
Eltrombopag Stada

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Eltrombopag Stada

How to use Eltrombopag Stada
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Eltrombopag Stada, 25 mg, coated tablets
Eltrombopag Stada, 50 mg, coated tablets
Eltrombopag Stada, 75 mg, coated tablets
Eltrombopag
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Eltrombopag Stada and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Eltrombopag Stada
- 3. How to take Eltrombopag Stada
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Eltrombopag Stada
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Eltrombopag Stada and what is it used for
Eltrombopag Stada contains eltrombopag, which belongs to a group of medicines called thrombopoietin receptor agonists. The medicine is used to increase the number of platelets in the patient's blood.
Platelets are blood cells that help reduce the risk of bleeding or prevent it.
- Eltrombopag Stada is used to treat a bleeding disorder called primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), in patients over 1 year of age who have already been treated with other medicines (corticosteroids or immunoglobulins) and in whom these medicines have not worked.
- Immune thrombocytopenia is caused by a low number of platelets in the blood (thrombocytopenia). People with immune thrombocytopenia are more prone to bleeding. Symptoms that patients with immune thrombocytopenia may notice include petechiae (small, flat, red spots under the skin), purpura, nosebleeds, bleeding gums, and an inability to stop bleeding in case of injury or trauma.
- Eltrombopag Stada may also be used to treat a low number of platelets in the blood (thrombocytopenia) in adults with hepatitis C virus infection, who have had difficulties due to side effects during treatment with interferon. Many people with hepatitis C have a low number of platelets in the blood, not only due to the disease but also as a result of the action of some antiviral drugs used in treatment. Taking Eltrombopag Stada may help patients complete a full course of antiviral treatment (peginterferon and ribavirin).
- Eltrombopag Stada can also be used to treat adults with a low number of blood cells caused by severe aplastic anemia (SAA). SAA is a disease in which the bone marrow is damaged, leading to a lack of red blood cells (anemia), white blood cells (leukopenia), and platelets (thrombocytopenia).
2. Important information before taking Eltrombopag Stada
When not to take Eltrombopag Stada
- If the patient is allergicto eltrombopag or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). Consult a doctorif the patient thinks they have this condition.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Eltrombopag Stada, the patient should discuss the following with their doctor:
- If the patient has liver disease. People with a low number of platelets in the blood, as well as advanced (long-standing) liver disease, are at a higher risk of side effects, including life-threatening liver damage and blood clots. If the doctor considers that the benefits of taking Eltrombopag Stada outweigh the risks, the patient will be closely monitored during treatment;
- If the patient is at risk of blood clots in the veins or arteries, or if there is a family history of blood clots.
Risk of blood clots may be increased:
- If the patient is elderly
- If the patient has been immobile for a long time
- If the patient has cancer
- If the patient is taking oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy
- If the patient has recently undergone surgery or had an injury
- If the patient is overweight
- If the patient smokes
- If the patient has advanced chronic liver diseaseInform your doctorbefore starting treatment if any of the above conditions apply to the patient. Do not take Eltrombopag Stada unless the doctor considers that the expected benefits outweigh the risk of blood clots.
- If the patient has cataracts
- If the patient has other blood disorders, such as myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Before starting treatment with Eltrombopag Stada, the doctor will perform tests to rule out this disease.
- If the patient has MDS and is taking Eltrombopag Stada, MDS may worsen. Inform your doctorif any of the above situations apply to the patient.
Eye examination
The doctor will recommend an eye examination to detect cataracts. If the patient does not undergo regular eye examinations, the doctor should schedule regular examinations. The occurrence of any bleeding in the retina (the light-sensitive layer of cells at the back of the eye) or near it may also be examined.
Regular tests will be necessary
Before starting treatment with Eltrombopag Stada, the doctor will perform blood tests to assess blood cells, including platelets. During treatment, these tests will be repeated at regular intervals.
Blood tests to assess liver function
Eltrombopag may cause changes in blood test results that may indicate liver damage - increased activity of certain liver enzymes, particularly alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, and bilirubin levels. If the patient is taking interferon-based treatment with Eltrombopag Stada for low platelet count associated with hepatitis C, some liver diseases may worsen.
Before starting treatment with Eltrombopag Stada and at regular intervals during treatment, the patient will undergo blood tests to assess liver function. It may be necessary to stop taking Eltrombopag Stada if the levels of these substances increase too much or if other signs of liver damage occur.
See "Liver function disorders" in section 4 of this leaflet.
Platelet count tests
If the patient stops taking Eltrombopag Stada, there is a risk of a low platelet count returning within a few days. The platelet count will be monitored, and the doctor will discuss appropriate precautions with the patient.
A very high platelet count may increase the risk of blood clots. However, blood clots can also occur when the platelet count is normal or too low. The doctor will adjust the dose of Eltrombopag Stada for the patient to avoid excessively increasing the platelet count.

The patient should seek immediate medical attentionif they experience any of the following symptoms of a blood clot:
- Swelling, painor tenderness in one leg
- Sudden shortness of breath, especially with severe chest pain or rapid breathing
- Abdominal pain (stomach), abdominal swelling, blood in stool
Bone marrow tests
In patients with bone marrow disorders, medicines like eltrombopag may worsen these disorders. Changes in the bone marrow may be indicated by abnormal blood test results. The doctor may order direct bone marrow tests during treatment with Eltrombopag Stada.
Tests to detect gastrointestinal bleeding
If the patient is taking interferon-based treatment with Eltrombopag Stada, they will be monitored for signs of gastrointestinal bleeding after stopping treatment with Eltrombopag Stada.
Heart tests
The doctor may consider it necessary to perform a heart test on the patient during treatment with Eltrombopag Stada and perform an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Elderly patients (65 years and older)
There is limited data on the use of eltrombopag in patients aged 65 and older. Caution should be exercised when taking Eltrombopag Stada in patients aged 65 and older.
Children and adolescents
Eltrombopag Stada is not recommended for children under 1 year of age with immune thrombocytopenia. The medicine is also not recommended for individuals under 18 years of age with low platelet count associated with hepatitis C virus infection or severe aplastic anemia.
Eltrombopag Stada and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take. This includes medicines obtained without a prescription and vitamins.
Certain commonly used medicines interact with Eltrombopag Stada- including both prescription and non-prescription medicines and mineral supplements. These include:
- Medicines that neutralize stomach acid used to treat indigestion, heartburn, stomach ulcers(see also "When to take the medicine" in section 3)
- Medicines called statins, which lower cholesterol levels
- Certain medicines used to treat HIV infection, such as lopinavir and (or) ritonavir
- Cyclosporine used in transplantsor immune system disorders
- Mineral products, such as iron, calcium, magnesium, aluminum, selenium, and zinc, which may be components of vitamin and mineral supplements(see also "When to take the medicine" in section 3)
- Medicines such as methotrexate and topotecan, used to treat cancerConsult a doctorif the patient is taking any of the above medicines. Some of them should not be taken during treatment with Eltrombopag Stada, while others may require dose adjustment or appropriate timing of administration. The doctor will review the patient's medicines and recommend changes if necessary.
If the patient is taking medicines to prevent blood clots, there is an increased risk of bleeding. The doctor will discuss this with the patient.
If the patient is taking corticosteroids, danazol, and (or) azathioprine, the doses of these medicines may be reduced or their use stopped during concurrent treatment with Eltrombopag Stada.
Taking Eltrombopag Stada with food and drink
Eltrombopag Stada should not be taken with dairy products or drinks, as the calcium in dairy products affects the absorption of the medicine. For more information, see "When to take the medicine" in section 3.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Eltrombopag Stada should not be taken during pregnancy, unless the doctor recommends it.
The effect of eltrombopag during pregnancy is unknown.
- The patient should inform their doctor if they are pregnant, think they may be pregnant, or plan to have a baby.
- The patient should use appropriate contraceptionto prevent pregnancy while taking Eltrombopag Stada.
- The patient should inform their doctor if they become pregnantwhile taking Eltrombopag Stada.
The patient should not breastfeed while taking Eltrombopag Stada. It is not known whether eltrombopag passes into breast milk.
The patient should inform their doctor if they are breastfeedingor plan to breastfeed.
Driving and using machines
Eltrombopag Stada may cause dizzinessand other side effects that reduce attention.
The patient should not drive or operate machineryunless they are sure that these symptoms do not occur.
Eltrombopag Stada contains sodium
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per coated tablet, which means that the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to take Eltrombopag Stada
This medicine should always be taken exactly as prescribed by the doctor. If the patient has any doubts, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist. The patient should not change the dose or dosing schedule of Eltrombopag Stada unless their doctor or pharmacist tells them to do so.
While taking Eltrombopag Stada, the patient will remain under the care of a doctor with experience in treating the disease.
How much to take
In the case of primary immune thrombocytopenia
Adults and children(aged 6 to 17 years) - the recommended initial dose for primary immune thrombocytopenia is one 50 mg tabletof Eltrombopag Stada per day.
Patients of East Asian/Southeast Asian origin may require a lower starting dose of 25 mg.
Children(aged 1 to 5 years) - the recommended initial dose for primary immune thrombocytopenia is one 25 mg tabletof Eltrombopag Stada per day.
In the case of hepatitis C
Adults- the recommended initial dose for hepatitis C is one 25 mg tabletof Eltrombopag Stada per day. Patients of East Asian/Southeast Asian origin should start treatment with the same dose of 25 mg.
In the case of SAA
Adults- the recommended initial dose for SAA is one 50 mg tabletof Eltrombopag Stada per day. Patients of East Asian/Southeast Asian origin may require a lower starting dose of 25 mg.
The onset of action of Eltrombopag Stada may occur after 1 to 2 weeks. Depending on the patient's response to treatment with Eltrombopag Stada, the doctor may recommend a change in the daily dose.
How to take the tablets
The tablets should be swallowed whole with water.
Eltrombopag Stada 25 mg and 50 mg coated tablets:
The tablet can be divided into equal doses.
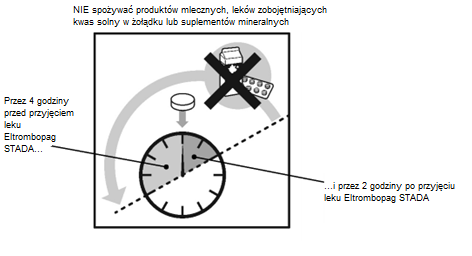
When to take the medicine
The patient should make sure that -
- 4 hours beforetaking Eltrombopag Stada
- and 2 hours aftertaking Eltrombopag Stada the patient will notconsume the following foods:
- dairy products, such as cheese, butter, yogurt, ice cream
- milkor drinks containing milk, yogurt, or cream
- medicines that neutralize stomach acid, used to treat indigestion and heartburn
- mineral supplementscontaining iron, calcium, magnesium, aluminum, selenium, and zinc (see also "When to take the medicine" in section 3)
If these recommendations are not followed, Eltrombopag Stada will not be properly absorbed by the body.
The patient should consult their doctor for more information about suitable foods and drinks.
Taking a higher dose of Eltrombopag Stada than recommended
The patient should contact their doctor or pharmacist immediately. If possible, they should show them the packaging of the medicine or this leaflet.
The patient's condition will be monitored for any side effects and appropriate treatment will be applied promptly.
Missing a dose of Eltrombopag Stada
The patient should take the next dose at the usual time. They should not take more than one dose of Eltrombopag Stada per day.
Stopping treatment with Eltrombopag Stada
The patient should not stop taking Eltrombopag Stada without consulting their doctor. If the doctor recommends stopping treatment, the patient's platelet count will be monitored weekly for four weeks. See also "Bleeding or bruising after stopping treatment" in section 4.
If the patient has any further doubts about taking this medicine, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Eltrombopag Stada can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Symptoms to watch out for: the patient should see a doctor
In patients taking Eltrombopag Stada for primary immune thrombocytopenia or low platelet count associated with hepatitis C, severe side effects may occur. It is essential to inform the doctorabout these symptoms.
Increased risk of blood clots
In some patients, the risk of blood clots may be increased, and medicines like eltrombopag may worsen this condition. Sudden blockage of a blood vessel by a blood clot is an uncommon side effect and may occur in up to 1 in 100 patients.

The patient should seek immediate medical attention if they experience any symptoms of a blood clot, such as:
- Swelling, pain, feeling of heat, rednessor tenderness in one leg
- Sudden shortness of breath, especially with severe chest pain or rapid breathing
- Abdominal pain (stomach), abdominal swelling, blood in stool.
Liver function disorders
Eltrombopag may cause changes in blood test results that may indicate liver damage. Liver function disorders (increased activity of enzymes in blood test results) are common and may occur in up to 1 in 10 patients. Other liver problems are uncommon and may occur in up to 1 in 100 patients.
If the patient experiences any of the following symptoms of liver function disorders:
- Yellowingof the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- abnormally dark urinethe patient should tell their doctor immediately.
Bleeding or bruising after stopping treatment
Usually, within two weeks of stopping treatment with Eltrombopag Stada, the patient's platelet count returns to the level before starting treatment with Eltrombopag Stada. A low platelet count may increase the risk of bleeding or bruising. The doctor will monitor the patient's platelet count for at least 4 weeks after stopping treatment with Eltrombopag Stada.
The patient should inform their doctorif they experience bruising or bleeding after stopping treatment with Eltrombopag Stada.
In some patients, gastrointestinal bleedingmay occur after stopping treatment with peginterferon, ribavirin, and eltrombopag. Symptoms include:
- black, tarry stools (a change in stool color, which is an uncommon side effect that may occur in up to 1 in 100 patients)
- blood in stool
- vomiting blood or coffee-ground-like material the patient should tell their doctor immediatelyif they experience any of these symptoms.
The following side effects have been reported in association with Eltrombopag Stada treatment in adult patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia:
Very common side effects
May occur in more than 1 in 10patients:
- cold
- nausea
- diarrhea
- cough
- infection of the nose, sinuses, throat, and upper respiratory tract (upper respiratory tract infection)
- back pain
Very common side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- increased activity of liver enzymes (alanine aminotransferase (ALT))
Common side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 10patients:
- muscle pain, muscle spasms, muscle weakness
- bone pain
- heavy menstrual bleeding
- sore throat and discomfort when swallowing
- eye disorders, including abnormal eye test results, dry eyes, eye pain
and blurred vision
- vomiting
- flu
- herpes simplex
- pneumonia
- sinusitis
- tonsillitis
- infection of the lungs, sinuses, nose, and throat
- gum inflammation
- loss of appetite
- tingling, prickling, or numbness
- reduced sensation
- drowsiness
- ear pain
- pain, swelling, and tenderness in one leg (usually the calf, with warmth of the skin in the affected area, symptoms of deep vein thrombosis)
- localized swelling filled with blood from a damaged blood vessel (hematoma)
- hot flashes
- disorders of the mouth, including dry mouth, mouth pain, tongue sensitivity, gum bleeding, mouth ulcers
- runny nose
- toothache
- abdominal pain
- abnormal liver function
- skin changes, including excessive sweating, rash, redness, itching, and skin discoloration
- hair loss
- foamy urine (presence of protein in the urine)
- high fever
- chest pain
- feeling of weakness
- difficulty sleeping, depression
- migraine
- blurred vision
- dizziness
- wind
Common side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- decreased red blood cell count (anemia)
- decreased platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
- decreased white blood cell count
- decreased hemoglobin level
- increased eosinophil count
- increased white blood cell count (leukocytosis)
- increased uric acid level
- decreased potassium level
- increased creatinine level
- increased alkaline phosphatase activity
- increased liver enzyme activity (aspartate aminotransferase (AST))
- increased bilirubin level in the blood (a substance produced by the liver)
- increased levels of certain proteins
Uncommon side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 100patients:
- allergic reaction
- interrupted blood flow to a part of the heart
- sudden shortness of breath, especially with severe chest pain and (or) rapid breathing, which may be a symptom of a pulmonary embolism (see "Increased risk of blood clots" above in section 4)
- loss of function of a part of the lung due to blockage of the pulmonary artery
- possible pain, swelling, and (or) redness in the area of the vein, which may be symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis
- yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice), which may be symptoms of bile duct obstruction, liver disease, or liver damage caused by inflammation (see "Liver function disorders" above in section 4)
- liver damage caused by the medicine
- rapid heartbeat, irregular heartbeat, blue discoloration of the skin, heart rhythm disorders (prolonged QT interval), which may be symptoms of a heart and blood vessel disorder
- blood clot
- redness
- painful swelling of the joints caused by uric acid (gout)
- lack of interest, mood changes, crying, which is difficult to control or occurs unexpectedly
- disorders of balance, speech, and nerve function, tremors
- painful or abnormal skin sensations
- paralysis of one side of the body
- migraine with aura
- nerve damage
- expansion or swelling of blood vessels causing headache
- eye disorders, including increased tearing, cataract, retinal bleeding, dry eyes
- respiratory tract infections, difficulty breathing
- mouth ulcers or blisters
- loss of appetite
- gastrointestinal disorders, including vomiting, abdominal pain, indigestion, constipation, bloating, taste disturbances, hemorrhoids, stomach pain or discomfort, and bleeding in the esophagus
- toothache
- liver problems, including liver tumor, yellowing of the whites of the eyes or skin (jaundice), liver damage caused by the medicine (see "Liver function disorders" above in section 4)
- skin changes, including rash, dry skin, rash, redness, itching, and excessive sweating
- joint pain, back pain, bone pain, limb pain (arms, legs, hands, or feet), muscle spasms
- irritability, general feeling of being unwell, skin reaction, such as redness or swelling and pain at the injection site, chest pain and discomfort, fluid accumulation in the body or limbs causing swelling
- infection of the nose, sinuses, throat, and upper respiratory tract, common cold (upper respiratory tract infection), bronchitis
- depression, anxiety, sleep disturbances, nervousness
Uncommon side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- changes in red blood cell shape
- presence of developing white blood cells, which may indicate certain diseases
- increased platelet count
- decreased calcium level
- decreased red blood cell count (anemia) caused by excessive destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia)
- increased myelocyte count
- increased neutrophil count
- increased urea level in the blood
- increased protein level in the urine
- increased albumin level in the blood
- increased total protein level
- decreased albumin level in the blood
- increased urine pH
- increased hemoglobin level
Side effects with unknown frequency
Frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- skin discoloration
- darkening of the skin
- liver damage caused by the medicine
The following side effects have been reported in association with Eltrombopag Stada treatment in children (aged 1 to 17 years) with ITP:
If these side effects worsen, the patient should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Very common side effects
May occur in more than 1 in 10children:
- infection of the nose, sinuses, throat, and upper respiratory tract, common cold (upper respiratory tract infection)
- diarrhea
- abdominal pain
- cough
- high fever
- nausea
Common side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 10children:
- difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- toothache
- nose and throat pain
- itchy nose, runny nose, or nasal congestion
- sore throat and runny nose, nasal congestion, and coughing
- mouth disorders, including dry mouth, mouth pain, tongue sensitivity, gum bleeding, mouth ulcers
The following side effects have been reported in association with eltrombopag treatment in combination with peginterferon and ribavirin in patients with hepatitis C:
Very common side effects
May occur in more than 1 in 10patients:
- headache
- loss of appetite
- cough
- nausea, diarrhea
- muscle pain, muscle weakness
- itching
- feeling of tiredness
- fever
- unusual hair loss
- weakness
- flu-like illness
- swelling of the hands or feet
- chills
Very common side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- decreased red blood cell count (anemia)
Common side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 10patients:
- urinary tract infections
- infection of the nose, sinuses, throat, and upper respiratory tract, common cold (upper respiratory tract infection), flu-like illness
- weight loss
- sleep disturbances, drowsiness, depression, anxiety
- dizziness, difficulty concentrating and remembering, mood changes
- brain disorder caused by liver damage
- tingling or numbness of the hands or feet
- fever, headache
- eye disorders, including cataract, dry eye syndrome, small yellow deposits in the retina, yellowing of the whites of the eyes
- retinal bleeding
- dizziness
- rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations), shortness of breath
- cough with sputum production, runny nose, flu, cold sore, sore throat and discomfort when swallowing
- gastrointestinal disorders, including vomiting, abdominal pain, indigestion, constipation, bloating, taste disturbances, hemorrhoids, stomach pain or discomfort, and bleeding in the esophagus
- toothache
- liver problems, including liver tumor, yellowing of the whites of the eyes or skin (jaundice), liver damage caused by the medicine (see "Liver function disorders" above in section 4)
- skin changes, including rash, dry skin, rash, redness, itching, and excessive sweating
- joint pain, back pain, bone pain, limb pain (arms, legs, hands, or feet), muscle spasms
- irritability, general feeling of being unwell, skin reaction, such as redness or swelling and pain at the injection site, chest pain and discomfort, fluid accumulation in the body or limbs causing swelling
- infection of the nose, sinuses, throat, and upper respiratory tract, common cold (upper respiratory tract infection), bronchitis
- depression, anxiety, sleep disturbances, nervousness
Common side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- increased blood sugar (glucose) level
- decreased white blood cell count
- decreased neutrophil count
- decreased albumin level in the blood
- decreased hemoglobin level
- increased bilirubin level in the blood (a substance produced by the liver)
- changes in enzymes that control blood clotting
Uncommon side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 100patients:
- pain when urinating
- heart rhythm disorders (prolonged QT interval)
- gastroenteritis (inflammation of the stomach and intestines), sore throat
- mouth ulcers or blisters, gastritis
- skin changes, including discoloration, peeling, redness, itching, and excessive sweating
- blood clots in the vein that carries blood to the liver (possible liver damage and (or) gastrointestinal damage)
- abnormal blood clotting in small blood vessels with kidney failure
- rash, bruising at the injection site, chest discomfort
- decreased red blood cell count (anemia) caused by excessive destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia)
- confusion, agitation
- liver failure
The following side effects have been reported in association with Eltrombopag Stada treatment in patients with severe aplastic anemia (SAA):
If these side effects worsen, the patient should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Very common side effects
May occur in more than 1 in 10patients:
- cough
- headache
- mouth and throat pain
- diarrhea
- nausea
- joint pain
- limb pain (arms, legs, hands, or feet)
- dizziness
- feeling of tiredness
- fever
- chills
- itching of the eyes
- mouth ulcers
- gum bleeding
- abdominal pain
- muscle spasms
Very common side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- abnormal changes in bone marrow cells
- increased liver enzyme activity (aspartate aminotransferase (AST))
Common side effects
May occur in up to 1 in 10patients:
- anxiety
- depression
- feeling of cold
- general feeling of being unwell
- eye disorders, including vision disturbances, blurred vision, cataract, retinal deposits, dry eyes, eye itching, yellowing of the whites of the eyes
- nosebleeds
- gastrointestinal disorders, including difficulty swallowing, mouth pain, tongue swelling, vomiting, loss of appetite, stomach pain or discomfort, bloating, gas, constipation, changes in bowel movements, which may cause constipation, bloating, diarrhea, and (or) the above symptoms, change in stool color
and fainting
- skin disorders, including small red or purple spots caused by bleeding into the skin (petechiae), rash, itching, hives, skin changes
- back pain
- muscle pain
- bone pain
- weakness
- swelling of the lower limbs due to fluid accumulation
- abnormal urine color
- interruption of blood flow to the spleen (splenic infarction)
- runny nose
Common side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- increased enzyme activity due to muscle breakdown (creatine phosphokinase)
- iron accumulation in the body (iron overload)
- decreased blood sugar level (hypoglycemia)
- increased bilirubin level in the blood (a substance produced by the liver)
- decreased white blood cell count
Side effects with unknown frequency
Frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- skin discoloration
- darkening of the skin
- liver damage caused by the medicine
5. How to store Eltrombopag Stada
The medicinal product should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicinal product after the expiry date stated on the carton and blister after EXP.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
There are no special precautions for storage.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
The active substance is eltrombopag (as eltrombopag olamine).
Each film-coated tablet contains eltrombopag olamine equivalent to 25 mg of eltrombopag.
Each film-coated tablet contains eltrombopag olamine equivalent to 50 mg of eltrombopag.
Each film-coated tablet contains eltrombopag olamine equivalent to 75 mg of eltrombopag.
Eltrombopag Stada, 25 mg, film-coated tablets
Tablet core
Microcrystalline cellulose, mannitol, povidone K90, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (type A), magnesium stearate
Tablet coating
Polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide (E 171), macrogol, talc
Eltrombopag Stada, 50 mg, film-coated tablets
Tablet core
Microcrystalline cellulose, mannitol, povidone K90, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (type A), magnesium stearate
Tablet coating
Polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide (E 171), macrogol, talc, yellow iron oxide (E 172), red iron oxide (E 172)
Eltrombopag Stada, 75 mg, film-coated tablets
Tablet core
Microcrystalline cellulose, mannitol, povidone K90, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (type A), magnesium stearate
Tablet coating
Polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide (E 171), macrogol, talc, red iron oxide (E 172)
What Eltrombopag Stada looks like and package contents
Eltrombopag Stada, 25 mg, film-coated tablets
White to light yellow, round, biconvex film-coated tablets with a score line on one side, dark red to brown at the break line.
Eltrombopag Stada, 50 mg, film-coated tablets
Brown, round, biconvex film-coated tablets with a score line on one side, dark red to brown at the break line.
Eltrombopag Stada, 75 mg, film-coated tablets
Pink, round, biconvex film-coated tablets.
Eltrombopag Stada is available in blisters containing 14, 28 or 84 film-coated tablets or single-dose blisters containing 14 x 1, 28 x 1 or 84 x 1 film-coated tablet.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
STADA Arzneimittel AG
Stadastrasse 2-18
61118 Bad Vilbel
Germany
Manufacturer/Importer
STADA Arzneimittel AG
Stadastrasse 2-18
61118 Bad Vilbel
Germany
STADA Arzneimittel GmbH
Muthgasse 36/2
1190 Vienna
Austria
Clonmel Healthcare Ltd.
Waterford Road
E91 D768 County Tipperary, Clonmel
Ireland
Centrafarm Services B.V.,
Van De Reijtstraat 31 E,
Breda, 4814
Netherlands
To obtain further information on this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Stada Pharm Sp. z o.o.
ul. Krakowiaków 44
02-255 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 737 79 20
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria, Croatia, Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia,
Finland, Greece, Spain, Netherlands,
Iceland, Lithuania, Latvia, Norway, Sweden,
Slovakia, Slovenia
Eltrombopag STADA
Eltrombopag Stada
Germany
Eltrombopag AL
France, Italy
Eltrombopag EG
Ireland, Malta
Eltrombopag Clonmel
Date of last revision of the leaflet: April 2025
Poland, Romania, Hungary
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterCentrafarm Services B.V. Clonmel Healthcare Ltd. STADA Arzneimittel AG STADA Arzneimittel AG
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Eltrombopag StadaDosage form: Tablets, 25 mgActive substance: eltrombopagPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 50 mgActive substance: eltrombopagPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 25 mgActive substance: eltrombopagPrescription required
Alternatives to Eltrombopag Stada in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Eltrombopag Stada in Spain
Alternative to Eltrombopag Stada in Ukraine
Online doctors for Eltrombopag Stada
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Eltrombopag Stada – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














