Klabax 250 mg/5 ml
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Klabax 250 mg/5 ml

How to use Klabax 250 mg/5 ml
1. What is Klabax and what is it used for
Clarithromycin belongs to a group of antibiotics called macrolides. This medicine works by killing certain types of bacteria that cause some infections. Clarithromycin can be used to treat bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, throat, sinuses, and ear (especially middle ear inflammation), as well as skin and subcutaneous tissue infections.
Clarithromycin in the form of a suspension is indicated for use in children over 6 months of age and adolescents up to 12 years of age.
2. Important information before using Klabax
Klabax should not be given to a child if:
- they are allergic to clarithromycin, other macrolide antibiotics, such as erythromycin or azithromycin, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- they have too low a level of potassium or magnesium in the blood (hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia);
- they have severe liver disorders combined with kidney function disorders;
- the patient or their family has a history of heart rhythm disorders (ventricular arrhythmias, including torsades de pointes) or abnormalities in the electrocardiogram (ECG, registration of the heart's electrical activity) called "long QT interval syndrome";
- they are taking:
- drugs called ergot alkaloids (e.g., ergotamine or dihydroergotamine) in tablet form or using ergotamine inhalers (used to treat migraines);
- drugs such as terfenadine or astemizole (used to treat hay fever or allergies), cisapride or pimozide. Concurrent use of these drugs may cause severe heart rhythm disorders. You should consult a doctor and establish alternative treatment;
- other drugs that may cause serious heart rhythm disorders;
- midazolam given orally (a sleeping pill);
- tikagrelor or ranolazine (used to prevent heart attack, chest pain, angina pectoris);
- colchicine (usually used to treat gout);
- lovastatin, simvastatin, or atorvastatin (lowering blood cholesterol levels);
- a drug containing lomitapide.
If any of the above situations apply to your child, you should consult a doctor who will recommend alternative treatment.
While using Klabax, special caution should be exercised
- If the child has too low a level of magnesium in the blood (hypomagnesemia) before taking the medicine, you should consult a doctor.
Warnings and precautions
You should contact a doctor or pharmacist before giving Klabax to a child if:
- they have liver or kidney disorders;
- they are resistant to other antibiotics, such as clindamycin, lincomycin;
- they have heart disorders (e.g., heart disease, heart failure, very slow heart rate)
- they are taking anticoagulant drugs, e.g., warfarin (blood-thinning drugs). The prothrombin time should be frequently monitored;
- drugs that may impair hearing, e.g., aminoglycosides, are being administered. If necessary, the doctor should check the child's hearing;
- they are taking drugs that lower blood sugar levels. Clarithromycin may enhance their effect;
- they have pneumonia, as the bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae) that cause it may be resistant to clarithromycin;
- they have tonsillitis and there is no hypersensitivity or other contraindications to the use of penicillins
- they have a fungal infection or are prone to such infections (e.g., thrush).
If bacteria are resistant to erythromycin A, they may also be resistant to clarithromycin.
You should consult a doctor if any of the above situations occur in your child.
You should stop using Klabax and contact a doctor if your child:
- experiences severe diarrhea during or after taking Klabax. You should avoid drugs that inhibit peristalsis (intestinal movement), such as drugs used to treat diarrhea.
- experiences jaundice (yellowing of the skin), skin irritation, dark urine, abdominal pain, or loss of appetite. These symptoms may indicate liver function disorders in the child.
- experiences another infection.
Klabax and other medicines
You should tell the doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines your child is taking, has recently taken, or is about to take.
You should stop using Klabax in your child and contact a doctor if they are taking any of the following medicines:
- astemizole or terfenadine (used to treat hay fever or allergies);
- cisapride (prescribed for stomach disorders);
- pimozide (prescribed for mental disorders);
- ergotamine and dihydroergotamine (given to treat migraines);
- tikagrelor or ranolazine (used to prevent heart attack, chest pain, angina pectoris);
- colchicine (usually used to treat gout);
- lovastatin, simvastatin, or atorvastatin (lowering blood cholesterol levels).
See also the section "Klabax should not be given to a child if"
The doctor may consider it necessary to monitor blood parameters or the effect of the medicine, adjust the dose, or interrupt (for some time) treatment if Klabax is used at the same time as medicines containing any of the following substances:
- digoxin (in heart failure);
- quinidine or disopyramide (taken in heart rhythm disorders);
- midazolam given intravenously or in the form of a solution for oral use (a sedative/sleeping pill);
- triazolam (a sleeping pill);
- alprazolam (prescribed for anxiety states);
- verapamil, diltiazem, or amlodipine (drugs that lower blood pressure);
- tolterodine (used to treat urinary incontinence);
- St. John's Wort (a herbal preparation used in depression);
- cyclosporine, tacrolimus, or sirolimus (helping to prevent rejection of a transplanted organ);
- theophylline (given in breathing difficulties, such as asthma);
- etravirine, efavirenz, ritonavir, zidovudine, nevirapine, atazanavir, or saquinavir (antiviral drugs used to treat HIV infection);
- rifampicin, rifabutin, or rifapentine (antibiotics used to treat certain bacterial infections);
- fluconazole, itraconazole (antifungal drugs);
- oral anticoagulant drugs, such as warfarin or any other anticoagulant drug, e.g., dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban (blood-thinning drugs). The prothrombin time should be frequently monitored in the child.
- rosuvastatin (a cholesterol-lowering drug). Statins may cause rhabdomyolysis (muscle tissue breakdown, which can lead to kidney damage). Symptoms of myopathy (muscle pain or weakness) should be monitored.
- phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, or phenobarbital (used in epilepsy);
- insulin or other antidiabetic drugs, e.g., repaglinide, nateglinide (drugs that lower blood glucose levels);
- gliclazide or glimepiride (sulfonylurea derivatives used to treat type 2 diabetes);
- sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil (used to treat impotence in adult men or to treat pulmonary hypertension);
- cylostazol (in circulatory disorders);
- methylprednisolone (a steroid);
- vinblastine (in cancer treatment);
- quetiapine or other antipsychotic drugs;
- other macrolide drugs;
- lincomycin or clindamycin (antibiotics from the lincosamide group).
- hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine (drugs used to treat autoimmune diseases).
The doctor will make a decision about what is appropriate for the child and may recommend continued use of Klabax.
If the patient is taking oral contraceptives and experiences diarrhea or vomiting, they should contact a doctor, as other methods of preventing pregnancy may be necessary (e.g., condoms).
Using Klabax with food and drink
Klabax can be used independently of food intake.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
The safety of using clarithromycin during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not known, and the drug is not usually given during pregnancy and breastfeeding, unless its use is considered necessary. If the patient is of childbearing age, in case of suspected or confirmed pregnancy before taking this medicine, they should consult a doctor.
Driving and using machines
Clarithromycin may cause dizziness, including vertigo, confusion, and disorientation. This may affect driving and using machines. Before driving, using machines, or engaging in any other activity that may be hazardous if you are not alert, you should make sure how the patient reacts to clarithromycin.
Klabax contains sucrose.If the child has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, they should contact a doctor before taking the medicine.
Klabax also contains aspartame,which is a source of phenylalanine. The medicine may be harmful to patients with phenylketonuria.
3. How to use Klabax
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. If you are unsure, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
You should not give more medicine than the doctor has prescribed. If you are unsure before giving clarithromycin, you should contact a doctor or pharmacist.
The dose of clarithromycin depends on the child's body weight and is usually about 7.5 mg per kilogram of body weight, twice a day, usually in the morning and evening. The suspension can be given independently of meals.
This medicine is usually given for 5 to 10 days. The doctor will recommend how long to give clarithromycin.
A spoon and a syringe (pipette) are attached to the Klabax packaging to facilitate dosing of the correct amount of medicine. The doctor or pharmacist will advise whether to use the spoon or pipette to give the correct dose. You should make sure this is understood before giving the suspension.
| Body weight (kg) | Approximate age (years) | Dose in milliliters of suspension (twice a day) administered with a syringe (pipette) | Number of 5-milliliter spoons to be given twice a day |
|
| 2.5 | ½ |
|
| 5 | 1 |
|
| 7.5 | 1½ |
|
| 10 | 2 |
The usual doses of Klabax 250 mg/5 ml are presented in the table below:
| Body weight (kg) | Approximate age (years) | Dose in milliliters of suspension (twice a day) administered with a syringe (pipette) | Number of 5-milliliter spoons to be given twice a day |
| 8 –11 |
| 1.25 | ¼ |
|
| 2.5 | ½ |
|
| 3.75 | ¾ |
|
| 5.0 | 1 |
For children weighing less than 8 kg, the doctor will recommend the appropriate dose.
In the treatment of severe infections, up to 500 mg of clarithromycin has been used twice a day.
If the child has mild to moderate kidney or liver function disorders, the doctor may prescribe a lower dose.
Preparing the suspension
60 ml bottle
Shake the bottle with the granules. Measure 34 ml of boiled, cooled water. Add part of the water to the dry substance in the bottle, shake vigorously. Add the rest of the water and shake vigorously until a suspension is obtained.
100 ml bottle
Shake the bottle with the granules. Measure 55 ml of boiled, cooled water. Add part of the water to the dry substance in the bottle, shake vigorously. Add the rest of the water and shake vigorously until a suspension is obtained.
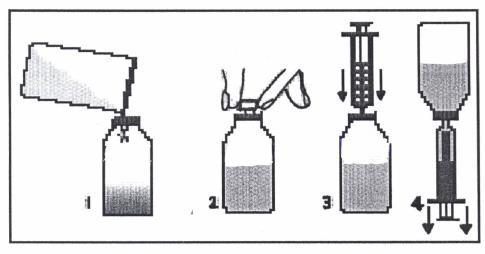
A spoon and a syringe (pipette) are attached to the Klabax packaging. When using the syringe, you should follow the instructions below. After using the spoon or syringe, you should wash them in warm water with dishwashing liquid and then rinse thoroughly.
- 1. Remove the cap (with a child safety lock) by pressing it and twisting it in the opposite direction to the clockwise direction.
- 2. Remove the plastic, round connector from the packaging and push it into the neck of the bottle. The connector should be tightly fitted and should not be removed after it has been put on.
- 3. Remove the syringe from the packaging and make sure the plunger is pushed all the way in. This will remove any air that may be in the syringe.
- 4. Place the tip of the syringe in the connector hole.
- 5. Turn the bottle upside down. Hold the bottle in one hand and the syringe in the other.
- 6. Holding the syringe, slowly pull out the plunger until the container is filled with the amount of medicine to be given to the child.
- 7. Turn the bottle right side up. Holding the syringe container, remove the syringe from the connector.
- 8. Place the tip of the syringe in the child's mouth. Give the medicine drop by drop by gently pressing the plunger, still holding the syringe. Do not rush the child; let them swallow the medicine slowly. You can also pour the measured dose from the syringe into the spoon and give the medicine to the child in this way.
- 9. Close the bottle with the cap.
- 10. Wash the syringe in warm water with dishwashing liquid and then rinse thoroughly. Hold the syringe under running water, moving the plunger up and down several times to make sure the inside is clean. The syringe should be stored in a hygienic place, together with the medicine.
Clarithromycin in suspension leaves a bitter taste. You should drink juice or water immediately after taking the medicine to prevent this.
Administering the medicine.
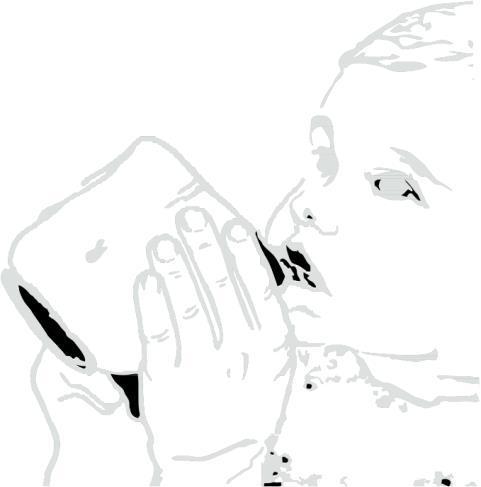

Administering water or juice after taking the medicine.
If you feel that the effect of the medicine is too strong or too weak, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
Using a higher dose of Klabax than recommended
If the child accidentally takes an extra dose of the medicine, you should immediately consult a doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department. You should take the leaflet or the suspension bottle with you and show it to the doctor, so they know what medicine the child has taken. Overdose of clarithromycin may cause vomiting and stomach pain.
Missing a dose of Klabax
You should give the medicine as soon as you notice this. If it is almost time for the next dose, you should give only the next dose at the usual time. You should not take a double dose to make up for missed doses.
Stopping the use of Klabax
You should not stop giving the medicine until the doctor recommends it, even if the child feels better, as the symptoms may recur.
If you have any doubts about using this medicine, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, clarithromycin can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Very serious side effects
You should stop using the medicine and immediately contact a doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department if you experience any of the following side effects:
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- sudden shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, swelling of the eyelids, face, or lips, rash, or itching. These may be symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Unknown frequency (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- if the patient experiences a severe skin reaction: a red, scaly rash with bumps under the skin and blisters (pustular psoriasis), you should contact a doctor immediately.
- severe skin symptoms, including rash, fever, swollen glands, and abnormal blood test results (Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, DRESS);
- severe or prolonged diarrhea, which may be bloody or contain mucus. Diarrhea may occur after stopping clarithromycin (see also: “Warnings and precautions”);
- rash, fever, abnormal blood test results, inflammation of internal organs. These may be symptoms of a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS);
- jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes), skin irritation, dark urine, abdominal pain, or loss of appetite. These symptoms may indicate liver function disorders in the child.
You should immediately contact a doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- abnormal liver function test results.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- heart attack, very fast heart rate, changes in the ECG, extra heartbeats, palpitations;
- blood clots in the lungs causing chest pain and shortness of breath.
Unknown frequency (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- changes in heart rhythm (known as torsades de pointes), rapid heart rate (tachycardia);
- pancreatitis (severe pain in the upper abdomen radiating to the back with nausea and vomiting);
- kidney inflammation (blood in the urine, fever, and back pain);
- hypoglycemia (abnormally low blood sugar levels, characterized by feelings of hunger, sweating, dizziness, and palpitations), especially when taking antidiabetic drugs;
- muscle weakness, especially tenderness or pain, if the child feels unwell or has a high temperature - this may be caused by muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), which can lead to kidney damage.
These are serious side effects, and the child may need medical attention.
Other side effects
You should immediately inform the doctor if you notice any of the following side effects in your child:
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- rash;
- excessive sweating;
- vasodilation;
- insomnia;
- headache;
- nausea (feeling sick), vomiting, stomach pain, indigestion, diarrhea;
- changes in taste (e.g., metallic or bitter taste).
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- skin inflammation with blisters, itching, rash, and hives, rash in the form of red spots on the skin covered with small merging papules (papular rash);
- cholestasis (bile stagnation);
- fever, sensitive or red skin, sometimes with fever and chills (inflammation of the connective tissue);
- nausea (mild to severe), vomiting, cramps, diarrhea. These symptoms may be caused by stomach and intestinal inflammation, usually caused by viruses;
- frequent infections, e.g., fever, severe chills, sore throat, or mouth ulcers. These symptoms may be caused by a low white blood cell count.
- increased white blood cell count, increased platelet count;
- increased levels of urea or creatinine (metabolic products) in the blood;
- changes in albumin, globulin, and various enzyme levels in the blood (alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase);
- loss of consciousness, uncontrolled convulsions, twitching, or sudden movements, drowsiness, tremors, or shakiness;
- shortness of breath, wheezing, cough, sometimes caused by physical exertion, and a feeling of pressure in the chest (asthma);
- dizziness, hearing disturbances, ringing in the ears (tinnitus);
- esophagitis, gastritis, oral mucositis, or tongue inflammation;
- a burning sensation in the chest that moves towards the throat (heartburn);
- constipation, dry mouth, gas, bloating, belching;
- rectal pain;
- fever, feeling unwell, chest pain, chills, fatigue, muscle pain, muscle stiffness, muscle cramps;
- decreased appetite, loss of appetite (anorexia);
- worsening of myasthenia symptoms (a disease in which muscles are weak and easily get tired)
- anxiety, nervousness, dizziness, screaming;
- general malaise;
- vaginal infections;
- thrush (fungal infection);
- nosebleeds;
- decreased granulocyte count.
Unknown frequency (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- intestinal inflammation;
- abnormal urine color;
- bacterial skin infections (erysipelas);
- severe kidney function disorders (kidney failure);
- deafness;
- seizures;
- decreased platelet count, which increases the risk of bleeding or bruising;
- bleeding;
- numbness and tingling of the arms and legs (paresthesia);
- tooth discoloration;
- muscle pain or weakness (myopathy);
- loss of taste (ageusia), tongue discoloration;
- inability to smell, change in sense of smell;
- acne;
- depression, hallucinations, abnormal thoughts (psychosis), disorientation, feeling of being outside the body (depersonalization), nightmares, confusion;
- prolonged bleeding and blood clotting time.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not mentioned in the leaflet, you should tell the doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, phone: 22 49-21-301, fax: 22 49-21-309,
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Klabax
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
You should not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Granules
There are no special precautions.
Suspension
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Do not store in the refrigerator or freeze.
Store in a tightly closed bottle. After 14 days, you should discard any unused portion or return it to the pharmacist.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Klabax contains
5 ml of the prepared suspension contains the active substance clarithromycin in an amount of 125 mg or 250 mg and the following excipients:
microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose 5 cps, hydroxypropylcellulose L, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, alginic acid, methacrylic acid copolymer (1:1), macrogol 1500, talc, carbomer (Carbopol 974 P), anhydrous colloidal silica, sucrose, aspartame (E951), xanthan gum, sodium citrate, sodium benzoate (E211), titanium dioxide (E171), peppermint flavor 517, Tutti Frutti flavor 051880 AP0551, sodium chloride.
What Klabax looks like and contents of the pack
Klabax is a white or off-white granular powder, which, when diluted with water, forms a white or off-white suspension. The resulting suspension has a fruity flavor.
Packaging
60 or 100 ml bottles with a syringe (pipette) and a spoon attached.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder:
Ranbaxy (Poland) Sp. z o.o.
Kubickiego Street 11
02-954 Warsaw
Manufacturer:
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Europe B.V.
Polarisavenue 87, 2132 JH,
Hoofdoorp,
Netherlands
Alkaloida Chemical Company Zrt.
Kabay János u. 29
H-4440 Tiszavasvári
Hungary
Terapia S.A.
Fabricii Street, no. 124,
400632 Cluj-Napoca,
Romania
Date of last revision of the leaflet:27.05.2022
IT/H/0720/IB/036 (with ring) approved 27.05.2022
3. How to Use Klabax
This medicine should always be used as directed by a doctor. In case of doubt, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
Do not give more medicine than prescribed by the doctor. If in doubt before administering clarithromycin, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
The dose of clarithromycin depends on the child's body weight and is usually about 7.5 mg per kilogram of body weight, twice a day, usually in the morning and evening. The suspension can be given with or without food.
This medicine is usually given for 5 to 10 days. The doctor will advise how long to give clarithromycin.
A measuring spoon and a syringe (pipette) are included with the Klabax packaging to facilitate dosing of the correct amount of medicine. The doctor or pharmacist will advise whether to use the spoon or pipette to administer the correct dose. Ensure that this is understood before administering the suspension.
The usual doses of Klabax 125 mg/5 ml are presented in the table below:
| Body Weight (kg) | Approximate Age (years) | Dose in Milliliters of Suspension (twice a day) Administered with a Syringe (Pipette) | Number of 5-milliliter Spoons to be Administered Twice a Day |
|
| 2.5 | ½ |
|
| 5 | 1 |
|
| 7.5 | 1½ |
|
| 10 | 2 |
The usual doses of Klabax 250 mg/5 ml are presented in the table below:
| Body Weight (kg) | Approximate Age (years) | Dose in Milliliters of Suspension (twice a day) Administered with a Syringe (Pipette) | Number of 5-milliliter Spoons to be Administered Twice a Day |
| 8 –11 |
| 1.25 | ¼ |
|
| 2.5 | ½ |
|
| 3.75 | ¾ |
|
| 5.0 | 1 |
For children weighing less than 8 kg, the doctor will recommend the appropriate dose.
In the treatment of severe infections, up to 500 mg of clarithromycin has been used twice a day.
If the child has mild to moderate kidney or liver function disorders, the doctor may prescribe a lower dose.
Preparing the Suspension
Add boiled, cooled water to the ring on the bottle and shake vigorously to create a suspension. Check if the suspension level is the same as indicated on the bottle; if not, add water to the ring and shake again.
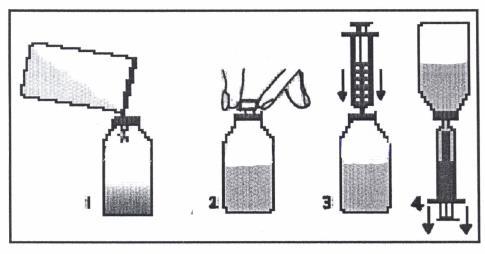
A measuring spoon or syringe (pipette) is included with the Klabax packaging. When using the syringe, follow the instructions below. After using the spoon or syringe, wash it with warm water and dish soap, and then rinse well.
- 1. Remove the cap (with a child safety lock) by pressing and twisting it in the opposite direction of the clock hands.
- 2. Remove the plastic, round connector from the packaging and insert it into the neck of the bottle. The connector should be tightly fitted and not removed after installation.
- 3. Remove the syringe from the packaging and ensure that the plunger is pushed all the way in. This will remove any air that may be in the syringe.
- 4. Place the tip of the syringe into the connector opening.
- 5. Turn the bottle upside down. Hold the bottle in one hand and the syringe in the other.
- 6. Holding the syringe, slowly pull out the plunger until the container is filled with the amount of medicine to be given to the child.
- 7. Turn the bottle right side up. Holding the syringe container, remove the syringe from the connector.
- 8. Place the tip of the syringe into the child's mouth. Administer the medicine drop by drop by gently pressing the plunger, continuing to support the syringe. Do not rush the child; allow them to swallow the medicine slowly. The measured dose can also be poured from the syringe into a spoon and given to the child in this way.
- 9. Close the bottle with the cap.
- 10. Wash the syringe with warm water and dish soap, and then rinse well. Hold the syringe under water, repeatedly moving the plunger up and down to ensure the inside is clean. Store the syringe in a hygienic place with the medicine.
Clarithromycin in suspension leaves a bitter taste. Drink juice or water immediately after taking the medicine to prevent this.
Administering the Medicine.
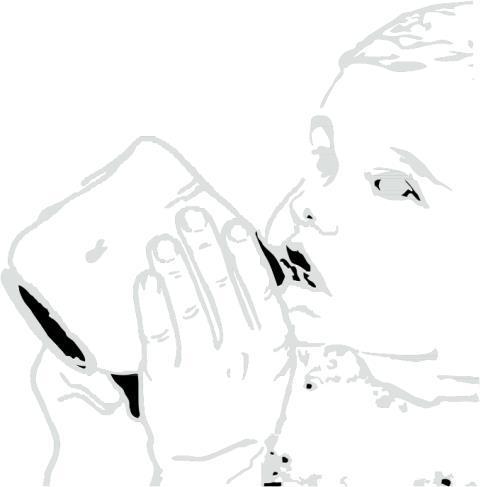

Administering Water or Juice After Taking the Medicine.
If you feel that the effect of the medicine is too strong or too weak, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
Using a Higher than Recommended Dose of Klabax
If a child accidentally takes an additional dose of the medicine, immediately consult a doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department. Take the package leaflet or suspension bottle with you and show it to the doctor so they know what medicine the child has taken. Overdose of clarithromycin may cause vomiting and abdominal pain.
Missing a Dose of Klabax
Give the medicine as soon as you notice. If it is almost time for the next dose, give only the next dose at the usual time. Do not give a double dose to make up for missed doses.
Stopping the Use of Klabax
Do not stop giving the medicine until the doctor advises, even if the child feels better, as symptoms may recur.
In case of doubts about the use of this medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, clarithromycin can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Very Serious Side Effects
Stop using the medicine and immediately consult a doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department if any of the following side effects occur:
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- sudden shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, swelling of the eyelids, face, or lips, rash, or itching. These may be symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Unknown frequency (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- if a patient experiences a severe skin reaction: red, blistering rash with bumps under the skin and blisters (pustular psoriasis), immediately consult a doctor.
- severe skin symptoms, including redness, temperature, blisters, or ulcers (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), severe rash, including redness, peeling, and itching of the skin, resembling severe burns (toxic epidermal necrolysis);
- severe or prolonged diarrhea, which may be bloody or contain mucus. Diarrhea may occur after stopping clarithromycin (see also: “Warnings and Precautions”);
- rash, fever, abnormal blood test results, inflammation of internal organs. These may be symptoms of a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS);
- jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes), skin irritation, pale stools, dark urine, abdominal pain, loss of appetite. These symptoms may indicate liver function disorders in the child.
Immediately consult a doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department if any of the following symptoms occur:
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- abnormal liver function test results.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- heart attack, dangerously fast heartbeat, changes in ECG, extra heartbeats, palpitations;
- blood clots in the lungs causing chest pain and shortness of breath.
Unknown frequency (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- changes in heart rhythm (known as torsade de pointes), rapid heartbeat (tachycardia);
- pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas, severe abdominal pain radiating to the back with nausea and vomiting);
- kidney inflammation (blood in the urine, fever, and back pain);
- hypoglycemia (abnormally low blood sugar levels, feeling hungry, sweating, dizziness, palpitations) especially after taking antidiabetic drugs;
- muscle weakness, especially tenderness or pain, if the child feels unwell or has a high temperature - may be caused by muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), which can lead to kidney disorders.
These are serious side effects, and the child may need medical attention.
Other Side Effects
Immediately inform the doctor if the child experiences any of the following side effects:
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- rash;
- excessive sweating;
- vasodilation;
- insomnia;
- headache;
- nausea (feeling sick), vomiting, abdominal pain, indigestion, diarrhea;
- changes in taste (e.g., metallic or bitter taste).
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- skin inflammation with blisters, itching, rash, and hives, rash in the form of red spots on the skin covered with small merging papules (papulovesicular rash);
- cholestasis (bile stagnation);
- fever, sensitive or reddened skin, sometimes with fever and chills (connective tissue inflammation);
- nausea (mild to intense), vomiting, cramps, diarrhea. These symptoms may be caused by stomach and intestinal inflammation, usually caused by viruses;
- frequent infections, e.g., fever, severe chills, sore throat, or mouth ulcers. These symptoms may be caused by a low white blood cell count.
- increased white blood cell count, increased platelet count;
- increased blood urea nitrogen or creatinine levels;
- changes in blood albumin, globulin, and various enzyme levels (alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase);
- loss of consciousness, uncontrolled convulsions, jerks, or sudden movements, drowsiness, tremors, or shakiness;
- shortness of breath, wheezing, cough, sometimes caused by physical exertion, and feeling of pressure in the chest (asthma);
- dizziness, hearing disturbances, ringing in the ears (tinnitus);
- esophagitis, gastritis, oral cavity or tongue inflammation;
- feeling of burning in the chest, moving towards the throat (heartburn);
- constipation, dry mouth, gas, bloating, belching;
- rectal pain;
- fever, feeling weak, chest pain, chills, fatigue, muscle pain, muscle stiffness, muscle cramps, muscle wasting;
- decreased appetite, loss of appetite (anorexia);
- worsening of myasthenia symptoms (a disease in which muscles are weakened and easily fatigued)
- anxiety, nervousness, dizziness, screaming;
- general malaise;
- vaginal infections;
- thrush (fungal infection);
- nasal bleeding;
- decreased neutrophil count.
Unknown frequency (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- enteritis;
- abnormal urine color;
- bacterial skin infections (erysipelas);
- severe kidney function disorders (renal failure);
- deafness;
- seizures;
- decreased platelet count, which increases the risk of bleeding or bruising;
- bleeding;
- numbness and tingling of arms and legs (paresthesia);
- tooth discoloration;
- muscle pain or weakness (myopathy);
- loss of taste (ageusia), tongue discoloration;
- inability to smell, change in smell perception;
- acne;
- depression, hallucinations, unusual thoughts (psychosis), disorientation, feeling of being outside the body (depersonalization), nightmares, confusion;
- prolonged bleeding and blood clotting time.
Reporting Side Effects
If any side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, inform the doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: 22 49-21-301, fax: 22 49-21-309,
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to Store Klabax
Store the medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
Granules
There are no special precautions.
Suspension
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Do not store in the refrigerator or freeze.
Store in a tightly closed bottle. After 14 days, discard any unused portion or return it to the pharmacist.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask the pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Other Information
What Klabax Contains
5 ml of the prepared suspension contains the active substance clarithromycin in the amount of 125 mg or 250 mg and the following excipients:
microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose 5 cps, hydroxypropyl cellulose L, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, alginic acid, copolymer (1:1) of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate, macrogol 1500, talc, carbomer (Carbopol 974 P), colloidal silicon dioxide, sucrose, aspartame (E951), xanthan gum, sodium citrate, sodium benzoate (E211), titanium dioxide (E171), peppermint flavor 517, Tutti Frutti flavor 051880 AP0551, sodium chloride.
What Klabax Looks Like and What the Package Contains
Klabax is a white or off-white granular powder that, when diluted with water, forms a white or off-white suspension. The resulting suspension has a fruity flavor.
Packaging
Bottles of 60 or 100 ml with a syringe (pipette) and measuring spoon included.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder:
Ranbaxy (Poland) Sp. z o.o.
ul. Kubickiego 11
02-954 Warsaw
Manufacturer:
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Europe B.V.
Polarisavenue 87, 2132 JH,
Hoofdoorp,
Netherlands
Alkaloida Chemical Company Zrt.
Kabay János u. 29
H-4440 Tiszavasvári
Hungary
Terapia S.A.
Str. Fabricii nr. 124,
400632 Cluj-Napoca,
Romania
Date of Last Update of the Leaflet:27.05.2022
- Country of registration
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterBasics GmbH Ranbaxy Ireland Ltd.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Klabax 250 mg/5 mlDosage form: Tablets, 500 mgActive substance: azithromycinPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 500 mgActive substance: azithromycinManufacturer: Krka Polska Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 250 mgActive substance: azithromycinManufacturer: Tarchomińskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne "Polfa" S.A.Prescription required
Alternatives to Klabax 250 mg/5 ml in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Klabax 250 mg/5 ml in Spain
Online doctors for Klabax 250 mg/5 ml
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Klabax 250 mg/5 ml – subject to medical assessment and local rules.