

Ibum Forte (o smaku bananovim)

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Ibum Forte (o smaku bananovim)

How to use Ibum Forte (o smaku bananovim)
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
IBUM FORTE
200 mg/5 ml, oral suspension
Ibuprofen
Oral suspension with a banana flavor
Before using the medicine, carefully read the contents of the leaflet, as it contains important information for the patient.
This medicine should always be used exactly as described in this patient leaflet or as directed by a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you need advice or additional information, consult a pharmacist.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
- If after 3 days there is no improvement or the patient feels worse, they should contact their doctor.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is the medicine I F and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using the medicine I F
- 3. How to use the medicine I F
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store the medicine I F
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is the medicine I F and what is it used for
The medicine I F contains ibuprofen - a substance from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which have analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory effects.
Indications for use
- febrile conditions of various origins, including influenza, colds, and post-vaccination reactions,
- pains of various origins with mild to moderate severity, such as:
- headaches, throat and muscle pains (e.g., in viral infections),
- toothaches, pains after dental procedures, teething pains,
- joint and bone pains due to injuries to the musculoskeletal system (e.g., sprains),
- pains due to soft tissue injuries,
- post-operative pains,
- ear pains occurring in middle ear inflammatory conditions.
2. Important information before using the medicine I F
When not to use the medicine I F:
- if the patient is hypersensitive to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- if the patient is hypersensitive to other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs),
- in patients with active or past gastric and duodenal ulcers, perforation (perforation) or bleeding, also occurring after the use of NSAIDs,
- in patients who have experienced any symptoms of allergy in the form of rhinitis, urticaria, dyspnea, or bronchial asthma while being treated with acetylsalicylic acid or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,
- in the case of taking other NSAID drugs (including COX-2 inhibitors such as celecoxib or etoricoxib),
- if there is severe liver, kidney, or heart failure,
- if there is cerebral bleeding (cerebral vascular bleeding) or other bleeding,
- if there are blood coagulation disorders, hemorrhagic diathesis (tendency to bleeding), or blood production disorders of unknown origin.
If adults use this medicine, it should not be taken in the last 3 months of pregnancy.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use the medicine I F, the patient should discuss it with their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- if the patient is taking other painkillers from the NSAID group or acetylsalicylic acid in a daily dose above 75 mg,
- if the patient has been diagnosed with certain skin diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease),
- if the patient has been diagnosed with gastrointestinal diseases and chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease),
- if the patient has been diagnosed with high blood pressure and/or heart function disorders,
- if the patient has been diagnosed with kidney function disorders,
- if the patient has been diagnosed with liver diseases,
- after a recent major surgery,
- if there is dehydration due to increased risk of kidney failure,
- in the case of current or past asthma, chronic rhinitis, nasal polyps, or allergic diseases, it is possible to experience dyspnea,
- when using other medicines that may increase the risk of ulcers or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids (e.g., prednisolone), blood thinners (e.g., acenocoumarol), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (antidepressants), and antiplatelet agents (such as acetylsalicylic acid).
During the use of ibuprofen, symptoms of allergic reactions to this medicine have occurred, including difficulty breathing, swelling around the face and neck (angioedema), chest pain.
- 4.
In connection with the use of ibuprofen, severe skin reactions have occurred, such as exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). If the patient experiences any of the symptoms associated with these severe skin reactions described in section 4, they should immediately stop using the medicine I F and seek medical attention.
If any of the above conditions apply to a child, the parents or guardians should consult a doctor before using the medicine I F.
In elderly patients, there is an increased risk of adverse reactions during the use of NSAID medicines, particularly those related to the stomach and intestines.
Patients who have previously experienced adverse reactions in the gastrointestinal tract, especially elderly patients, should report any unusual symptoms in the abdominal cavity (especially gastrointestinal bleeding), especially in the initial stage of treatment.
Medicine I F and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take:
- corticosteroids (e.g., prednisolone), as they may increase the risk of ulcers or bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract,
- other NSAID medicines (including COX-2 inhibitors, such as celecoxib or etoricoxib),
- certain anticoagulant medicines (e.g., acetylsalicylic acid, acenocoumarol, ticlopidine),
- certain antihypertensive medicines (ACE inhibitors, e.g., captopril), other medicines that may be affected by or affect the treatment with ibuprofen,
- antiplatelet agents (such as acetylsalicylic acid) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (antidepressants), as they increase the risk of adverse reactions in the gastrointestinal tract,
- medicines used to treat high blood pressure and diuretics, as NSAID medicines may weaken the effect of these medicines and there is a risk of increased kidney damage. In such cases, it is essential for the child to drink plenty of water during the day,
- lithium (a medicine used in depression), as the effect of lithium may increase,
- methotrexate (a medicine used in the treatment of cancer or rheumatic diseases), as the effect of methotrexate may increase,
- tacrolimus (an immunosuppressive medicine), as there is an increased risk of toxic effects on the kidneys,
- cyclosporin (an immunosuppressive medicine), as there are limited data on the increased risk of toxic effects on the kidneys,
- zydovudine (a medicine used in the treatment of AIDS), as the use of the medicine I F may increase the risk of bleeding into the joints or bleeding leading to swelling (in patients with hemophilia and a positive HIV antibody test),
- sulfonylurea derivatives (oral hypoglycemic agents): there may be clinical interactions between these medicines and NSAID medicines. It is recommended to monitor blood glucose levels,
- probenecid and sulfinpyrazone (medicines used in the treatment of gout): they may delay the excretion of ibuprofen,
- digitalis glycosides, phenytoin, and lithium: ibuprofen may increase the plasma concentration of these medicines,
- quinolone antibiotics: they may increase the risk of seizures,
- cholestyramine: it may delay and reduce the absorption of NSAID medicines,
- voriconazole and fluconazole (antifungal medicines): they may increase the exposure to NSAID medicines.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
The medicine I F should not be used if the patient is in the last 3 months of pregnancy, as it may harm the unborn child or cause complications during delivery. It may cause kidney and heart problems in the unborn child.
It may increase the risk of bleeding in the patient and their child and cause delayed or prolonged labor. During the first 6 months of pregnancy, the medicine should not be used unless it is absolutely necessary and recommended by a doctor. If treatment is necessary during this period or when trying to conceive, the smallest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible time. From the 20th week of pregnancy, the medicine I F may cause kidney problems in the unborn child if used for more than a few days, which may lead to a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the child (oligohydramnios) or narrowing of the arterial duct (ductus arteriosus) in the child's heart. If treatment is necessary for a longer period, the doctor may recommend additional monitoring.
Breastfeeding
Ibuprofen passes into breast milk in small amounts. With short-term use of ibuprofen in recommended doses, harmful effects on infants are unlikely.
Fertility
Ibuprofen may make it more difficult to become pregnant. If the patient plans to become pregnant or is having trouble becoming pregnant, they should inform their doctor.
Driving and using machines
Short-term use of the medicine does not have a significant effect on the ability to drive and use machines.
Medicine I F contains maltitol liquid, sodium benzoate (E 211), propylene glycol (E 1520), and sodium
Maltitol liquid
The medicine contains 1.119 g of maltitol liquid in each 5 ml of suspension. If the patient has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, they should consult their doctor before taking the medicine.
Sodium benzoate (E 211)
The medicine contains 3.357 mg of sodium benzoate in each 5 ml of suspension.
Propylene glycol (E 1520)
The medicine contains 4.532 mg of propylene glycol in each 5 ml of suspension.
Sodium
The medicine contains 18.4 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in each 5 ml of suspension.
This corresponds to 0.92% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
3. How to use the medicine I F
This medicine should always be used exactly as described in this patient leaflet or as directed by a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
The medicine is for oral use. Before use, the bottle should be shaken.
The daily dose of the medicine I F depends strictly on the patient's body weight and is: 20-30 mg/kg body weight, in divided doses, according to the following table.
| Child's age (child's weight) | Single dose | Maximum daily dose |
| 3-6 months (5-7.6 kg) 6-12 months (7.7-9 kg) 1-3 years (10-15 kg) 4-6 years (16-20 kg) 7-9 years (21-29 kg) 10-12 years (30-40 kg) over 40 kg | 1.25 ml (50 mg) 1.25 ml (50 mg) 2.5 ml (100 mg) 3.75 ml (150 mg) 5 ml (200 mg) 7.5 ml (300 mg) 7.5-10 ml (300-400 mg) | 3 times 1.25 ml = 150 mg 3-4 times 1.25 ml = 150-200 mg 3 times 2.5 ml = 300 mg 3 times 3.75 ml = 450 mg 3 times 5 ml = 600 mg 3 times 7.5 ml = 900 mg 3-4 times 7.5 ml = 900-1200 mg |
The medicine should be given at intervals of at least 6 hours.
In infants under 6 months of age, the medicine can be given only after consulting a doctor.
A higher dose of the medicine than recommended should not be used.
The smallest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible time to relieve symptoms. If the symptoms of the infection (such as fever and pain) persist or worsen, the patient should consult their doctor immediately (see section 2).
Without consulting a doctor, the medicine should not be used for more than 3 days.
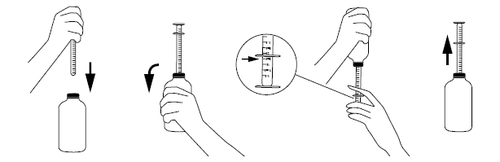
A measuring spoon is attached to the packaging.
Instructions for dosing with the measuring spoon:
- before the first use of the spoon, it should be washed in warm (not boiling) water with a detergent,
- after unscrewing the cap, the spoon should be placed on the cork in the neck of the bottle,
- to fill the spoon, the bottle should be shaken vigorously, turned upside down, and then the plunger of the spoon should be carefully moved down, drawing in the suspension in the desired amount indicated on the scale,
- to accurately measure the dose, the collar of the spoon should be set to the line on the scale on the plunger,
- the bottle should be turned back to its original position and the spoon should be carefully removed from the cork,
- the tip of the spoon should be placed in the child's mouth, and then, slowly pressing the plunger, the contents of the spoon should be carefully emptied,
- after use, the bottle should be closed, and the measuring spoon should be washed in warm (not boiling) water with a detergent and dried.
The medicine is intended for temporary use, so if the symptoms worsen or do not improve after 3 days, or if new symptoms appear, the patient should consult their doctor.
In patients with sensitive stomachs, it is recommended to use the medicine I F during meals.
The medicine does not contain sugar and alcohol. It can be used by people with diabetes (5 ml of the medicine I F suspension contains 1.119 g of maltitol liquid, which corresponds to approximately 0.07 carbohydrate units).
Using a higher dose of the medicine I F than recommended
If the patient has used a higher dose of the medicine I F than recommended or if a child has accidentally taken the medicine, they should always consult a doctor or go to the nearest hospital to get an opinion on the possible risk to their health and advice on what actions to take in such a case.
Symptoms may include nausea, stomach pain (abdominal pain), vomiting (which may contain blood), headaches, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), disorientation, and nystagmus. After taking a large dose, drowsiness, chest pain, palpitations, loss of consciousness, seizures (mainly in children), weakness, and dizziness may occur, as well as blood in the urine, feeling cold, breathing problems, eyelid twitching, vision disturbances, and rarely low blood pressure and changes in blood composition and kidney function disorders.
Missing a dose of the medicine I F
A double dose should not be used to make up for a missed dose.
In case of any further doubts about the use of this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The occurrence of side effects can be reduced by using the smallest effective dose for the shortest possible time to relieve symptoms.
If side effects occur or in case of doubts, the patient should stop using the medicine and talk to their doctor as soon as possible.
Elderly patients using this medicine belong to a group with an increased risk of complications related to side effects.
STOP USING the medicine and immediately consult a doctor if the child experiences:
- symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding, such as: severe abdominal pain, black stools, bloody vomiting, or dark particles that resemble coffee grounds,
- symptoms of rare but serious allergic reactions, such as: worsening of asthma, unexplained wheezing or shortness of breath, swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, palpitations, and a drop in blood pressure leading to shock. Symptoms may occur even after the first use of the medicine. If any of these symptoms occur, the patient should immediately contact their doctor,
and
- symptoms of severe skin reactions, such as:
- red, non-raised, target-like or circular patches on the torso, often with blisters in the center, peeling of the skin, ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes. These severe skin rashes may be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis),
- widespread rash, high body temperature, and swollen lymph nodes (DRESS syndrome),
- red, scaly rash with nodules under the skin and blisters, usually located in skin folds, on the torso, and upper limbs, with fever occurring at the beginning of treatment (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis). If such symptoms occur, the patient should stop using the medicine I F and seek medical attention immediately. See also section 2,
Other possible side effects include:
Frequently(occurring in 1 to 10 patients out of 100):
- heartburn, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating with gas, diarrhea, constipation.
Less frequently(occurring in 1 to 10 patients out of 1,000):
- gastritis, colitis, and worsening of Crohn's disease (inflammatory bowel disease),
- headaches, dizziness, insomnia, agitation, irritability, or fatigue,
- vision disturbances,
- gastric ulcers, which may bleed or perforate,
- mouth ulcers and/or swelling and irritation of the mouth,
- allergic reactions with rash and itching, asthma attacks (with possible drop in blood pressure).
Rarely(occurring in 1 to 10 patients out of 10,000):
- tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
Very rarely(occurring in less than 1 patient out of 10,000):
- esophagitis or pancreatitis, intestinal obstruction,
- severe skin reactions, including rash with redness and blisters, which may peel and be accompanied by fever, chills, and muscle pain, malaise, Stevens-Johnson syndrome. In rare cases, severe skin infections have occurred during chickenpox (chickenpox),
- reduced urine output and swelling (possible acute kidney failure or kidney inflammation). Kidney damage or increased urea levels in the blood (the first symptoms are reduced urine output, cloudy urine, blood in the urine, back pain, possible swelling of the legs, and general malaise),
- blood production problems (the first symptoms are fever, sore throat, superficial mouth ulcers, flu-like symptoms, severe fatigue, nosebleeds, and unexplained or atypical bruising),
- psychotic reactions and depression,
- worsening of inflammatory conditions due to infection. If symptoms of infection occur or worsen during the use of the medicine I F, the patient should consult their doctor,
- swelling, high blood pressure, palpitations, heart failure, heart attack,
- liver function disorders or hepatitis. Liver failure or damage, especially during long-term use, manifested by yellowing of the skin and eyes or light-colored stools and dark urine,
- very rarely, during the use of ibuprofen, symptoms of aseptic meningitis have been observed, accompanied by stiffness of the neck, headaches, malaise, fever, or changes in consciousness. Patients with autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease) are more prone to side effects. The patient should immediately consult their doctor if these symptoms occur.
Frequency not known(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- chest pain, which may be a symptom of a potentially serious allergic reaction called Kounis syndrome.
- severe skin reactions known as DRESS syndrome. The symptoms of DRESS syndrome include: skin rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and an increased number of eosinophils (a type of white blood cell),
- red, scaly rash with nodules under the skin and blisters, usually located in skin folds, on the torso, and upper limbs, with fever occurring at the beginning of treatment (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis). If such symptoms occur, the patient should stop using the medicine I F and seek medical attention immediately. See also section 2,
- the skin becomes sensitive to light.
Taking such medicines as I F may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack (myocardial infarction) or stroke.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Aleje Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw
tel.: 22 49 21 301, fax: 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, it is possible to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store the medicine I F
Store in the original packaging, at a temperature below 25°C.
Shelf life after first opening: 6 months.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the given month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What the medicine I F contains
- The active substance of the medicine is ibuprofen. 5 ml of the suspension contains 200 mg of ibuprofen.
- The other ingredients (excipients) are: maltitol liquid, glycerol, xanthan gum, sodium saccharin, sodium benzoate (E 211), fumaric acid, disodium phosphate dodecahydrate, banana flavor (contains propylene glycol E 1520), purified water.
What the medicine I F looks like and what the packaging contains
The packaging of the medicine is a brown glass bottle with a screw cap, cork, and a guarantee ring, which contains 130 g or 100 g of banana-flavored oral suspension. The bottle is placed in a cardboard box with a patient leaflet and a measuring spoon.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
"PRZEDSIĘBIORSTWO PRODUKCJI FARMACEUTYCZNEJ HASCO-LEK" S.A.
51-131 Wrocław, ul. Żmigrodzka 242 E
Information about the medicine
tel.: 22 742 00 22
e-mail: [email protected]
Date of the last update of the leaflet:
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterPrzedsiębiorstwo Produkcji Farmaceutycznej HASCO-LEK S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Ibum Forte (o smaku bananovim)Dosage form: Suspension, 40 mg/mlActive substance: ibuprofenManufacturer: Laboratorios Basi - Industria Farmaceutica, S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 400 mgActive substance: ibuprofenPrescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 600 mgActive substance: ibuprofenManufacturer: Aristo Pharma GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Ibum Forte (o smaku bananovim) in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Ibum Forte (o smaku bananovim) in Испания
Alternative to Ibum Forte (o smaku bananovim) in Украина
Online doctors for Ibum Forte (o smaku bananovim)
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Ibum Forte (o smaku bananovim) – subject to medical assessment and local rules.















