension), adenosine (a medicine used in arrhythmias), benzodiazepines (medicines with anxiolytic, sedative, hypnotic, anticonvulsant effects), and pancuronium (a medicine used during general anesthesia to facilitate intubation and muscle relaxation during surgical procedures).
- Theophylline enhances the effect of diuretics.
- There is evidence that in people receiving ketamine (a rapidly acting anesthetic) at the same time, the seizure threshold may be lowered.
- The use of halothane (an agent used for general anesthesia) in patients treated with theophylline may cause severe arrhythmias.
Lower theophylline concentrations are found in tobacco smokers.
In the case of taking medications that affect theophylline concentration in serum, the dose should be adjusted accordingly.
You should inform about the use of medications that may enhancethe effect of Theospirex retard and increase the risk of its side effects:
- cimetidine (a medicine used in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease of the stomach and duodenum),
- allopurinol (a medicine that reduces the content of uric acid in the blood and urine, inhibits the formation of urate stones in the urinary tract, prevents the deposition of urate deposits in muscles and kidneys),
- fluoroquinolone antibiotics (enoxacin, lomefloxacin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin). It is recommended to frequently monitor theophylline concentrations in patients treated with such antibiotics,
- macrolide antibiotics (erythromycin, clarithromycin),
- disulfiram (a medicine used in the treatment of alcohol dependence),
- estrogens (hormonal medicines used, among others, in hormone replacement therapy),
- fluvoxamine (an antidepressant from the group of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors),
- interferon-alpha (a medicine used in the treatment of cancer),
- isoniazid (a medicine used in the prevention and treatment of tuberculosis),
- methotrexate (a medicine used in the treatment of cancer),
- mexiletine and propafenone (medicines used in arrhythmias),
- rofecoxib (a medicine used in the treatment of pain in rheumatic diseases),
- propranolol (a medicine used, among others, in hypertension),
- ticlopidine (a medicine that prevents the formation of blood clots),
- calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem) used in heart diseases,
- viloxazine (an antidepressant). In such cases, the doctor may recommend reducing the dose of Theospirex retard.
Alcohol causes an increase in theophylline concentration in the blood, so during treatment with Theospirex retard, you should not consume alcoholic beverages.
You should inform about the use of medications that may weakenthe effect of Theospirex retard and reduce its effectiveness:
- aminoglutethimide (a medicine used in the treatment of certain prostate cancers),
- carbamazepine (a medicine used in the treatment of epilepsy),
- isoprenaline (a medicine used in asthma),
- phenobarbital (an antiepileptic medicine),
- phenytoin (a medicine with anticonvulsant effect),
- primidone (an antiepileptic medicine),
- rifampicin (a medicine used in tuberculosis),
- sucralfate (a medicine used in peptic ulcer disease of the stomach and duodenum),
- sulfinpyrazone (a medicine that increases the excretion of uric acid in the urine, used in gout),
- medicines containing St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum). If you are taking any of the above medicines, your doctor may recommend increasing the dose of Theospirex retard.
Theospirex retard with food and drink
A low-carbohydrate diet (sugars) and high-protein diet, as well as parenteral nutrition and consuming large amounts of grilled beef, reduce the amount of theophylline in the body and weaken its effect.
A high-carbohydrate and low-protein diet may lead to an increase in the amount of theophylline in the body, enhancement of its effect, and an increased risk of side effects.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy
The safety of theophylline use during pregnancy has not been established, as no adequate studies have been conducted.
Theophylline crosses the placental barrier and may cause side effects in the fetus.
Theophylline should not be used during pregnancy, especially in the first three months, unless it is absolutely necessary. In the second and third trimester of pregnancy, theophylline can be used only when the benefits to the mother outweigh the risk to the fetus.
Theophylline crosses the placental barrier and may cause side effects in the fetus.
The degree of theophylline binding to plasma proteins and clearance may decrease during pregnancy. It may be necessary to reduce the dose to avoid side effects.
The use of theophylline in late pregnancy may inhibit uterine contractions. It is recommended to closely monitor newborns exposed to theophylline in late pregnancy to detect any symptoms caused by its effect.
Breastfeeding
You should not use the medicine during breastfeeding.
Theophylline passes into breast milk and during breastfeeding may cause side effects in breastfed infants. Its concentration in breast milk of a nursing mother may be 60-90% of the concentration of this medicine in the blood.
Driving and using machines
Theophylline may affect your ability to drive and use machines. You should be careful, as there is a risk of drowsiness and dizziness.
3. How to take Theospirex retard
This medicine should always be taken as directed by your doctor. If you are unsure, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
The dose of theophylline should be adjusted individually, taking into account the effectiveness of the medicine and its tolerance by the patient. The dosage is best determined after measuring the theophylline concentration in serum (therapeutic concentration range: 8-20 μg/ml). Monitoring the theophylline concentration in serum is particularly recommended in case of side effects or insufficient response to treatment.
If the patient has previously taken theophylline or its derivatives, this should be taken into account when determining the initial dose and it should be reduced accordingly. The dose should be calculated based on the lean body mass, as theophylline does not penetrate into fatty tissue.
Dosage
The daily maintenance dose of theophylline in adults is approximately 11 to 13 mg/kg body weight.
This corresponds to a total daily dose of 900 mg (6 tablets).
- Adults and adolescents over 16 years old (8 to 12 mg/kg body weight per day): 300 mg of theophylline (2 tablets) every 12 hours (morning and evening).
- Adolescents between 13 and 16 years old (8 to 15 mg/kg body weight per day): 225 to 300 mg of theophylline (1 and ½ tablets to 2 tablets) every 12 hours (morning and evening).
- Children between 10 and 12 years old (11 to 15 mg/kg body weight per day): 225 mg of theophylline (1 and ½ tablets) every 12 hours (morning and evening).
- Children between 6 and 9 years old (10 to 17 mg/kg body weight per day): 150 mg of theophylline (1 tablet) every 12 hours (morning and evening).
In case of insufficient improvement, the daily dose is gradually increased every 3 days by about 25% until clinical improvement is achieved or the maximum daily dose is reached, as follows:
Adults and adolescents over 16 years old:
13 mg/kg body weight per day
Adolescents between 13 and 16 years old:
18 mg/kg body weight per day
Children between 10 and 12 years old:
20 mg/kg body weight per day
Children between 6 and 9 years old:
24 mg/kg body weight per day
In case it is not possible to monitor the blood concentration of the medicine, the daily dose should not be exceeded:
- in children between 6 and 9 years old: 600 mg (4 tablets),
- in children over 9 to 12 years old: 750 mg (5 tablets),
- in adolescents over 12 years old and adults: 900 mg (6 tablets).
In case it is necessary to maintain the above maximum doses, it is recommended to monitor the theophylline concentration in the blood.
If a medicine containing theophylline with unmodified release is to be replaced with a medicine with modified release, it may be necessary to reduce the daily dose.
In case of changing the theophylline-containing medicine to another theophylline-containing medicine, the doctor will monitor the treatment, controlling the theophylline concentration in the serum.
Children under 6 years old
Theospirex retard should not be used in children under 6 years old.
Smoking
Smokers, due to faster theophylline elimination, should be given a higher dose of theophylline, taking into account their body weight, than non-smoking adult patients.
Particular caution should be exercised when adjusting the dose in smokers who are quitting, as the theophylline concentration in the serum is higher in them compared to non-smokers.
Special patient groups
Generally, theophylline elimination is slower in patients with heart failure, severe hypoxia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pneumonia, acute pulmonary edema, viral infections (especially influenza), untreated fever, in the elderly, in patients taking certain medications (see section 2. "Theospirex retard and other medicines"), and in people who consume large amounts of alcohol. Therefore, such patients require the use of smaller doses of theophylline and special caution when deciding to increase the dose.
It has also been reported that theophylline elimination is reduced after influenza and tuberculosis vaccination.
In such cases, it may be necessary to reduce the dose of theophylline.
Patients with liver and (or) kidney function disorders
Very often, in patients with liver disorders, theophylline elimination is slower.
In patients with severe kidney function disorders, theophylline metabolites may accumulate. Therefore, in these patients, smaller doses should be used and special caution should be exercised when increasing the dose.
Method of administration
Tablets should be taken orally, after a meal.
Single doses should be taken at equal intervals throughout the day. When taking the medicine twice a day, the dose is usually taken in the morning and evening.
Tablets can be divided into two equal doses along the dividing line.
Tablets should not be chewed or crushed.
Duration of treatment
The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor, depending on the type, severity, and course of the disease.
Using a higher dose of Theospirex retard than recommended
Symptoms of overdose
Symptoms of theophylline overdose may occur if its serum concentration is higher than 20 μg/ml, and worsen with higher concentrations.
Usually, the first symptom to appear is tachycardia (rapid heart rate), followed by gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, bloody vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea), central nervous system stimulation (anxiety, headaches, insomnia, dizziness), excessive thirst, tinnitus, and arrhythmias. Excessive sweating and muscle tremors may also occur.
In case of significant overdose (theophylline concentration in serum is higher than 25 μg/ml), seizures, circulatory failure, hyperthermia (elevated body temperature), severe arrhythmias, including ventricular arrhythmias, and even cardiac arrest and death may occur.
In patients with increased sensitivity to theophylline, severe overdose symptoms may occur even when the theophylline concentration in serum is less than 20 μg/ml.
Procedure in case of overdose
In case of any symptoms of overdose, you should immediately contact a doctor or the emergency department of the nearest hospital. In case of life-threatening symptoms, you should immediately call the emergency services.
In case of mild overdose symptoms:
You should stop taking the medicine and measure the theophylline concentration in the serum. If treatment is resumed, the dose should be reduced accordingly.
If symptoms from the central nervous system occur (e.g., anxiety and seizures):
- you should administer diazepam intravenously at a dose of 0.1-0.3 mg/kg body weight, up to a maximum of 15 mg.
If overdose symptoms are potentially life-threatening, you should:
- monitor vital functions and maintain airway patency,
- administer oxygen,
- if necessary, administer intravenous fluids to increase blood volume,
- control and, if necessary, correct fluid and electrolyte deficiencies,
- use hemoperfusion (see below).
In case of life-threatening arrhythmias:
- in patients who do not have asthma, you should administer propranolol intravenously at a dose of 1 mg in adults; 0.02 mg/kg body weight in children. The dose can be repeated every 5-10 minutes until a normal heart rhythm is restored, up to a maximum dose of 0.1 mg/kg body weight.
Warning:
In patients with asthma, propranolol may cause severe bronchospasm, so in these patients, verapamil should be administered instead of propranolol.
In very severe cases of poisoning, when the above procedure is ineffective, and in patients with very high theophylline concentrations in the serum, rapid and complete detoxification can be achieved through hemoperfusion or hemodialysis. However, this is usually not necessary, as theophylline is metabolized sufficiently quickly.
Missing a dose of Theospirex retard
You should not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping treatment with Theospirex retard
If you have any further doubts about the use of this medicine, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
During treatment with Theospirex retard, the following side effects may occur:
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Very common (in more than 1 in 10 patients): irritation of the gastrointestinal tract mucosa, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea, loss of appetite, anorexia. There have been reports of bloody vomiting after theophylline. Existing gastroesophageal reflux may worsen at night due to the relaxation of the esophageal sphincter.
Nervous system and psychiatric disorders:
Very common (in more than 1 in 10 patients): central nervous system stimulation: headaches, irritability, anxiety, insomnia, dizziness, increased reflexes, muscle tremors, and seizures.
Cardiac disorders:
Very common (in more than 1 in 10 patients): arrhythmias, rapid heart rate, extra beats, and ventricular arrhythmias, palpitations.
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders:
Very common (in more than 1 in 10 patients): rapid breathing.
Vascular disorders:
Very common (in more than 1 in 10 patients): decreased blood pressure.
Renal and urinary disorders:
Very common (in more than 1 in 10 patients): increased urine excretion related to the diuretic effect of theophylline, proteinuria, and hematuria may occur. There have also been reports of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH).
Immune system disorders:
Uncommon (in less than 1 in 100 but more than 1 in 1,000 patients): hypersensitivity reactions, urticaria, generalized itching, angioedema - allergic reactions, such as skin reactions and sudden swelling of the skin and mucous membranes (e.g., throat or tongue), breathing difficulties, and (or) itching and rash.
Diagnostic tests:
Very common (in more than 1 in 10 patients): increased glucose concentration in serum, (decreased potassium concentration in blood), increased creatinine concentration in serum, changes in electrolyte concentrations in blood, increased uric acid concentration in blood.
Side effects may be more severe in people with hypersensitivity to theophylline or in case of overdose (theophylline concentration in serum higher than 20 mg/l).
In particular, when the theophylline concentration in serum is higher than 25 mg/l, toxic effects may occur, such as seizures, sudden drop in blood pressure, ventricular arrhythmias, and severe gastrointestinal symptoms (including gastrointestinal bleeding).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
tel.: +48 22 49 21 301
fax: +48 22 49 21 309
e-mail: [email protected]
By reporting side effects, you can help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Theospirex retard
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Store at a temperature below 25°C.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Theospirex retard contains
- The active substance of the medicine is anhydrous theophylline. One prolonged-release tablet contains 150 mg of anhydrous theophylline.
- The other ingredients are: ammonium methacrylate copolymer (type B) (Eudragit RSPO), povidence 25, talc, magnesium stearate, purified water, hypromellose HPMC 5-6, hypromellose HPMC 2910, titanium dioxide (E171), triacetin, macrogol 6000.
What Theospirex retard looks like and what the package contains
White, round, coated tablets with a dividing line on both sides, with a smooth surface, without damage, stains, and chips.
Tablets are packaged in aluminum/PVC blisters, placed in a cardboard box.
The package contains 50 tablets (5 blisters of 10 each).
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Biofarm Sp. z o.o.
ul. Wałbrzyska 13
60-198 Poznań
Tel.: +48 61 66 51 500
Fax: +48 61 66 51 505
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterBiofarm Sp. z o.o.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Theospirex retardDosage form: Capsules, 200 mgActive substance: theophyllineManufacturer: Takeda GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Capsules, 300 mgActive substance: theophyllineManufacturer: Takeda GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 1.2 mg/mlActive substance: theophyllineManufacturer: Bieffe Medital S.p.A.Prescription not required
Alternatives to Theospirex retard in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Theospirex retard in Ukraine
Alternative to Theospirex retard in Spain
Online doctors for Theospirex retard
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Theospirex retard – subject to medical assessment and local rules.