
Paracetamol Forte Apteo Med
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Paracetamol Forte Apteo Med

How to use Paracetamol Forte Apteo Med
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Paracetamol, 40 mg/ml, oral suspension
Paracetamolum
Read the leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
This medicine should always be taken exactly as described in the patient leaflet or as directed by a doctor or pharmacist.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you need advice or additional information, consult a pharmacist.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in the leaflet, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
- If there is no improvement after 2 days or the patient feels worse, they should contact their doctor.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Paracetamol and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Paracetamol
- 3. How to take Paracetamol
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Paracetamol
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Paracetamol and what is it used for
Paracetamol contains paracetamol. Paracetamol is a pain-relieving and antipyretic medicine used to treat mild to moderate pain and/or fever.
Paracetamol is used for the short-term, symptomatic treatment of fever (high temperature) and/or mild to moderate pain (e.g., headache, pain and/or fever in the course of flu or cold, earache, toothache, painful teething, menstrual pain, muscle and bone pain, pain and/or fever associated with post-vaccination reaction, as a pain reliever before and after surgical procedures (e.g., pain after tonsillectomy)).
Paracetamol is used to treat mild to moderate pain and/or fever in infants (over 3 months), children, adolescents, and adults (including the elderly).
In children under 3 months, the medicine is used only on the advice of a doctor.
If there is no improvement after 2 days of taking the medicine or the patient feels worse, they should contact their doctor.
2. Important information before taking Paracetamol
When not to take Paracetamol
- if the patient is hypersensitive (allergic) to paracetamol or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- if the patient has severe liver disease.
Warnings and precautions
The medicine contains paracetamol.
Due to the risk of overdose, do not take Paracetamol at the same time as other medicines containing paracetamol, and do not take higher doses than recommended. In case of overdose, consult a doctor immediately, even if the patient feels well. Taking a multiple daily dose of paracetamol can lead to severe, life-threatening liver damage; in such cases, there may be no loss of consciousness. However, medical advice should be sought immediately. See also section 3 "Taking a higher dose of Paracetamol than recommended".
Before taking Paracetamol, discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist.
Consult a doctor or pharmacist before taking Paracetamol:
- if the patient has kidney function disorders,
- if the patient has liver disease (including Gilbert's syndrome, which causes yellowing of the skin and/or eyes),
- if the patient is taking other medicines that affect liver function,
- if the patient has a deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase,
- if the patient has hemolytic anemia (abnormal breakdown of red blood cells),
- if the patient has alcoholism,
- if the patient is dehydrated or chronically malnourished.
While taking Paracetamol, inform your doctor immediately if the patient experiences severe diseases, including severe kidney function disorders or sepsis (when bacteria and their toxins circulate in the blood, leading to organ damage) or malnutrition, chronic alcoholism, or when the patient is also taking flucloxacillin (an antibiotic). In these situations, patients have developed a severe condition called metabolic acidosis (a blood and fluid disorder), which requires urgent treatment (see section 2).
Metabolic acidosis symptoms may include: severe breathing difficulties, including rapid deep breathing, drowsiness, nausea (nausea) and vomiting.
Incorrect use of large amounts of painkillers for a long time can cause headaches. Do not treat these headaches with higher doses of Paracetamol.
Long-term use may cause kidney damage, including tissue destruction (renal papillary necrosis).
Do not take or give Paracetamol to a child without consulting a doctor or pharmacist in the following cases:
- high fever (above 39°C),
- fever lasting longer than 3 days,
- fever that disappears and then returns (recurring fever).
These situations may require evaluation and treatment determined by a doctor or pharmacist.
Paracetamol and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines the patient is taking, has recently taken, or plans to take. This is especially important when taking:
- warfarin (an anticoagulant),
- probenecid (a medicine used to treat gout),
- glycopyrronium and propanteline (anticholinergic medicines that may reduce paracetamol absorption),
- antiepileptic medicines, such as carbamazepine, phenobarbital, and phenytoin,
- sedatives,
- rifampicin (a medicine used to treat tuberculosis),
- chloramphenicol (an antibiotic),
- zidovudine (an antiviral medicine used to treat AIDS),
- flucloxacillin (an antibiotic), due to the serious risk of blood and fluid disorders (called metabolic acidosis), which must be urgently treated (see section 2).
Paracetamol is a common ingredient in many medicines in combination with other active substances. This fact should be taken into account to avoid exceeding the maximum daily dose.
Do not take Paracetamol at the same time as medicines that delay gastric emptying (e.g., propanteline) or accelerate it (e.g., metoclopramide and domperidone).
When taking cholestyramine (a medicine that lowers blood cholesterol levels), it is recommended to take Paracetamol 1 hour before or 4 hours after taking cholestyramine.
Taking Paracetamol with food, drink, and alcohol
Paracetamol is a ready-to-use medicine and can be taken with food and drink. Do not drink alcohol while taking Paracetamol. Alcohol may increase the toxicity of paracetamol in the liver.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a baby, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
During pregnancy, before taking any medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
Pregnancy
Paracetamol can be used during pregnancy if clinically justified. Take the smallest possible recommended dose, for the shortest possible time, and as infrequently as possible. Consult a doctor if the pain and/or fever do not decrease or if the patient needs to take the medicine more frequently. During pregnancy, paracetamol should not be taken in combination with other medicines.
Breastfeeding
After oral administration, paracetamol passes into breast milk. However, in principle, there is no need to interrupt breastfeeding during treatment with Paracetamol, as no adverse effects on breastfed infants have been reported so far.
Driving and using machines
Paracetamol does not affect the ability to drive or use machines. However, if the patient experiences slight drowsiness and dizziness as side effects, they should not drive vehicles or operate machines.
Paracetamol contains sucrose, methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218), propyl parahydroxybenzoate (E216), ethanol, and sodium
This medicine contains sucrose (500 mg/ml). If the patient has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, they should consult their doctor before taking the medicine.
A dose above 10 ml of oral suspension contains more than 5 g of sucrose per dose, which should be considered in patients with diabetes. Sucrose may be harmful to teeth.
This medicine contains 0.68 mg/ml of methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218) and 0.12 mg/ml of propyl parahydroxybenzoate (E216), which may cause allergic reactions (possible late reactions).
This medicine contains 2.25 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per 1 ml of suspension, which is equivalent to 191.25 mg/85 ml (0.225% w/v). The amount of alcohol in 85 ml of this medicine is equivalent to less than 4.78 ml of beer or 1.91 ml of wine. The small amount of alcohol in this medicine will not have noticeable effects.
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per ml, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to take Paracetamol
This medicine should always be taken exactly as described in the patient leaflet or as directed by a doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
The dose depends on the patient's age and weight. The usual single dose is 10-20 mg/kg of body weight, up to a maximum of 60 mg/kg of body weight per day.
Paracetamol can be given at intervals of 6 to 8 hours, up to:
- 3-4 times a day, provided that the maximum daily dose is not exceeded.
Do not take with other medicines containing paracetamol due to the risk of overdose.
Instructions for sample dosing:
Volume of a single dose of the medicine (single dose of paracetamol)
Maximum daily dose is 60 mg/kg of body weight
Body weight
Volume of the medicine (paracetamol dose in mg)
15 mg/kg of body weight every 6 hours 20 mg/kg of body weight every 8 hours (maximum 4 times a day) (maximum 3 times a day)
times a day)
times a day)
3 kg
1.0 ml
(40 mg)
1.5 ml
(60 mg)
4.5 ml
(180 mg)
6.0 ml
(240 mg)
4 kg
1.5 ml
(60 mg)
2.0 ml
(80 mg)
7.5 ml
(300 mg)
5 kg
1.75 ml
(70 mg)
2.5 ml
(100 mg)
3.0 ml
(120 mg)
9.0 ml
(360 mg)
6 kg
2.25 ml
(90 mg)
| 7 kg | 2.5 ml (100 mg) | 3.5 ml (140 mg) | 10.5 ml (420 mg) |
| 8 kg | 3.0 ml (120 mg) | 4.0 ml (160 mg) | 12.0 ml (480 mg) |
| 9 kg | 3.25 ml (130 mg) | 4.5 ml (180 mg) | 13.5 ml (540 mg) |
| 10 kg | 3.75 ml (150 mg) | 5.0 ml (200 mg) | 15.0 ml (600 mg) |
| 11-12 kg | 4.0 to 4.5 ml (160 to 180 mg) | 5.5 to 6.0 ml (220 to 240 mg) | 16.5 to 18 ml (660 to 720 mg) |
| 13-15 kg | 4.75 to 5.5 ml (190 to 220 mg) | 6.5 to 7.5 ml (260 to 300 mg) | 19.5 to 22.5 ml (780 to 900 mg) |
| 16-18 kg | 6.0 to 6.75 ml (240 to 270 mg) | 8.0 to 9.0 ml (320 to 360 mg) | 24.0 to 27.0 ml (960 to 1080 mg) |
| 19-21 kg | 7.0 to 7.75 ml (280 to 310 mg) | 9.5 to 10.5 ml (380 to 420 mg) | 28.5 to 31.5 ml (1140 to 1260 mg) |
| 22-25 kg | 8.25 to 9.25 ml (330 to 370 mg) | 11.0 to 12.5 ml (440 to 500 mg) | 33.0 to 37.5 ml (1320 to 1500 mg) |
| 26-29 kg |
| 13.0 to 14.5 ml (520 to 580 mg) | 39.0 to 43.5 ml (1560 to 1740 mg) |
| 30-32 kg | 11.25 to 12.0 ml (450 to 480 mg) | 15.0 to 16.0 ml (600 to 640 mg) | 45.0 to 48.0 ml (1800 to 1920 mg) |
5 ml (full oral syringe) of oral suspension = 200 mg of paracetamol
6 ml (full oral syringe) of oral suspension = 240 mg of paracetamol
When taking other medicines containing paracetamol, be careful not to exceed the maximum daily dose of paracetamol.
The above dosing is for guidance only and the doctor's or pharmacist's recommendations should be taken into account. In children under 3 months, the medicine is used only on the advice of a doctor. If there is no improvement after 2 days of taking the medicine or the patient feels worse, they should contact their doctor.
Duration of treatment
If there is no improvement after 2 days of taking the medicine or the patient feels worse, they should contact their doctor.
Method and route of administration
Oral administration.
Shake the bottle before use. Inside the packaging, there is a measuring syringe with a scale for accurate dosing.
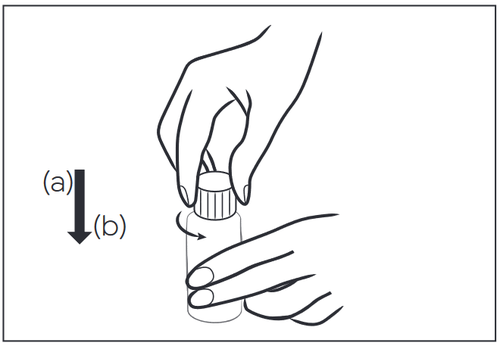
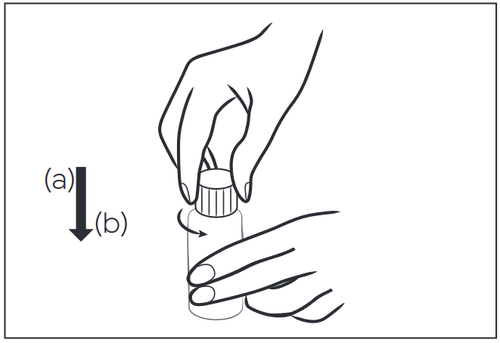
- 1. Unscrew the child-resistant cap by pressing down (a) and turning in the opposite direction of the arrow (b).
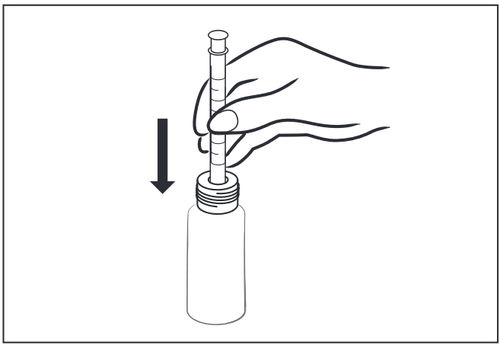
- 2 – Insert the clean, dry measuring syringe into the bottle until it is secured on the lower part of the adapter.
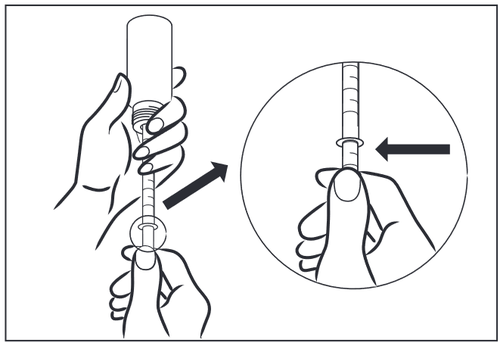
- 3 – To fill the syringe without air bubbles, carefully turn the bottle upside down. Hold the measuring syringe and slowly pull the plunger down until the desired dose in milliliters (ml) is reached. If air bubbles appear or the desired dose is exceeded, you can completely or partially return the syrup to the bottle by pulling the plunger up and re-dosing. If it is necessary to administer more than 5 ml, fill the syringe several times as needed.
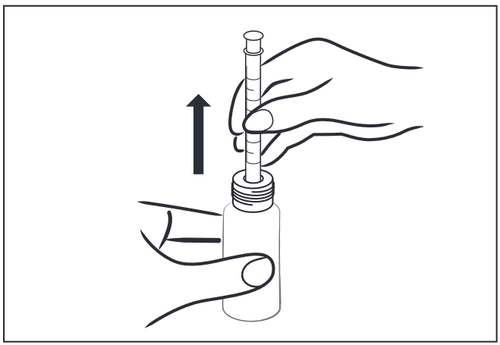
- 4 – Straighten the bottle with the inserted syringe and remove it, twisting and pulling the syringe out of the bottle.
Bottle without syringe adapter
- 1 – Unscrew the child-resistant cap by pressing down (a) and turning in the opposite direction of the arrow (b).
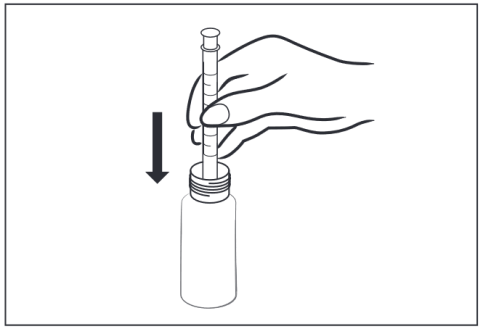
- 2 – Insert the clean, dry measuring syringe into the bottle and submerge it in the suspension.
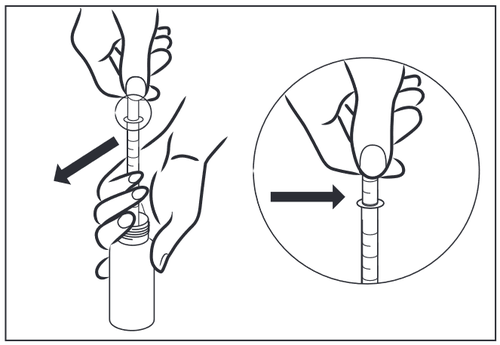
- 3 – Hold the measuring syringe and slowly pull the plunger up until the desired dose in milliliters (ml) is reached. If air bubbles appear or the desired dose is exceeded, you can completely or partially return the syrup to the bottle. If it is necessary to administer more than 5 ml, fill the syringe several times as needed.
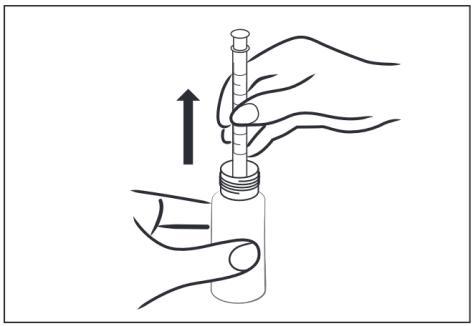
- 4 – Remove the syringe from the bottle.
The syrup can be administered directly into the child's mouth using the syringe or with a spoon.
When administering directly into the mouth, the child should be properly positioned. It is best to slowly empty the syringe into the inner side of the cheek. To avoid choking, adjust the rate of emptying the syringe to the child's swallowing rate.
After administration, clean the syringe. To do this, completely disassemble the syringe. Both parts should be thoroughly rinsed with hot water and then dried.
Special patient groups
Patients with liver, kidney, or Gilbert's syndrome problems should consult their doctor to determine the appropriate dose and intervals between doses.
Taking a higher dose of Paracetamol than recommended
In case of taking a higher dose of the medicine than recommended, consult a doctor immediately, even if the patient feels well. If the overdose occurred less than 1 hour ago, induce vomiting. Immediately consult a doctor, as specialized treatment may be necessary in a hospital setting.
Symptoms may include: nausea, vomiting, excessive sweating, drowsiness, and general weakness. These symptoms may resolve the next day, despite the fact that liver damage is starting to develop, which will then become apparent with abdominal distension, return of nausea, and jaundice.
Other symptoms may include: tremors, restlessness, insomnia, increased blood pressure, significant acceleration of heart rate, paleness of the skin, urinary retention. Death may occur.
Missing a dose of Paracetamol
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose, but take the dose of Paracetamol at the usual time.
If you have any further doubts about taking this medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Paracetamol can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Stop taking the medicine and consult a doctor if the patient experiences swelling of the face, especially around the mouth (tongue and/or throat), difficulty breathing, sweating, nausea, or a sudden drop in blood pressure. These symptoms may indicate a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction, which is very rare (affects less than 1 in 10,000 people).
The following side effects may occur:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- mild drowsiness,
- nausea,
- vomiting.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- dizziness,
- drowsiness,
- nervousness,
- burning sensation in the throat,
- diarrhea,
- abdominal pain (including cramps and heartburn),
- constipation,
- headache,
- increased sweating,
- decreased body temperature.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- redness of the skin.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- blood disorders (reduced platelet count, reduced white blood cell count, sometimes severe; overall decrease in all blood components),
- breathing difficulties (analgesic-induced asthma) in more sensitive individuals,
- allergic reactions. Very rare cases of severe skin reactions have been reported.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Elevated liver function test values, particularly transaminases.
- A serious condition that can cause acidification of the blood (called metabolic acidosis), in patients with severe disease taking paracetamol (see section 2).
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including those not listed in the leaflet, inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products: Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel. +48 22 49 21 301, fax +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Paracetamol
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature below 30°C.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and on the label of the bottle after "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Shelf life after first opening: 6 months.
Do not use this medicine if signs of deterioration are visible.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Paracetamol contains
- The active substance of the medicine is paracetamol. 1 ml of oral suspension contains 40 mg of paracetamol.
- The other ingredients are: citric acid monohydrate, sodium citrate, sucrose, methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218), propyl parahydroxybenzoate (E216), xanthan gum, purified water, orange flavor (natural flavors, artificial flavors, ethanol, butylhydroxyanisole (E320)).
What Paracetamol looks like and what the package contains
Paracetamol is a viscous liquid with a white to almost white uniform appearance, characteristic odor, and orange flavor.
Paracetamol is supplied in a type III orange glass bottle containing 85 ml of oral suspension with a child-resistant HDPE/PP/LDPE cap, an oral syringe of 5 ml capacity with a scale graduated every 0.25 ml, and instructions for opening in a cardboard box.
Paracetamol is supplied in a type III orange glass bottle containing 85 ml of oral suspension with a child-resistant PP cap, an oral syringe of 6 ml capacity with a scale graduated every 0.25 ml, a syringe adapter, and instructions for opening in a cardboard box.
Marketing authorization holder
Synoptis Pharma Sp. z o.o.
ul. Krakowiaków 65
02-255 Warsaw
tel. +48 607 696 231
Manufacturer
Laboratórios Basi – Indústria Farmacêutica, S.A.
Parque Industrial Manuel Lourenço Ferreira
Lotes 8, 15 e 16
3450-232 Mortágua
Portugal
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterLaboratórios Basi – Indústria Farmaceutica, S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Paracetamol Forte Apteo MedDosage form: Tablets, 500 mgActive substance: paracetamolManufacturer: Farmaceutyczna Spółdzielnia Pracy "Galena"Prescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 300 mgActive substance: paracetamolManufacturer: Farmaceutyczna Spółdzielnia Pracy "Galena"Prescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 325 mgActive substance: paracetamolManufacturer: US Pharmacia Sp. z o.o.Prescription not required
Alternatives to Paracetamol Forte Apteo Med in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Paracetamol Forte Apteo Med in Spain
Alternative to Paracetamol Forte Apteo Med in Ukraine
Online doctors for Paracetamol Forte Apteo Med
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Paracetamol Forte Apteo Med – subject to medical assessment and local rules.















