
Oxinador
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Oxinador

How to use Oxinador
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Oxynador, 10 mg + 5 mg, prolonged-release tablets
Oxynador, 20 mg + 10 mg, prolonged-release tablets
Oxynador, 40 mg + 20 mg, prolonged-release tablets
Oxycodone hydrochloride + naloxone hydrochloride
Read the leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Oxynador and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Oxynador
- 3. How to take Oxynador
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Oxynador
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Oxynador and what is it used for
Oxynador is a prolonged-release tablet, which means that the active substances are released from the tablet over a prolonged period. Their effect lasts for 12 hours. These tablets can only be used in adults.
Pain relief
Oxynador is indicated for the treatment of severe pain that can only be adequately controlled with opioid analgesics.
How the tablets work to relieve pain
Oxynador contains oxycodone hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride as active substances. Oxycodone hydrochloride is responsible for the analgesic effect of Oxynador and is a strong opioid analgesic. The second active substance of Oxynador, naloxone hydrochloride, is intended to alleviate some of the side effects that occur during treatment with opioid analgesics.
2. Important information before taking Oxynador
When not to take Oxynador
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Oxynador, consult a doctor or pharmacist:
- in the case of elderly and frail patients,
Breathing difficulties during sleep
Oxynador may cause breathing difficulties related to sleep, such as sleep apnea (pauses in breathing during sleep) and sleep-related hypoxemia (low oxygen levels in the blood). Symptoms may include pauses in breathing during sleep, waking up due to shortness of breath, difficulty falling asleep, or excessive daytime sleepiness. If the patient or another person observes such symptoms, they should contact a doctor. The doctor may recommend reducing the dose of the medicine.
Tolerance, dependence, and addiction
This medicine contains oxycodone, which is an opioid. Repeated use of opioid medicines can lead to reduced effectiveness of the medicine (the patient gets used to it, which is called tolerance). Repeated use of Oxynador may lead to dependence and abuse, which can lead to life-threatening overdose. The risk of these side effects may increase with increasing dose and longer treatment duration.
- The patient or someone in their family has previously abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription drugs, or illicit drugs;
- The patient smokes;
- The patient has had mood problems (depression, anxiety, or personality disorders) or has been treated by a psychiatrist for other mental illnesses.
If the patient notices any of the following symptoms while taking Oxynador, it may indicate that they are developing tolerance to the medicine or are becoming dependent:
- The patient needs to take the medicine for longer than the doctor recommended.
- The patient needs to take a higher dose than recommended.
- The patient uses the medicine for reasons other than those recommended by the doctor, e.g., "to feel calm" or "to help with sleep".
- The patient has repeatedly tried to stop or control the use of the medicine but has been unsuccessful.
- The patient feels unwell after stopping the medicine and feels better after taking it again ("withdrawal symptoms").
If the patient observes any of these symptoms, they should contact their doctor to discuss the best treatment path, including when to stop taking the medicine and how to safely stop treatment (see section 3 "Stopping Oxynador treatment").
Incorrect use of Oxynador tablets
The tablets are not suitable for treating withdrawal symptoms. Never abuse Oxynador, especially if you are dependent on drugs. In people dependent on substances such as heroin, morphine, or methadone, abusing these tablets can cause severe withdrawal symptoms because they contain naloxone. Existing withdrawal symptoms may worsen.
Do not misuse these tablets by dissolving and injecting the contents of the tablets (e.g., into blood vessels). The tablets contain talc, which can cause local tissue breakdown (necrosis) and changes in lung tissue (pulmonary granulomas). Such abuse can also lead to other serious consequences and even death.
Taking these tablets may result in a positive test for stimulants (doping). Using Oxynador as a stimulant can be life-threatening.
Oxynador and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
The risk of side effects increases if you take antidepressant medicines (such as citalopram, duloxetine, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, venlafaxine). These medicines may interact with oxycodone, which can cause the following symptoms: involuntary, rhythmic muscle contractions, including muscles that control eye movements, agitation, excessive sweating, tremors, increased reflexes, increased muscle tone, and elevated body temperature above 38°C.
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor.
Taking opioids, including oxycodone hydrochloride, and sedative medicines such as benzodiazepines or similar medicines, increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory failure), coma, and can be life-threatening. Therefore, taking these medicines together should only be considered when other treatment options are not possible.
If your doctor prescribes Oxynador with sedative medicines, they should limit the dose and duration of concurrent use.
Tell your doctor about all sedative medicines you are taking and follow your doctor's dosage instructions carefully. It may be helpful to inform friends or relatives to be aware of the above symptoms. If such symptoms occur, contact your doctor.
Examples of sedative medicines or medicines with similar effects are:
- other strong painkillers (opioids);
- medicines used to treat epilepsy, pain, and anxiety, such as gabapentin and pregabalin;
- sleeping pills and sedatives (including benzodiazepines and anxiolytics)
- medicines used to treat depression;
- medicines used to treat allergies, motion sickness, or nausea (antihistamines or antiemetics);
- medicines used to treat mental or psychiatric disorders (antipsychotics containing phenothiazines, neuroleptics);
- muscle relaxants;
- medicines used to treat Parkinson's disease.
If you take these tablets and other medicines at the same time, the effect of both the tablets and the medicines may change.
Tell your doctor if you are taking medicines such as:
- medicines that reduce blood clotting (coumarin derivatives), as the blood clotting time may be prolonged or shortened;
- macrolide antibiotics (e.g., clarithromycin, erythromycin, or telithromycin);
- azole antifungal medicines (such as ketoconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole, or posaconazole);
- protease inhibitors used to treat HIV (e.g., ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, and saquinavir);
- cimetidine (a medicine for stomach ulcers, indigestion, or heartburn);
- rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis);
- carbamazepine (used to treat seizures, shocks, or certain types of pain);
- phenytoin (used to treat seizures, shocks, or certain types of pain);
- St. John's Wort (also known as Hypericum perforatum);
- quinidine (a medicine for heart rhythm disorders).
No interaction is expected between Oxynador and paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid, or naltrexone.
Oxynador with food, drink, and alcohol
Drinking alcohol while taking Oxynador may cause drowsiness or increase the risk of serious side effects, such as shallow breathing with a risk of apnea and loss of consciousness. It is not recommended to drink alcohol while taking Oxynador. You should avoid drinking grapefruit juice while taking these tablets.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy
Avoid taking these tablets during pregnancy if possible. Taking prolonged-release tablets for a long time during pregnancy may cause withdrawal symptoms in the newborn. If oxycodone hydrochloride is used during delivery, it may cause respiratory depression in the newborn (slow and shallow breathing).
Breastfeeding
You should stop breastfeeding while taking these tablets. Oxycodone hydrochloride passes into breast milk. It is not known whether naloxone hydrochloride also passes into breast milk. Therefore, the risk to the breastfed infant cannot be excluded if the mother takes Oxynador for a long time.
Driving and using machines
Oxynador may affect your ability to drive and use machines. This effect can be expected especially at the beginning of treatment with Oxynador, after each dose increase, or when switching to another medicine. However, when you have been taking Oxynador for a long time at a fixed dose, this effect should subside.
Taking Oxynador has been associated with drowsiness and sudden sleep attacks. If you experience this side effect, you should not drive or operate machinery. You should discuss this with your doctor if you experience such side effects.
You should consult your doctor about the possibility of driving or operating machinery.
Oxynador contains lactose
The medicine contains lactose (milk sugar). If you have been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, you should consult your doctor before taking these tablets.
3. How to take Oxynador
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. If you are not sure, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Before starting treatment and regularly during treatment, your doctor will discuss with you the expected symptoms of taking Oxynador, when and for how long you should take it, when you should contact your doctor, and when you should stop taking Oxynador (see "Stopping Oxynador treatment").
Oxynador is available as prolonged-release tablets, which means that the active substances are released over a prolonged period. Their effect lasts for 12 hours.
Swallow the prolonged-release tablets whole, without chewing, with a sufficient amount of liquid (½ glass of water). You can take the tablets with or without food. Take the tablets every 12 hours, according to the established treatment plan (e.g., in the morning at 8:00 AM, in the evening at 8:00 PM). Do not break, chew, or crush the prolonged-release tablets (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions").
Unless the doctor has prescribed otherwise, the usual dose of Oxynador is:
Pain relief
Adults
The usual starting dose is 10 mg of oxycodone hydrochloride + 5 mg of naloxone hydrochloride in the form of prolonged-release tablets every 12 hours. Your doctor will decide on any necessary dose adjustments during treatment. Your doctor will adjust the dose according to the severity of the pain and your individual sensitivity. You should receive the smallest effective dose to control the pain. If you have previously taken opioid analgesics, treatment with Oxynador can be started at a higher dose.
The maximum daily dose is 160 mg of oxycodone hydrochloride and 80 mg of naloxone hydrochloride. If you need a higher dose, your doctor may recommend additional doses of oxycodone hydrochloride without naloxone hydrochloride. However, do not take more than 400 mg of oxycodone hydrochloride per day.
If additional doses of oxycodone hydrochloride without naloxone hydrochloride are taken, the beneficial effect of naloxone hydrochloride on bowel function may be disrupted. If your doctor switches you from Oxynador to another opioid medicine, bowel function may worsen.
If you experience pain before the next dose of Oxynador is due, you may need to take a fast-acting painkiller. These tablets are not intended for this purpose. In such cases, consult your doctor or pharmacist. Your doctor will decide what dose you should take daily and how to divide the daily dose into morning and evening doses.
If you feel that the effect of the tablets is too strong or too weak, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Elderly patients
Usually, dose adjustment is not necessary in elderly patients with normal liver and/or kidney function.
Impaired liver or kidney function
If you have impaired kidney function or mild liver failure, your doctor will prescribe these tablets with caution. If you have moderate to severe liver failure, you should not take these tablets (see also section 2 "When not to take Oxynador" and "Warnings and precautions").
Children and adolescents under 18 years of age
Oxynador has not been studied in children and adolescents under 18 years of age. The safety and efficacy of the medicine in children and adolescents have not been established. Therefore, Oxynador should not be used in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Method of administration
Oral use. Swallow the tablets whole (without chewing), with a sufficient amount of liquid (½ glass of water). You can take the tablets with or without food. Take the tablets every 12 hours, according to the established treatment plan (e.g., in the morning at 8:00 AM, in the evening at 8:00 PM). Do not break, chew, or crush the prolonged-release tablets (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions").
This only applies to single-dose blisters with a child-resistant closure:
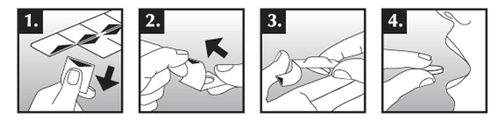
- 1. Hold the edge of the blister and separate one unit from the rest of the blister by gently tearing it off along the perforation.
- 2. Pull the edge of the foil and completely remove the foil.
- 3. Push the prolonged-release tablet out onto your hand.
- 4. Swallow the prolonged-release tablet whole, with a sufficient amount of liquid, with or without food.
Duration of treatment
As a rule, do not take these tablets for longer than necessary. If you are undergoing long-term treatment with these tablets, your treating doctor should regularly check if you still need them.
Taking a higher dose of Oxynador than recommended
If you have taken a higher dose of the tablets than recommended, contact your doctor immediately.
Overdose of the medicine may cause:
- pupil constriction,
- slow and shallow breathing (respiratory depression),
- a state similar to narcotic intoxication (drowsiness to loss of consciousness),
- reduced muscle tone (hypotonia),
- slow heart rate,
- decreased blood pressure,
- brain disorders (toxic leukoencephalopathy).
In severe cases, loss of consciousness (coma), water retention in the lungs, and circulatory collapse may occur, which can be fatal in some cases. Avoid activities that require increased attention, such as driving vehicles.
Missing a dose of Oxynador
or taking a lower dose than prescribed may result in inadequate pain relief. If you have missed a dose, follow these instructions:
- If there are 8 hours or more until the next dose is due: take the missed dose immediately and continue taking the medicine according to the established schedule.
- If there are less than 8 hours until the next dose is due: take the missed dose. Then, wait 8 hours before taking the next dose. Try to return to your original dosing schedule (e.g., 8:00 AM and 8:00 PM). Do not take more than one dose in 8 hours.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping Oxynador treatment
Do not stop taking Oxynador without consulting your doctor. If treatment is no longer necessary, you should gradually reduce the daily dose after consulting your doctor. This way, you can avoid withdrawal symptoms such as restlessness, especially agitation, sweating, and muscle pain. If you have any further doubts about taking these tablets, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Oxynador can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Important information about side effects and what to do if they occur:
If you experience any of the following side effects, contact your doctor immediately.
Shallow breathing (respiratory depression) is the main risk associated with opioid overdose. It usually occurs in elderly and frail patients. Opioids can also cause a severe drop in blood pressure in sensitive patients.
The following side effects have been observed in patients treated for pain:
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- abdominal pain
- constipation
- diarrhea
- dry mouth
- indigestion
- vomiting
- nausea
- bloating (gas)
- decreased appetite to loss of appetite
- dizziness or "spinning" sensation
- headache
- hot flashes
- fatigue or exhaustion
- feeling of unusual weakness
- itching
- skin reactions, rash
- sweating
- dizziness
- sleep disturbances
- sleepiness
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- abdominal distension
- abnormal thinking
- restlessness
- disorientation
- depression
- anxiety
- chest tightness, especially if you have coronary artery disease
- decreased blood pressure
- withdrawal symptoms, e.g., agitation
- fainting
- feeling of lack of energy
- thirst
- taste disturbances
- palpitations
- biliary colic
- chest pain
- general malaise
- pain
- swelling of hands, ankles, and feet
- concentration problems
- speech difficulties
- tremors
- breathing difficulties
- restlessness, especially agitation
- chills
- increased liver enzyme activity
- increased blood pressure
- decreased libido
- runny nose
- cough
- hypersensitivity/allergic reactions
- weight loss
- accidents
- increased urge to urinate
- muscle spasms
- muscle twitching
- muscle pain
- vision disturbances
- seizures (especially in people with a history of seizure disorders or predisposition to seizures)
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- increased heart rate
- addiction to the medicine
- changes in teeth
- weight gain
- yawning
Unknown(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- aggression
- euphoric mood
- excessive sleepiness
- erectile dysfunction
- nightmares
- hallucinations
- shallow breathing
- urination difficulties
- tingling sensation (numbness and tingling)
- belching
- sleep apnea (pauses in breathing during sleep).
Known side effects of the active substance oxycodone hydrochloride when not combined with naloxone hydrochloride:
Oxycodone may cause breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), pupil constriction, bronchial spasms, and smooth muscle spasms, as well as inhibition of the cough reflex.
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- mood and personality changes (e.g., depression, feeling extremely happy)
- decreased activity
- increased activity
- urination difficulties
- hiccups
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- concentration problems
- migraines
- increased muscle tone
- involuntary muscle contractions
- abnormal bowel function (intestinal obstruction)
- dry skin
- tolerance to the medicine
- decreased sensitivity to pain and touch
- coordination problems
- voice changes (hoarseness)
- fluid retention
- hearing problems
- mouth ulcers
- swallowing difficulties
- toothache
- perception disturbances (e.g., hallucinations, derealization)
- skin redness
- dehydration
- agitation
- decreased sex hormone levels, which can affect sperm production in men or the menstrual cycle in women
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- itchy rash (hives)
- infections, such as herpes (which can cause blisters around the mouth or genitals)
- increased appetite
- black (tarry) stools
- bleeding gums
Unknown(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- severe generalized allergic reactions (anaphylactic reactions)
- increased sensitivity to pain
- amenorrhea
- neonatal withdrawal syndrome
- bile duct problems: disorders affecting the bile duct sphincter, which can cause severe abdominal pain (bile duct disorders)
- tooth decay
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. You can also report side effects directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products: Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. You can also report side effects to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Oxynador
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging after "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month. The batch number is stated on the packaging after "Lot". Do not store above 30°C. Keep the medicine in its original packaging to protect it from moisture. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Oxynador contains
- The active substances of Oxynador are oxycodone hydrochloride and naloxone hydrochloride. 10 mg + 5 mg, prolonged-release tablets Each prolonged-release tablet contains 10 mg of oxycodone hydrochloride, equivalent to 9 mg of oxycodone, and 5 mg of naloxone hydrochloride as 5.45 mg of naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate, equivalent to 4.5 mg of naloxone. 20 mg + 10 mg, prolonged-release tablets Each prolonged-release tablet contains 20 mg of oxycodone hydrochloride, equivalent to 18 mg of oxycodone, and 10 mg of naloxone hydrochloride as 10.9 mg of naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate, equivalent to 9 mg of naloxone. 40 mg + 20 mg, prolonged-release tablets Each prolonged-release tablet contains 40 mg of oxycodone hydrochloride, equivalent to 36 mg of oxycodone, and 20 mg of naloxone hydrochloride as 21.8 mg of naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate, equivalent to 18 mg of naloxone.
- Other ingredients are hydroxypropylcellulose, ethylcellulose, glycerol distearate, lactose monohydrate, talc, and magnesium stearate, and in the tablet coating: polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide (E 171), macrogol 3350, talc, iron oxide red (E 172) - only in 20 mg + 10 mg tablets, and iron oxide yellow (E 172) - only in 40 mg + 20 mg tablets. See section 2 "Oxynador contains lactose".
What Oxynador looks like and contents of the pack
10 mg + 5 mg, prolonged-release tablets (tablets): white, oval, slightly biconvex, film-coated prolonged-release tablets with "10" embossed on one side of the tablet (dimensions: 9.5 mm x 4.5 mm)
20 mg + 10 mg, prolonged-release tablets (tablets): light pink, oval, slightly biconvex, film-coated prolonged-release tablets with "20" embossed on one side of the tablet (dimensions: 9.5 mm x 4.5 mm)
40 mg + 20 mg, prolonged-release tablets (tablets): brown-yellow, capsule-shaped, slightly biconvex, film-coated prolonged-release tablets with "40" embossed on one side of the tablet (dimensions: 14.0 mm x 6.0 mm)
10 mg + 5 mg:
Packaging:10, 14, 20, 28, 30, 50, 56, 60, 90, 98, 100, or 112 prolonged-release tablets in child-resistant blisters, in a cardboard box.
20 mg + 10 mg, 40 mg + 20 mg:
Packaging:10, 20, 28, 30, 50, 56, 60, 90, 98, 100, or 112 prolonged-release tablets in child-resistant blisters, in a cardboard box.
This only applies to single-dose blisters with a child-resistant closure:
10 mg + 5 mg:
Packaging:10x1, 14x1, 20x1, 28x1, 30x1, 50x1, 56x1, 60x1, 90x1, 98x1, 100x1, or 112x1 prolonged-release tablet in single-dose child-resistant blisters, in a cardboard box.
20 mg + 10 mg, 40 mg + 20 mg:
Packaging:10x1, 20x1, 28x1, 30x1, 50x1, 56x1, 60x1, 90x1, 98x1, 100x1, or 112x1 prolonged-release tablet in single-dose child-resistant blisters, in a cardboard box.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
KRKA, d.d., Novo mesto, Šmarješka cesta 6, 8501 Novo mesto, Slovenia
Manufacturer
KRKA, d.d., Novo mesto, Šmarješka cesta 6, 8501 Novo mesto, Slovenia
TAD Pharma GmbH, Heinz-Lohmann-Straße 5, 27472 Cuxhaven, Germany
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
To obtain more detailed information on this medicine, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
KRKA-POLSKA Sp. z o.o.
ul. Równoległa 5
02-235 Warsaw
Tel. 22 57 37 500
Date of last revision of the leaflet:08.08.2024
| Belgium, Germany | Oxycodon/Naloxon Krka |
| Bulgaria | Адолакс |
| Czech Republic, Estonia | Noldoxen |
| Denmark, Finland, Sweden | Oxycodone/Naloxone Krka |
| Ireland | Nolxado |
| Croatia, Slovenia, Slovakia | Adolax |
| Hungary, Latvia | Oxynador |
| Lithuania, Romania | Dolnada |
| Portugal | Oxicodona + Naloxona TAD |
| United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) | Oxycodone hydrochloride/Naloxone hydrochloride |
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterKrka, d.d., Novo mesto TAD Pharma GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to OxinadorDosage form: Tablets, 5 mg + 2.5 mgActive substance: oxycodone and naloxonePrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 10 mg + 5 mgActive substance: oxycodone and naloxonePrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 20 mg + 10 mgActive substance: oxycodone and naloxonePrescription required
Alternatives to Oxinador in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Oxinador in Espanha
Online doctors for Oxinador
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Oxinador – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














