
Lamitrin S
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Lamitrin S

How to use Lamitrin S
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Lamitrin S, 2 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension
Lamitrin S, 5 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension
Lamitrin S, 25 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension
Lamitrin S, 50 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension
Lamitrin S, 100 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension
Lamitrin S, 200 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension
Lamotrigine
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
1 What is Lamitrin S and what is it used for
2 Important information before taking Lamitrin S
3 How to take Lamitrin S
4 Possible side effects
5 How to store Lamitrin S
6 Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Lamitrin S and what is it used for
Lamitrin S belongs to a group of medicines called antiepileptic drugs. It is used to treat two diseases – epilepsy and bipolar affective disorders.
The action of Lamitrin S in the treatment of epilepsyis based on blocking impulses in the brain that cause epileptic seizures.
- In adults and children over 13 years of age, Lamitrin S may be used alone (as a single medicine) or in combination with other medicines to treat epilepsy. Lamitrin S may also be used in combination with other medicines to treat epileptic seizures associated with a condition called Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
- In children between 2 and 12 years of age, Lamitrin S may be used in combination with other medicines to treat these diseases. It may be used as the only medicine to treat a type of epilepsy called typical absence seizures.
Lamitrin S is also used to treat bipolar affective disorders.
In patients with bipolar affective disorders (sometimes called manic-depressive psychosis), there are extreme mood swings with episodes of mania (excitement or euphoria) alternating with episodes of depression (deep sadness or despair). In adults over 18 years of age, Lamitrin S may be used alone or in combination with other medicines to prevent depressive episodes in bipolar affective disorders. The mechanism by which Lamitrin S works in the brain is not yet known.
2. Important information before taking Lamitrin S
When not to take Lamitrin S
- If the patient is hypersensitive(allergic) to lamotrigine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). In this case: The doctor should be informedand Lamitrin S should not be taken.
Warnings and precautions
When to exercise special caution when taking Lamitrin S
Before starting to take Lamitrin S, the patient should consult their doctor if:
- The patient has any kidney disease;
- The patient has ever had a rashafter taking lamotrigine or other medicines used to treat bipolar affective disorders or epilepsy;
- The patient has ever had a rash or sunburnafter taking lamotrigine and being exposed to sunlight or artificial light (e.g. in a solarium). The doctor will verify the treatment used by the patient and may advise avoiding sunlight or using sun protection (e.g. using a sunscreen or wearing protective clothing);
- The patient has ever had meningitisafter taking lamotrigine (read the description of symptoms in section 4 of this leaflet: Rare side effects);
- The patient is taking a medicine containing lamotrigine;
- The patient has a condition called Brugada syndrome or other heart diseases.Brugada syndrome is a genetically determined heart condition characterized by disturbances in the electrical function of the heart. Abnormal ECG recordings are associated with arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm), which may be caused by taking lamotrigine.
If any of these conditions occur:
The doctor should be informed, who may recommend reducing the dose or decide that Lamitrin S is not a suitable medicine for the patient.
Important information about life-threatening reactions
In a small number of patients taking Lamitrin S, an allergic reaction or potentially life-threatening skin reaction may occur, which may worsen if left untreated. Such reactions may occur more frequently during the first few months of taking Lamitrin S, especially when the patient has been given too high a dose, the dose has been increased too quickly, or when the patient is taking Lamitrin S in combination with another medicine called valproate. Some of these reactions occur more frequently in children, so parents should pay special attention to them.
These reactions include:
- skin rash or redness, which may worsen to severe or life-threatening skin reactions, including a rash with ring-shaped lesions resembling a target ( erythema multiforme), widespread rash with blisters and peeling of the skin, especially around the mouth, nose, eyes, and genitals ( Stevens-Johnson syndrome), widespread peeling of the skin (affecting more than 30% of the body surface - toxic epidermal necrolysis) or widespread rash accompanied by changes in the liver, blood, and other organs ( Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, DRESS)
- mouth ulcers, throat ulcers, nose ulcers, or genital ulcers
- eye ulcers, redness, and swelling( conjunctivitis)
- high fever(fever), flu-like symptoms, or drowsiness
- swelling of the face, enlarged lymph nodesin the neck, armpits, and groin
- unexpected bleeding, bruising, or blue discoloration of the fingers
- sore throator more frequent infections (such as colds)
- increased liver enzymes in blood tests
- increased white blood cell count (eosinophilia)
- enlarged lymph nodes
- changes affecting other organs, including the liver and kidneys.
In many cases, these are symptoms of less severe side effects. However, they can be life-threatening and, if left untreated, can develop into serious conditions, such as organ failure. If any of these symptoms are noticed:
The doctor should be informed immediately. The doctor may decide to perform liver, kidney, or blood tests and may recommend discontinuing Lamitrin S. If the patient develops Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis, the doctor will inform them that they should never take lamotrigine again.
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)(see section 2. Important information before taking Lamitrin S).
My thoughts of self-harm or suicide
Antiepileptic medicines are used to treat various diseases, including epilepsy and bipolar affective disorders. In patients with bipolar affective disorders, thoughts of self-harm or suicide may sometimes occur. If the patient has bipolar affective disorders, such thoughts may occur more frequently:
- when starting treatment for the first time
- if the patient has had thoughts of self-harm or suicide before
- if the patient is under 25 years of age. If the patient experiences disturbing thoughts or feelings, or if their condition worsens while taking Lamitrin S, or if new symptoms appear:
The patient should see a doctor as soon as possible
for help.
It may be helpful to inform a relative, caregiver, or friend that the patient may experience depression or significant mood changes and ask them to read this leaflet.
The patient may ask them to inform them if they notice that the patient is depressed or has disturbing changes in behavior.
In a small number of patients treated with antiepileptic medicines, such as Lamitrin S, thoughts of self-harm or suicide have also occurred. If the patient has ever had such thoughts, they should inform their doctor immediately.
Taking Lamitrin S for the treatment of epilepsy
Seizures in some types of epilepsy may sometimes worsen or occur more frequently when taking Lamitrin S. In some patients, severe seizures may occur, which can pose a serious threat to the patient's health. If the patient experiences more frequent seizures or a severe seizure while taking Lamitrin S:
they should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Lamitrin S should not be used to treat bipolar affective disorders in patients under 18 years of age.
Medicines used to treat depression or other mental disorders increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Lamitrin S and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are taking
currently or recently, as well as any medicines they plan to take, including herbal medicines or other medicines available without a prescription.
The doctor should know that the patient is taking other medicines used to treat epilepsy or mental disorders. This will allow the doctor to determine the appropriate dose of Lamitrin S. These medicines include:
- oxcarbazepine, felbamate, gabapentin, levetiracetam, pregabalin, topiramate, zonisamide, used to treat epilepsy
- olanzapine or aripiprazole, used to treat mental disorders
- bupropion, used to treat mental disordersor nicotine addiction
- paracetamol, used to treat pain or fever
The doctor should be informedif the patient is taking any of these medicines.
Some medicines interact with Lamitrin S or increase the risk of side effects. These medicines include:
- valproate, used to treat epilepsy or mental disorders
- carbamazepine, used to treat epilepsy or mental disorders
- phenytoin, primidone, or phenobarbital, used to treat epilepsy
- risperidone, used to treat mental disorders
- rifampicin, which is an antibiotic
- medicines used to treat HIV infection(a combination of lopinavir with ritonavir or atazanavir with ritonavir)
- hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills ( see below) The doctor should be informedif the patient is taking, has taken, or is about to take any of these medicines.
Hormonal contraceptives (such as birth control pills) may affect the action of Lamitrin S
The doctor may recommend using a specific type of hormonal contraceptive or another method of contraception, such as a condom, diaphragm, or intrauterine device. If the patient is using hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, the doctor may recommend blood tests to check the level of Lamitrin S in the blood. If the patient is using or plans to use hormonal contraceptives:
they should discuss this with their doctorto choose an appropriate method of contraception.
Lamitrin S may also affect the action of hormonal contraceptives, although it is unlikely to reduce their effectiveness. If the patient is using hormonal contraceptives and notices any changes in their menstrual cycle, such as bleeding or spotting:
they should inform their doctor. Such symptoms may indicate that Lamitrin S is affecting the action of the contraceptive.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or thinks they may be pregnant or is planning to become pregnant, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
- The patient should not stop taking the medicine without consulting their doctor first.This is especially important if the patient has epilepsy.
- Pregnancy may change the effectiveness of Lamitrin S, so there may be a need for blood tests and adjustment of the dose of Lamitrin S.
- There may be a small increased risk of birth defects, including cleft lip and palate, if Lamitrin S is taken during the first three months of pregnancy.
- If the patient is planning to become pregnant or is pregnant, the doctor may recommend taking folic acidin addition.
During breastfeeding or if the patient plans to breastfeed, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before taking
this medicine. The active substance of Lamitrin S passes into breast milk and may affect the baby. The doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of breastfeeding while taking Lamitrin S, and if the patient decides to breastfeed, the doctor will periodically check the baby for excessive sleepiness, rash, or poor weight gain. If any of these symptoms are noticed in the baby, the patient should inform the doctor.
Driving and using machines
Lamitrin S may cause dizziness and double vision.
The patient should not drive or operate machinery unless they are sure that these symptoms do not occur.
If the patient has epilepsy, they should discuss driving and operating machinery with their doctor.
Lamitrin S chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension contain less than 1 mmol
(23 mg) of sodium per tablet, which means that the medicine is considered sodium-free.
3. How to take Lamitrin S
This medicine should always be taken as directed by the doctor. If the patient has any doubts, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
What dose of Lamitrin S should be taken
Determining the appropriate dose of Lamitrin S for the patient may take time. The dose taken by the patient depends on:
- the patient's age
- whether the patient is taking Lamitrin S in combination with other medicines
- whether the patient has any kidney or liver disease.
The doctor will initially prescribe a small dose and then gradually increase it over several weeks until an effective dose is reached for the patient (called the effective dose). The patient should never take a higher dose of Lamitrin S than recommended by their doctor.
Usually, the effective dose of Lamitrin S in adults and children over 13 years of age is between 100 mg and 400 mg per day.
In children between 2 and 12 years of age, the effective dose depends on the child's weight - usually between 1 mg and 15 mg per kilogram of body weight, up to a maximum maintenance dose of 200 mg per day.
Lamitrin S is not recommended for children under 2 years of age.
Taking the dose of Lamitrin S
The dose of Lamitrin S should be taken once or twice a day, as directed by the doctor. Lamitrin S can be taken with or without food.
- The patient should always take the entire doseprescribed by the doctor. The patient should never take only part of a tablet.
The doctor may also recommend starting or stopping other medicines, depending on the indication and the patient's response to treatment.
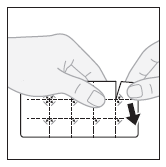
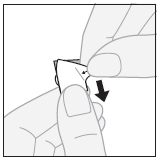
Lamitrin S chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension can be swallowed whole with a small amount of water or chewed and taken in a liquid form after mixing with water. The patient should never take only part of the suspension.
Preparing an oral suspension
- the tablet should be placed in a glass and enough water should be added to cover the tablet;
- the mixture should be stirred or left until the tablet is completely dissolved;
- the prepared suspension should be taken in its entirety;
- a small amount of water should be added to the glass and taken to ensure that the medicine is not left in the glass.
Taking a higher dose of Lamitrin S than recommended
The patient should contact a doctor or the nearest emergency department immediately.
If possible, the patient should show the packaging of Lamitrin S.
Taking too high a dose of Lamitrin S may increase the risk of serious side effects, which can be fatal.
If a person has taken too high a dose of Lamitrin S, they may experience:
- rapid, involuntary eye movements ( nystagmus)
- uncoordinated movements, lack of coordination, inability to maintain balance ( ataxia)
- heart rhythm disturbances (detected by ECG)
- loss of consciousness, seizures, or coma.
Missing a single dose of Lamitrin S
The patient should not take extra tablets to make up for the missed dose. The patient should take the next dose at the usual time.
If the patient misses several doses of Lamitrin S
The patient should consult their doctor about restarting
treatment with Lamitrin S. This is important for the patient.
The patient should not stop taking Lamitrin S unless their doctor recommends it
Lamitrin S must be taken for as long as the doctor recommends. The patient should not stop taking it unless their doctor recommends it.
Taking Lamitrin S for the treatment of epilepsy
To stop taking Lamitrin S, the dose should be gradually reducedover about two weeks. If the patient stops taking Lamitrin S suddenly, their epilepsy symptoms may return or worsen.
Taking Lamitrin S for the treatment of bipolar affective disorders
It may take some time before Lamitrin S starts to work, so it is unlikely that an improvement will occur immediately. When stopping treatment with Lamitrin S, there is no need to gradually reduce the dose. However, the patient should consult their doctor if they plan to stop taking Lamitrin S.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Lamitrin S can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Life-threatening reactions: the patient should contact a doctor immediately.
In a small number of patients taking Lamitrin S, an allergic reaction or potentially life-threatening skin reaction may occur, which may worsen if left untreated. Such reactions may occur more frequently during the first few months of taking Lamitrin S, especially when the patient has been given too high a dose, the dose has been increased too quickly, or when the patient is taking Lamitrin S in combination with another medicine called valproate. Some of these reactions occur more frequently in children, so parents should pay special attention to them.
These reactions include:
- skin rash or redness, which may worsen to severe or life-threatening skin reactions, including a rash with ring-shaped lesions resembling a target ( erythema multiforme), widespread rash with blisters and peeling of the skin, especially around the mouth, nose, eyes, and genitals ( Stevens-Johnson syndrome), widespread peeling of the skin (affecting more than 30% of the body surface - toxic epidermal necrolysis) or widespread rash accompanied by changes in the liver, blood, and other organs ( Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, DRESS)
- mouth ulcers, throat ulcers, nose ulcers, or genital ulcers
- eye ulcers, redness, and swelling( conjunctivitis)
- high fever(fever), flu-like symptoms, or drowsiness
- swelling of the face, enlarged lymph nodesin the neck, armpits, and groin
- unexpected bleeding, bruising, or blue discoloration of the fingers
- sore throator more frequent infections (such as colds)
- increased liver enzymes in blood tests
- increased white blood cell count (eosinophilia)
- enlarged lymph nodes
- changes affecting other organs, including the liver and kidneys.
In many cases, these are symptoms of less severe side effects. However, they can be life-threatening and, if left untreated, can develop into serious conditions, such as organ failure. If any of these symptoms are noticed:
The doctor should be informed immediately. The doctor may decide to perform liver, kidney, or blood tests and may recommend discontinuing Lamitrin S. If the patient develops Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis, the doctor will inform them that they should never take lamotrigine again.
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)(see section 2. Important information before taking Lamitrin S).
Very common side effects
May occur in more than 1 in 10patients:
- headache
- skin rash.
Common side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 10patients:
- aggression or irritability
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- tremor
- difficulty sleeping ( insomnia)
- feeling of excitement
- diarrhea
- dry mouth
- nausea or vomiting
- feeling of tiredness
- back pain, joint pain, or pain in any other location.
Uncommon side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 100patients:
- uncoordinated movements and lack of coordination ( ataxia)
- double or blurred vision
- unusual hair loss ( alopecia)
- skin rash or sunburn after exposure to sunlight or artificial light (phototoxicity).
Rare side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 1,000patients:
- skin reaction that causes red spots and patches on the skin, which may look like a target or "bull's eye" with a dark red center surrounded by lighter red rings ( erythema multiforme)
- a life-threatening skin reaction (Stevens-Johnson syndrome: also see the information at the beginning of section 4)
- a group of symptoms including fever, nausea, vomiting, headache, stiff neck, extreme sensitivity to bright light. This may be caused by inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord ( meningitis). These symptoms usually go away after stopping treatment, but if they worsen, the patient should contact a doctor.
- rapid, involuntary eye movements ( nystagmus)
- itchy eyes with discharge ( conjunctivitis).
Very rare side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 10,000patients:
- a life-threatening skin reaction (toxic epidermal necrolysis: also see the information at the beginning of section 4)
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)(see section 4)
- high fever(fever) ( also see the information at the beginning of section 4)
- swelling of the face, enlarged lymph nodesin the neck, armpits, and groin ( generalized lymphadenopathy: also see the information at the beginning of section 4)
- changes in liver function, which have been detected in blood tests or liver failure ( also see the information at the beginning of section 4)
- severe blood clotting disorder, which can cause unexpected bleeding or bruising ( disseminated intravascular coagulation: also see the information at the beginning of section 4)
- hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) (see section 2. Important information before taking Lamitrin S)
- changes in blood test results, including decreased red blood cell count ( anemia), decreased white blood cell count ( leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis), decreased platelet count ( thrombocytopenia), decreased count of all blood cells ( pancytopenia), and a bone marrow disorder called aplastic anemia
- hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not real)
- disorientation
- feeling of instability or loss of balance while moving
- involuntary repetitive movements of the body and/or sounds or words (tics), involuntary muscle contractions affecting the eyes, head, and trunk (choreoathetosis), or other unusual body movements, such as jerks, tremors, or stiffness
- increased frequency of seizures in patients with previously diagnosed epilepsy
- worsening of symptoms in patients with diagnosed Parkinson's disease
- a condition that may include back or joint pain, which may be accompanied by fever and/or general feeling of being unwell (serum sickness-like reaction).
Other side effects
Other side effects have occurred in a small number of patients, but the frequency is unknown.
- Reports of bone disorders, including osteopenia and osteoporosis (bone weakness) and fractures. If the patient is taking antiepileptic medicines for a long time, has had osteoporosis before, or is taking steroids, they should discuss this with their doctor or pharmacist
- Kidney inflammation ( tubulointerstitial nephritis) or simultaneous kidney and eye inflammation ( tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis)
- Nightmares
- Decreased immunity due to lower levels of antibodies in the blood, called immunoglobulins, which help protect the body against infections
- Red lumps or spots on the skin (pseudolymphoma).
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety, Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych, Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Lamitrin S
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
The patient should not take this medicine after the expiry date stated on the blister, carton, or bottle. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
There are no special precautions for storing Lamitrin S.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Lamitrin S chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension contain
The active substance is lamotrigine. Each chewable/disintegrating tablet / for oral suspension contains 2 mg, 5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, or 200 mg of lamotrigine, respectively.
The other ingredients are calcium carbonate, hydroxypropylcellulose, aluminomagnesium silicate, sodium carboxymethylcellulose (type A), povidone K30, sodium saccharin, magnesium stearate, blackcurrant flavor.
What Lamitrin S chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension look like and what the pack contains:
Lamitrin S chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension (all strengths) are white to almost white and may be slightly speckled. They have a blackcurrant flavor. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Lamitrin S, 2 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension are round. They are marked with "LTG" above "2" on one side; on the other side, there are two intersecting ellipses at a right angle. Each bottle contains 30 tablets.
Lamitrin S, 5 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension are oval, biconvex. They are marked with "GS CL2" on one side and "5" on the other side. Each pack contains 10, 14, 28, 30, 42, 50, or 56 tablets in blisters or 14, 28, 30, 42, 56, or 60 tablets in a bottle.
Lamitrin S, 25 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension are multi-faceted, square with rounded corners. They are marked with "GSCL5" on one side and "25" on the other side. Each pack contains 10, 14, 21, 28, 30, 42, 50, 56, or 60 tablets in blisters.
Lamitrin S, 50 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension are multi-faceted, square with rounded corners. They are marked with "GSCX7" on one side and "50" on the other side. Each pack contains 10, 14, 28, 30, 42, 50, 56, 60, 90, 98, 100, 196, or 200 tablets in blisters.
Lamitrin S, 100 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension are multi-faceted, square with rounded corners. They are marked with "GSCL7" on one side and "100" on the other side. Each pack contains 10, 14, 28, 30, 42, 50, 56, 60, 90, 98, 100, 196, or 200 tablets in blisters.
Lamitrin S, 200 mg, chewable/disintegrating tablets / for oral suspension are multi-faceted, square with rounded corners. They are marked with "GSEC5" on one side and "200" on the other side. Each pack contains 10, 14, 28, 30, 42, 50, 56, 60, 90, 98, 100, 196, or 200 tablets in blisters.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder:
GlaxoSmithKline Trading Services Limited
12 Riverwalk
Citywest Business Campus
Dublin 24
D24 YK11
Ireland
Manufacturer:
Delpharm Poznań Spółka Akcyjna
ul. Grunwaldzka 189
60-322 Poznań
Poland
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
| Austria Lamictal | Belgium Lamictal | Bulgaria Lamictal |
| Croatia Lamictal | Cyprus Lamictal | Czech Republic Lamictal |
| Denmark Lamictal | Estonia Lamictal | Finland Lamictal |
| France Lamictal Lamicstart | Germany Lamictal | Greece Lamictal |
| Hungary Lamictal | Iceland Lamictal | Ireland Lamictal |
| Italy Lamictal | Latvia Lamictal | Lithuania Lamictal |
| Luxembourg Lamictal | Malta Lamictal | Netherlands Lamictal |
| Norway Lamictal | Poland Lamitrin S | Portugal Lamictal |
| Romania Lamictal | Slovakia Lamictal | Slovenia Lamictal |
| Spain Lamictal | Sweden Lamictal |
For more information, the patient should contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder:
GSK Services Sp. z o. o.
tel. +48 22 576 90 00
Date of last revision of the leaflet:January 2025
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterDelpharm Poznań S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Lamitrin SDosage form: Tablets, 100 mgActive substance: lamotriginePrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 50 mgActive substance: lamotriginePrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 100 mgActive substance: lamotriginePrescription required
Alternatives to Lamitrin S in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Lamitrin S in Spain
Alternative to Lamitrin S in Ukraine
Online doctors for Lamitrin S
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Lamitrin S – subject to medical assessment and local rules.







