
Relanium

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Relanium

How to use Relanium
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
RELANIUM, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection
Diazepam
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Relanium and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Relanium
- 3. How to use Relanium
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Relanium
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Relanium and what is it used for
Relanium contains the active substance diazepam. Diazepam belongs to a group of medicines called benzodiazepines. It has anxiolytic, sedative, hypnotic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. Relanium is intended for use in emergency situations.
Relanium is administered intravenously or intramuscularly:
- in acute anxiety states or excitement, delirium tremens(also known as alcoholic hallucinosis, which can be life-threatening);
- in acute states characterized by increased muscle tension, including tetanus;
- in acute convulsive states occurring during an epileptic seizure, high fever (febrile convulsions), or in the course of poisoning;
- for patient preparation (premedication) before various procedures, e.g., before surgery, endoscopy.
2. Important information before using Relanium
When not to use Relanium
- if the patient is allergic to diazepam (or other benzodiazepines) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has:
- myasthenia gravis (a chronic disease characterized by muscle weakness);
- severe respiratory failure, respiratory depression (very severe breathing difficulties);
- sleep apnea syndrome (characterized by short pauses in breathing during sleep);
- severe liver failure (severe liver dysfunction);
- phobias (fear of specific objects or situations) or obsessions (compulsive, repetitive thoughts or behaviors);
- chronic psychoses (psychiatric disorders characterized by severe disruption of perception of reality and loss of sense of self).
- The medicine should not be used in newborns and premature infants.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Relanium, the patient should discuss it with their doctor.
The doctor will exercise particular caution when using Relanium and will take appropriate action in the case of patients:
- of advanced age;
- with liver failure;
- with chronic pulmonary insufficiency;
- with brain damage resulting from, e.g., injury, atherosclerosis, stroke;
- in a severe condition, especially with heart and breathing problems;
- with chronic respiratory insufficiency;
- addicted to drugs or alcohol;
- who have lost loved ones and are in a period of mourning. Patients with the above-mentioned diseases should inform their doctor about them.
Relanium should not be used as the only medicine in the treatment of depression or anxiety associated with depression.
The doctor will appropriately select the dose of the medicine and determine the duration of treatment. The use of Relanium should last as short as possible.
The medicine should not be used for a long time, as this may increase the risk of dependence.
Children
- The medicine should not be used in newborns and premature infants due to the presence of benzyl alcohol - see section 2. "Relanium contains benzyl alcohol, ethanol, sodium benzoate, propylene glycol, and sodium".
- During the use of Relanium in children, so-called paradoxical reactions (symptoms listed in section 4. "Possible side effects") may occur. If these symptoms occur, the use of the medicine should be discontinued.
Relanium and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
Relanium and other medicines used at the same time may affect each other's action.
In particular, this applies to the following medicines listed below:
- strong painkillers (called opioid analgesics, e.g., morphine, buprenorphine); if the administration of diazepam with opioid analgesics is necessary, diazepam should be administered last,
- medicines used in psychiatric disorders (e.g., haloperidol),
- medicines used in the treatment of depression (fluoxetine, fluvoxamine),
- sedatives, anxiolytics, and hypnotics,
- anticonvulsants (e.g., phenobarbital),
- anesthetics and some medicines used in the treatment of allergies (with a sedative effect),
- cimetidine and omeprazole (medicines used in the treatment of ulcers),
- phenytoin and valproic acid (a medicine used in the treatment of epilepsy),
- rifampicin (an antibiotic).
The concomitant use of Relanium and opioids (strong painkillers, drugs used in substitution therapy for addiction, and some cough medicines) increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), coma, and can be life-threatening. For this reason, concomitant use of these medicines can only be considered when other treatment methods are not possible.
If, however, the doctor has prescribed Relanium together with opioid medicines, the attending doctor should reduce the dose and recommend the shortest possible treatment time.
The patient should inform their doctor about all opioid medicines they are taking and strictly follow the doctor's instructions regarding dosing. It may be helpful to inform friends or relatives about the risk, so they are aware of the above-mentioned symptoms. If such symptoms occur, the patient should contact their doctor.
Relanium and alcohol (ethanol)
Alcohol (ethanol) enhances the sedative effect of diazepam. The patient should not drink alcohol while using Relanium.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Relanium should not be used in pregnant women, especially during the first and third trimesters, and during breastfeeding, unless the doctor considers it necessary.
Driving and operating machinery
After using the medicine, drowsiness, concentration disorders, and other side effects may occur, which can adversely affect the performance of tasks requiring increased attention. The patient should not drive vehicles or operate machinery for at least 24 hours after administration of Relanium.
Relanium contains benzyl alcohol, ethanol, sodium benzoate, propylene glycol, and sodium
The medicine contains 15 mg of benzyl alcohol in 1 ml of solution. Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions.
Administration of benzyl alcohol to newborns is associated with a risk of severe side effects, including breathing disorders (so-called "gasping syndrome").
The medicine should not be administered to newborns (up to 4 weeks of age) without a doctor's recommendation.
Due to the increased risk of benzyl alcohol accumulation in small children, the medicine should not be administered to children under 3 years of age for more than a week.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, patients with liver or kidney disease should consult their doctor before using the medicine, as a large amount of benzyl alcohol may accumulate in their body and cause side effects (so-called metabolic acidosis).
The medicine contains 12.4% v/v ethanol (alcohol), i.e., up to 200 mg per 2 ml ampoule, which is equivalent to 4.75 ml of beer or 1.98 ml of wine per 2 ml ampoule.
Harmful to individuals with alcoholism.
This should be taken into account when using the medicine in pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, and individuals at high risk, such as patients with liver disease or epilepsy.
The medicine contains 450 mg of propylene glycol in each 1 ml. Before administering the medicine to a child under 5 years of age, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist, especially if the child is taking other medicines containing propylene glycol or alcohol.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, patients with kidney or liver dysfunction should not take this medicine without a doctor's recommendation. The doctor may decide to perform additional tests on such patients.
The medicine contains 48.8 mg of sodium benzoate in 1 ml of solution. Sodium benzoate may increase the risk of jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) in newborns (up to 4 weeks of age).
The medicine contains 15.6 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) per 2 ml ampoule (7.8 mg of sodium per 1 ml).
This corresponds to 0.78% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
The medicine may be diluted in a 0.9% NaCl solution or glucose. When calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine, the sodium from the diluent should be taken into account.
To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, the patient should read the leaflet for the diluent used.
3. How to use Relanium
This medicine should always be used in accordance with the doctor's instructions. If the patient has any doubts, they should consult their doctor.
- Relanium is administered by medical personnel.
- The medicine is administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
- The doctor will determine the dosage of the medicine and the duration of treatment individually for each patient. The patient should strictly follow the doctor's instructions.
- The patient should remain under the doctor's supervision for at least one hour after administration of the medicine.
- At home, the patient should always be accompanied by a responsible adult. The patient should be accompanied until the symptoms have resolved.
Detailed dosing and administration instructions are provided at the end of the leaflet, in the section "Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals".
Use of a higher than recommended dose of Relanium
The medicine is administered exclusively by medical personnel, so it is unlikely that the patient will receive more medicine than they should.
After an overdose of diazepam, the following may occur: drowsiness, confusion (disorders of consciousness, disorientation, anxiety), and lethargy (very deep sleep). In severe cases, there may also be impaired mobility, decreased blood pressure, severe breathing difficulties, coma, and death (very rarely). If the patient thinks they have received a higher dose of the medicine than recommended, they should immediately consult their doctor, who will provide appropriate treatment.
Discontinuation of Relanium
After discontinuation of Relanium, symptoms of a so-called withdrawal syndrome may occur, but this is unlikely, as the medicine is used in emergency situations. The symptoms of the syndrome include: headaches and muscle pain, anxiety, tension, restlessness, confusion, irritability. In severe cases, the following may occur: loss of sense of reality or self, numbness and tingling of limbs, increased sensitivity to light, noise, and touch, hallucinations, and seizures. The doctor will appropriately select the dose of the medicine and the duration of treatment to minimize the risk of these symptoms occurring.
If the patient has any further doubts about the use of this medicine, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Relanium can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
After intravenous injection of the medicine, the following may occur:
- local reactions (pain, redness) and thrombophlebitis and venous thrombosis;
- apnea or decreased blood pressure (in rare cases);
- very severe circulatory and respiratory disorders (rarely, after too rapid injection).
After intramuscular injection of the medicine, the following may occur:
- pain at the injection site (relatively frequently);
- redness at the injection site.
The following may also occur: fatigue, drowsiness, and muscle weakness.
The use of the medicine (even in therapeutic doses) may lead to dependence. Abuse of benzodiazepine medicines has been observed.
Rarely (in 1 to 10 people per 10,000), the following other side effects have been observed, such as:
- confusion, decreased emotional reactivity, decreased level of consciousness, impaired mobility, tremors,
- anterograde amnesia (the patient does not remember events that occurred a few hours after the use of Relanium - to minimize the risk of amnesia, patients should have conditions for uninterrupted sleep for 7 to 8 hours after administration of the medicine),
- depression,
- double or blurred vision,
- speech disorders or unclear speech,
- gastrointestinal disorders, nausea, dry mouth or excessive salivation, constipation, increased appetite,
- headache, dizziness,
- decreased blood pressure, changes in heart rate, depressive circulatory disorders (significant slowing of heart rate), changes in blood count (visible in the so-called morphology test),
- urinary incontinence or urinary retention,
- increased or decreased libido,
- skin allergic reactions.
Very rarely (in less than 1 person per 10,000), the following have been observed: increased activity of certain enzymes (transaminases and alkaline phosphatase), jaundice, and cases of cardiac arrest.
After the use of diazepam (especially in children and elderly patients), the following may occur: restlessness, excitement, hallucinations, changes in behavior, aggression, nightmares, psychoses (so-called paradoxical reactions).
In elderly and weakened patients, the following may occur: increased side effects.
After the use of diazepam, latent depression may be revealed.
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Relanium
Store at a temperature below 25°C.
Store the ampoules in the outer packaging to protect them from light. Do not freeze.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and ampoule. The expiry date refers to the last day of the stated month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Relanium contains
- The active substance of the medicine is diazepam. Each 1 ml of solution contains 5 mg of diazepam.
- The other ingredients are: propylene glycol, ethanol 96%, benzyl alcohol (15 mg), sodium benzoate, glacial acetic acid, acetic acid 10%, water for injections.
What Relanium looks like and what the packaging contains
Relanium is a colorless or yellowish-green, clear liquid.
The carton contains 5 or 50 ampoules of 2 ml each, made of orange or colorless glass.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Polpharma S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:December 2024
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
RELANIUM, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection
Diazepam
- The medicine is intended for intravenous or intramuscular administration.
- Treatment should be limited to the necessary minimum, and the medicine should be administered only under strict medical supervision.
- To reduce the likelihood of side effects during intravenous sedation, the medicine should be injected slowly (0.5 ml of solution over half a minute) until the patient becomes drowsy, their eyelids drop, and their speech becomes slurred, while the patient is still able to follow instructions.
- It is recommended to perform intravenous injections of the medicine into a large vein in the elbow pit, and the patient should be lying on their back during the procedure. The medicine should not be administered into small veins. It is essential to avoid intra-arterial administration and extravasation of the medicine. Following the above recommendations for intravenous administration of the medicine significantly reduces the risk of hypotension or apnea. Except in emergency situations, a second person should always be present during intravenous administration of the medicine, and a resuscitation kit should always be available. It is recommended that patients remain under medical supervision for at least one hour after administration of the medicine. At home, the patient should always be accompanied by a responsible adult.
- As a rule, Relanium should not be diluted. An exception is the administration of the medicine in a slow intravenous infusion in a large volume of 0.9% NaCl solution or glucose in the treatment of tetanus and status epilepticus. The medicine should not be diluted more than 40 mg of diazepam (8 ml of solution) in 500 ml of infusion solution. The solution should be prepared immediately before administration and used within 6 hours.
More than 50% of the diazepam solution may be adsorbed onto the walls of plastic containers for infusion; therefore, such containers should not be used to administer diazepam solutions. Adsorption onto plastic tubes of the intravenous infusion set may also cause a significant initial decrease in the concentration of diazepam administered, which then slowly increases over several hours. The infusion rate should be frequently adjusted according to the patient's current condition.
- The medicine should not be mixed with other medicines in an infusion solution or in the same syringe, as the stability of the medicine cannot be guaranteed if this recommendation is not followed.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
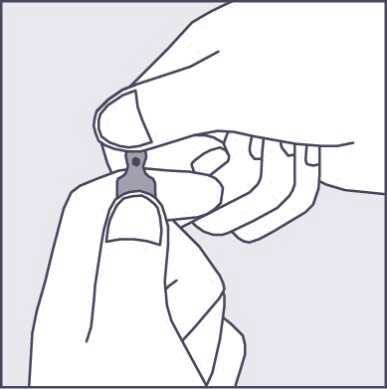
Before opening the ampoule, the patient should make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
The patient can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with their finger to facilitate the flow of the solution.
A colored dot is marked on each ampoule (see Figure 1), as a mark indicating the break point located below it.
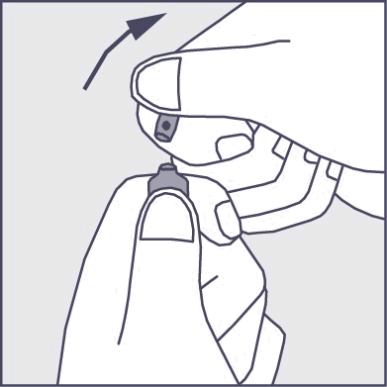
- To open the ampoule, the patient should hold it vertically in both hands with the colored dot facing them - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused product should be disposed of in accordance with the applicable regulations.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
DOSAGE
Adults
Acute anxiety states or excitement: 10 mg intravenously or intramuscularly;
the injection can be repeated no earlier than 4 hours later.
Delirium tremens: 10 to 20 mg intravenously or intramuscularly. Larger doses may be necessary depending on the severity of symptoms.
Acute muscle spasms: 10 mg intravenously or intramuscularly; the injection can be repeated no earlier than 4 hours later.
Tetanus: the initial dose administered intravenously is 0.1 mg/kg to 0.3 mg/kg; it can be repeated every 1 to 4 hours. It can also be administered in a continuous intravenous infusion lasting 24 hours, in a dose of 3 mg/kg to 10 mg/kg. The selected dose should depend on the severity of symptoms; in very severe cases, larger doses can be used.
Status epilepticus, convulsions in the course of poisoning: 10 to 20 mg intravenously or intramuscularly; the dose can be repeated after 30-60 minutes. If necessary, a slow intravenous infusion (maximum dose 3 mg/kg over 24 hours) can be used.
Preoperative or pre-diagnostic procedure sedation: 0.2 mg/kg. The usual dose in adults is 10 to 20 mg, but larger doses may be necessary depending on the clinical response.
Elderly or weakened patients
The doses administered should not be higher than half of the usually recommended doses.
Patients in this group should be regularly monitored at the beginning of treatment to minimize the doses administered and (or) the frequency of administration, in order to avoid overdose due to accumulation of the medicine.
Use in children
Status epilepticus, convulsions in the course of poisoning, febrile convulsions: 0.2 mg/kg to 0.3 mg/kg intravenously or intramuscularly, or 1 mg per year of age.
Tetanus: the same dosage as in adults.
Preoperative or pre-diagnostic procedure sedation: 0.2 mg/kg.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to RelaniumDosage form: Tablets, 2 mgActive substance: diazepamManufacturer: Santa S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 10 mg/2 mlActive substance: diazepamManufacturer: AS GrindeksPrescription not required
Alternatives to Relanium in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Relanium in Spain
Alternative to Relanium in Ukraine
Online doctors for Relanium
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Relanium – subject to medical assessment and local rules.









