
How to use Meaxin
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Meaxin, 100 mg, tablets for oral suspension
Meaxin, 400 mg, tablets for oral suspension
Imatinib
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed to you by a doctor and is intended for your use only. Do not give it to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Meaxin and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Meaxin
- 3. How to take Meaxin
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Meaxin
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Meaxin and what is it used for
Meaxin is a medicine that contains the active substance imatinib. This medicine works by inhibiting the growth of abnormal cells in the course of diseases listed below. These include certain types of cancer.
Meaxin is indicated for the treatment of adult patients and children with:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)- a cancer that originates from white blood cells. White blood cells usually help the body fight infections. Chronic myeloid leukemia is a type of cancer in which certain abnormal white blood cells (called myeloid cells) begin to multiply uncontrollably.
- Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph-positive ALL)- a cancer that originates from white blood cells. Usually, white blood cells help the body fight infections. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a type of cancer in which certain abnormal white blood cells (called lymphoblasts) begin to multiply uncontrollably. Meaxin inhibits the growth of these cells.
Meaxin is also indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD)- a group of blood diseases in which certain white blood cells begin to multiply uncontrollably. Meaxin inhibits the growth of these cells in certain subtypes of these diseases.
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and (or) chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL)- blood diseases in which certain blood cells (called eosinophils) begin to multiply uncontrollably. Meaxin inhibits the growth of these cells in certain subtypes of these diseases.
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST)- a tumor of the stomach and intestines. GIST arises from the uncontrolled growth of connective tissue cells in these organs.
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)- a skin tumor and subcutaneous tissue in which certain cells begin to multiply uncontrollably. Meaxin inhibits the growth of these cells.
In the rest of the leaflet, abbreviations of the disease names listed above will be used.
If you have any questions about how Meaxin works or why it has been prescribed, you should consult a doctor.
2. Important information before taking Meaxin
Meaxin is prescribed to patients only by doctors experienced in the use of medicines used to treat blood cancers or solid tumors.
You should strictly follow the doctor's recommendations, even if they differ from the general information contained in this leaflet.
When not to take Meaxin
Meaxin.
If you suspect an allergy but are not sure, you should consult a doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Meaxin, you should discuss it with your doctor:
While taking Meaxin, you may become more sensitive to the sun. It is important to cover areas of skin exposed to the sun and use sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF). These precautions should also be taken in children.
You should tell your doctor immediately if you experience very rapid weight gain during treatment with Meaxin. Meaxin may cause water retention in the body (severe fluid retention).
During treatment with Meaxin, your health will be regularly assessed by your doctor to determine if the treatment is effective. Blood tests and weight measurements will be regularly performed while taking this medicine.
Children and adolescents
Meaxin is also used to treat children with CML. There is no experience with the use of Meaxin in children with CML under the age of 2. Experience with the use of Meaxin in children with Ph-positive ALL is limited, and experience with the use of Meaxin in children with MDS/MPD, DFSP, GIST, and HES/CEL is very limited.
In some children and adolescents taking Meaxin, growth may be slower than normal. The doctor will monitor growth during regular visits.
Meaxin and other medicines
You should tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking now or have taken recently, as well as any medicines you plan to take, including those that are available without a prescription (such as paracetamol) and herbal medicines (such as St. John's Wort [Hypericum perforatum]). Some medicines may affect the action of Meaxin if taken at the same time. They may enhance or weaken the action of Meaxin, which may lead to increased side effects or make Meaxin less effective. Similarly, Meaxin may affect some other medicines.
You should tell your doctor if you are taking medicines to prevent blood clots.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, you should consult a doctor before taking this medicine.
- Meaxin is not recommended for pregnant women unless absolutely necessary, as it may harm the baby. The doctor will discuss the possible risks that may occur during treatment with Meaxin during pregnancy.
- Women who may become pregnant should use effective contraception during treatment with Meaxin and for 15 days after the end of treatment.
- You should not breastfeed while taking Meaxin and for 15 days after the end of treatment, as it may harm the baby.
- Patients concerned about their fertility during treatment with Meaxin should consult a doctor.
Driving and using machines
While taking Meaxin, you may experience dizziness, drowsiness, or vision disturbances.
In this case, you should not drive vehicles or operate any tools or machines until you feel better.
Meaxin contains sodium
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per tablet, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to take Meaxin
Your doctor has prescribed Meaxin because of your serious condition. Meaxin may help improve your condition.
However, this medicine should always be taken according to the doctor's or pharmacist's recommendations. It is important to take the medicine for as long as the doctor or pharmacist recommends. If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
You should not stop taking Meaxin unless your doctor recommends it.
If you cannot take the prescribed medicine or think you no longer need it, you should contact your doctor immediately.
What dose of Meaxin to take
Adult patients
The doctor will determine the exact number of Meaxin tablets you should take.
In the case of CML treatment:
Depending on your condition, the initial dose is usually 400 mg or 600 mg:
- 400 mgtaken as 4 tablets of 100 mg oncea day or
- 400 mgtaken as 1 tablet of 400 mg oncea day.
- 600 mgtaken as 6 tablets of 100 mg oncea day or
- 600 mgtaken as 1 tablet of 400 mg and 2 tablets of 100 mg, oncea day.
In the case of GIST treatment:
The initial dose is 400 mg, taken as:
- 4 tablets (100 mg) oncea day or
- 1 tablet (400 mg) oncea day.
In the case of CML and GIST treatment, the doctor may prescribe a higher or lower dose depending on the response to treatment. If the daily dose is 800 mg, you should take:
- 4 tablets in the morning and 4 tablets in the evening (for 100 mg tablets),
- 1 tablet in the morning and 1 tablet in the evening (for 400 mg tablets).
In the case of Ph-positive ALL treatment:
The initial dose is 600 mg, taken as:
- 6 tablets (100 mg) oncea day,
- 1 tablet of 400 mg and 2 tablets of 100 mg, oncea day.
In the case of MDS/MPD treatment:
The initial dose is 400 mg, taken as:
- 4 tablets (100 mg) oncea day,
- 1 tablet (400 mg) oncea day.
In the case of HES/CEL treatment:
The initial dose is 100 mg, taken as 1 tablet (100 mg) oncea day.
Depending on the patient's response to treatment, the doctor may decide to increase the dose to 400 mg taken as 4 tablets of 100 mg oncea day or 1 tablet of 400 mg oncea day.
In the case of DFSP treatment:
The daily dose is 800 mg, taken as:
- 4 tablets in the morning and 4 tablets in the evening (for 100 mg tablets),
- 1 tablet in the morning and 1 tablet in the evening (for 400 mg tablets).
Children and adolescents
The doctor will determine the number of tablets to give to the child. The dose of the medicine will depend on the child's condition, weight, and height. The total daily dose in children should not exceed 800 mg in the case of CML and 600 mg in the case of Ph-positive ALL. The dose can be given to the child once a day or divided into two doses (half the dose in the morning and half the dose in the evening).
When and how to take Meaxin
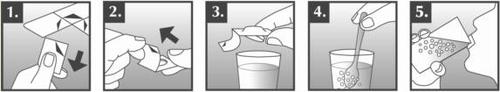
Meaxin should be taken with foodto protect the stomach while taking Meaxin. Before taking the medicine, the tablet for oral suspension should be suspended in non-carbonated water or apple juice. The tablets should not be chewed or swallowed whole.
The tablet should be removed from the blister in the following way:
- 1. Holding the blister by the edges, separate the square of the blister with the tablet from the rest of the blister by tearing it along the perforation.
- 2. Pull the edge of the foil and completely remove it.
- 3. Place the required number of tablets in a glass of water or apple juice. Use one-third of a glass of water or apple juice (at least 25 ml) for one 100 mg tablet or a glass of water or apple juice (at least 100 ml) for one 400 mg tablet.
- 4. Mix with a spoon until the tablets are completely dispersed.
- 5. After dispersing the tablets, immediately drink the entire contents of the glass. After drinking the suspension, any remaining tablet residue should be re-suspended in a small amount of water or apple juice, mixed, and also drunk.
How long to take Meaxin
You should take Meaxin every day for as long as your doctor recommends.
Taking more than the recommended dose of Meaxin
Patients who have accidentally taken too many tablets should immediatelytell their doctor, as they may require medical attention. You should take the packaging of the medicine with you.
Missing a dose of Meaxin
If you forget to take a dose, you should take it as soon as you remember. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, you should skip the missed dose.
Then continue with your regular dosing schedule.
You should not take a double dose to make up for the missed dose.
If you have any further doubts about taking this medicine, you should consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Meaxin can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
They are usually mild to moderate.
Some side effects can be serious. You should tell your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following side effects.
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people) or common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people) side effects:
- Rapid weight gain. Meaxin may cause water retention in the body (severe fluid retention).
- Infection symptoms, such as fever, chills, sore throat, and mouth ulcers. Meaxin may reduce the number of white blood cells in the blood, which can increase the risk of infection.
- Unexpected bleeding or bruising (even without injury).
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people) or rare (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people) side effects:
- Chest pain, irregular heartbeat (symptoms of heart disorders).
- Cough, difficulty breathing, or chest pain (symptoms of lung disorders).
- Dizziness, fainting, or low blood pressure.
- Nausea with loss of appetite, dark urine, yellowing of the skin or eyes (symptoms of liver disorders).
- Rash, redness of the skin with blisters on the lips, around the eyes, on the skin, or in the mouth, peeling of the skin, fever, swollen red or purple spots on the skin, itching, burning sensation, pustular rash (symptoms of skin disorders).
- Severe abdominal pain, blood in vomit, stool, or urine, black stools (symptoms of stomach and intestine disorders).
- Significantly reduced urine output, feeling of thirst (symptoms of kidney disorders).
- Nausea with diarrhea and vomiting, abdominal pain, or fever (symptoms of intestine disorders).
- Severe headache, weakness, or paralysis of limbs or face, difficulty speaking, sudden loss of consciousness (symptoms of nervous system disorders, such as bleeding or swelling in the skull/brain).
- Pale skin, feeling of tiredness and shortness of breath, and dark urine (symptoms of red blood cell deficiency).
- Eye pain or vision disturbances, bleeding in the eyes.
- Bone or joint pain (symptoms of bone necrosis).
- Blisters on the skin or mucous membranes (symptoms of pemphigus).
- Numbness or cold sensation in the fingers and toes (symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome).
- Unexpected swelling and redness of the skin (symptoms of skin infection called cellulitis).
- Hearing loss.
- Muscle weakness and muscle cramps with irregular heartbeat (symptoms of changes in potassium levels in the blood).
- Bruising.
- Abdominal pain with nausea.
- Muscle cramps with fever, reddish-brown urine, muscle pain, or weakness (symptoms of muscle disorders).
- Pelvic pain, sometimes with nausea and vomiting, with sudden vaginal bleeding, dizziness, or fainting due to low blood pressure (symptoms of ovarian or uterine disorders).
- Nausea, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, cloudy urine, fatigue, and (or) joint disorders with accompanying laboratory abnormalities (e.g., high potassium, uric acid, and calcium levels and low phosphorus levels in the blood).
- Blood clots in small blood vessels (thrombotic microangiopathy).
Frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Co-occurrence of widespread, severe rash, nausea, fever, high levels of certain white blood cells, or yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice) with shortness of breath, chest pain/discomfort, significantly reduced urine output, and feeling of thirst, etc. (symptoms of allergic reaction related to treatment).
- Chronic kidney failure.
- Reactivation (recurrence) of hepatitis B virus infection (liver infection) in patients who have had this disease in the past.
If you experience any of the above side effects, you should tell your doctor immediately.
Other side effects may include:
Very common side effects (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Headache or fatigue.
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, indigestion.
- Rash.
- Muscle cramps or joint pain, muscle pain, or bone pain during or after taking imatinib.
- Swelling, such as swelling of the ankles or around the eyes.
- Weight gain.
If any of the above side effects worsen, you should tell your doctor.
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Lack of appetite, weight loss, or taste disorders.
- Dizziness or weakness.
- Sleep disturbances (insomnia).
- Eye discharge with itching, redness, and swelling, increased tearing, or blurred vision.
- Nosebleeds.
- Abdominal pain or swelling, bloating with gas, heartburn, or constipation.
- Itching.
- Excessive hair loss or thinning.
- Numbness of hands or feet.
- Mouth ulcers.
- Joint pain with swelling.
- Dry mouth, dry skin, or dry eyes.
- Decreased or increased skin sensitivity.
- Hot flashes, chills, or night sweats.
If any of the above side effects worsen, you should tell your doctor.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Painful red lumps on the skin, skin pain, redness of the skin (inflammation of the fatty tissue under the skin).
- Cough, runny nose, or stuffy nose, feeling of pressure or pain when pressing on the area above or to the side of the nose, nasal congestion, sneezing, sore throat, which may be accompanied by headache or not (symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection).
- Severe headache, usually felt as a pulsating pain or sensation of pulsation, usually on one side of the head, which is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light or sounds (symptoms of migraine).
- Flu-like symptoms (flu).
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating, elevated body temperature, pain in the groin or pelvic area, red or brown urine, or cloudy urine (symptoms of urinary tract infection).
- Pain and swelling of the joints (symptoms of joint pain).
- Feeling of persistent sadness and loss of interest, preventing the patient from performing daily activities (symptoms of depression).
- Feeling of anxiety or apprehension with physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, dry mouth (symptoms of anxiety).
- Drowsiness/excessive drowsiness.
- Trembling or muscle twitching.
- Memory disorders.
- Irrepressible need to move the legs (restless legs syndrome).
- Hearing noises (e.g., ringing, buzzing) in the ears that do not come from outside (tinnitus).
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- Belching.
- Stomatitis.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Increased sweating.
- Skin discoloration.
- Brittle nails.
- Red bumps or white pimples that form around hair roots, which can cause pain, itching, or burning sensation (symptoms of folliculitis).
- Skin rash with peeling skin (exfoliative dermatitis).
- Breast enlargement (can occur in men or women).
- Pelvic pain, sometimes with nausea and vomiting, with sudden vaginal bleeding, dizziness, or fainting due to low blood pressure (symptoms of ovarian or uterine disorders).
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Difficulty achieving or maintaining sexual arousal.
- Decreased libido.
- Nipple pain.
- General malaise.
- Viral infection, such as a cold.
- Back pain due to kidney disorders.
- Increased urination frequency.
- Increased appetite.
- Pain or burning sensation in the upper abdomen and (or) chest (heartburn), nausea, vomiting, acid reflux, feeling of fullness, and bloating, black stools (symptoms of stomach ulcer).
- Stiffness of the joints and muscles.
- Abnormal laboratory test results. If any of the above side effects worsen, you should tell your doctor.
Rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people):
- Confusion.
- Nail discoloration.
Frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Redness or swelling of the palms and soles, which may be accompanied by tingling and burning pain.
- Skin changes with pain and (or) blistering.
- Slowed growth in children and adolescents.
If any of the above side effects worsen, you should tell your doctor.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Meaxin
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
You should not take this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and blister. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Store in the original packaging to protect from moisture and light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Meaxin contains
- The active substance of Meaxin is imatinib. Each tablet for oral suspension contains 100 mg or 400 mg of imatinib (as imatinib mesylate).
- Other ingredients are: mannitol (E 421), microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal anhydrous silica, calcium silicate, microcrystalline cellulose silanized, anhydrous citric acid, crospovidone type A, magnesium stearate, and sodium stearyl fumarate. See section 2 "Meaxin contains sodium".
What Meaxin looks like and contents of the pack
Meaxin, 100 mg, tablets for oral suspension: yellowish-white, round tablets with beveled edges, with a dividing line on one side and a diameter of 12 mm. The tablet can be divided into equal doses.
Meaxin, 400 mg, tablets for oral suspension: yellowish-white, round, biconvex tablets with a diameter of 21 mm.
Meaxin, 100 mg, tablets for oral suspension
Pack size: 20 x 1, 30 x 1, 60 x 1, 90 x 1, 120 x 1, and 180 x 1 tablet for oral suspension in blisters, in a cardboard box
Meaxin, 400 mg, tablets for oral suspension
Pack size: 10 x 1, 30 x 1, 60 x 1, and 90 x 1 tablet for oral suspension in blisters, in a cardboard box
Marketing authorization holder
KRKA, d.d. Novo mesto, Šmarješka cesta 6, 8501 Novo mesto, Slovenia
Manufacturer
KRKA, d.d. Novo mesto, Šmarješka cesta 6, 8501 Novo mesto, Slovenia
KRKA – FARMA d.o.o., V. Holjevca 20/E, 10450 Jastrebarsko, Croatia
To obtain more detailed information on the names of medicines in other EU member states, you should contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder:
KRKA-POLSKA Sp. z o.o.
ul. Równoległa 5
02-235 Warsaw
Phone: 22 57 37 500.
Date of last revision of the leaflet:10.11.2022
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterKrka, d.d., Novo mesto
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to MeaxinDosage form: Tablets, 400 mgActive substance: imatinibManufacturer: Biofarm Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Capsules, 100 mgActive substance: imatinibManufacturer: Przedsiębiorstwo Farmaceutyczne LEK-AM Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Capsules, 400 mgActive substance: imatinibManufacturer: Przedsiębiorstwo Farmaceutyczne LEK-AM Sp. z o.o.Prescription required
Alternatives to Meaxin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Meaxin in Spain
Alternative to Meaxin in Ukraine
Online doctors for Meaxin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Meaxin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.







