
Fenactil

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Fenactil

How to use Fenactil
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
FENACTIL, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection
FENACTIL, 25 mg/ml, solution for injection
Chlorpromazine hydrochloride
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Fenactil and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Fenactil
- 3. How to take Fenactil
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Fenactil
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Fenactil and what is it used for
Fenactil contains chlorpromazine, as the active substance, and belongs to a group of medicines called neuroleptics.
The medicine is intended for the treatment of diseases that affect thinking, feeling, and behavior. These diseases can cause:
- states of disorientation, confusion, and bewilderment;
- seeing, hearing, or feeling things that do not exist (hallucinations);
- erroneous judgments, inconsistent with reality, considered true by the patient (delusions);
- excessive suspiciousness;
- excessive excitement, stimulation, enthusiasm (mania);
- uncontrolled aggression and other impulsive behaviors.
Fenactil is also used:
- in the treatment of nausea and vomiting in terminal illnesses, such as cancer (when other medicines are not effective or available);
- in persistent, treatment-resistant hiccups;
- as a medicine to facilitate the introduction of hypothermia (prevention of shivering);
- in autism.
2. Important information before taking Fenactil
When not to take Fenactil
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Fenactil, you should discuss it with your doctor if:
- the patient has heart failure, suffers or has suffered from certain heart diseases, causing slow or very fast heart rate with rhythm disturbances (so-called arrhythmia) or if someone in the immediate family has suddenly died of heart disease;
- laboratory tests have shown low levels of mineral components in the blood (ions, e.g., calcium, potassium, sodium, magnesium);
- the patient has been malnourished for a longer period or is malnourished;
- the patient has kidney or liver disorders;
- the patient suffers from epilepsy or has had seizures in the past;
- the patient has depression;
- the patient has thyroid disorders (hypothyroidism);
- the patient has been diagnosed with a pheochromocytoma (a tumor located in the glands above the kidneys);
- the patient has myasthenia (muscle weakness);
- the patient has been diagnosed with prostate enlargement;
- the patient has glaucoma (increased pressure in the eyes) with a narrow angle of filtration;
- the patient has agranulocytosis (low white blood cell count), which manifests as, e.g., a tendency to infections;
- the patient suddenly develops fever, excessive sweating, blood pressure fluctuations - these symptoms should be reported to the doctor immediately, as they may be symptoms of a serious disease;
- the patient abuses alcohol;
- the patient suffers from Parkinson's disease.
In some cases, the patient may require more frequent medical check-ups, especially:
- elderly patients with dementia;
- patients whose close relatives have had disorders related to blood clot formation in the past.
Before starting treatment, the doctor may recommend an electrocardiogram (ECG) or a test of the mineral components in the blood.
During treatment with the medicine, you should avoid exposure to the sun.
Fenactil should be used with caution in elderly patients, when the ambient temperature is high or low, due to the risk of overheating or hypothermia. Elderly people are particularly prone to sudden drops in blood pressure and fainting after administration of the medicine.
Fenactil and other medicines
You should tell your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
Particular caution should be exercised if the patient is taking lithium and Fenactil at the same time. If symptoms such as fever, uncontrolled body movements, disorientation, headache, balance difficulties, drowsiness occur, both medicines should be discontinued immediately
and you should consult your doctor, as these may be symptoms of a serious disease.
You should necessarily tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines, as Fenactil may affect the action of other medicines and vice versa - some medicines may affect the action of Fenactil. These are:
- sedatives and sleeping pills;
- medicines used in diseases that affect thinking, feeling, or behavior (antipsychotic and neuroleptic medicines);
- medicines used in the treatment of depression (fluoxetine);
- medicines used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease (levodopa);
- medicines that lower blood pressure (guanethidine, clonidine, propranolol);
- antacids;
- medicines used in severe allergic reactions (adrenaline);
- medicines that change heart rate and affect heart rhythm;
- medicines that lower blood sugar levels;
- medicines that lower iron levels in the blood (deferoxamine);
- anxiolytics (prochlorperazine);
- cholinolytics (e.g., atropine);
- medicines used in the treatment of cancer (cytotoxic medicines);
- antiepileptic medicines (phenobarbital, carbamazepine);
- medicines used in bacterial infections (some antibiotics). Amphetamine has an effect opposite to that of chlorpromazine.
Fenactil with food, drink, and alcohol
You should avoid drinking alcohol while taking the medicine, as it may cause drowsiness, reduced psychophysical fitness, and serious breathing difficulties.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, suspects that she may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, she should consult a doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
The doctor will decide whether to use Fenactil during pregnancy.
The following symptoms may occur in newborns of mothers who have taken Fenactil in the last trimester (last three months of pregnancy): tremors, stiffness, and/or muscle weakness, drowsiness, excitement, breathing difficulties, and sucking difficulties. If the patient's child experiences any of these symptoms, she should contact a doctor.
The medicine should not be used during breastfeeding, as it may pass into breast milk.
Driving and using machines
Fenactil may make it difficult to drive vehicles and operate machines (excessive sedation and concentration disorders may occur), especially during the initial treatment period and after high doses of the medicine. You should not perform these activities until the disorders have subsided.
Fenactil contains sodium hydrogen sulfate, sodium
The medicine may rarely cause severe hypersensitivity reactions and bronchospasm due to the presence of sodium hydrogen sulfate.
Fenactil 5 mg/ml
The medicine contains 13.35 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in a 5 ml ampoule. This corresponds to 0.67% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake in the diet for adults.
Fenactil 25 mg/ml
The medicine contains 5.92 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in a 2 ml ampoule. This corresponds to 0.30% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake in the diet for adults.
The medicine may be diluted in a 0.9% NaCl solution. The sodium content from the diluent should be taken into account when calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, you should read the patient information leaflet of the diluent used.
3. How to take Fenactil
This medicine should always be taken according to the doctor's instructions. If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor.
Fenactil solution for injection is usually administered by medical personnel, in deep intramuscular injections.
The doctor will determine the doses of Fenactil and the duration of treatment, depending on the patient's condition.
Using a higher dose of Fenactil than recommended
The medicine is administered by medical personnel, so using a higher dose than recommended is unlikely. However, if any of the following symptoms occur, such as excessive drowsiness, low blood pressure, rapid heart rate, heart rhythm disorders, you should tell your doctor.
In case of using a higher dose of the medicine than recommended by the doctor, you should immediately contact a doctor or go to the nearest hospital.
Missing a dose of Fenactil
The medicine is usually administered by medical personnel, so missing a dose is unlikely.
You should not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping treatment with Fenactil
The medicine should be taken for the period recommended by the doctor. The full effect of the medicine is felt after some time has passed.
If the doctor does not recommend otherwise, treatment should be stopped gradually. Abrupt discontinuation of the medicine may cause nausea, vomiting, sleep disturbances. You should follow the doctor's instructions regarding the discontinuation of the medicine.
If you have any further doubts about taking this medicine, you should consult a doctor.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
You should immediately call a doctor or take the patient to the hospital if any of the following symptoms occur, as they may require immediate treatment:
- blood clots in blood vessels, especially in the legs (manifested by swelling, pain, and redness of the legs), which can move through the blood vessels towards the lungs, causing chest pain and breathing difficulties;
- swelling of the face and throat, rash (known as urticaria or hives), severe irritation or redness, or blisters on the skin. These are symptoms of allergic reactions and occur in a small number of patients;
- rapid heart rate, changes in blood pressure, fever, and excessive sweating, rapid breathing, muscle stiffness, decreased consciousness, and coma (a serious side effect known as malignant neuroleptic syndrome);
- rapid, involuntary movements of the tongue, face, lips, or jaw (symptoms of late dyskinesia) and slowing down, motor inhibition, muscle stiffness, tremors of limbs and head, excessive salivation, tremors, and involuntary movements of the tongue, face, lips, jaw, throat (symptoms of parkinsonism). If any of these symptoms occur, the doctor will decide on the use of additional medicine;
- jaundice (yellowing of the skin and/or eyes); these may be symptoms of liver disorders and are rare;
- repeated infections, manifested by fever, sore throat, mouth ulcers; these may be symptoms of blood disorders (leukopenia). Mild leukopenia occurs very frequently.
You should consult a doctor if any of the following side effects occur, which have been reported in patients taking chlorpromazine:
- decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytosis), decrease in the number of neutrophils (agranulocytosis) - occurs rarely and is not dose-dependent;
- allergic reactions, such as angioedema, bronchospasm, urticaria; anaphylactic shock, systemic lupus erythematosus (a serious skin and internal organ disease) occurs very rarely - see information at the beginning of section 4 of the leaflet;
- increased levels of the hormone prolactin in the blood (hyperprolactinemia), leading to unexpected milk secretion (galactorrhea), breast enlargement in men (gynecomastia), absence of menstruation, and impotence;
- acute dystonias (muscle tone disorders) or dyskinesias (impairment of precise movements, especially of hands and fingers) usually transient - occur more frequently in children and adolescents, usually during the first days of treatment or after increasing the dose; akathisia (motor restlessness forcing frequent changes of limb or whole body position) usually occurs after high initial doses of the medicine; parkinsonism - occurs more frequently in adults and elderly patients, usually after several weeks of treatment with the medicine - see information at the beginning of section 4 of the leaflet; late dyskinesias may occur after long-term use of high doses of the medicine, as well as after discontinuation of treatment - see information at the beginning of section 4 of the leaflet; insomnia and agitation;
- changes in the eyes and metal gray-pink discoloration of exposed skin - occur mainly in women treated with chlorpromazine for a long time (from 4 to 8 years);
- heart rhythm disorders (atrial arrhythmia, atrioventricular block, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation) probably dose-dependent; the occurrence of these disorders is more likely in patients with heart disease, elderly patients, and patients with low potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia); changes in the ECG recording, usually mild (QT interval prolongation, ST segment depression, U wave, and T wave changes);
- hypotension, usually orthostatic (manifested by a drop in blood pressure, dizziness, and fainting, especially when standing up) - occurs more frequently after intramuscular administration of the medicine in patients with reduced blood volume and elderly patients;
- cases of venous thromboembolism, including pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis, have been reported in patients taking antipsychotic medicines - see information at the beginning of section 4 of the leaflet;
- dry mouth;
- respiratory depression (inhibition of breathing), feeling of nasal congestion;
- jaundice - usually transient; a symptom preceding its occurrence may be sudden fever, occurring after 1-3 weeks of treatment; if jaundice occurs, treatment should be discontinued; liver damage (rare) and may lead to death;
- contact allergy - symptoms of hypersensitivity occurring in people who have frequent contact with chlorpromazine; skin rashes; increased skin sensitivity to sunlight in patients taking high doses of the medicine - patients should avoid direct exposure to sunlight;
- withdrawal syndrome in newborns;
- priapism (painful and prolonged erection);
- malignant neuroleptic syndrome - see information at the beginning of section 4 of the leaflet.
In elderly patients with dementia, a small increase in the number of deaths has been reported in patients taking neuroleptic medicines, compared to those who did not take these medicines. It is not known exactly how often such cases occur.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Fenactil
Do not store above 25°C. Store the ampoules in the outer packaging to protect them from light. Do not freeze.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer used. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What does Fenactil contain
- The active substance of the medicine is chlorpromazine hydrochloride. Each ml of the solution contains 5 mg or 25 mg of chlorpromazine hydrochloride.
- The other ingredients are: ascorbic acid, sodium chloride, sodium hydrogen sulfate (40% solution), sodium carbonate, water for injections.
What does Fenactil look like and what does the packaging contain
Fenactil is a colorless or light yellow or light green transparent liquid.
The packaging of Fenactil 5 mg/ml contains 5 ampoules made of orange glass with a capacity of 5 ml.
The packaging of Fenactil 25 mg/ml contains 10 ampoules made of colorless glass with a capacity of 2 ml.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Warsaw Pharmaceutical Works Polfa S.A.
ul. Karolkowa 22/24; 01-207 Warsaw
To obtain more detailed information, you should contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Warsaw Pharmaceutical Works Polfa S.A.
ul. Karolkowa 22/24; 01-207 Warsaw
phone: 22 691 39 00
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
Information intended only for healthcare professionals:
FENACTIL, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection
FENACTIL, 25 mg/ml solution for injection
Chlorpromazine hydrochloride
Method of administration of Fenactil
- Fenactil should be used parenterally in emergency situations.
- Administer only in deep intramuscular injections.
- Do not administer subcutaneously, as the medicine administered by this route has a strong irritating effect.
- If possible, repeated intramuscular injections should be avoided.
Note: Fenactil should not be combined with benzylpenicillin potassium, pentobarbital sodium, or phenobarbital sodium, as it shows incompatibility.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to help the solution flow down.
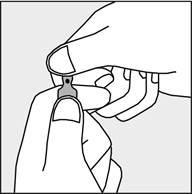
A colored dot has been placed on each ampoule (see Figure 1) as a mark indicating the break point below it.
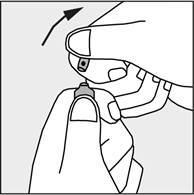
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, with both hands, with the colored dot facing each other - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused product should be destroyed in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Dosage of Fenactil
- Schizophrenia and other psychoses, mania and hypomania, anxiety states, psychomotor excitement, aggressive or dangerous impulsive behavior, childhood schizophrenia, and autism
Adults
Usually 25 mg to 50 mg of chlorpromazine in deep intramuscular injection. If necessary, injections can be repeated every 6-8 hours.
Treatment with oral chlorpromazine is recommended to be continued.
Elderly patients
Treatment should be started with the smallest doses used in adults, usually 25 mg of chlorpromazine every 8 hours.
Children
Children aged 6 to 12 years: 0.5 mg/kg body weight of chlorpromazine every 6-8 hours. The dose should not exceed 75 mg per day.
Children from 1 year of age to 6 years: 0.5 mg/kg body weight of chlorpromazine every 6-8 hours. The dose should not exceed 40 mg per day.
Children under 1 year of age: use only in life-threatening conditions.
- Refractory hiccups
Adults
Administer 25 mg to 50 mg of chlorpromazine in deep intramuscular injection. If there is no improvement, 25 mg to 50 mg of chlorpromazine can be administered in slow intravenous infusion, after dilution in 500-1000 ml of 0.9% NaCl solution.
Elderly patients and children: no data available.
- Induction of hypothermia
Administer in deep intramuscular injection.
Adults
25 mg to 50 mg of chlorpromazine every 6-8 hours.
Elderly patients: no data available.
Children
Children from 1 year of age to 12 years: initial dose from 0.5 mg/kg body weight to 1 mg/kg body weight of chlorpromazine. Maintenance dose: 0.5 mg/kg body weight every 4-6 hours.
Children under 1 year of age: not recommended.
- Nausea and vomiting in terminal illnesses
Administer in deep intramuscular injection.
Adults
Initial dose is 25 mg, then 25 mg to 50 mg of chlorpromazine every 3-4 hours, until vomiting subsides. Then, oral chlorpromazine is recommended.
Elderly patients: not recommended.
Children
Children aged 6 to 12 years: 0.5 mg/kg body weight of chlorpromazine every 6-8 hours. The dose should not exceed 75 mg per day.
Children from 1 year of age to 6 years: 0.5 mg/kg body weight of chlorpromazine every 6-8 hours. The dose should not exceed 40 mg per day.
Children under 1 year of age: use only in life-threatening conditions.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterWarszawskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLFA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FenactilDosage form: Solution, 25 mg/mlActive substance: chlorpromazineManufacturer: Warszawskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLFA S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Drops, 40 mg/gActive substance: chlorpromazineManufacturer: Zakłady Farmaceutyczne "UNIA" Spółdzielnia PracyPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 25 mgActive substance: levomepromazinePrescription required
Alternatives to Fenactil in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Fenactil in Ucrania
Alternative to Fenactil in España
Online doctors for Fenactil
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Fenactil – subject to medical assessment and local rules.









