

Kidofen max

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Kidofen max

How to use Kidofen max
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Kidofen max, 250 mg/5 mL, oral suspension
Ibuprofen
You should carefully read the contents of this leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
This medicine should always be taken exactly as described in this patient leaflet or as directed by your doctor or pharmacist.
- You should keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you need advice or additional information, you should consult your pharmacist.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
- If after 1 day (infants 3-5 months old) or 3 days (infants over 6 months old, children, and adolescents) there is no improvement or the patient feels worse, they should contact their doctor.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Kidofen max and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Kidofen max
- 3. How to take Kidofen max
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Kidofen max
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Kidofen max and what is it used for
Kidofen max is a pain-relieving, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory medicine. It belongs to a group of medicines called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The active substance is ibuprofen.
Indications for use
Fever of various origins (including viral infections, post-vaccination reactions).
Pain of various origins, mild to moderate:
- headaches, sore throats, and muscle pain, e.g., with viral infections;
- muscle, joint, and bone pain due to injuries to the musculoskeletal system (sprains, strains);
- pain due to soft tissue injuries, post-operative pain;
- toothaches, pain after dental procedures, pain due to teething;
- headaches;
- earaches occurring in middle ear inflammation.
Kidofen max is intended for short-term use. If symptoms persist or worsen, or if new symptoms appear, you should consult your doctor.
2. Important information before taking Kidofen max
When not to take Kidofen max
- if the patient is allergic to ibuprofen or other similar pain-relieving medicines (from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - NSAIDs) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has ever experienced shortness of breath, asthma, runny nose, swelling of the face and/or hands, or hives after taking acetylsalicylic acid or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as Kidofen max may cause similar side effects in these patients;
- if the patient currently has or has ever had stomach or duodenal ulcers or bleeding (two or more confirmed cases of ulcers or bleeding);
- if the patient has ever had bleeding or perforation (hole) of the gastrointestinal tract associated with the use of NSAIDs;
- if the patient has severe liver or kidney failure;
- if the patient has severe heart failure;
- if the patient has had bleeding in the brain (cerebral hemorrhage) or other active bleeding;
- if the patient has blood disorders of unknown origin;
- in patients with severe dehydration (caused by vomiting, diarrhea, or insufficient fluid intake). The medicine should not be taken during the last 3 months of pregnancy.
Warnings and precautions
During the use of ibuprofen, symptoms of an allergic reaction to this medicine have occurred, including difficulty breathing, swelling in the face and neck area (angioedema), and chest pain.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should stop taking Kidofen max immediately and contact your doctor or emergency medical services immediately.
Before starting to take Kidofen max, you should discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist:
- if the patient has certain skin diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or mixed connective tissue disease);
- if the patient has inherited blood disorders (e.g., acute intermittent porphyria);
- if the patient has or has had intestinal diseases (such as chronic enteritis, ulcerative colitis, or Crohn's disease), as symptoms may worsen (see section 4: "Possible side effects");
- if the patient has or has had high blood pressure and/or heart failure;
- if the patient has liver or kidney function disorders - during long-term use of the medicine, liver function, kidney function, and blood morphology should be monitored;
- if the patient has blood clotting disorders (ibuprofen may prolong bleeding time);
- if the patient has asthma or allergies (current or past), as taking the medicine may cause bronchospasm;
- if the patient has hay fever, nasal polyps, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, as there is an increased risk of allergic reactions. Allergic reactions may occur as asthma attacks (so-called analgesic-induced asthma), angioedema, or hives;
- if the patient is taking other medicines that may increase the risk of ulcers or bleeding (such as oral corticosteroids - e.g., prednisolone, anticoagulant medicines - e.g., warfarin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (antidepressants), and antiplatelet agents (such as acetylsalicylic acid));
- if the patient is taking other NSAIDs (including COX-2 inhibitors, such as celecoxib or etoricoxib), as concurrent use of these medicines should be avoided;
- if the patient has recently undergone major surgery;
- if the patient is over 65 years old, as the risk of adverse effects of the medicine increases, especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation of the stomach or duodenum, which can be fatal. The patient should inform their doctor about any unusual symptoms related to the gastrointestinal tract (especially bleeding and pain), especially during the initial treatment period;
- if the patient has chickenpox - it is not recommended to use this medicine in this case;
- due to the long-term use of any pain-relieving medicines, headaches may occur, which should not be treated with increased doses of this medicine.
In such a case, the medicine should be discontinued, and a doctor consulted. The diagnosis of headache caused by medication overuse should be suspected in patients who have frequent or daily headaches despite (or due to) regular use of pain-relieving medicines;
- constant use (of several types) of pain-relieving medicines may lead to persistent serious kidney diseases. This risk may increase during physical exertion associated with salt loss and dehydration. Therefore, it should be avoided if the patient is dehydrated, as kidney damage may occur;
- if the patient has heart diseases, such as heart failure, angina pectoris (chest pain), the patient has had a heart attack, bypass surgery, or has peripheral arterial disease (poor blood circulation in the legs due to narrowing or blockage of arteries) or if the patient has had any stroke (including mini-stroke or transient ischemic attack - TIA);
- if the patient has high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol levels, or if there is a history of heart disease or stroke in the patient's family, or if the patient smokes;
- if the patient has an infection - see below: "Infections". Bleeding, ulcers, or perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, which can be fatal, have been reported during treatment with all NSAIDs with warning signs or without, or in patients who have had serious gastrointestinal diseases. If bleeding or ulcers occur, treatment should be stopped immediately. The risk of bleeding, ulcers, or perforation of the gastrointestinal tract increases with the increase in the dose of NSAIDs in patients who have had ulcers, especially with bleeding or perforation (see section 2: "When not to take Kidofen max") and in the elderly. In such patients, treatment should be started with the smallest effective dose. In these patients, as well as in patients who require concurrent administration of acetylsalicylic acid in small doses or medicines that increase the risk of gastrointestinal reactions, concomitant treatment with protective medicines (e.g., misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors) should be considered.
Taking anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving medicines, such as ibuprofen, may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack or stroke, especially when used in high doses. Do not exceed the recommended dose and duration of treatment.
In elderly patients, the dose of the medicine can be reduced, using the smallest possible dose for the shortest possible period, to reduce the risk of side effects.
Infections
Kidofen max may mask the symptoms of infection, such as fever and pain. Therefore, Kidofen max may delay the use of appropriate infection treatment and consequently lead to an increased risk of complications. This has been observed in bacterial pneumonia and bacterial skin infections associated with chickenpox. If the patient is taking this medicine during an infection, and the symptoms of the infection persist or worsen, they should consult their doctor immediately.
Skin reactions
Severe skin reactions have been reported with the use of ibuprofen, such as exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). If the patient experiences any of the symptoms associated with these severe skin reactions described in section 4, they should stop taking Kidofen max immediately and seek medical attention.
Infants
The medicine should not be used in infants under 3 months old or with a body weight below 5 kg.
Kidofen max and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
Do not take the following medicines at the same time as Kidofen max. Kidofen max may affect the action of other medicines, and other medicines may affect the action of Kidofen max. The patient should inform their doctor if they are taking any of the following medicines.
Kidofen max may affect the action of other medicines or other medicines may affect the action of Kidofen max.
For example:
- medicines with anticoagulant action (i.e., blood thinners/preventing blood clots, such as acetylsalicylic acid, warfarin, ticlopidine);
- medicines that lower blood pressure (ACE inhibitors, such as captopril, beta-blockers, such as atenolol, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, such as losartan).
Medicines that may increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding:
- acetylsalicylic acid (used to relieve pain and reduce fever);
- corticosteroids (steroid medicines used to treat, e.g., asthma);
- antiplatelet agents (medicines that reduce the risk of blood clots);
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (medicines used to treat depression);
- other NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors (medicines used to treat rheumatic diseases).
Medicines that may cause kidney damage:
- tacrolimus (a medicine used to treat, e.g., atopic dermatitis);
- cyclosporin (a medicine used in patients after organ transplantation).
Kidofen max may enhance the effect of:
- lithium (a medicine used to treat depression);
- methotrexate (a medicine used to treat certain cancers and rheumatoid arthritis);
- phenytoin (a medicine used to treat epilepsy).
Kidofen max may reduce the effectiveness of:
- diuretics (medicines that increase urine production).
Do not take Kidofen max at the same time as:
- zidovudine (a medicine used to treat HIV infection), as it may prolong bleeding time;
- ritonavir (a medicine used to treat HIV infections), as it may increase the concentration of NSAIDs in the blood;
- digitalis glycosides, e.g., digoxin, as NSAIDs may increase the symptoms of heart failure and increase the concentration of digitalis glycosides in the blood;
- quinolone antibiotics, as this may increase the risk of seizures;
- aminoglycosides, as NSAIDs may decrease their excretion;
- probenecid and sulfinpyrazone (medicines used to treat gout), as they may delay the excretion of ibuprofen;
- sulfonylurea derivatives (medicines used to treat diabetes);
- baclofen (a muscle relaxant), as ibuprofen may cause baclofen toxicity;
- voriconazole and fluconazole (used to treat fungal infections) - these medicines may increase the effect of ibuprofen;
- cholestyramine (a medicine used to lower cholesterol levels) - medicines should be administered with a few hours' interval.
Other medicines may also be affected by or affect the treatment with Kidofen max.
Therefore, before taking Kidofen max with other medicines, you should always consult your doctor or pharmacist.
If the patient is unsure whether they are taking any of the above medicines, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
Kidofen max with food and alcohol
In patients with sensitive stomachs, it is recommended to take the medicine with food.
Do not consume alcohol while taking Kidofen max. Some side effects, such as those related to the gastrointestinal tract or central nervous system, may be more likely when taking alcohol and this medicine at the same time.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy
Kidofen max should not be taken if the patient is in the last 3 months of pregnancy, as it may harm the unborn child or cause complications during delivery. It may cause kidney and heart problems in the unborn child. It may increase the risk of bleeding in the patient and their child and prolong or delay delivery. During the first 6 months of pregnancy, Kidofen max should not be used unless the doctor considers it absolutely necessary. If treatment is necessary during this period or when trying to conceive, the smallest possible dose should be used for the shortest possible time. From the 20th week of pregnancy, Kidofen max may cause the unborn child to have a narrowed blood vessel (ductus arteriosus) in the heart or kidney problems, which can lead to low levels of amniotic fluid surrounding the child (oligohydramnios). If treatment is necessary for a longer period than a few days, the doctor may recommend additional monitoring.
Breastfeeding
Ibuprofen passes into breast milk in small amounts.
No harmful effect of the medicine on infants has been reported, so breastfeeding can be continued during short-term use of ibuprofen in doses used to treat pain and fever.
Fertility
Kidofen max belongs to a group of medicines (NSAIDs) that may affect fertility in women.
This effect is temporary after stopping the medicine.
Driving and using machines
Short-term use of Kidofen max has no effect or has a negligible effect on the ability to drive and use machines.
Kidofen max contains propylene glycol (E 1520), liquid maltitol (E 965), ethanol, sodium benzoate (E 211), sodium, and benzyl alcohol
Propylene glycol (E 1520)
The medicine contains 10.64 mg of propylene glycol in each 5 mL of suspension.
Liquid maltitol (E 965)
If the patient has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, they should consult their doctor before taking the medicine.
Etanol
The medicine contains 6.6 mg of ethanol (alcohol) in each dose (5 mL), which is equivalent to 0.13% (v/v). The amount of alcohol in a dose of this medicine is equivalent to less than 1 mL of beer or 1 mL of wine.
A small amount of alcohol in this medicine will not have noticeable effects.
Sodium benzoate (E 211)
The medicine contains 3.45 mg of sodium benzoate in each 5 mL of suspension.
Sodium
The medicine contains 9.3 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in each 5 mL of suspension.
This is equivalent to 0.5% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
Benzyl alcohol
The medicine contains 0.27 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 5 mL of suspension.
Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions.
Do not give to small children (under 3 years old) for more than a week without consulting a doctor or pharmacist.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women and patients with liver or kidney disease should consult their doctor before taking the medicine, as a large amount of benzyl alcohol may accumulate in their body and cause side effects (so-called metabolic acidosis).
3. How to take Kidofen max
This medicine should always be taken exactly as described in this patient leaflet or as directed by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
The medicine is for oral use. Shake before use.
Use the smallest effective dose for the shortest possible period necessary to relieve symptoms. If the symptoms of an infection (such as fever and pain) persist or worsen, consult your doctor immediately (see section 2).
Recommended dose
The daily dose of ibuprofen is 20-30 mg/kg body weight, divided into doses.
| Age/weight of the child | Single dose | Maximum daily dose of ibuprofen Doses should be given every 6 to 8 hours |
| 3-6 months/ 5-7.6 kg | 1 mL (50 mg) | 3 times 1 mL (3 times 50 mg = 150 mg) |
| 6-12 months/ 7.7-9 kg | 1 mL (50 mg) | 3 to 4 times 1 mL (3 or 4 times 50 mg = 150 mg or 200 mg) |
| 1-3 years/ 10-15 kg | 2 mL (100 mg) | 3 times 2 mL (3 times 100 mg = 300 mg) |
| 4-6 years/ 16-20 kg | 3 mL (150 mg) | 3 times 3 mL (3 times 150 mg = 450 mg) |
| 7-9 years/ 21-29 kg | 4 mL (200 mg) | 3 times 4 mL (3 times 200 mg = 600 mg) |
| 10-12 years/ 30-40 kg | 6 mL (300 mg) | 3 times 6 mL (3 times 300 mg = 900 mg) |
Adults and adolescents over 12 years old:the recommended dose for symptomatic relief of pain and fever:
3 times 8 mL per day, until symptoms resolve.
Elderly patients:the dose should be determined individually by the doctor.
Consider reducing the dose. In patients with kidney failure, the dose should be adjusted according to the degree of kidney function.
Do not exceed the recommended dose.
In patients with sensitive stomachs, it is recommended to take the medicine with food.
Infants
The medicine should not be used in infants under 3 months old or with a body weight below 5 kg.
Duration of treatment
The medicine is intended for short-term use only. If symptoms persist or worsen, or if new symptoms appear, consult your doctor.
In infants over 6 months old, children up to 12 years old, and adolescents, consult a doctor if the medicine needs to be given for more than 3 days, or if symptoms worsen.
In infants 3-5 months old, with a body weight of 5 kg or more, consult a doctor if symptoms worsen or do not improve after 24 hours.
To administer the medicine, use the oral syringe with an adapter provided with the packaging. This allows for accurate dosing.
Instructions for using the oral syringe with an adapter are at the end of this leaflet.
Taking a higher dose of Kidofen max than recommended
If the patient has taken a higher dose of Kidofen max than recommended or if a child has accidentally taken the medicine, they should always consult their doctor or go to the nearest hospital to get an opinion on the possible risk to their health and advice on what to do in such a case.
Symptoms of overdose may include: nausea, stomach pain, vomiting (which may contain blood), gastrointestinal bleeding (see also section 4 below), diarrhea, headache, ringing in the ears, disorientation, and nystagmus. There may also be agitation, drowsiness, disorientation, or coma. Rarely, patients may experience seizures. After taking large doses, drowsiness, chest pain, palpitations, loss of consciousness, seizures (mainly in children), weakness, and dizziness have been reported, as well as blood in the urine, low potassium levels in the blood, feeling cold, and breathing difficulties. Additionally, the prothrombin time/INR may be prolonged, probably due to the disruption of circulating clotting factors in the blood. Acute kidney failure and liver damage may occur. In patients with asthma, asthma symptoms may worsen. Additionally, low blood pressure and breathing difficulties may occur.
Missing a dose of Kidofen max
Continue taking the medicine, without increasing the next dose.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
If you have any further doubts about taking this medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Stop taking this medicine and contact your doctor or go to the emergency department of the nearest hospital if you experience:
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, which may cause difficulty breathing or swallowing, worsening of asthma, unexplained wheezing, or shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure (anaphylaxis, angioedema, or severe shock). Symptoms may occur even after the first use of the medicine;
- symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding (severe stomach pain, vomiting blood or coffee grounds-like material, black stools or blood in stools); severe skin reactions, such as: widespread rash, peeling, blistering, and shedding of the skin;
- chest pain, which may be a sign of a potentially serious allergic reaction called Kounis syndrome;
- -severe skin reactions, such as: blisters and peeling of the skin and (or) mucous membranes, often accompanied by fever, muscle and joint pain (this is called Stevens-Johnson syndrome), erythema multiforme (purple-red spots on the skin, sometimes with blisters) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome);
- severe skin reactions known as DRESS syndrome. Symptoms of DRESS syndrome include: skin rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and an increased number of eosinophils (a type of white blood cell);
- a red scaly rash with thickening of the skin and blisters, mainly in skin folds, on the trunk and upper limbs, with fever at the beginning of treatment (this is called acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis).
Frequently(may occur in up to 1 in 10 people):
- gastrointestinal disorders, such as: stomach pain, nausea, and indigestion, diarrhea, bloating with gas, constipation, heartburn, vomiting, minor gastrointestinal bleeding, which in rare cases may lead to anemia. Uncommonly(may occur in up to 1 in 100 people):
- stomach or duodenal ulcers;
- perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding;
- ulcerative stomatitis;
- worsening of symptoms of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease;
- gastritis;
- headaches, dizziness, insomnia, agitation, irritability, or fatigue;
- vision disorders;
- hives and itching;
- various skin rashes.
Rarely(may occur in up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- ringing in the ears (tinnitus);
- side pain and (or) stomach pain, blood in the urine, and fever may be symptoms of kidney damage (renal papillary necrosis);
- increased urea levels in the blood;
- decreased hemoglobin levels.
Very rarely(may occur in up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- psychotic reactions, depression;
- passing less urine than usual and swelling (in patients with high blood pressure or kidney failure), interstitial nephritis, which may lead to acute kidney failure, swelling, and clouding of the urine (nephrotic syndrome);
- high blood pressure;
- vasculitis;
- heart failure, palpitations, heart attack, and swelling of the face or hands;
- esophagitis, pancreatitis, formation of intestinal strictures;
- liver function disorders, liver damage (the first symptoms may be skin discoloration), especially during long-term treatment, liver failure, acute hepatitis;
- blood disorders - the first symptoms are: fever, sore throat, superficial mouth ulcers, flu-like symptoms, severe fatigue, nosebleeds, or bruising. In such cases, treatment should be stopped immediately and a doctor consulted. Do not treat yourself with pain-relieving or antipyretic medicines;
- severe skin and soft tissue infections during chickenpox;
- worsening of inflammatory conditions (e.g., worsening of abscesses). If symptoms of infection worsen or appear, the patient should immediately consult their doctor, who will initiate appropriate treatment;
- hair loss (alopecia);
- stiffness of the neck, headaches, nausea, vomiting, fever, and changes in consciousness (these are symptoms of aseptic meningitis).
Frequency not known(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- skin becomes sensitive to light. Medicines like Kidofen max may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack (myocardial infarction) or stroke.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, stop taking the medicine and contact your doctor.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Kidofen max
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and carton.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Store below 25°C. Do not store in the refrigerator or freeze.
Shelf life after first opening the bottle: 3 months.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Kidofen max contains
- The active substance of the medicine is ibuprofen.
- 5 mL of oral suspension contains 250 mg of ibuprofen.
- The other ingredients are: liquid maltitol (E 965), glycerol, sodium chloride, citric acid (E 330), sodium citrate, sucralose (E 955), polysorbate 80, xanthan gum, sodium benzoate (E 211), strawberry flavor (contains ethanol, propylene glycol (E 1520), benzyl alcohol), purified water.
What Kidofen max looks like and contents of the packaging
Kidofen max is a white to cream-colored oral suspension with a strawberry flavor and aroma.
The packaging of the medicine is a 115 mL brown glass bottle, type III, with an aluminum screw cap with a LDPE seal, an oral syringe made of LDPE and polystyrene, and an adapter made of LDPE, in a cardboard box.
The packaging contains 100 mL of suspension.
Marketing authorization holder
Aflofarm Farmacja Polska Sp. z o.o.
Partyzancka 133/151
95-200 Pabianice
Phone: +48 42 22-53-100
Manufacturer
Aflofarm Farmacja Polska Sp. z o.o.
Krzywa 2
95-030 Rzgów
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
Instructions for using the oral syringe with an adapter
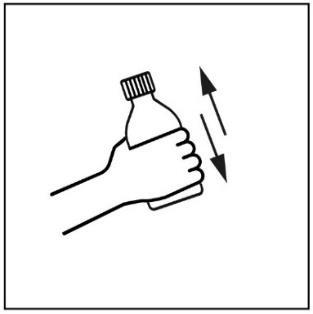
- 1. Before each use, shake the bottle thoroughly.
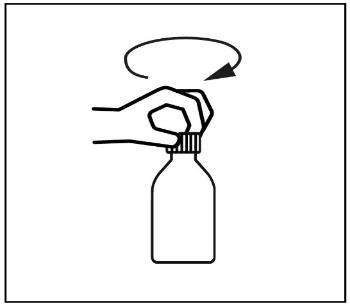
- 2. Unscrew the bottle cap.
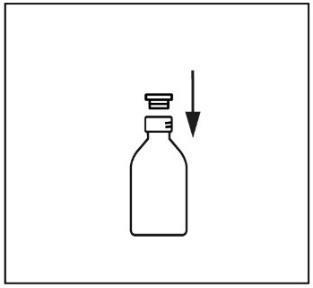
- 3. Place the provided adapter into the bottle neck opening.
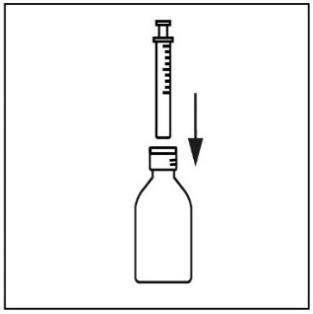
- 4. Insert the oral syringe firmly into the adapter.
- 5. To fill the syringe, turn the bottle upside down and carefully push the syringe plunger down, drawing the suspension to the desired mark on the syringe.
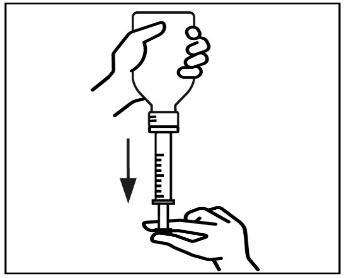
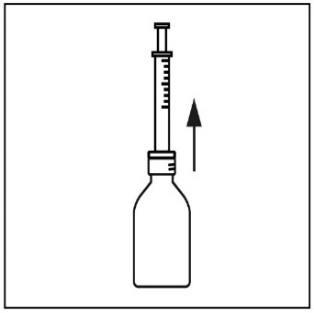
- 6. Turn the bottle back to its original position and carefully remove the syringe from the bottle.
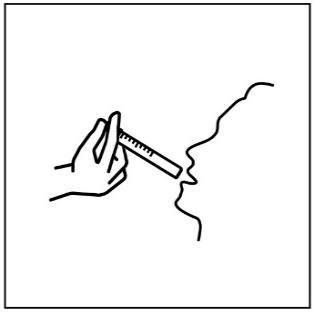
- 7. Place the syringe in the mouth and, pressing the plunger slowly, administer the suspension, being careful not to choke.
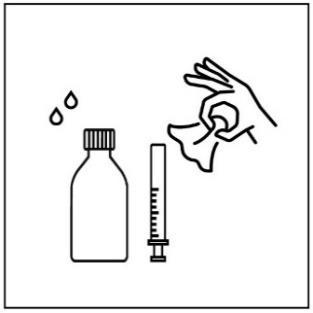
- 8. After use, close the bottle and wash and dry the syringe.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAflofarm Farmacja Polska Sp. z o.o.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Kidofen maxDosage form: Suspension, 40 mg/mlActive substance: ibuprofenManufacturer: Laboratorios Basi - Industria Farmaceutica, S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 400 mgActive substance: ibuprofenPrescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 600 mgActive substance: ibuprofenManufacturer: Aristo Pharma GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Kidofen max in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Kidofen max in Spain
Alternative to Kidofen max in Ukraine
Online doctors for Kidofen max
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Kidofen max – subject to medical assessment and local rules.















