
Mig dla dzieci

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Mig dla dzieci

How to use Mig dla dzieci
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
MIG for children
20 mg/ml, oral suspension
For children with a body weight from 5 kg (from 6 months) to 29 kg (up to 9 years)
Ibuprofen
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
This medicine should always be used exactly as described in this patient leaflet or as directed by your doctor or pharmacist.
- You should keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you need advice or additional information, you should consult a pharmacist.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
- If there is no improvement after 3 days or if the patient feels worse, you should contact your doctor.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is MIG for children and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using MIG for children
- 3. How to use MIG for children
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store MIG for children
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is MIG for children and what is it used for
MIG for children is an anti-inflammatory and analgesic medicine (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, NSAID) with antipyretic properties.
MIG for children is used for the short-term symptomatic treatment of:
- Mild to moderate pain
- Fever
MIG for children is used in children with a body weight from 5 kg (from 6 months) to 29 kg (up to 9 years).
2. Important information before using MIG for children
When not to use MIG for children
- If the child is allergic to ibuprofen or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- If the patient has a history of bronchospasm, asthma, nasal polyps, angioedema, or skin reactions (hives) after taking acetylsalicylic acid or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- In unexplained bleeding disorders
- In active or recurrent peptic ulcer disease (gastric and/or duodenal ulcers) or gastrointestinal bleeding (two or more separate episodes of proven ulceration or bleeding)
- In cases of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation in the past, associated with previous NSAID treatment
- If the patient has cerebral hemorrhage (cerebrovascular bleeding) or other active bleeding
- In severe liver or kidney failure
- In severe heart failure
- In severe dehydration (significant loss of body fluids due to e.g. vomiting, diarrhea, or inadequate fluid intake)
- In the last three months of pregnancy.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with MIG for children, you should discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist.
If the patient has an infection - see below, section entitled "Infections".
Side effects can be minimized by using the smallest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms.
Gastrointestinal safety
You should avoid concomitant use of MIG for children with other NSAIDs, including so-called COX-2 inhibitors (selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors).
Elderly patients
The frequency of side effects during NSAID treatment, especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation, which can be fatal, is higher in the elderly. Therefore, during treatment in the elderly, careful medical monitoring is recommended.
Gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcer disease, and perforation
There have been reports of gastrointestinal bleeding, gastric and/or duodenal ulcers, and perforations, which can be fatal, with the use of all NSAIDs, occurring at any time during treatment, with or without warning symptoms and with or without previous serious gastrointestinal side effects.
The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, gastric and/or duodenal ulcers, and perforation increases with increasing NSAID doses in patients with a history of gastric and/or duodenal ulcers, especially if complicated by bleeding or perforation (see section 2. "When not to use MIG for children") and in the elderly. In such patients, treatment should be started with the smallest available doses.
In such patients, as well as in patients requiring concomitant administration of low-dose acetylsalicylic acid or other drugs that may increase the risk of gastrointestinal side effects, consideration should be given to concomitant use with drugs that have a protective effect on the gastric mucosa (e.g. misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors).
If the child has a history of gastrointestinal side effects, all unusual abdominal symptoms (especially gastrointestinal bleeding) should be reported, especially at the start of treatment.
Caution is advised when administering the drug to a child who is also taking drugs that may increase the risk of gastric ulcers or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants (e.g. warfarin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (used to treat depression), or antiplatelet agents (e.g. acetylsalicylic acid) (see section 2. "MIG for children and other medicines").
In the event of gastrointestinal bleeding or gastric and/or duodenal ulcers in a child, MIG for children should be discontinued. You should immediately inform your doctor if the child experiences any unusual abdominal symptoms.
NSAIDs should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease), as they may exacerbate the disease (see section 4. "Possible side effects").
Effect on the cardiovascular system
Taking anti-inflammatory/pain-relieving medicines like ibuprofen may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack or stroke, especially when used at high doses.
- Heart diseases, such as heart failure, angina pectoris (chest pain), if the patient has had a heart attack, bypass surgery, or if the patient has peripheral artery disease (poor blood circulation in the legs or feet due to narrowing or blockage of arteries) or if the patient has had any stroke (including "mini-stroke" or transient ischemic attack - "TIA")
- Hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol levels, if there is a history of heart disease or stroke in the patient's family, or if the patient smokes
During ibuprofen treatment, symptoms of allergic reactions to this medicine have been reported, including difficulty breathing, swelling of the face and neck (angioedema), chest pain.
In case of any of these symptoms, you should immediately stop taking MIG for children and contact your doctor or medical emergency services immediately.
Skin reactions
Severe skin reactions have been reported with ibuprofen use, such as exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). If the patient experiences any symptoms related to these severe skin reactions described in section 4, you should immediatelystop taking MIG for children and seek medical attention.
During chickenpox (varicella), it is recommended to avoid using MIG for children.
Infections
MIG for children may mask the symptoms of infection, such as fever and pain. Therefore, MIG for children may delay the use of appropriate treatment, which can lead to increased risk of complications. This has been observed in the course of bacterial pneumonia and bacterial skin infections associated with chickenpox. If the patient is taking this medicine during an infection, and the symptoms of the infection persist or worsen, you should immediatelyconsult a doctor.
Respiratory disorders
Caution is advised when administering MIG for children to patients with asthma or a history of asthma, as NSAIDs have been reported to cause bronchospasm in these patients.
Other notes
MIG for children should be used in children after careful consideration of the benefit-to-risk ratio:
- In certain congenital blood disorders (e.g. intermittent porphyria)
- In certain autoimmune disorders (systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease). There is an increased risk of developing aseptic meningitis (see section 4. "Possible side effects").
MIG for children can only be used under close medical supervision in the following cases:
- If the patient has gastrointestinal disorders or if the patient has a history of chronic inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease)
- In cases of high blood pressure or heart failure
- In cases of kidney or liver dysfunction
- In cases of dehydration
- Immediately after major surgical procedures
- In cases of allergies (e.g. skin reactions to other medicines, asthma, hay fever), in mild nasal polyps (nasal polyps), in chronic nasal congestion or in chronic respiratory diseases with airway obstruction
Very rarely, severe, acute hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. anaphylactic shock) have been observed.
After the first symptoms of severe hypersensitivity after administration of MIG for children, treatment should be immediatelydiscontinued and a doctor should be consulted.
Ibuprofen, the active substance of MIG for children, may occasionally inhibit platelet aggregation. Therefore, during treatment, patients with coagulation disorders should be closely monitored.
During long-term use of MIG for children, regular monitoring of liver enzymes, kidney function, and blood morphology is required.
Before surgical procedures, the doctor or dentist should be informed about the use of MIG for children.
Long-term use of painkillers for headache treatment may lead to worsening of the headache. If such a situation is detected or suspected, medical advice should be sought and treatment should be discontinued. The possibility of medication-overuse headache should be considered in patients suffering from frequent or daily headaches despite regular use (or due to the use) of painkillers.
Generally, habitual use of painkillers, especially combinations of several pain-relieving substances, can lead to permanent kidney damage and is associated with the risk of developing kidney failure (analgesic nephropathy).
Children and adolescents
There is a risk of kidney function disorder in dehydrated children and adolescents.
MIG for children and other medicines
You should tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines the patient is currently taking or has recently taken, as well as any medicines the patient plans to use.
MIG for children may affect the action of other medicines or other medicines may affect the action of MIG for children. For example:
- Anticoagulant medicines (e.g. acetylsalicylic acid, warfarin, ticlopidine)
- Blood pressure-lowering medicines (e.g. ACE inhibitors such as captopril, beta-blockers such as atenolol, angiotensin II receptor antagonists such as losartan).
Also, some other medicines may be affected or have an effect on MIG for children treatment.
Therefore, before using MIG for children with other medicines, you should always consult a doctor or pharmacist.
In particular, you should inform your doctor or pharmacist if the patient is taking:
- Digoxin (used to strengthen the heart), phenytoin (used to treat seizures), or lithium (used to treat certain mental disorders), as the levels of these medicines in the blood may increase. Monitoring of lithium, digoxin, and phenytoin levels in the blood is not generally required if ibuprofen is used as recommended (not longer than 3 days);
- Diuretics and antihypertensive medicines;
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (medicines used to treat heart failure and high blood pressure): increased risk of kidney function disorders;
- Potassium-sparing diuretics (certain diuretics): concomitant use may lead to increased potassium levels;
- Acetylsalicylic acid and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pain-relieving medicines, including COX-2 inhibitors (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (medicines used to treat depression), as well as corticosteroids (medicines containing cortisone): increased risk of gastric ulcers and bleeding;
- Low-dose acetylsalicylic acid: the antiplatelet effect may be weakened (see section 2. "Warnings and precautions");
- Anticoagulant medicines such as warfarin;
- Sulfonylurea derivatives (used to lower blood sugar levels): clinical studies have shown interactions between NSAIDs and sulfonylurea derivatives. During concomitant use, blood sugar levels should be monitored as a precaution;
- Probenecid or sulfinpyrazone (medicines used to treat gout): they may delay the elimination of ibuprofen from the body. This may lead to accumulation of ibuprofen in the body and enhancement of its side effects.
- Zidovudine (a medicine used to treat AIDS): increased risk of hemorrhages and bruising in patients with hemophilia infected with HIV;
- Methotrexate (a medicine used to treat cancer and certain rheumatic diseases): MIG for children should not be used within 24 hours before or after methotrexate administration. This may lead to increased methotrexate levels in the blood and enhancement of its side effects;
- Pemetrexed (a medicine used to treat cancer): concomitant use of pemetrexed with NSAIDs may enhance the effect of pemetrexed, so caution is advised when administering high doses of NSAIDs;
- Cyclosporin (an immunosuppressive medicine used e.g. after transplants and in the treatment of rheumatism): there is a risk of kidney damage;
- Tacrolimus (a medicine used to prevent transplant rejection): there is a risk of kidney damage;
- Quinolone antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin: concomitant use may increase the risk of seizures;
- CYP2C9 inhibitors such as voriconazole and fluconazole (medicines used to treat fungal infections): concomitant use of ibuprofen and CYP2C9 inhibitors may increase the exposure of the body to ibuprofen (a CYP2C9 substrate). In a study using voriconazole and fluconazole (CYP2C9 inhibitors), an increase in exposure to S(+)-ibuprofen by about 80-100% was observed. When concomitantly administering strong CYP2C9 inhibitors, consideration should be given to reducing the ibuprofen dose, especially if high doses of ibuprofen are administered concomitantly with voriconazole or fluconazole.
- Deferasirox (a medicine given to patients receiving long-term blood transfusions in certain types of anemia): concomitant use of deferasirox with NSAIDs (e.g. ibuprofen) may increase the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. Therefore, medical monitoring is necessary during concomitant use with NSAIDs;
in this regard, medical monitoring is necessary during concomitant use with NSAIDs;
Mifepristone (used to terminate pregnancy): if NSAIDs are used during days 8-12 after mifepristone administration, they may reduce the effectiveness of mifepristone;
MIG for children and alcohol
You should avoid consuming alcohol while using MIG for children. Some side effects, especially those related to the gastrointestinal tract or central nervous system, are more likely to occur when alcohol is consumed with MIG for children.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
You should not take MIG for children if you are in the last three months of pregnancy, as it may harm the unborn baby or cause complications during delivery. It may cause kidney and heart problems in the unborn baby.
It may increase the risk of bleeding in the mother and child and cause prolongation or delay of labor. During the first six months of pregnancy, you should not use MIG for children unless your doctor considers it absolutely necessary. If treatment is necessary during this period or when trying to conceive, the smallest dose should be used for the shortest possible time. From the 20th week of pregnancy, MIG for children may cause constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus or kidney problems in the unborn baby, which may lead to reduced amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios) if used for more than a few days. If treatment is necessary for a longer period, your doctor may recommend additional monitoring.
Breastfeeding
Only small amounts of ibuprofen and its metabolites pass into breast milk.
Since no harmful effects have been observed in infants to date, breastfeeding does not usually need to be discontinued during short-term use. However, during long-term use or when using high doses, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Driving and using machines
Since large doses of MIG for children may cause side effects from the central nervous system, such as fatigue and dizziness, reaction time may be affected and the ability to participate in traffic or operate machinery may be impaired. This is especially true when combined with alcohol.
The patient may lose the ability to react quickly and appropriately to unexpected or sudden situations. In this case, you should not drive a car or other vehicles! Do not operate machinery! Do not work without a secure footing!
MIG for children contains liquid maltitol (E 965)
If the child has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, you should consult a doctor before taking this medicine.
MIG for children contains sodium
The medicine contains 3.8 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per 1 ml. This corresponds to 0.2% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
MIG for children contains sodium benzoate (E 211)
The medicine contains 1 mg of sodium benzoate per 1 ml.
MIG for children contains benzyl alcohol
The medicine contains 0.0002 mg of benzyl alcohol per 1 ml.
Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions.
Do not give to small children (under 3 years) for more than a week without the advice of a doctor or pharmacist.
Pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and patients with kidney or liver dysfunction should consult a doctor before using the medicine, as large amounts of benzyl alcohol may accumulate in their bodies and cause side effects (so-called "metabolic acidosis").
3. How to use MIG for children
This medicine should always be used exactly as described in this patient leaflet or as directed by your doctor or pharmacist.
In case of doubt, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
You should use the smallest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms. If the symptoms of the infection (such as fever and pain) persist or worsen, you should immediatelyconsult a doctor (see section 2).
Dosage
The recommended dose is:
Body weight Single dose Maximum daily dose (24 hours)
5 kg - 6 kg
(Infants aged
(Age)
2.5 ml of oral suspension
7.5 ml of oral suspension
(corresponding to 50 mg
(corresponding to 150 mg
of ibuprofen)
7 kg - 9 kg
(Infants aged 6 -
- 8 months) of ibuprofen ) 2.5 ml of oral suspension 10 ml of oral suspension (corresponding to 50 mg (corresponding to 200 mg of ibuprofen)
10 kg - 15 kg
(Children aged 1 - 3 years)
11 months)
of ibuprofen)
15 ml of oral suspension
5 ml of oral suspension (corresponding
to 100 mg
(corresponding to 300 mg
of ibuprofen)
16 kg - 19 kg
(Children aged 4 - 5 years)
of ibuprofen)
22.5 ml of oral suspension
7.5 ml of oral suspension
(corresponding to 450 mg
of ibuprofen)
20 kg - 29 kg
(Children aged 6 - 9 years)
(corresponding to 150 mg
of ibuprofen)
30 ml of oral suspension
10 ml of oral suspension
(corresponding to 200 mg
(corresponding to 600 mg
of ibuprofen)
MIG for children is not recommended for use in children under 6 months of age or under 5 kg of body weight.
Intervals between doses should be at least 6 hours.
Do not exceed the recommended dose and duration of treatment (maximum 3 days).
Elderly patients
No special dose adjustment is required (see section 2. "Warnings and precautions").
Kidney or liver function disorders
In mild and moderate kidney or liver function disorders, dose reduction is not required.
Method of administration
Oral administration in children.
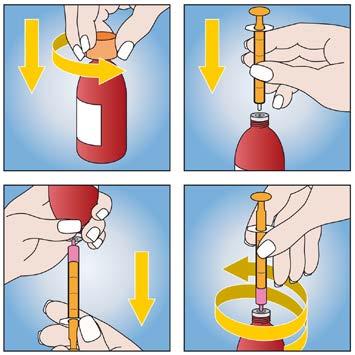
To facilitate accurate dosing, a measuring oral syringe (with 0.5 ml gradations up to 5 ml) is included with the packaging.
- 1. Before use, shake the bottle.
- 2. To open the bottle, press the cap and turn it in the direction indicated by the arrows.
- 3. Then, place the oral syringe in the bottle opening.
- 4. Turn the bottle upside down, holding the oral syringe, and pull the plunger until the required amount of medicine is obtained.
- 5. Turn the bottle right side up and remove the oral syringe, turning it gently.
- 6. To administer the suspension, place the tip of the syringe in the child's mouth and slowly press the plunger into the cylinder. The rate of administration should be adjusted to the child's swallowing rate.
After use, the bottle should be closed with the cap. Then, the plunger should be removed from the oral syringe cylinder, washed with warm water, and left to dry. The oral syringe should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
In some patients, mild gastrointestinal upset may occur after using MIG for children. If such discomfort occurs, the medicine should be given to the child during meals.
If the patient feels that MIG for children is too strong or too weak, they should talk to their doctor.
Duration of treatment
The medicine is intended for short-term use only.
If there is a need to take this medicine for more than 3 days or if symptoms worsen, you should consult a doctor.
Do not use MIG for children for more than 3 days without consulting a doctor or dentist.
Overdose of MIG for children
MIG for children should be taken as recommended by your doctor or as described in the dosing instructions in this leaflet. If the child's pain-relieving effect seems too weak, you should not increase the dose without consulting a doctor.
If the patient has taken more than the recommended dose of MIG for children or if the child has accidentally taken the medicine, you should always consult a doctor or go to the nearest hospital to get an opinion on the possible risk to health and advice on what to do.
Symptoms of overdose may include:
Symptoms of overdose may include nausea, stomach pain, vomiting (which may contain blood), headache, ringing in the ears, disorientation, and nystagmus. Additionally, gastrointestinal bleeding may occur. After taking a large dose, drowsiness, a feeling of impending fainting, chest pain, palpitations, loss of consciousness, seizures (mainly in children), weakness, and dizziness have been reported, as well as blood in the urine, low potassium levels in the blood, liver and kidney function disorders, respiratory depression, decreased blood pressure, cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes), feeling of cold, and breathing difficulties. There is no specific antidote.
Missed dose of MIG for children
You should not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
In case of any further doubts about using this medicine, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Possible side effects
The following side effects are all the side effects reported during ibuprofen use, including side effects reported during long-term use of ibuprofen in high doses in patients with rheumatic diseases. Side effects more frequent than very rare are side effects that occur during short-term use at daily doses not exceeding the maximum dose of 1200 mg of ibuprofen in the case of oral medicines and a maximum dose of 1800 mg of ibuprofen in the case of suppositories.
Regarding the following side effects, it should be noted that they usually show a dose-dependent relationship and are characterized by high individual variability.
The most commonly observed side effects are gastrointestinal disorders. Gastric and/or duodenal ulcers, perforation, or gastrointestinal bleeding may occur, sometimes leading to death, especially in the elderly (see section 2. "Warnings and precautions").
After administration of the medicine, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bloating, constipation, indigestion, abdominal pain, black stools, bloody vomiting, and oral mucosal ulceration (ulcerative stomatitis) have been reported, as well as exacerbation of inflammatory bowel diseases, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn's disease (see section 2. "Warnings and precautions").
Less commonly, gastritis (gastric mucosal inflammation) has been observed. The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding is dose- and duration-dependent.
Gastrointestinal side effects have been reported with NSAID use, including fluid retention, hypertension, and heart failure.
Taking medicines like MIG for children may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack (myocardial infarction) or stroke.
You should IMMEDIATELY STOPtaking this medicine and seek medical attention if the patient or child experiences any of the following side effects:
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- Symptoms of gastrointestinal bleedingsuch as severe stomach pain, blood in the stool, and/or black tarry stools, bloody vomiting or coffee-ground-like vomiting.
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- Symptoms of severe allergic reactionssuch as swelling of the face, tongue, or throat with constriction of the airways, difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, and a sudden drop in blood pressure, which can be life-threatening. These symptoms can occur even after a single dose of the medicine.
- Red, non-raised, target-like, or circular patches on the torso, often with blisters in the center, peeling of the skin, ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes. These severe skin reactions may be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis).
Frequency not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- Widespread rash, high fever, swollen lymph nodes, and an increased number of eosinophils (a type of white blood cell) (DRESS syndrome).
- A red, peeling rash with bumps under the skin and blisters, mainly in skin folds, on the torso, and upper limbs, with fever. Symptoms usually appear at the start of treatment (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis).
You should talk to your doctor and also read the instructions below if the patient or child experiences any of the following side effects:
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Gastrointestinal disorders, such as heartburn, stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and minor gastrointestinal bleeding, which may occasionally lead to anemia.
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- Allergic reactions with skin rashes and itching, as well as asthma attacks (with possible accompanying low blood pressure): in such cases, you should immediatelyinform your doctor and discontinue MIG for children.
- Central nervous system disorders, such as headache, dizziness, insomnia, overexcitement, irritability, or fatigue.
- Visual disturbances: in such cases, treatment should be discontinued and a doctor should be consulted.
- Gastric and/or duodenal ulcers, potentially with bleeding and perforation, oral mucosal ulceration (ulcerative stomatitis), exacerbation of inflammatory bowel diseases, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn's disease (see section 2. "Warnings and precautions").
- Various skin rashes.
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- Tinnitus, hearing loss.
Very rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people
- Asthma, bronchospasm (constriction of the airways), shortness of breath (dyspnea).
- Exacerbation of infections (e.g. development of necrotizing fasciitis) has been reported during treatment with some anti-inflammatory medicines
(non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including MIG for children).
Jałowego zapalenia opon mózgowych (aseptycznego zapalenia opon mózgowo-rdzeniowych), takie jak nasilony ból głowy,
nudności, wymioty, gorączka, sztywność karku i przymglenie świadomości. Pacjenci z
chorobami układu immunologicznego (toczniem rumieniowatym układowym, mieszaną
chorobą tkanki łącznej) wydają się być bardziej narażeni.
Jeśli podczas stosowania leku MIG dla dzieci, pojawią się lub zaostrzą objawy infekcji (np.
zaczerwienienie, obrzęk, nadmierne rozgrzanie, ból, gorączka), należy niezwłocznie
skontaktować się z lekarzem.
- Zaburzenia krwiotworzenia (niedokrwistość, leukopenia, małopłytkowość, pancytopenia, agranulocytoza). Pierwszymi objawami tych zaburzeń może być: gorączka, ból gardła, nadżerki błony śluzowej jamy ustnej, objawy podobne do objawów grypy, znaczne zmęczenie, krwawienia z nosa i krwawienia ze skóry. W takich przypadkach należy natychmiastodstawić lek i skonsultować się z lekarzem. Nie należy podejmować prób leczenia we własnym zakresie lekami przeciwbólowymi lub przeciwgorączkowymi.
- Ciężkie ogólne reakcje nadwrażliwości.
- Reakcje psychotyczne, depresja.
- Kołatanie serca (palpitacje), niewydolność serca, atak serca (zawał serca).
- Wysokie ciśnienie krwi (nadciśnienie tętnicze), zapalenie naczyń krwionośnych.
- Zapalenie przełyku, zapalenie trzustki, powstawanie błonowatych zwężeń w jelicie cienkim i grubym (błoniaste zwężenia jelit).
- Zaburzenia czynności wątroby, uszkodzenie wątroby, zwłaszcza podczas długotrwałego leczenia, niewydolność wątroby, ostre zapalenie wątroby. Podczas długotrwałego leczenia, należy regularnie wykonywać próby wątrobowe.
- Wypadanie włosów (łysienie).
- Zwiększenie gromadzenia się płynów w tkankach (obrzęki), zwłaszcza u pacjentów z nadciśnieniem tętniczym lub zaburzeniami czynności nerek, zespół nerczycowy (zatrzymanie płynów [obrzęki] oraz wydalanie białka z moczem), choroba nerek przebiegająca ze stanem zapalnym (śródmiąższowe zapalenie nerek), któremu może towarzyszyć ostra niewydolność nerek. Może również wystąpić uszkodzenie nerek (martwica brodawek nerkowych) oraz zwiększone stężenie kwasu moczowego we krwi. Zmniejszenie ilości wydalanego moczu, gromadzenie płynu w tkankach (obrzęki) jak również ogólne złe samopoczucie może być oznaką zaburzeń czynności nerek, a nawet niewydolności nerek. W razie wystąpienia lub zaostrzenia się któregokolwiek z wyżej wymienionych objawów, należy odstawić lek MIG dla dzieci i niezwłocznieskonsultować się z lekarzem.
Frequency not known: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- Chest pain, which may be a symptom of a potentially severe allergic reaction called Kounis syndrome.
- The skin becomes sensitive to light.
In exceptional cases, during chickenpox (varicella), severe skin and soft tissue infections and complications may occur (see also "very rare" regarding "exacerbation of infections").
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store MIG for children
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the bottle and carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
This medicine does not require any special storage precautions.
Shelf life after first opening the bottle: 6 months, do not store above 25°C.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What MIG for children contains
The active substance of MIG for children is ibuprofen.
1 ml of oral suspension contains 20 mg of ibuprofen.
The other ingredients are:
Sodium benzoate (E 211); citric acid anhydrous; sodium citrate; sodium saccharin; sodium chloride; hypromellose 15 cP; xanthan gum; liquid maltitol (E 965); glycerol (E 422); strawberry flavor (containing natural and identical to natural flavorings, natural flavors, corn maltodextrin, triethyl citrate [E 1505], propylene glycol, and benzyl alcohol);
purified water.
How the medicine MIG for children looks like and what the packaging contains
MIG for children is a white or almost white, viscous oral suspension.
MIG for children may be available in bottles of 100 ml or 200 ml of oral suspension.
A measuring cup (with a 0.5 ml scale up to 5 ml) is attached to the packaging.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Responsible entity and manufacturer
Responsible entity
Berlin-Chemie AG (Menarini Group)
Glienicker Weg 125
12489 Berlin
Germany
Manufacturer
Berlin-Chemie AG
Glienicker Weg 125
12489 Berlin
Germany
Laboratorios Alcalá Farma, S.L.
Avenida de Madrid, 82
28802 Alcalá de Henares - Madrid
Spain
To obtain more detailed information about this medicinal product, please contact
the local representative of the responsible entity:
Berlin-Chemie/Menarini Polska Sp. z o.o.
Tel.: +48 22 566 21 00
Fax: +48 22 566 21 01
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area
under the following names:
Bulgaria МИГ за деца
Estonia IBUSTAR
Germany Eudorlin Ibuprofen 20 mg/ml Suspension zum Einnehmen
Hungary Ibustar 20mg/ml belsőleges szuszpenzió gyermekek részére
Latvia Ibustar bērniem 100 mg/5 ml suspensija iekšķīgai lietošanai
Lithuania Ibustar 20mg / ml oral suspension, for children
Poland MIG for children
Romania MIG pediatric 20 mg/ml suspensie orală
Slovakia MIG Junior 2%
Date of last revision of the leaflet:01/2025
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterBerlin-Chemie AG LABORATORIOS ALCALÁ FARMA, S.L.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Mig dla dzieciDosage form: Suspension, 40 mg/mlActive substance: ibuprofenManufacturer: Laboratorios Basi - Industria Farmaceutica, S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 400 mgActive substance: ibuprofenPrescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 600 mgActive substance: ibuprofenManufacturer: Aristo Pharma GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Mig dla dzieci in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Mig dla dzieci in Hiszpania
Alternative to Mig dla dzieci in Ukraina
Online doctors for Mig dla dzieci
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Mig dla dzieci – subject to medical assessment and local rules.















