

Lignocainum hidrohloricum 1%

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Lignocainum hidrohloricum 1%

How to use Lignocainum hidrohloricum 1%
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
LIGNOCAINUM HYDROCHLORICUM WZF 1% 10 mg/ml solution for injection
Lidocaini hydrochloridum
LIGNOCAINUM HYDROCHLORICUM WZF 2% 20 mg/ml solution for injection
Lidocaini hydrochloridum
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if necessary.
- In case of any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2%
- 3. How to use Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2%
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2%
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% and what is it used for
WZF 2% and what is it used for
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug, administered by a doctor.
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% are used:
- for regional anesthesia - infiltration, nerve blocks, plexus blocks, epidural, and spinal - in general surgery, urology, orthopedics, gynecology, obstetrics, as well as in various diagnostic and therapeutic procedures;
- for ventricular arrhythmias (premature contractions, ventricular tachycardia), especially in the course of acute myocardial infarction or after overdosing with cardiac glycosides.
- for pain treatment in the perioperative period, as a component of preventive (pre-emptive) and multimodal analgesia.
- for the treatment of neuropathic pain, as a second-line drug.
2. Important information before using Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1%
and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2%
When not to use Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2%:
- if the patient is allergic to lidocaine or any other component of the medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has a history of allergy to other local anesthetics;
- if there are contraindications to performing specific anesthesia techniques, especially epidural and spinal - this will be decided by the doctor.
Intravenous infusion of lidocaine used for pain treatment in the perioperative period is contraindicated if regional anesthesia is used at the same time, especially if a local anesthetic is administered in a bolus or in large doses (e.g., epidural or plexus block).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2%, the patient should discuss it with their doctor or pharmacist.
The patient should tell their doctor if:
- they have heart disease, high blood pressure - especially severe;
- they have neurological diseases, such as neuromuscular disorders, multiple sclerosis, hemiplegia, transverse myelitis;
- they have liver problems;
- they have blood disorders (reduced blood volume);
- they have electrolyte and water balance disorders (symptoms include: dry mouth, thirst, weakness, lethargy, drowsiness, restlessness, seizures, disorientation, muscle cramps, muscle fatigue, hypotension, oliguria, tachycardia, nausea, and vomiting).
Anesthetics are performed by a doctor who knows the technique of performing procedures and is trained in the diagnosis and treatment of lidocaine overdose.
During the administration of Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% or Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2%, the doctor:
- will ensure access to resuscitation equipment, oxygen, and necessary medications and will take appropriate actions in case of complications;
- will continuously monitor heart rate and breathing, level of consciousness, and other vital functions.
After repeated administration of lidocaine, toxic symptoms may occur - see section 4 of the leaflet. In the case of epidural administration of a large dose of the medicine, severe cardiovascular and respiratory disorders may occur.
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
The patient should tell their doctor if they are taking:
- antiepileptic drugs, such as phenytoin;
- antiarrhythmic drugs;
- antihypertensive drugs, such as propranolol;
- drugs for stomach and duodenal ulcers, such as cimetidine.
High doses of lidocaine may enhance the effect of muscle relaxants (e.g., suxamethonium).
Lidocaine administered intravenously may enhance the analgesic effect of painkillers used in monotherapy. The perioperative use of lidocaine reduces the need for opioids.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
The use of the medicine during pregnancy and breastfeeding will be decided by the doctor.
Driving and operating machines
The effect of lidocaine on the ability to drive and operate machines depends on the type of procedure performed and the dose of the medicine used.
The patient should not drive or operate machines for at least 24 hours after the procedure with lidocaine.
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% contain sodium
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% contains 2.75 mg of sodium in each ml of solution.
Ampoules of 2 ml:
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% contains 5.5 mg of sodium (main component of table salt) in each ampoule (2 ml of solution). This corresponds to 0.28% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
Vials of 20 ml:
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% contains 55 mg of sodium (main component of table salt) in each vial (20 ml of solution). This corresponds to 2.75% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% contains 2.36 mg of sodium in each ml of solution.
Ampoules of 2 ml:
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% contains 4.72 mg of sodium (main component of table salt) in each ampoule (2 ml of solution). This corresponds to 0.24% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
Vials of 20 ml:
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% contains 47.2 mg of sodium (main component of table salt) in each vial (20 ml of solution). This corresponds to 2.36% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
The medicine can be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride solution. The sodium content from the diluent should be taken into account when calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used for dilution, the patient should read the patient information leaflet for the diluent used.
In patients with reduced kidney function, the sodium content in the ready-to-use medicine should be taken into account.
3. How to use Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2%
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% are administered by a doctor.
The doctor will adjust the dose of the medicine to the patient's overall condition, age, weight, accompanying diseases, type of procedure, anesthesia, and medications used.
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% can be used intravenously, infiltration, epidurally, and spinal.
Using a higher dose of Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% than recommended
Overdose may occur if the medicine is administered directly into a blood vessel or into a highly vascularized area, or if the recommended dose is exceeded. The symptoms of overdose are listed below in section 4 "Possible side effects".
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If the patient experiences the first symptoms of hypersensitivity (e.g., facial swelling, lip swelling, tongue swelling, throat swelling, causing difficulty breathing or swallowing), they should immediately tell their doctor. Such symptoms are very rare. The doctor will then assess the severity of the symptoms and decide on further action.
Lidocaine side effects most often occur as a result of exceeding the permissible concentrations in body fluids, e.g., due to overdose, absorption disorders, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, or due to the use of an inappropriate injection technique.
Very rare (less than 1 in 10,000 people):
- allergic reactions (skin changes, hives, swelling);
- loss of sensation, inability to move (paralysis).
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- anaphylactoid reactions (symptoms similar to allergic reactions, but with a different mechanism of action);
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- feeling of dizziness;
- excitement;
- restlessness;
- euphoria;
- muscle tremors;
- drowsiness;
- disorders of consciousness;
- headache;
- tinnitus;
- feeling of heat, cold, or numbness;
- loss of consciousness;
- seizures;
- decreased blood pressure;
- slowing of heart rate, which in severe cases can lead to cardiac arrest;
- increased difficulty breathing, which in severe cases can lead to respiratory arrest;
- vision disorders;
- nausea, vomiting.
After intravenous administration of lidocaine in multimodal analgesia (multimodal), the most common side effects were: drowsiness, feeling of fatigue, nausea, numbness of the lips, metallic taste in the mouth, and dizziness.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2%
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging and ampoule or vial after: EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light, at a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze.
After the first dose is taken, any unused contents of the vial should be discarded within 24 hours. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What does Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% contain
- The active substance of the medicine is lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate. Each ml of solution contains 10 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate. Each ampoule (2 ml of solution) contains 20 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate. Each vial (20 ml of solution) contains 200 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate.
- The other ingredients are: sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide 10% (to adjust pH), water for injections.
What does Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% contain
- The active substance of the medicine is lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate. Each ml of solution contains 20 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate. Each ampoule (2 ml of solution) contains 40 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate. Each vial (20 ml of solution) contains 400 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate.
- The other ingredients are: sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide 10% (to adjust pH), water for injections.
What does Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% look like and what does the packaging contain
The solution is colorless and clear.
The packaging consists of 10 ampoules of 2 ml or 5 vials of 20 ml in a cardboard box.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Manufacturer
Warszawskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne Polfa S.A.
ul. Karolkowa 22/24, 01-207 Warsaw
Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
Date of last update of the leaflet:
Information intended only for healthcare professionals:
LIGNOCAINUM HYDROCHLORICUM WZF 1% 10 mg/ml solution for injection
Lidocaini hydrochloridum
LIGNOCAINUM HYDROCHLORICUM WZF 2% 20 mg/ml solution for injection
Lidocaini hydrochloridum
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% or Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% do not contain preservatives.
Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Lignocainum hydrochloricum WZF 2% can be used intravenously, infiltration, epidurally, and spinal.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to help the solution flow down.
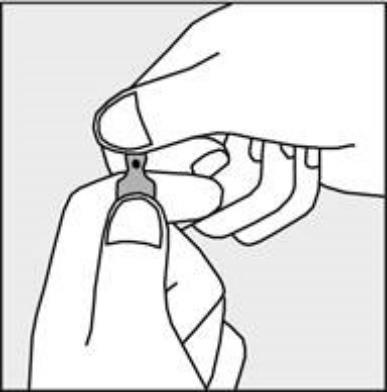
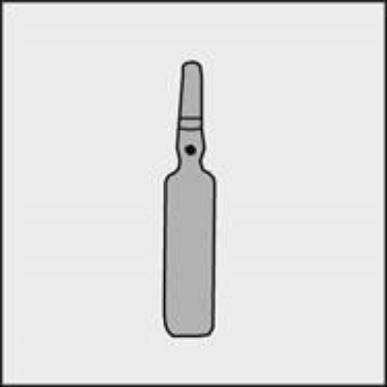
A colored dot is placed on each ampoule (see Figure 1) as a mark indicating the location of the break point below it.
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, in both hands, with the colored dot facing you - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
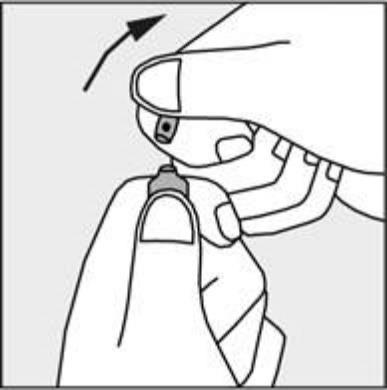
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. Any unused contents of the ampoule should be discarded in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Dosing
The medicine can be used intravenously, infiltration, epidurally, and spinal.
Regional anesthesia
The maximum single dose of lidocaine for an adult patient is 200 mg (4.5 mg/kg body weight). The doses given are for guidance and apply to adults in good general health, without accompanying diseases.
In children, the dose should not exceed 3 mg/kg body weight. Lidocaine should be dosed individually, based on the patient's body weight and overall condition. During anesthesia, the patient should be monitored and their vital functions monitored.
The strength and duration of lidocaine's action depend on the concentration and volume of the solution used. Increasing the volume and concentration accelerates, prolongs, and enhances the local anesthetic effect.
Lidocaine, like other local anesthetics, should be administered slowly, after performing an aspiration test, which allows avoiding unintended intravascular administration.
During the performance of epidural anesthesia, the administration of the main dose of the anesthetic should be preceded by a test dose (3 to 5 ml of lidocaine hydrochloride with adrenaline added). After accidental intravascular administration of the test dose, the adrenaline contained in it causes a pronounced acceleration of heart rate. Therefore, for 5 minutes after administration, the EKG recording should be monitored on the monitor screen. A negative test result authorizes the injection (at a rate of 25 to 50 mg/min) of the remaining dose of the anesthetic. During this time, constant verbal contact with the patient should be maintained, and if even mild symptoms of overdose appear, the administration should be stopped immediately. The test dose also allows avoiding the risks associated with unintended spinal administration of the medicine and subsequent total spinal anesthesia.
The intervals between consecutive doses of the medicine administered epidurally should not be less than 90 minutes.
The maximum dose of lidocaine administered during cervical block (during childbirth and in gynecology) should not exceed 200 mg every 90 minutes.
The smallest effective dose of lidocaine should always be used to minimize the risk of overdose. The medicine can be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
| Concentration of the medicine | Type of anesthesia | Maximum dose |
| 0.5 to 2% | Infiltration anesthesia | Up to 200 mg |
| 0.5 to 2% | Nerve and plexus blocks | Up to 200 mg |
| 0.5 to 2% | Epidural anesthesia | Up to 200 mg |
| 1 to 2% | Spinal anesthesia | Up to 80 mg (1.5 to 4 ml) |
| 0.5 to 1% | Intravenous regional anesthesia | Up to 200 mg |
Arrhythmias
To treat arrhythmias in adults, lidocaine is administered intravenously in a single dose of 50 to 100 mg, or in divided doses of 25 to 50 mg per minute. If the initial dose is not effective, the next dose (50 to 100 mg) can be administered after 5 minutes. The dose should not exceed 200 to 300 mg per hour.
In patients with a tendency to recur arrhythmias or resistant to the action of oral antiarrhythmic drugs, a continuous intravenous infusion of lidocaine can be used at a rate of 1 to 4 mg/min (20 to 50 μg/kg body weight/min) under constant EKG monitoring. The infusion should be discontinued when the arrhythmias disappear or when symptoms of overdose appear. In elderly patients, the dose should be adjusted according to the patient's overall condition.
Arrhythmias in children are treated with lidocaine administered intravenously in a dose of 0.8 to 1 mg/kg body weight, which can be repeated if necessary up to a total dose of 3 to 5 mg/kg body weight. Lidocaine can also be administered in a continuous intravenous infusion at a rate of 10 to 50 μg/kg body weight/min.
Treatment of pain in the perioperative period
Lidocaine administered intravenously in the perioperative period is used in adults as an adjuvant in multimodal (multimodal) therapy and in preventive (pre-emptive) analgesia.
Lidocaine is administered intravenously during surgical procedures with minor to significant and extensive tissue trauma.
Typical dosing:
- loading dose of 1.5 mg/kg body weight administered in a bolus, followed by a continuous infusion of 1.5 to 3 mg/kg body weight/hour during surgery; it is recommended to start administering lidocaine 30 minutes before the induction of anesthesia, but no later than during the induction of anesthesia;
- in the postoperative period: 1 to 3 mg/kg body weight/hour in a continuous infusion for 24 to 48 hours.
If the patient is using lidocaine as a local anesthetic (e.g., infiltration along the planned incision line) and in intravenous infusion, the total dose of lidocaine should be reduced.
If necessary, the intravenous infusion of lidocaine can be started 4 to 8 hours after the administration of the last dose (in a bolus) of the medicine used in regional anesthesia. In the case of failed epidural anesthesia, after stopping the continuous infusion into the epidural space and without administering a dose into the epidural space in a bolus, the continuous intravenous infusion of lidocaine can be started immediately, but without administering an intravenous bolus.
The dose of lidocaine should be reduced in conditions where the free fraction of the medicine in the serum may increase - acidosis, hypercapnia, hypoxia, hypoproteinemia, and liver and/or kidney function disorders. In patients with circulatory, liver, and/or kidney failure, the dose of lidocaine should be reduced and the patient's circulatory function monitored.
Treatment of patients with neuropathic pain
Adults
Continuous intravenous infusion at a dose of 3-5 mg/kg body weight for at least 30 minutes, but no longer than 6 hours, once a day.
Note: the medicine is incompatible and should not be mixed in the same syringe with solutions containing sodium bicarbonate and other alkaline solutions.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterWarszawskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLFA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Lignocainum hidrohloricum 1%Dosage form: Solution, 10 mg/mlActive substance: lidocainePrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 20 mg/mlActive substance: lidocainePrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 20 mg/mlActive substance: lidocaineManufacturer: Warszawskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLFA S.A.Prescription required
Alternatives to Lignocainum hidrohloricum 1% in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Lignocainum hidrohloricum 1% in Ukraine
Alternative to Lignocainum hidrohloricum 1% in Spain
Online doctors for Lignocainum hidrohloricum 1%
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Lignocainum hidrohloricum 1% – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










