

Lignocainum 2% c. noradrenalino 0,00125% Vzf

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Lignocainum 2% c. noradrenalino 0,00125% Vzf

How to use Lignocainum 2% c. noradrenalino 0,00125% Vzf
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
LIGNOCAINUM 2% with NORADRENALINE 0.00125% WZF
(20 mg + 0.025 mg)/ml, solution for injection
Lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate + Noradrenaline tartrate
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF
- 3. How to use Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF and what is it used for
used for
The medicine contains lidocaine, an amide-type anesthetic substance. The addition of noradrenaline limits the rate of lidocaine absorption from tissues into the circulatory system, resulting in a prolonged duration of action and reduced serum concentration.
The medicine is used for regional anesthesia - infiltration, nerve blocks, and plexus blocks - in general surgery, urology, orthopedics, gynecology, obstetrics, dentistry, and various diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
2. Important information before using Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF
0.00125% WZF
When not to use Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF
- if the patient is allergic to lidocaine or other amide-type local anesthetics, or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- for anesthesia of body areas with anatomical or functional end-arterial circulation (e.g. fingers and toes, tip of the nose, ears, penis), as the noradrenaline it contains may cause vasoconstriction, resulting in tissue ischemia and necrosis.
Warnings and precautions
Caution should be exercised when using the medicine in patients:
- with severe cardiovascular disorders (hypertension, coronary artery disease, mitral stenosis);
- with hyperthyroidism, diabetes, pheochromocytoma, or narrow-angle glaucoma;
- with epilepsy;
- with respiratory disorders;
- in the elderly and patients in poor general condition, adjusting the dose according to body weight and health status;
- with partial or complete conduction block, as local anesthetics may inhibit the conduction of the heart;
- using anti-arrhythmic drugs of class III (e.g. amiodarone) - they should be under close supervision and consideration should be given to monitoring the ECG, as the effects of lidocaine and class III anti-arrhythmic drugs on the heart muscle may be additive;
- with liver function disorders, as the medicine should be used with caution due to the possibility of high concentrations in body fluids;
- with advanced liver disease or severe kidney function disorders;
- with acute porphyria.
Anesthesia should be performed by a doctor familiar with the technique of performing procedures and trained in the diagnosis and treatment of lidocaine overdose. Delayed resuscitation, hypoxia, or excessive reaction to lidocaine may cause acidosis, cardiac arrest, and even patient death.
Access to a vein, oxygen, appropriate resuscitation equipment, and necessary medications should be ensured.
Continuous monitoring of heart and respiratory function, level of consciousness, and other vital functions is necessary.
Early symptoms of lidocaine toxicity on the central nervous system may include: metallic taste in the mouth, anxiety, tinnitus, dizziness, visual disturbances, tremors or drowsiness. If these occur, the doctor should be informed immediately.
Children
In children, the dose should be adjusted according to body weight and health status.
Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF and other medicines
The doctor should be informed about all medicines currently being taken or recently taken, as well as any medicines the patient plans to take.
- Particular caution should be exercised if lidocaine is used in patients who are also taking other local anesthetics or drugs with a similar chemical structure to amide-type local anesthetics, such as anti-arrhythmic drugs (e.g. mexiletine). The toxic effects of these drugs may be additive.
- Studies on the interaction of lidocaine with anti-arrhythmic drugs of class III (e.g. amiodarone) have not been conducted, but caution should be exercised when both drugs are used together.
- Anticonvulsant hydantoin derivatives (e.g. phenytoin) may enhance the inhibitory effect of lidocaine on the heart and accelerate its metabolism.
- The use of other anti-arrhythmic drugs with lidocaine may increase the risk of side effects.
- Beta-adrenergic blockers (e.g. propranolol) used with lidocaine may slow down its hepatic metabolism and increase its toxicity.
- Cimetidine (a drug used for stomach and duodenal ulcers) inhibits lidocaine metabolism, reduces its hepatic clearance, and increases its serum concentration.
- High doses of lidocaine may enhance the effect of muscle relaxants (e.g. suxamethonium).
- Noradrenaline may cause a sudden increase in blood pressure in patients taking tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, or guanethidine (an antihypertensive drug).
- Noradrenaline may weaken the effect of oral antidiabetic drugs and cause cardiac arrhythmias.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks she may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, she should consult a doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
The medicine may be used during pregnancy only if absolutely necessary.
Caution should be exercised when using the medicine during breastfeeding.
Driving and operating machinery
The patient should not drive or operate machinery for at least 24 hours after the procedure with lidocaine.
Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF contains sodium metabisulfite (E 223)
The medicine contains sodium metabisulfite, which may rarely cause severe hypersensitivity reactions and bronchospasm.
The medicine contains 4 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) in each ampoule (2 ml). This corresponds to 0.2% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
The medicine may be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride solution. The sodium content from the diluent should be taken into account when calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used for dilution, the patient information leaflet of the diluent should be consulted.
3. How to use Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF
Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF is administered by a doctor.
The medicine is intended for local anesthesia - infiltration and conduction anesthesia.
Lidocaine should be dosed individually, based on the patient's body weight and general condition.
During anesthesia, the patient must be monitored and their vital functions should be monitored.
Using a higher dose of Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF than recommended
WZF
Symptoms of lidocaine poisoning include: numbness of the lips and tongue, metallic taste in the mouth, slurred speech, dizziness, tinnitus, visual disturbances, shivering, excitement, muscle tremors, seizures.
Additionally, the following may occur: drowsiness, quickly progressing to loss of consciousness, respiratory and cardiac arrest, too fast or too slow heart rate, increased blood pressure.
High doses of noradrenaline may cause general symptoms from the cardiovascular system: rapid heart rate, increased blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmias.
Symptoms of poisoning are an indication to immediately stop administering the medicine. If the symptoms are mild (visual disturbances, dizziness), the doctor will administer oxygen to breathe. In case of more severe symptoms, such as impaired or lost consciousness, muscle tremors, or seizures, the doctor will use treatment according to the principles of intensive therapy.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Lidocaine side effects are usually the result of excessively high concentrations in body fluids due to the use of too high a dose, kinetic disorders, or improper injection technique.
The following side effects may occur:
- decreased blood pressure;
- nausea, vomiting;
- metallic taste in the mouth, feeling of dizziness, excitement, anxiety, euphoria, muscle tremors, impaired consciousness, loss of consciousness, headaches and dizziness, tinnitus, visual disturbances, feeling of heat, cold or numbness, seizures, central nervous system depression;
- slow heart rate, cardiac arrest (in extremely severe cases);
- skin changes, urticaria, edema, anaphylactoid symptoms.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
The ampoules should be stored in the original packaging, protected from light, in a refrigerator (2°C-8°C). Do not freeze.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and ampoule. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF contains
- The active substances of the medicine are: lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate and noradrenaline tartrate. Each ml of the solution contains 20 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate and 0.025 mg of noradrenaline tartrate.
- The other ingredients are: sodium chloride, sodium metabisulfite (E 223), water for injections.
What Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF looks like and contents of the pack
Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF is a colorless or almost colorless, clear solution.
The packaging consists of 10 ampoules of 2 ml in a cardboard box.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Polpharma S.A.
Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
Phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF (20 mg + 0.025 mg)/ml, solution for injection
Lidocaine hydrochloride + Noradrenaline tartrate
The medicine is intended for local anesthesia.
Lignocainum 2% with Noradrenaline 0.00125% WZF is used for regional anesthesia - infiltration, nerve blocks, and plexus blocks - in general surgery, urology, orthopedics, gynecology, obstetrics, dentistry, and various diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Local anesthesia with lidocaine should only be performed by doctors who are well familiar with the technique of performing anesthesia and trained in the diagnosis and treatment of lidocaine overdose, which may occur during regional anesthesia.
The room where anesthesia is performed must have a source of oxygen, resuscitation equipment, and necessary medications. Before starting anesthesia, access to a vein must be ensured. Delayed resuscitation may lead to hypoxia, acidosis, cardiac arrest, and even patient death.
Each lidocaine injection should be preceded by an aspiration test to avoid accidental intravascular administration.
The conditions for safe use of lidocaine are: proper dosing, correct anesthesia technique, adherence to precautions, and readiness to perform resuscitation.
Injection into inflamed or infected areas should be avoided, as these conditions may reduce the effectiveness of local anesthesia.
Repeating lidocaine doses may lead to a dangerous increase in its serum concentration. Since the overall reaction to high concentrations of this agent depends on the patient's condition, in debilitated patients, the elderly, and children, the lidocaine dose should be adjusted according to body weight and health status.
Lidocaine is metabolized in the liver, so in cases of liver failure, higher concentrations of the agent in body fluids should be expected.
Despite local anesthesia being considered an optimal anesthesia technique, some patients should be treated with particular caution to minimize the risk of severe side effects. These patients include:
- those with epilepsy;
- those with respiratory disorders;
- the elderly and patients in poor general condition;
- those with partial or complete conduction block, as local anesthetics may inhibit the conduction of the heart;
- those with advanced liver disease or severe kidney function disorders;
- those taking anti-arrhythmic drugs of class III (e.g. amiodarone) - they should be under close supervision and consideration should be given to monitoring the ECG, as the effects of lidocaine and class III anti-arrhythmic drugs on the heart muscle may be additive;
- those with acute porphyria. Lidocaine may increase porphyrin synthesis, so it should be used in patients with acute porphyria only if justified or in emergency situations. In all patients with porphyria, appropriate precautions should be taken.
Certain local anesthesia methods may be associated with severe side effects, regardless of the type of local anesthetic used, e.g.:
- injection into the head and neck area may accidentally administer the medicine into an artery, causing central nervous system symptoms even at low doses.
- Cervical block may occasionally cause bradycardia or tachycardia in the fetus, so it is necessary to closely monitor fetal heart rate.
- There have been post-marketing reports of chondrolysis in patients receiving postoperative continuous intra-articular infusion of local anesthetics. Most reports concerned chondrolysis in the shoulder joint. Due to the many factors that may contribute to the development of chondrolysis and the inconsistency in the scientific literature, a causal relationship has not been established. Continuous intra-articular infusion has not been approved as an indication for the use of lidocaine.
Caution should be exercised when using lidocaine with noradrenaline in patients with severe cardiovascular disorders (hypertension, coronary artery disease, mitral stenosis), hyperthyroidism, diabetes, pheochromocytoma, or narrow-angle glaucoma.
During anesthesia, both the level of consciousness and the function of the circulatory and respiratory systems should be constantly monitored. Early symptoms of toxic lidocaine concentrations in the central nervous system include: metallic taste in the mouth, anxiety, tinnitus, dizziness, visual disturbances, muscle tremors, or drowsiness.
Solutions containing preservatives should not be administered into the subarachnoid space, epidural space, or cerebrospinal fluid, nor by any other route where contact with cerebrospinal fluid would occur, as well as intrathecally or perineurally.
Local anesthetics administered during labor can easily cross the placenta, potentially causing toxicity in both the mother and the fetus. Lidocaine toxicity depends on the method and technique of anesthesia, as well as the dose used. Fetal heart rate should be closely monitored, as lidocaine can cause bradycardia in about 30% of fetuses. Anesthesia may also inhibit uterine contractions and prolong labor. When deciding to use cervical block in special obstetric situations, such as premature labor, eclampsia, and fetal distress, the potential benefits should be weighed against the potential risks.
In newborns whose mothers received local anesthetics during labor, decreased muscle tone has been observed in the first two days of life. However, it is not known whether this phenomenon is associated with any long-term consequences.
Warning!
Due to the noradrenaline tartrate in the composition, the medicine should not be mixed with alkaline or oxidizing agents, as incompatibilities may occur.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to help the solution flow down.
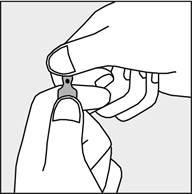
A colored dot is marked on each ampoule (see Figure 1) as a sign of the break point located below it.
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, with both hands, with the colored dot facing you - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped so that the thumb is above the colored dot.
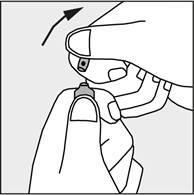
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused medicine should be disposed of in accordance with the applicable regulations.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Dosage
The maximum single dose of lidocaine with noradrenaline for an adult patient in good general condition and without concomitant diseases is 500 mg and should not exceed 7 mg/kg body weight.
Lidocaine should be dosed individually, based on the patient's body weight and general condition.
During anesthesia, the patient must be monitored and their vital functions should be monitored.
The strength and duration of lidocaine's action depend on the concentration and volume of the administered solution. Increasing the volume and concentration accelerates, prolongs, and intensifies the anesthetic effect. The addition of noradrenaline is intended to slow down the absorption of lidocaine from the injection site.
The minimum effective dose of lidocaine should always be used to minimize the risk of overdose. The product can be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
Regional anesthesia
| Concentration of the medicine | Type of anesthesia | Maximum dose of lidocaine with noradrenaline |
| 0.5 - 2% | Infiltration anesthesia | Up to 500 mg |
| 0.5 - 2% | Nerve and plexus blocks | Up to 500 mg |
The solution should be used immediately after opening the ampoule. The remaining unused solution should be discarded.
Overdose
Toxic symptoms occur after exceeding a certain concentration of lidocaine in the blood and depend on the dose administered, the addition of vasoconstrictor drugs, the injection site, tissue distribution, metabolism, and the patient's general condition.
Overdose may be the result of:
- relative overdose, when the medicine is administered directly into a blood vessel or into a highly vascularized area;
- absolute overdose, when the permissible dose is exceeded.
Symptoms of overdose:
- phase of central nervous system stimulation - numbness of the lips and tongue, metallic taste in the mouth, slurred speech, dizziness, tinnitus, visual disturbances, shivering, excitement, muscle tremors, seizures;
- phase of central nervous system depression - coma, respiratory and cardiac depression. Additionally, the following may occur: tachycardia, increased blood pressure and vascular resistance, decreased heart automatism, bradycardia, asystole, bronchodilation.
Symptoms of poisoning are an indication to immediately stop administering the medicine. If the symptoms are mild (visual disturbances, dizziness), the doctor will administer oxygen to breathe. In case of more severe symptoms, such as impaired or lost consciousness, muscle tremors, or seizures, the doctor will use treatment according to the principles of intensive therapy.
High doses of noradrenaline may cause general symptoms from the cardiovascular system: rapid heart rate, increased blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmias. In these cases, symptomatic treatment should be used.
Dialysis is not effective in cases of acute lidocaine overdose.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Lignocainum 2% c. noradrenalino 0,00125% VzfDosage form: Cream, (25 mg + 25 mg)/gActive substance: lidocaine, combinationsManufacturer: Pierre Fabre Medicament ProductionPrescription requiredDosage form: Gel, (3.3 mg + 1 mg)/gActive substance: lidocaine, combinationsManufacturer: Delpharm OrleansPrescription not requiredDosage form: Plaster, 25 mg + 25 mgActive substance: lidocaine, combinationsPrescription not required
Alternatives to Lignocainum 2% c. noradrenalino 0,00125% Vzf in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Lignocainum 2% c. noradrenalino 0,00125% Vzf in Spain
Alternative to Lignocainum 2% c. noradrenalino 0,00125% Vzf in Ukraine
Online doctors for Lignocainum 2% c. noradrenalino 0,00125% Vzf
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Lignocainum 2% c. noradrenalino 0,00125% Vzf – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














