
Levonor
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Levonor

How to use Levonor
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
LEVONOR, 1 mg/ml, concentrate for solution for infusion
Noradrenaline
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Levonor and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Levonor
- 3. How to use Levonor
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Levonor
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Levonor and what is it used for
Levonor contains the active substance noradrenaline and belongs to a group of medicines that affect adrenergic and dopaminergic receptors.
Levonor causes constriction of peripheral blood vessels, increases blood pressure and stimulates heart activity. This action of the medicine is used when administering it in life-threatening conditions, when there is a sudden drop in blood pressure.
Levonor is used:
- intravenously in severe hypotension to restore normal blood pressure.
2. Important information before using Levonor
Note: in life-threatening conditions, there are no absolute contraindications to the administration of Levonor.
Levonor.
When not to use Levonor
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Levonor, discuss it with your doctor.
The doctor will exercise special caution when using Levonor and take appropriate action:
Children
Levonor is not intended for children.
Levonor and other medicines
Tell your doctor about all medicines you are taking or have recently taken, and about medicines you plan to take, if possible and your condition allows.
If possible, inform your doctor if you have taken or are taking certain antidepressants from the group called monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or plan to have a child, consult your doctor before using this medicine.
If you are pregnant, your doctor will decide whether you can be given Levonor, as noradrenaline may be harmful to the unborn child.
There is no data on the use of noradrenaline in breastfeeding women.
Driving and using machines
Not applicable - Levonor is used in life-threatening conditions.
Levonor contains sodium metabisulfite and sodium
The medicine contains sodium metabisulfite (E 223), which can rarely cause severe hypersensitivity reactions and bronchospasm.
Ampoule of 1 ml capacity
The medicine contains 3.39 mg of sodium (main component of common salt) in a 1 ml ampoule.
This corresponds to 0.17% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
Ampoule of 4 ml capacity
The medicine contains 13.56 mg of sodium (main component of common salt) in a 4 ml ampoule.
This corresponds to 0.68% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
The medicine may be diluted in: 0.9% NaCl solution, 5% glucose solution or isotonic glucose solution in physiological saline (5% glucose solution and 0.9% NaCl solution 1:1). The sodium content from the diluent should be taken into account when calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, refer to the patient information leaflet of the diluent used.
3. How to use Levonor
Levonor is always administered by medical personnel.
The medicine should be administered after prior dilution, slowly, by intravenous infusion (using appropriate equipment, with controlled administration rate).
The dose of the medicine is determined by the doctor. The applied dose depends on the patient's age, weight and overall health.
Use of a higher dose of Levonor than recommended
After using high doses of the medicine, exceeding the recommended ones, especially for many hours, the following have been reported: severe hypertension, bradycardia and other heart rhythm disorders. These symptoms may be accompanied by severe headache, photophobia, vomiting, chest pain, pallor, excessive sweating.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects have been reported
Frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- excessive increase in blood pressure, which may be accompanied by peripheral tissue hypoperfusion;
- headache, limb hypoperfusion (which can cause gangrene);
- excessive bradycardia (less than 60 beats per minute);
- heart rhythm disorders (in patients with reduced oxygen supply to organs or excessive carbon dioxide levels in the body, during the administration of inhalation anaesthetics), stress-induced cardiomyopathy (most often manifested by: chest pain, shortness of breath, anxiety, fainting, heart rhythm disorders;
- decrease in blood plasma volume.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department for Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Levonor
Store in a refrigerator (2°C-8°C). Protect from light. Do not freeze.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the ampoule and carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Levonor contains
- The active substance of the medicine is noradrenaline. Each 1 ml of concentrate contains 1 mg of noradrenaline (as noradrenaline bitartrate). A 1 ml ampoule contains 1 mg of noradrenaline. A 4 ml ampoule contains 4 mg of noradrenaline.
- The other ingredients are: sodium chloride, sodium metabisulfite (E223), water for injections.
What Levonor looks like and contents of the pack
Levonor is a colourless concentrate.
Colourless glass ampoules containing 1 ml or 4 ml of concentrate, packed in a cardboard box.
The cardboard box contains: 10 ampoules of 1 ml or 5 ampoules of 4 ml.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Polpharma S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
LEVONOR, 1 mg/ml, concentrate for solution for infusion
Noradrenaline
Method of preparation of Levonor for administration
- For dilution of the medicine, the following infusion solutions are allowed:
- 5% glucose solution,
- 0.9% NaCl solution,
- isotonic glucose solution in physiological saline (5% glucose solution and 0.9% NaCl solution 1:1).
- The dilution should be prepared in controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
- Due to the possibility of pharmaceutical incompatibilities, the medicine should not be mixed with alkaline agents or oxidizing agents, barbiturates, chlorpheniramine, chlorothiazide, nitrofurantoin, novobiocin, phenytoin, sodium bicarbonate, sodium iodide, streptomycin.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to facilitate the flow of the solution.
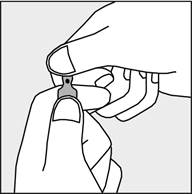
A coloured dot (see figure 1) has been placed on each ampoule as a mark indicating the location of the break point below it.
To open the ampoule, hold it vertically in both hands, with the coloured dot facing each other - see figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the coloured dot.
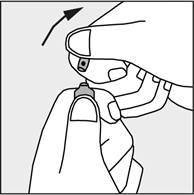
Press according to the arrow on figure 3.
The ampoules are intended for single use only, they should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused product should be destroyed in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Method of administration of Levonor
Administer intravenously by infusion, after prior dilution (method of dilution - see below), through a port inserted into a central vein or through a cannula placed in a sufficiently large vein, such as the veins of the forearm, elbow pit or external jugular vein, to minimize the risk of extravasation and subsequent tissue necrosis. The infusion rate should be controlled using an infusion pump or a drop counter.
Method of dilution
- 1. If noradrenaline is to be administered using an infusion pump: 2 mg of noradrenaline (2 ml of Levonor 1 mg/ml) should be added to 48 ml of diluent.
- 2. If noradrenaline is to be administered using a drop counter: 20 mg of noradrenaline (20 ml of Levonor 1 mg/ml) should be added to 480 ml of diluent.
The resulting noradrenaline concentration after dilution in both cases is 40 mg/l. If a different dilution is necessary, the doses should be carefully recalculated.
In the case of administration of noradrenaline into peripheral veins, a concentration of 20 mg/l (e.g. 1 ml of the product added to 49 ml of diluent) or lower should be used.
The dilution should be prepared in controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
The prepared solution, within the concentration range of 10 mg/l (0.01 mg/ml) to 40 mg/l (0.04 mg/ml), is chemically and physically stable for 24 hours at a temperature below 30°C, does not require protection from light.
From a microbiological point of view, the solution should be prepared immediately before use.
WARNING:The medicine with changed colour is not suitable for use.
Dosage
Adults
Dosage is determined individually, depending on the patient's condition.
During administration, constant monitoring of arterial blood pressure is required.
Initially 10 ml/h to 20 ml/h (0.16 ml/min to 0.33 ml/min), which corresponds to 0.4 mg/h to 0.8 mg/h of noradrenaline.
In the case of administration into a peripheral vein, noradrenaline should be used at a dose of up to 0.1 μg/kg/min, higher doses may only be administered for a short period, until a central line is inserted.
If administration of noradrenaline is necessary for a period of more than 12 hours, insertion of a central line should also be considered.
Maintenance doses - the infusion rate depends on the blood pressure values. The goal of treatment is to achieve a systolic blood pressure value at the lower limit of normal (100-120 mmHg) or an appropriate mean arterial blood pressure value (above 80 mmHg).
Duration of treatment: noradrenaline should be administered until improvement of the patient's condition. During administration of the medicine, the patient should be monitored.
Elderly patients
See section 2, subsection "Warnings and precautions".
Children
Not recommended.
During the use of Levonor:
- frequently monitor arterial blood pressure and infusion rate. During peripheral administration of noradrenaline, a blood pressure cuff should not be placed on the limb with the inserted vascular access;
- administer noradrenaline only to patients with adequately filled vascular bed (adequately hydrated);
- frequently monitor the infusion site and avoid administering the medicine extravascularly, as tissue necrosis may occur. The site where extravasation has occurred should be infiltrated with phentolamine.
During peripheral administration of noradrenaline, the anatomical structure of the vein into which the medicine is administered affects the safety of administration. A higher frequency of extravasation has been found when administering into smaller veins or areas with slower circulation, such as the wrist or ankle area. Larger veins (such as the veins of the forearm, elbow pit or external jugular vein) provide adequate dilution of noradrenaline and are less prone to spasm.
When using a continuous infusion of noradrenaline into a peripheral vein, do not administer other medicines through the same access.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to LevonorDosage form: Concentrate, 1mg/mlActive substance: norepinephrinePrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 0.2 mg/mlActive substance: norepinephrinePrescription not requiredDosage form: Concentrate, 1 mg/mlActive substance: norepinephrineManufacturer: Labesfal Laboratorios Almiro S.A.Prescription not required
Alternatives to Levonor in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Levonor in Hiszpania
Alternative to Levonor in Ukraina
Online doctors for Levonor
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Levonor – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










