
Klabax Ec
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Klabax Ec

How to use Klabax Ec
1. What is Klabax and what is it used for
Klabax contains the active substance clarithromycin.
Clarithromycin belongs to a group of medicines called macrolide antibiotics, which inhibit the growth of certain bacteria.
Klabax is indicated for the treatment of:
- lower respiratory tract infections, such as bronchitis, pneumonia;
- throat and sinus infections;
- skin and soft tissue infections;
- ear infections, especially acute otitis media.
This medicine is used in children from 6 months to 12 years old.
2. Important information before using Klabax
When not to use Klabax:
- if the patient is allergic to clarithromycin, other macrolide antibiotics (such as erythromycin or azithromycin) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- 6)
- if the patient is taking ergot alkaloids in tablet form (such as ergotamine or dihydroergotamine) or is taking ergot alkaloids for migraine in inhalation form.
- if the patient is taking terfenadine or astemizole (medicines often used for hay fever or allergies), cisapride or domperidone (a medicine used for stomach disorders), pimozide (a medicine used for psychiatric disorders), as concomitant use of these medicines may cause serious heart rhythm disturbances. The patient should consult their doctor for advice on taking other medicines.
- if the patient is taking other medicines that may cause serious heart rhythm disturbances.
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013
- if the patient is taking lovastatin or simvastatin (statins - HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, used to lower cholesterol levels in the blood).
- if the patient is taking midazolam orally (a sedative).
- if the patient has low potassium or magnesium levels in the blood (hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia).
- if the patient has severe liver disease with concomitant kidney disease.
- if the patient or their family members have had heart rhythm disturbances (ventricular arrhythmias, including torsades de pointes) or abnormalities in the electrocardiogram (ECG - a recording of the heart's electrical activity) known as "long QT syndrome”.
- if the patient is taking ticagrelor, ivabradine or ranolazine (for angina or to reduce the risk of heart attack or stroke).
- if the patient is taking colchicine (usually for gout).
- if the patient is taking a medicine containing lomitapide.
Warnings and precautions
The patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Klabax,
if:
- the patient has heart problems (such as heart disease, heart failure, very slow heart rate).
- the patient has kidney or liver problems.
- the patient has a fungal infection or is prone to fungal infections (such as thrush).
Klabax and other medicines
Klabax should not be used if the patient is taking any of the medicines listed above in "When not to use Klabax".
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines the child is currently taking or has recently taken, as well as any medicines planned to be given to the child, as a dose adjustment or regular monitoring may be necessary:
- digoxin, quinidine, disopyramide (used for heart rhythm disorders)
- warfarin or any other anticoagulant, such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban (medicines used to thin the blood)
- carbamazepine, valproate, phenobarbital or phenytoin (antiepileptic medicines)
- atorvastatin, rosuvastatin [HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, also known as statins, medicines that lower cholesterol levels (a type of fat) in the blood]. Statins may cause rhabdomyolysis (a condition that causes muscle tissue to break down, which can lead to kidney damage). The patient should be monitored for signs of muscle damage (muscle pain or weakness).
- nateglinide, pioglitazone, repaglinide, rosiglitazone or insulin (medicines that lower blood sugar levels)
- glipizide or glimepiride (sulfonylurea derivatives used for type 2 diabetes)
- theophylline (used for breathing difficulties, such as asthma)
- triazolam, alprazolam or midazolam given intravenously or orally (sedatives)
- cilostazol (a medicine used for circulation disorders)
- methylprednisolone (a corticosteroid)
- ibrutinib or vinblastine (used for cancer treatment)
- cyclosporin, sirolimus and tacrolimus (medicines that suppress the immune system)
- etravirine, efavirenz, nevirapine, ritonavir, zidovudine, atazanavir, saquinavir (antiviral medicines used for HIV treatment)
- rifabutin, rifampicin, rifapentine, fluconazole, itraconazole (used for certain bacterial or fungal infections)
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013
- tolterodine (a medicine used for overactive bladder)
- verapamil, amlodipine, diltiazem (used for high blood pressure)
- sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil (medicines used for erectile dysfunction in adult men or for pulmonary hypertension [high blood pressure in the blood vessels of the lungs])
- St. John's Wort (a herbal medicine used for depression)
- quetiapine or other antipsychotic medicines
- other macrolide antibiotics
- lincosamide antibiotics: lincomycin and clindamycin
- hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine (used for rheumatoid arthritis or for the treatment or prevention of malaria). Taking these medicines with clarithromycin may increase the risk of heart rhythm disturbances and other serious side effects affecting the heart.
- oral, injectable or inhaled corticosteroids (used to suppress the immune system, which is useful in the treatment of many different diseases)
- omeprazole (used for stomach and/or intestinal disorders).
The patient should consult their doctor if they are a woman of childbearing age, taking oral contraceptives, and experience diarrhea or vomiting, as additional contraceptive measures may be necessary, such as using a condom.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
The safety of clarithromycin during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been established.
If the medicine is to be given to a woman of childbearing age (who is pregnant or thinks she may be pregnant), she should consult her doctor before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
There is no data on the effect of clarithromycin on the ability to drive and use machines.
Before driving or using machines, the patient should consider that while taking the medicine, dizziness, confusion and disorientation may occur.
Klabax contains sucrose
5 ml of the suspension contains 3194 mg of sucrose.
This should be taken into account in patients with diabetes.
If the patient has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, they should tell their doctor before starting to use this medicine.
Klabax contains aspartame
This medicine contains 1 mg of aspartame in each 5 ml of the suspension, which corresponds to 0.2 mg/ml.
Aspartame is a source of phenylalanine. It may be harmful to patients with phenylketonuria. This is a rare genetic disorder in which phenylalanine accumulates in the body due to its improper excretion.
Klabax contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium in 5 ml of the suspension, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free”.
Klabax contains sodium benzoate
This medicine contains 10 mg of sodium benzoate in 5 ml of the suspension, which corresponds to 2 mg/ml.
3. How to use Klabax
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubts, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013
The recommended doses of Klabax are given below:
Dosage
| Body weight (in kg) | Age (in years) | Dose in ml (to be given twice a day) |
|
| 2.5 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 7.5 |
|
| 10 |
Children who weigh less than 8 kg should receive a dose of 0.3 ml/kg body weight twice a day. In certain situations, the doctor may prescribe higher or lower doses than described.
Klabax should be taken twice a day (in the morning and early evening). The medicine can be given with food if it is more convenient for the patient.
Administration methodThe medicine is for oral use, after preparation of the suspension. The instructions for preparing the suspension are given below.
Before each administration of the medicine, the bottle should be shaken well, and after administration, the cap should be tightened firmly.
Duration of treatmentKlabax is usually given for 5 to 10 days.
Instructions for preparing the suspension
Step A
Take the bottle out of the box.

Step B
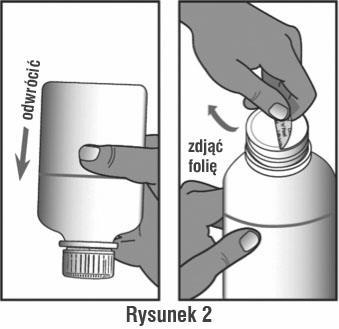
Invert the bottle and shake it to loosen the powder from the bottom. Check this by looking at the inverted bottle in the light. Open the cap according to the instructions below, remove the protective foil (see Figure 2).
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013
Step C
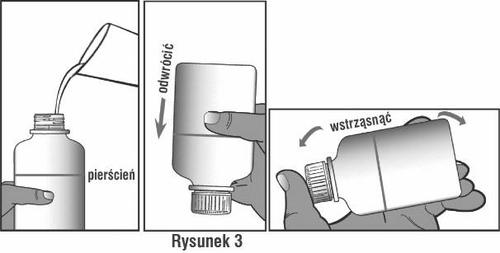
Slowly add water to the ring mark on the bottle. Looking at the light, you can check if the bottle is filled to the correct level. Close the bottle, invert and shake vigorously for about 1 minute, until the powder is no longer stuck to the bottom of the bottle (see Figure 3). You should look at the inverted bottle in the light to check this.
If necessary, wait a moment and add more water to the ring mark, as described in Step D.
Step D
If necessary, add more water to the ring mark on the bottle. If necessary, hold the bottle up to the light to check if it is filled to the correct level.
Close the bottle. Invert and shake vigorously until the powder is no longer stuck to the bottom of the bottle (see Figure 4). You should check this by holding the inverted bottle up to the light.
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013
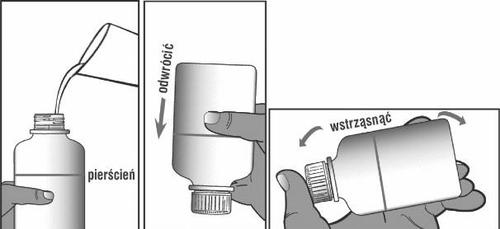
Figure 4
Instructions for use
A measuring spoon and adapter are provided with the Klabax packaging to facilitate measuring the correct amount of medicine to be given to the child.
The patient should follow the instructions below carefully.
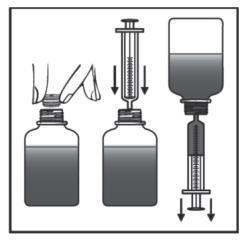
- 1. To open the bottle, the patient should remove the cap (which has a child-resistant closure) by pressing it and turning it in the opposite direction to the arrow.
- 2. Take the plastic, round adapter out of the packaging and push it into the neck of the bottle. The adapter should fit tightly and should not be removed after it has been put on.
- 3. Take the measuring spoon out of the packaging and make sure the plunger is pushed all the way in. This will remove any air that may be in the spoon.
- 4. Place the tip of the measuring spoon into the adapter opening.
- 5. Invert the bottle and hold it in one hand, and the measuring spoon in the other.
- 6. Holding the measuring spoon, slowly pull out the plunger until the spoon is filled with the correct amount of suspension to be given to the child.
- 7. Turn the bottle right side up. Holding the measuring spoon container, remove the spoon from the adapter.
- 8. Place the tip of the spoon in the child's mouth. Give the medicine by pressing the plunger gently, while still holding the spoon. Do not rush the child; give them time to swallow the medicine slowly. The measured dose can also be poured into a spoon and given to the child in this way.
- 9. Close the bottle with the cap.
- 10. Wash the measuring spoon in warm soapy water, then rinse well. Hold the spoon under running water, moving the plunger up and down several times to make sure the inside is clean. The spoon should be stored in a hygienic manner, together with the medicine.
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013

Administration of the suspension
Klabax may cause a bitter taste. This can be prevented by eating something, drinking juice or water immediately after taking the suspension.

Administration of water or juice after taking the medicine.
The patient can also add the following amounts of water to the bottle for the corresponding package sizes:
| Package size | Volume of water to be added |
| 50 ml bottle | 27 ml |
| 60 ml bottle | 33 ml |
| 70 ml bottle | 38 ml |
| 100 ml bottle | 54 ml |
| 140 ml bottle | 76 ml |
Close the bottle and shake it vigorously.
Overdose of Klabax
In case the child has been given a larger amount of Klabax than prescribed by the doctor within a day, or if the child has accidentally swallowed more medicine, the patient should immediately consult a doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department.
Overdose of Klabax may cause vomiting and stomach pain.
Missed dose of Klabax
If a dose of Klabax is missed, it should be given as soon as possible. The patient should not give more Klabax in a day than prescribed by the doctor.
Stopping Klabax treatment
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013
The patient should not stop taking this medicine even if the child feels better. It is important to use this medicine for as long as the doctor has prescribed, otherwise the symptoms of the disease may recur.
In case of any further doubts about the use of this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Klabax can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Serious side effects
If the patient experiences any of the following side effects, they should STOP taking the medicine and consult their doctor immediately:
- severe or prolonged diarrhea, possibly with blood or mucus. Diarrhea may occur even two months after finishing clarithromycin treatment, in which case the patient should also consult their doctor.
- rash, difficulty breathing, fainting or swelling of the face, tongue, lips, eyes and throat. These are symptoms of an allergic reaction.
- yellowing of the skin (jaundice), skin irritation, pale stools, dark urine, tenderness to the touch of the abdomen or loss of appetite. These may be symptoms of liver inflammation and liver failure.
- severe skin reactions, such as painful blisters on the skin, in the mouth, on the lips, eyes and genitals (symptoms of a rare allergic reaction called Stevens-Johnson syndrome / toxic epidermal necrolysis).
- red, scaly rash with bumps under the skin and blisters (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis). The frequency of this side effect is unknown (it cannot be estimated from the available data).
- rare allergic skin reactions causing severe diseases with ulcers of the mouth, lips and skin with a rash, fever and inflammation of the internal organs (DRESS)
- muscle pain or weakness called rhabdomyolysis (a condition that causes muscle tissue to break down, which can lead to kidney damage).
Other side effects
Common (occurring in less than 1 in 10 patients):
- insomnia
- taste disorders
- headache
- vasodilation
- stomach disorders, such as nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, indigestion, diarrhea
- excessive sweating
Uncommon (occurring in less than 1 in 100 patients):
- high temperature
- swelling, redness or itching of the skin
- thrush of the mouth or vagina
- gastritis or enteritis
- decreased platelet count (which helps to stop bleeding)
- decreased white blood cell count (leukopenia)
- decreased granulocyte count (neutropenia)
- muscle stiffness
- chills
- increased eosinophil count (white blood cells responsible for immunity)
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013
- excessive immune response to foreign substances
- loss of appetite or decreased appetite
- restlessness, nervousness
- drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness or tremors
- involuntary muscle contractions
- balance disorders
- tinnitus or hearing loss
- chest pain or heart rhythm disorders, such as palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- asthma: a lung disease related to bronchial constriction, making breathing difficult
- nasal bleeding
- blood clots causing sudden blockage of blood flow in the pulmonary artery (pulmonary embolism)
- inflammation of the esophageal and stomach mucosa
- anal pain
- bloating, constipation, bloating with gas, belching
- dry mouth
- a condition in which bile (a fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder) does not flow from the gallbladder into the duodenum (bile stasis)
- skin inflammation with blisters, itching and painful rash
- muscle cramps, muscle pain or muscle tissue loss. If the child has myasthenia (a disease in which the muscles are weak and easily get tired), clarithromycin may worsen these symptoms
- abnormal, increased blood test results indicating kidney and liver function, abnormal, increased blood test results
- feeling of weakness, fatigue and lack of energy
Frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- inflammation of the intestine
- bacterial skin infection
- decreased count of certain blood cells (which may cause more frequent infections or increase the risk of bruising or bleeding)
- confusion, psychotic disorder, hallucinations (seeing things that are not there), change in perception of reality or panic attacks, depression, unusual dreams or nightmares and mania (feeling of excessive joy or excitement)
- seizures (seizure attacks)
- sensory disturbances (tingling)
- loss of taste or smell or inability to perceive smells correctly
- hearing loss
- heart rhythm disorders such as torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia
- bleeding (hemorrhage)
- pancreatitis
- discoloration of the tongue or teeth
- acne
- changes in the levels of substances produced by the kidneys, kidney inflammation, kidney failure (which may cause fatigue, swelling of the face, bags under the eyes, swelling in the abdomen, legs or ankles, or difficulty urinating)
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any not listed in this leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw,
Phone: 22 49 21 301
Fax: 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Klabax
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
The medicine should not be used after the expiry date stated on the bottle or carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Store in a temperature below 30°C. The prepared suspension should not be stored in the refrigerator or frozen.
The shelf life of the prepared suspension is 14 days.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Klabax contains
The active substance of Klabax is clarithromycin.
5 ml of the prepared suspension contains 125 mg of clarithromycin.
The other ingredients are: methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate copolymer (1:1), dispersion 30%, macrogol 1500, talc, carbomer, silicon dioxide, sucrose, aspartame (E 951), xanthan gum (E 415), sodium citrate, sodium benzoate (E 211), titanium dioxide (E 171), peppermint flavor (containing flavoring substances, modified starch), tutti frutti flavor (containing corn maltodextrin, natural identical flavoring substances, propylene glycol (E 1520), modified corn starch (E 1450), flavoring and aroma substances of synthetic origin).
What Klabax looks like and contents of the pack
Granules for oral suspension
Klabax EC is a white to off-white granule for preparation of a suspension.
Package sizes:1 bottle containing 41.66 – 46.04 g of granules for preparation of 60 ml of oral suspension or
1 bottle containing 48.61 – 53.72 g of granules for preparation of 70 ml of oral suspension or
1 bottle containing 69.44 – 76.75 g of granules for preparation of 100 ml of oral suspension.
Not all package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
Ranbaxy (Poland) Sp. z o.o.
ul. Idzikowskiego 16
00-710 Warsaw
phone: 22 642 07 75
DE/H/5210/II/012/G_IB/013
Manufacturer/Importer
SUN Pharmaceutical Industries (Europe) B.V.
Polarisavenue 87
2132JH Hoofddorp
Netherlands
Alkaloida Chemical Company Zrt.
Kabay János u. 29.
4440 Tiszavasvári
Hungary
S.C. Terapia S.A.
Str. Fabricii nr.124,
400632 Cluj-Napoca, Jud. Cluj
Romania
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Germany CLARITHROMYCIN BASICS 125 mg/5 ml Granulat zur Herstellung einer
Suspension zum Einnehmen
Italy Claritromicina SUN
Romania Klabax 125mg/5ml granule pentru suspensie orală
United Kingdom Clarithromycin 125 mg/5ml granules for oral suspension
(Northern Ireland)
Date of last revision of the leaflet:31.07.2024
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAlkaloida Chemical Co. Zrt. S.C. Terapia S.A. Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Europe B.V.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Klabax EcDosage form: Powder, 500 mgActive substance: clarithromycinManufacturer: Adamed Pharma S.A. ANFARM HELLAS S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 250 mgActive substance: clarithromycinManufacturer: Synoptis Industrial Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 500 mgActive substance: clarithromycinManufacturer: Synoptis Industrial Sp. z o.o.Prescription required
Alternatives to Klabax Ec in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Klabax Ec in Spain
Alternative to Klabax Ec in Ukraine
Online doctors for Klabax Ec
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Klabax Ec – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














