
Luteina

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Luteina

How to use Luteina
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Luteina, 100 mg, vaginal tablets
Progesterone
Read the leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Luteina and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Luteina
- 3. How to take Luteina
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Luteina
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Luteina and what is it used for
Luteina is a medicine containing a synthetically obtained natural female sex hormone, progesterone.
In the body, progesterone acts through specific receptors located in the uterus, breast tissue, central nervous system, and pituitary gland.
The most important effects of progesterone on the reproductive organs are: enabling ovulation, transforming the endometrium to allow implantation of a fertilized egg, inhibiting excessive growth of the endometrium caused by estrogen, and cyclic changes in the epithelium of the fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina. Progesterone and estrogen also act on the breast tissue, stimulating the growth of glands and ductal epithelium, and enabling lactation.
Progesterone is a hormone necessary for proper preparation of the endometrium for implantation of the embryo, for maintaining pregnancy throughout its duration: it suppresses the spontaneous contractile activity of the pregnant uterus, inhibits the mother's immune response to fetal antigens, is a basic substance for the production of fetal hormones, and initiates labor.
Indications for use of Luteina:
- States of endogenous progesterone deficiency in the form of menstrual cycle disorders, painful menstruation, anovulatory cycles, premenstrual tension syndrome, and functional uterine bleeding.
- Endometriosis.
- In vitro fertilization.
- Infertility associated with luteal insufficiency.
- Habitual and threatened miscarriages.
- Luteal phase insufficiency in the premenopausal period.
- Hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women with an intact uterus, who are receiving hormone replacement therapy, to protect the endometrium.
- Prevention of premature labor in singleton pregnancies in some women [with a short cervix (in ultrasound examination, cervix length in the middle of the second trimester ≤ 25 mm) and (or) with a history of spontaneous premature labor].
2. Important information before taking Luteina
When not to take Luteina:
- If the patient is allergic to progesterone or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- If the patient has vaginal bleeding of unknown origin;
- If the patient has severe liver failure;
- If the patient has a liver tumor;
- If the patient has a breast or genital tumor or suspected tumor;
- If the patient has an active venous thrombosis (thrombophlebitis), e.g., in the limbs (deep vein thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism), and if such blood clots have occurred in the past;
- If the patient is at risk of intracranial bleeding;
- If the patient has a rare blood disease called porphyria, which is inherited from generation to generation (genetic disease);
- If there has been a miscarriage and there is a suspicion that some tissue still remains in the uterus or if the pregnancy is developing outside the uterus.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to take this medicine, discuss it with your doctor.
This medicine, when used as recommended, does not have a contraceptive effect.
Before starting hormone replacement therapy during menopause (and later at regular annual intervals), consult your doctor, who will perform a breast and pelvic examination. You should tell your doctor if:
- you have a history of blood clots in the veins (venous thrombosis);
- you have uterine bleeding. You should stop taking this medicine in case of:
- any vision disturbances (e.g., visual impairment, double vision, vascular changes in the retina);
- blood clots (thromboembolic disease of the veins or blood clots);
- severe headaches. If you experience a lack of menstruation during treatment, you should ensure that you are not pregnant. During treatment, the endometrium may start to overgrow (endometrial hyperplasia) or this overgrowth may worsen. If, during long-term treatment, at the end of treatment, or after treatment, unexpected bleeding or spotting occurs and persists, you should contact your doctor.
Children and adolescents
There is a lack of sufficient data on the safety and efficacy of Luteina in children and adolescents.
Luteina and other medicines
Tell your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
Some medicines may affect the action of Luteina:
- barbiturates used in sleep disorders or anxiety treatment,
- medicines used in epilepsy (carbamazepine, phenytoin),
- certain antibiotics (ampicillins, tetracyclines, rifampicin),
- phenylbutazone (anti-inflammatory medicine),
- spironolactone (diuretic),
- certain antifungal medicines (ketoconazole, griseofulvin). Similarly, Luteina may affect the action of certain medicines used to treat diabetes. Herbal products containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) may weaken the action of Luteina. Luteina may enhance the action of cyclosporine.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility Pregnancy
- If you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
Breastfeeding
- Breastfeeding women should not take this medicine. Before starting to take this medicine, discuss it with your doctor.
Fertility
- This medicine may be taken by women who have difficulty getting pregnant. This medicine does not have any harmful effect on fertility.
Driving and using machines
Luteina administered vaginally does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and use machines. In case of side effects such as drowsiness, concentration and attention disorders, and dizziness, it is not recommended to drive vehicles and use machines (see section 4).
3. How to take Luteina
Take this medicine always as directed by your doctor. If you have any doubts, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
The dosage of progesterone should be determined individually each time, depending on the indications and efficacy of the action. For doses other than 100 mg, vaginal tablets of 50 mg and 200 mg are available.
In menstrual cycle disorders, painful menstruation, premenstrual tension syndrome, and luteal phase insufficiency in the premenopausal period, 25 to 50 mg of progesterone is administered vaginally 2 times a day in the second phase of the menstrual cycle (natural or induced) for 10-12 days.
In menstrual cycle disorders, painful menstruation, and premenstrual tension syndrome, treatment with progesterone is continued for 3-6 consecutive cycles.
In luteal phase insufficiency in the premenopausal period, treatment with progesterone should be continued until menopause occurs.
In hormone replacement therapy in combination with estrogens, 25 to 50 mg of progesterone is administered vaginally 2 times a day in sequential therapy from the 15th to the 25th day of the cycle or in continuous therapy every day.
In the progesterone test in secondary amenorrhea, progesterone is administered vaginally in a dose of 50 mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days. Bleeding should occur within 7-10 days after discontinuation of progesterone.
In the treatment of functional uterine bleeding, 50 mg of progesterone is administered vaginally 2 times a day for 5-7 days. Treatment should be continued for the next 2-3 months, administering progesterone in a dose of 25 to 50 mg 2 times a day vaginally from the 15th to the 25th day of the cycle.
In endometriosis, 50 to 100 mg of progesterone is administered 2 times a day vaginally in continuous therapy for 6 months.
In habitual and threatened miscarriages, 200 to 400 mg of progesterone is administered vaginally 2 times a day.
In the case of habitual miscarriages, supplementation with progesterone should be started in the cycle in which pregnancy is planned. Treatment should be continued continuously until the 18th-22nd week of pregnancy.
In anovulatory cycles and induced cycles, 50 to 150 mg of progesterone is administered vaginally 2 times a day.
In in vitro fertilization programs, 200 to 400 mg of progesterone is administered vaginally 2 times a day.
Treatment is continued until the 77th day after embryo transfer.
Termination of therapy should be done by gradually reducing the administered dose of the medicine.
In the prevention of premature labor in singleton pregnancies in some women with a short cervix and (or) a history of spontaneous premature labor, 200 mg of progesterone is administered vaginally once a day from about the 20th week of pregnancy to the 34th week of pregnancy.
Instructions for use
Luteina should be placed in the vagina using the enclosed applicator. The applicator enclosed with Luteina is a product for personal use and is intended for use by one patient only.
In pregnant women, due to the softened cervix, it is recommended to apply the medicine with the index finger.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING THE APPLICATOR
- 1. Unpack the applicator.
- 2. Place one Luteina tablet in the designated place at the end of the applicator. The tablet should fit tightly against the applicator walls and should not fall out.
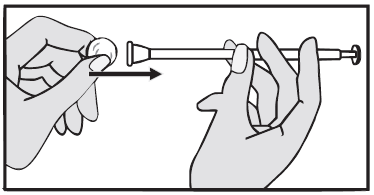
- 3. The applicator can be inserted into the vagina in a convenient position (standing, sitting, lying on your back with bent knees).
- 4. Insert the applicator into the vagina until the raised line felt with your finger is at the level of the labia majora.
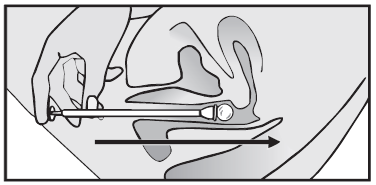
- 5. Press the applicator plunger to release the tablet.
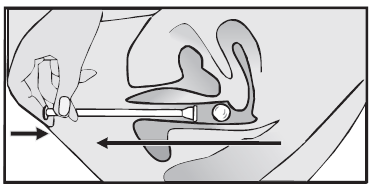
- 6. Then, withdraw the applicator, rinse it thoroughly with warm running water, and dry it with a soft cloth.
- 7. The applicator should be kept for reuse.
Using a higher dose of Luteina than recommended
In case of taking a higher dose of this medicine than recommended, contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
Symptoms of overdose that may occur include drowsiness, dizziness, and depression.
These symptoms usually resolved spontaneously after reducing the dose of the medicine. Consult your doctor beforehand.
Missing a dose of Luteina
Take the missed dose of Luteina as soon as you remember, unless it is almost time for the next dose. Do not take a double dose to make up for the missed dose.
Stopping treatment with Luteina
If you have any further doubts about taking this medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Stop taking this medicine immediately if you experience:
- stroke, blood clots, or intracranial bleeding,
- blood clots in the veins of the limbs or pelvis,
- sudden severe headaches,
- vision disturbances,
- jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes).
The following side effects are common (in 1 in 10 patients):
- headaches,
- bloating,
- abdominal pain,
- nausea,
- uterine cramps.
The following side effects are uncommon (in 1 in 100 patients):
- dizziness,
- drowsiness,
- diarrhea,
- constipation,
- hives (allergic rash),
- rash,
- genital and vaginal disorders (e.g., vaginal discomfort, burning, discharge, dryness, and bleeding),
- vaginal yeast infection,
- breast disorders (e.g., breast pain, breast swelling, breast tenderness),
- itching in the genital area,
- peripheral edema (swelling due to fluid accumulation).
The following side effects have been observed after the introduction of progesterone vaginal medicines to the market.
The frequency of occurrence is unknown(cannot be determined based on available data):
- fatigue,
- vomiting,
- hypersensitivity reactions.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Luteina
Store in a temperature below 30°C.
Keep the medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the packaging. The expiration date refers to the last day of the given month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Luteina contains
- The active substance of the medicine is progesterone. One tablet contains 100 mg of progesterone.
- The other ingredients are: lactose monohydrate, cornstarch, sodium croscarmellose, hypromellose, citric acid monohydrate, magnesium stearate, anhydrous colloidal silica.
What Luteina looks like and what the package contains
A round vaginal tablet, white or off-white in color, with the inscription "100" on one side and "22" on the other side.
The box contains 30 vaginal tablets or 60 vaginal tablets and one applicator marked vaginal applicator 100.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Adamed Pharma S.A.
Pieńków, ul. M. Adamkiewicza 6A
05-152 Czosnów
tel.: +48 22 732 77 00
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAdamed Pharma S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to LuteinaDosage form: Gel, 80 mg/gActive substance: progesteronePrescription requiredDosage form: Suppositories, 400 mgActive substance: progesteroneManufacturer: Fulton Medicinali S.p.A. Gedeon Richter Plc.Prescription requiredDosage form: Suppositories, 400 mgActive substance: progesteronePrescription required
Alternatives to Luteina in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Luteina in Spain
Alternative to Luteina in Ukraine
Online doctors for Luteina
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Luteina – subject to medical assessment and local rules.









