
Tapamol
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Tapamol

How to use Tapamol
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
TAPAMOL
240 mg/5 mL, oral suspension
Paracetamol
Read the leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains
important information for the patient.
This medicine should always be taken exactly as described in this patient leaflet or as advised by
your doctor or pharmacist.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you need advice or additional information, consult your pharmacist.
- If you experience any side effects, including any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
- If after 3 days there is no improvement or you feel worse, contact your doctor.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is TAPAMOL and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking TAPAMOL
- 3. How to take TAPAMOL
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store TAPAMOL
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is TAPAMOL and what is it used for
TAPAMOL oral suspension is an antipyretic and analgesic medicine intended for use in infants and children, containing paracetamol as the active substance.
Indications for use
Fever and pain of various origins (e.g. after surgical procedures, pain associated with teething, mild to moderate headache) and symptoms accompanying the body's reaction to vaccination (pain, fever, local reaction).
The medicine is used in infants from 0 to 3 months of age (with a body weight of up to 4 kg) for the symptomatic treatment of fever lasting no longer than 3 days and pain of mild to moderate severity.
In children under 3 months of age, use only after a doctor's recommendation.
Do not use without consulting a doctor for more than 3 days.
2. Important information before taking TAPAMOL
When not to take TAPAMOL:
- if the patient is allergic to paracetamol or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- in patients with severe liver failure or viral hepatitis,
- in patients with severe kidney failure,
- in alcoholism.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with TAPAMOL, discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist.
Do not take with other medicines containing paracetamol due to the risk of overdose. In case of overdose, consult your doctor immediately, even if you feel well.
Taking a multiple daily dose of paracetamol at once may lead to severe liver damage; in such cases, there is no loss of consciousness. However, medical advice should be sought immediately.
Do not take for more than 3 days without consulting a doctor.
Do not exceed the recommended dose.
The medicine should be used with caution in patients with liver and kidney failure. Particular risk of liver damage occurs in malnourished individuals. Caution should be exercised when using in patients with reduced glutathione levels (such as sepsis).
Paracetamol may increase the risk of metabolic acidosis. Caution should be exercised when using paracetamol in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and methemoglobin reductase deficiency.
During treatment with TAPAMOL, inform your doctor immediately if the patient experiences severe diseases, including severe kidney dysfunction or sepsis (when bacteria and their toxins are present in the blood, leading to organ damage) or malnutrition, chronic alcoholism, or if the patient is also taking flucloxacillin (an antibiotic).
Severe metabolic acidosis (a blood and fluid disorder) has been reported in patients who take paracetamol in regular doses for a longer period or when taking paracetamol with flucloxacillin. Symptoms of metabolic acidosis may include: severe breathing difficulties, including rapid deep breathing, drowsiness, feeling of nausea (nausea) and vomiting.
In patients with asthma, allergic to salicylates (e.g. acetylsalicylic acid), an allergy to paracetamol may occur.
Available study results indicate that paracetamol administration may be a risk factor for the development of asthma and allergic diseases in children.
TAPAMOL and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or plan to take.
Do not take with centrally acting analgesics or alcohol, as it enhances their effect. When used concomitantly: barbiturates, antiepileptic drugs (including glutethimide, phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine), rifampicin, it increases the harmful effect of paracetamol on the liver. Paracetamol increases the toxicity of chloramphenicol.
Prolonged use of paracetamol in high doses enhances the effect of oral anticoagulant medicines from the coumarin group.
Concomitant use of paracetamol with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) increases the risk of kidney function disorders. Paracetamol used concomitantly with MAO inhibitors may cause a state of excitement and high temperature.
Paracetamol absorption is accelerated by drugs that accelerate gastric emptying (e.g. metoclopramide, domperidone) and delayed by drugs that delay gastric emptying (e.g. cholestyramine).
Using paracetamol in combination with zidovudine may cause neutropenia. Salicylamide prolongs the elimination time of paracetamol.
Using paracetamol may be the cause of false results of some laboratory tests (e.g. blood glucose measurement).
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking flucloxacillin (an antibiotic), due to a serious blood and fluid disorder (called metabolic acidosis), which requires urgent treatment (see section 2).
TAPAMOL with alcohol
Medicine intended for children.
Do not consume alcohol while taking the medicine.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Medicine intended for children.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women may take this medicine if, in the doctor's opinion, it is necessary.
Driving and using machines
The medicine has no effect on the ability to drive and use machines.
TAPAMOL contains 3.7 g of sucrose in 5 mL of suspension
This should be taken into account in patients with diabetes. If you have previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, you should consult your doctor before taking the medicine.
TAPAMOL contains sodium metabisulfite
Sodium metabisulfite may rarely cause severe hypersensitivity reactions and bronchospasm.
TAPAMOL contains 7.0659 mg of sodium benzoate in 5 mL of suspension
Sodium benzoate may increase the risk of jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes) in newborns (up to 4 weeks of life).
TAPAMOL contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per 5 mL of suspension, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
TAPAMOL contains 10.575 mg of propylene glycol in 5 mL of suspension
Before administering the medicine to a child under 4 weeks of age, consult your doctor or pharmacist, especially if the child is taking other medicinal products containing propylene glycol or alcohol.
3. How to take TAPAMOL
This medicine should always be taken exactly as described in the patient leaflet or as advised by your doctor or pharmacist. If in doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
The medicine is taken orally. A measuring cup is attached to the packaging.
Before use, shake vigorously to obtain a uniform suspension.
The recommended dose is:
The average single dose of paracetamol is 10 mg to 15 mg per kilogram of body weight.
If necessary, the dose can be repeated, but not more often than every 4-6 hours, and not more than 4 times a day, i.e. a maximum of 60 mg/kg body weight/day.
In children under 3 months of age, use only after a doctor's recommendation.
Do not take for more than 3 days without consulting a doctor.
Do not exceed the maximum daily dose. The medicine is used as needed, when symptoms occur.
In case of high fever, symptoms of secondary infection, or prolonged symptoms, consult your doctor.
The table below shows an example dosing schedule for the medicine:
| Age (child's body weight) | Recommended single dose of the medicine (paracetamol) | Maximum daily dose of the medicine (paracetamol) |
| from 0 to 3 months (up to 4 kg) | 1.25 mL (60 mg) | 5 mL (240 mg) |
| from 4 to 8 months (up to 7 kg) | 2 mL (96 mg) | 8 mL (384 mg) |
| from 9 to 11 months (up to 8 kg) | 2.5 mL (120 mg) | 10 mL (480 mg) |
| from 1 to 2 years (up to 10.5 kg) | 3.25 mL (156 mg) | 13 mL (624 mg) |
| from 2 to 3 years (up to 13 kg) | 4 mL (192 mg) | 16 mL (768 mg) |
| from 4 to 5 years (up to 18.5 kg) | 5.75 mL (276 mg) | 23 mL (1104 mg) |
| from 6 to 8 years (up to 24 kg) | 7.5 mL (360 mg) | 30 mL (1440 mg) |
| from 9 to 10 years (up to 32 kg) | 10 mL (480 mg) | 40 mL (1920 mg) |
| from 11 to 12 years (up to 45.6 kg) | 14.25 mL (684 mg) | 57 mL (2736 mg) |
5 mL of oral suspension contains 240 mg of paracetamol (one full measuring cup).
Dosing instructions using the measuring cup:
- before the first use of the measuring cup, it must be washed in warm (not boiling) water with a detergent,
- after unscrewing the cap, put the measuring cup on the plug in the neck of the bottle,
- to fill the measuring cup, shake the bottle vigorously, turn it upside down, and then carefully move the plunger down, drawing in the suspension in the desired amount indicated on the scale,
- turn the bottle back to its original position and carefully remove the measuring cup from the plug (see picture),
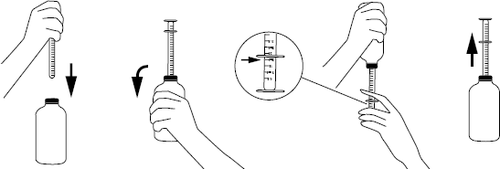
- put the tip of the measuring cup in the child's mouth and, slowly pressing the plunger, carefully empty the measuring cup (the child should be held in a vertical or sitting position),
- after use, close the bottle and wash the measuring cup in warm (not boiling) water with a detergent and dry it.
There are no special instructions for taking with food.
Taking a higher dose of TAPAMOL than recommended
In case of taking a higher dose of the medicine than recommended, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately, even if you feel well.
Severe poisoning may occur in children after taking 200 mg of paracetamol/kg body weight/day.
Accidental or intentional overdose of paracetamol may cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, excessive sweating, drowsiness, and general weakness within a few or several hours. These symptoms may resolve the next day, despite the slow development of severe liver damage, manifested by a feeling of fullness in the upper abdomen, nausea, and jaundice.
Treatment of paracetamol poisoning must be carried out in a hospital, under intensive medical care. If it has not been more than an hour since taking paracetamol, induce vomiting and give activated charcoal.
Missing a dose of TAPAMOL
The medicine should be taken as recommended in section 3.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
If you have any further doubts about taking this medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Rare(in 1 to 10 patients out of 10,000):
skin allergic reactions: urticaria, rash, skin inflammation.
Very rare(in less than 1 patient out of 10,000):
decreased platelet count (thrombocytopenia),
decreased white blood cell count (leukopenia, agranulocytosis),
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,
liver function disorders.
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from the available data):
a serious disease that can make the blood more acidic (so-called metabolic acidosis), in patients with severe disease taking paracetamol (see section 2).
Long-term use or overdose of the medicine may cause liver and kidney damage, as well as methemoglobinemia with symptoms of cyanosis (gray-blue skin discoloration).
There are reports of very rare cases of severe skin reactions (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Pharmacovigilance of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181 C, 02-222 Warsaw,
phone: 22 49 21 301, fax: 22 49 21 309,
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store TAPAMOL
Store in a temperature below 25°C. Store the bottle in a vertical position.
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
After the first opening of the packaging, the medicine retains its potency for 12 months.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What TAPAMOL contains
- The active substance of the medicine is paracetamol. 5 mL of suspension contains 240 mg of paracetamol.
- The other ingredients (excipients) are: sucrose, xanthan gum (E 415), citric acid monohydrate (E 330), sodium benzoate (E 211), sodium metabisulfite (E 223), natural strawberry flavor AR 2143 (contains natural flavoring substances, including d-limonene and propylene glycol), purified water.
What TAPAMOL looks like and what the pack contains
Milky to light yellow suspension with a strawberry smell.
The pack contains 100 mL or 85 mL of oral suspension.
The bottle is made of orange glass type III with an HDPE cap, a guarantee ring, and an LDPE connector for the measuring cup, as well as a measuring cup made of LDPE/PS with a capacity of 5 mL, with a scale every 0.25 mL, in a cardboard box.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
"PRZEDSIĘBIORSTWO PRODUKCJI FARMACEUTYCZNEJ HASCO-LEK" S.A.
51-131 Wrocław, ul. Żmigrodzka 242 E
Medicine information
phone: 22 742 00 22
e-mail: [email protected]
Date of last update of the leaflet:01/2025
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterPrzedsiębiorstwo Produkcji Farmaceutycznej HASCO-LEK S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to TapamolDosage form: Tablets, 500 mgActive substance: paracetamolManufacturer: Farmaceutyczna Spółdzielnia Pracy "Galena"Prescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 300 mgActive substance: paracetamolManufacturer: Farmaceutyczna Spółdzielnia Pracy "Galena"Prescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 325 mgActive substance: paracetamolManufacturer: US Pharmacia Sp. z o.o.Prescription not required
Alternatives to Tapamol in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Tapamol in Іспанія
Alternative to Tapamol in Україна
Online doctors for Tapamol
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Tapamol – subject to medical assessment and local rules.















