
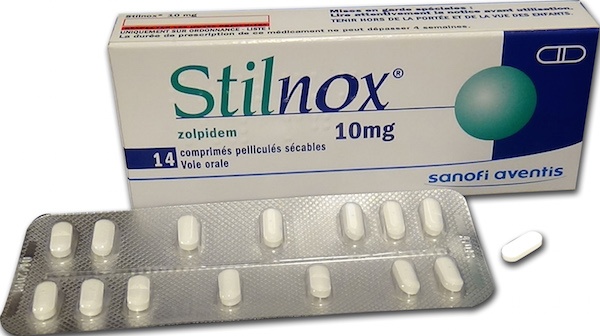
Stilnox

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Stilnox

How to use Stilnox
Leaflet attached to the packaging: information for the user
Warning! Keep the leaflet! Information on the immediate packaging in a foreign language.
Stilnox(Stilnoct)
10 mg, coated tablets
Zolpidem tartrate
Stilnox and Stilnoct are different trade names for the same medicine.
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if necessary.
- In case of any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed to a specific person. It should not be given to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if the symptoms of their illness are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Stilnox and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Stilnox
- 3. How to take Stilnox
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Stilnox
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Stilnox and what is it used for
Stilnox is available in the form of coated tablets and contains the active substance zolpidem.
Zolpidem belongs to a group of sedative and hypnotic medicines.
The medicine facilitates falling asleep, reduces the number of nocturnal awakenings, prolongs the duration of sleep, and improves its quality.
Stilnox is used for short-term treatment of insomnia in patients over 18 years of age when insomnia causes the patient disabling weakness or severe suffering.
It should not be used for a long time. Treatment should last as short as possible, as the risk of dependence increases with the duration of treatment.
2. Important information before taking Stilnox
Stilnox should not be taken in the following cases:
- hypersensitivity to zolpidem or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- severe liver impairment
- sleep apnea syndrome
- acute and/or severe respiratory failure
- myasthenia gravis
- long-term therapy. Treatment should last as short as possible, as the risk of dependence increases with the duration of treatment.
- if the patient has ever experienced sleepwalking or other unusual behaviors during sleep (such as driving, eating, making phone calls, or having sex, etc.), when they did not wake up completely after taking Stilnox or another medicine containing zolpidem.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Stilnox, you should discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist.
In each case, it should be determined, if possible, the causes of insomnia and, if possible, eliminate the factors that cause it, before the doctor recommends taking a sleeping medicine.
Persistence of insomnia after 7-14 days of treatment may indicate the existence of primary mental or physical disorders that require diagnosis and evaluation by a doctor at regular intervals.
Respiratory failure:
Due to the fact that sedatives can inhibit the activity of the respiratory center, caution should be exercised when taking Stilnox in patients with respiratory function disorders (see section 4).
Liver function disorders:
Liver function disorders - see section 3. "How to take Stilnox"
In patients with severe liver impairment, Stilnox should not be taken. Taking Stilnox in patients with severe liver impairment may lead to encephalopathy - a disorder of the central nervous system caused by liver failure (see section 2. "Important information before taking Stilnox").
Elderly or weakened patients:
Elderly or weakened patients should take a lower dose of the medicine, see section 3.
Mental illnesses:
Sedatives, such as Stilnox, are not recommended for initial treatment of mental illnesses.
Psychomotor disorders the next day (see also "Driving and operating machinery"):
Like other sedatives, zolpidem has a sedative effect on the central nervous system.
The next day after taking Stilnox, the risk of psychomotor disorders, including impaired driving ability, may be increased if:
- The patient took the medicine less than 8 hours before activities that require increased alertness.
- The patient took a higher dose than recommended.
- The patient took zolpidem while being treated with other medicines that have a sedative effect on the central nervous system or other medicines that increase the concentration of zolpidem in the blood, while consuming alcohol or taking prohibited substances.
A single dose should be taken directly before bedtime.
A second dose should not be taken on the same night.
Amnesia:
Sedatives and hypnotics can cause anterograde amnesia. It usually occurs a few hours after taking the medicine. To reduce the risk, the patient should have the opportunity to sleep uninterrupted for 8 hours.
Suicidal thoughts, suicide attempts, suicide, and depression:
Some studies have shown an increased risk of suicidal thoughts, suicide attempts, and suicide in patients taking certain sedatives and hypnotics, including this medicine. However, it has not been established whether this is caused by taking the medicine or other factors. If the patient has suicidal thoughts, they should contact their doctor as soon as possible to receive medical advice.
Although no clinically significant interactions have been found between zolpidem and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (see section: Stilnox and other medicines) and other sedatives and hypnotics, caution should be exercised when taking zolpidem as well as other sedatives and hypnotics in patients with symptoms of depression.
In this group of patients, suicidal tendencies may occur, so the doctor should prescribe the smallest dose of the medicine to prevent intentional overdose. Previously occurring depression may manifest during zolpidem treatment. Since insomnia can be a symptom of depression, in case of persistent insomnia, the doctor should re-examine the patient.
Other psychological reactions and "paradoxical":
The use of sedatives and hypnotics, such as zolpidem, may be accompanied by other psychological reactions and paradoxical reactions, such as anxiety, increased insomnia, excitement, irritability, aggression, delusions, outbursts of anger, nightmares, hallucinations, inadequate behavior, and other behavioral disorders.
In such cases, treatment should be discontinued. The occurrence of such reactions is more likely in elderly patients.
Somnambulism and similar behaviors:
Stilnox may cause sleepwalking or other unusual behaviors during sleep (such as driving, eating, making phone calls, or having sex, etc.), when the patient has not woken up completely. The next morning, the patient may not remember the activities performed during the night. If any of the above behaviors occur in the patient, treatment with Stilnox should be discontinued immediately and the doctor should be consulted, as such behaviors during sleep can pose a serious risk of injury to the patient or their environment.
Consuming alcohol or taking other medicines that cause drowsiness at the same time as Stilnox may increase the risk of such behaviors during sleep, as well as taking zolpidem in doses exceeding the maximum recommended dose.
Tolerance:
In the case of long-term use of sedatives and hypnotics containing zolpidem, including Stilnox, for more than a few weeks, a decrease in their sedative effect may occur.
Dependence:
Taking Stilnox may lead to misuse of the medicine and/or development of psychological or physical dependence.
If the patient has ever had mental disorders, misused or been dependent on alcohol, prohibited substances, or medicines, they should tell their doctor. The risk of dependence is higher when Stilnox is taken for more than 4 weeks and in patients with mental disorders and/or a history of alcohol, prohibited substances, or medicine misuse.
In cases where physical dependence has developed, sudden discontinuation of treatment will be accompanied by withdrawal symptoms. These may include headaches and muscle pain, increased anxiety and tension, restlessness, confusion, and irritability. In severe cases, symptoms such as derealization, depersonalization, increased hearing acuity, numbness and tingling of limbs, hypersensitivity to light, noise, and touch, hallucinations, and seizures may occur.
Rebound insomnia (rebound insomnia):
After discontinuation of hypnotic treatment, a transient syndrome may occur, in which the symptoms that led to the initiation of sedative and hypnotic treatment recur in an intensified form.
These symptoms may be accompanied by other reactions, such as mood changes, anxiety, and fear.
It is essential to inform the patient about the possibility of rebound insomnia and take appropriate measures to minimize the risk of anxiety and other symptoms if they occur during treatment discontinuation.
In the case of short-acting sedatives and hypnotics, the withdrawal syndrome may occur between doses.
Severe injuries:
The medicine may cause drowsiness and impaired consciousness, which can lead to falls and, consequently, severe injuries.
Patients with a prolonged QT interval syndrome:
The potential consequences of taking zolpidem in patients with a congenital prolonged QT interval syndrome are unknown. As a precaution, the doctor should carefully weigh the benefits and risks of zolpidem treatment in patients with a diagnosed, congenital prolonged QT interval syndrome.
Children and adolescents
Stilnox should not be taken in children and adolescents under 18 years of age, as the safety and efficacy of zolpidem have not been established in this age group.
Stilnox and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
Alcohol:
Concomitant consumption of alcohol is not recommended.
The sedative effect of zolpidem may be enhanced during concomitant alcohol consumption. This may affect the ability to drive and operate machinery.
Medicines with a sedative effect on the central nervous system:
When taking zolpidem with certain medicines, sedation and psychomotor disorders the next day, including impaired driving ability, may be enhanced. These medicines include:
- Medicines used to treat certain mental health disorders (antipsychotics)
- Medicines used to treat sleep disorders (sedatives)
- Sedatives or anxiolytics
- Medicines used to treat depression
- Medicines used to treat moderate to severe pain (opioid analgesics)
- Medicines used to treat epilepsy
- Medicines used for anesthesia
- Medicines used to treat hay fever, rash, or other allergies that may cause drowsiness in the patient (sedating antihistamines). When taking zolpidem with antidepressants, including bupropion, desipramine, fluoxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine, the patient may see things that are not real (visual hallucinations). It is not recommended to take zolpidem with fluvoxamine or ciprofloxacin.
Concomitant use of Stilnox and opioids (strong painkillers, substitution therapy medicines, and some cough medicines) increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory failure), coma, and can be fatal. Therefore, concomitant use of these medicines should only be considered when other treatment methods are not possible.
However, when the doctor prescribes Stilnox together with opioids, the dose and duration of concomitant use should be limited by the doctor.
The patient should inform their doctor about all opioid medicines they are taking and strictly follow the dosage instructions. It may be helpful to inform friends and family members to be aware of the above signs and symptoms.
In case of their occurrence, the patient should contact their doctor.
Cytochrome P450 inhibitors and inducers:
Certain medicines that inhibit liver enzymes (especially cytochrome P450) may enhance the effect of certain sedatives, such as zolpidem.
Concomitantly used CYP3A4 inducers, such as rifampicin and St. John's wort, decrease the pharmacodynamic effect of zolpidem.
When concomitantly used with St. John's wort, the concentration of zolpidem in the blood may decrease. It is not recommended to take zolpidem with St. John's wort.
Concomitant administration of zolpidem with ketokonazole (at a dose of 200 mg twice a day) may enhance its sedative effect.
Other medicines:
No significant pharmacokinetic interactions have been observed when zolpidem is concomitantly used with warfarin, digoxin, and ranitidine.
Stilnox with food and drink
The medicine should be taken directly before bedtime or after lying down.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Pregnancy
Stilnox is not recommended during pregnancy. If the patient is pregnant, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a baby, they should consult their doctor before taking this medicine.
The medicine taken during pregnancy may affect the baby. Some studies have shown an increased risk of cleft lip and palate (sometimes called "hare lip") in newborns.
There may be decreased fetal movement and variable fetal heart rate if the mother takes Stilnox in the second and/or third trimester of pregnancy.
If the patient takes Stilnox in late pregnancy or during childbirth, their baby may show muscle weakness, low body temperature, feeding difficulties, and breathing difficulties (respiratory depression).
If the patient regularly takes Stilnox in late pregnancy, their baby may develop physical dependence and experience withdrawal symptoms, such as agitation or seizures. In such a case, the newborn should be closely monitored in the postnatal period.
Breastfeeding
Stilnox should not be taken during breastfeeding, as a small amount of the medicine passes into breast milk.
Driving and operating machinery
Stilnox has a major impact on the ability to drive and operate machinery and may cause events such as "falling asleep at the wheel". The next day after taking Stilnox (like other sedatives), it may happen that:
- the patient feels drowsy, sleepy, dizzy, or disoriented,
- the patient needs more time to make quick decisions (impaired reflexes),
- the patient may see double or blurred vision,
- the patient may be less alert.
To minimize the risk of the above events, it is recommended to maintain an interval of at least 8 hours between taking zolpidem and driving, operating machinery, or working at heights.
Alcohol or psychoactive substances should not be consumed while taking Stilnox, as this may enhance the above effects.
Stilnox contains lactose monohydrate
Stilnox contains lactose monohydrate. If the patient has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, they should consult their doctor before taking the medicine.
Stilnox contains sodium
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per tablet, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to take Stilnox
This medicine should be taken as directed by the doctor. In case of doubts, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
The medicine should be taken orally.
Stilnox acts quickly, so it should be taken directly before bedtime or after lying down.
Like all sedatives, long-term use of Stilnox is not recommended. The recommended treatment duration should not exceed 4 weeks.
In some cases, it may be necessary to extend the treatment period by the doctor beyond the maximum recommended duration, but this should not be done without re-evaluating the patient's clinical condition by the doctor.
Adults
The recommended dose of Stilnox is 10 mg (1 tablet) per day (24 hours). Some patients may be prescribed a lower dose by their doctor. Stilnox should be taken:
- in a single dose,
- directly before bedtime.
The patient must maintain an interval of at least 8 hours between taking the medicine and engaging in activities that require increased concentration.
The dose should not exceed 10 mg per 24 hours.
Elderly patients:
In elderly or weakened patients who may be particularly sensitive to zolpidem, a dose of 5 mg of Stilnox (half a tablet) is recommended. In this group of patients, the daily dose should not exceed 10 mg.
Patients with liver function disorders:
In patients with liver function disorders, the doctor will reduce the initial dose to 5 mg, exercising particular caution, especially in elderly patients.
In adults (under 65 years of age), the doctor may increase the dose to 10 mg if the patient's condition is good and the medicine is well tolerated, but only if the medicine is ineffective at a lower dose.
Children and adolescents:
The safety and efficacy of zolpidem have not been established in children and adolescents under 18 years of age. Therefore, Stilnox should not be taken in this group of patients (see section 2).
If the patient feels that the effect of Stilnox is too strong or too weak, they should consult their doctor.
Overdose of Stilnox
In case of taking a higher dose than recommended, the patient should immediately consult their doctor.
In cases of overdose with zolpidem alone or concomitantly with other medicines that have a sedative effect on the central nervous system (including alcohol), impaired consciousness of varying degrees has been observed - from increased drowsiness to coma, as well as very severe symptoms, including death.
After an overdose of zolpidem, symptomatic and supportive treatment is recommended; gastric lavage or activated charcoal may be performed to reduce the absorption of the medicine from the gastrointestinal tract.
Sedatives should be discontinued, even in case of agitation.
In case of severe symptoms, the doctor will consider administering flumazenil, but the use of flumazenil may cause neurological symptoms (seizures).
Zolpidem is not eliminated from the body by hemodialysis.
Missing a dose of Stilnox
The patient should take the medicine the next day at the usual time. They should not take two doses of the medicine at the same time or at short intervals.
Discontinuation of Stilnox
Stilnox should not be discontinued abruptly, as this increases the risk of withdrawal symptoms. The doctor will inform the patient about how to stop treatment by gradually reducing the dose.
In case of any further doubts about taking this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Stilnox can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
There is evidence that the side effects associated with taking the medicine, especially side effects from the central nervous system, depend on the dose of the medicine. Side effects are less severe if the medicine is taken directly before bedtime or after lying down (see section 3). They are most commonly observed in elderly patients.
The following side effects may occur:
- Common (may occur in up to 1 in 10 people):
- drowsiness, headache, dizziness, increased insomnia, anterograde amnesia (amnesia may be associated with unusual behavior)
- hallucinations, excitement, nightmares, depression (see section 2)
- fatigue
- diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain
- infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract
- back pain
- Uncommon (may occur in up to 1 in 100 people):
- confusion, irritability, restlessness, aggression, somnambulism (see section 2), euphoria
- double vision
- paresthesia (tingling, prickling), tremors
- attention disorders, speech disorders
- blurred vision
- increased liver enzyme activity
- rash, itching, excessive sweating
- eating disorders
- joint pain, muscle pain, muscle cramps, neck pain, muscle weakness
- Stilnox may cause sleepwalking or other unusual behaviors during sleep (such as driving, eating, making phone calls, or having sex, etc.), when the patient has not woken up completely (see section: Warnings and precautions).
- Rare (may occur in up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- libido disorders (sex drive)
- consciousness disorders
- liver damage caused by the toxic effect of the medicine
- hives
- vision disorders
- gait disorders, falls (especially in elderly patients and when the medicine is not taken as recommended) - see section 2.
Very rare (may occur in up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- delusions, dependence (after discontinuation of treatment, withdrawal symptoms or rebound phenomenon may occur)
- respiratory depression (breathing difficulties) - see section 2.
Frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- anger, behavioral disorders. Most psychological side effects are associated with paradoxical reactions.
- angioedema (severe allergic reaction - edema may involve the face, limbs, mouth, and throat, and cause breathing difficulties)
- tolerance to the medicine
- delirium (sudden and severe change in mental state, which causes the person to appear disoriented or confused).
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Stilnox
There are no special precautions for storage.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
The medicine should not be taken after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Stilnox contains
- The active substance of Stilnox is zolpidem tartrate.
Each coated tablet contains 10 mg of zolpidem tartrate.
- The other ingredients are: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose (type A), magnesium stearate. Coating:hypromellose, titanium dioxide (E 171), macrogol 400.
What Stilnox looks like and contents of the pack
Stilnox is a white, elongated, coated tablet with a dividing line and "SN10" engraved. The tablet can be divided into two halves.
The pack contains 14 coated tablets.
For more detailed information, the patient should consult the marketing authorization holder or parallel importer.
Marketing authorization holder in Ireland, the country of export:
Sanofi-aventis Ireland Limited T/A SANOFI
Citywest Business Campus
Dublin 24, Ireland
Manufacturer:
Delpharm Dijon
6, Boulevard de l’Europe
21800 Quétigny, France
Parallel importer:
InPharm Sp. z o.o.
ul. Strumykowa 28/11
03-138 Warsaw
Repackaged by:
InPharm Sp. z o.o. Services sp. k.
ul. Chełmżyńska 249
04-458 Warsaw
Ireland, the country of export, marketing authorization number:PA 540/160/2
Parallel import license number:28/22
Date of leaflet approval: 21.06.2022
[Information about the trademark]
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Marketing authorisation holder (MAH)sanofi-aventis Ireland Ltd. T/A SANOFI
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to StilnoxDosage form: Tablets, 10 mgActive substance: zolpidemPrescription required
Alternatives to Stilnox in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Stilnox in Spain
Online doctors for Stilnox
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Stilnox – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














