
Diovan
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Diovan

How to use Diovan
Leaflet attached to the packaging: information for the user
Diovan, 3 mg/ml, oral solution
Valsartanum
You should read the contents of the leaflet before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Diovan and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Diovan
- 3. How to take Diovan
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Diovan
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Diovan and what is it used for
Diovan contains the active substance: valsartan and belongs to a group of medicines called angiotensin II receptor antagonists, which help control high blood pressure. Angiotensin II is a substance produced in the human body that causes blood vessels to constrict, thereby increasing blood pressure. Diovan works by blocking the action of angiotensin II. As a result, blood vessels dilate, and blood pressure decreases. Diovan in the form of an oral solution may be used to treat high blood pressure in children and adolescents from 1 to less than 18 years of age.High blood pressure increases the burden on the heart and blood vessels. Untreated high blood pressure can lead to damage to blood vessels in the brain, heart, and kidneys, and can cause stroke, heart failure, or kidney failure. High blood pressure increases the risk of heart attack. Lowering blood pressure to normal values reduces the risk of these disorders.
2. Important information before taking Diovan
When not to take Diovan:
- if the patient has been diagnosed with hypersensitivity(allergy) to valsartan or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (see section 6);
- if the patient has severe liver disease;
- if the patient is pregnant more than 3 months(it is also not recommended to take Diovan in early pregnancy - see the section on pregnancy);
- if the patient has diabetes or kidney problems and is being treated with a blood pressure-lowering medicine containing aliskiren.
If any of the above conditions are met, do not take Diovan.
Warnings and precautions
You should inform your doctor before taking Diovan:
- if the patient has liver disease;
- if severe kidney disease has been diagnosed or if the patient is on dialysis;
- in case of renal artery stenosis;
- if the patient has recently received a kidney transplant (the patient has received a new kidney);
- if the patient has ever had swelling of the tongue and face caused by an allergic reaction, known as angioedema, after taking another medicine (including ACE inhibitors), they should tell their doctor. If such symptoms occur while taking Diovan, the patient should stop taking Diovan immediately and never take it again. See also section 4, "Possible side effects";
- if the patient experiences abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea after taking Diovan, they should discuss this with their doctor. The doctor will decide on further treatment. The patient should not stop taking Diovan on their own;
- if the patient is taking medicines that increase the amount of potassium in the blood, including potassium supplements or salt substitutes containing potassium, potassium-sparing medicines, and heparin. Regular monitoring of potassium levels in the blood may be necessary;
- if the patient has aldosteronism (a disease in which the adrenal glands produce too much of a hormone called aldosterone), they should not take Diovan;
- in case of significant fluid loss (dehydration) due to diarrhea, vomiting, or the use of high doses of diuretics;
- if the patient is taking any of the following medicines used to treat high blood pressure: an ACE inhibitor (such as enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril) especially if the patient has kidney problems related to diabetes, or aliskiren.
The doctor may monitor kidney function, blood pressure, and electrolyte levels (such as potassium) in the blood at regular intervals. See also the information under the heading "When not to take Diovan". If the patient suspects they are pregnant (or plan to become pregnant), they should tell their doctor. It is not recommended to take Diovan in early pregnancy, and it should not be taken after the 3rd month of pregnancy, as it may seriously harm the baby if taken at this stage (see the section on "Pregnancy").
If any of the above conditions are met, the patient should inform their doctor before taking Diovan.
Diovan and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take. Taking Diovan with certain other medicines may affect treatment. A dose change, other precautions, or discontinuation of one of the medicines may be necessary. This applies to both prescription and over-the-counter medicines, in particular:
- other blood pressure-lowering medicines, especially diuretics(such as hydrochlorothiazide), ACE inhibitors (such as enalapril, lisinopril, etc.) or aliskiren (see also the information under the heading "When not to take Diovan" and "When to exercise caution when taking Diovan");
- medicines that increase the amount of potassium in the blood; including potassium supplements or salt substitutes containing potassium, potassium-sparing medicines, and heparin;
- certain types of painkillersknown as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- some antibiotics (such as rifampicin), a medicine used to prevent transplant rejection (cyclosporin), or an antiretroviral medicine used to treat HIV/AIDS (ritonavir). These medicines may enhance the effect of Diovan;
- lithium(a medicine used to treat certain types of mental illness).
Taking Diovan with food and drink
Diovan can be taken with or without food.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- The patient should tell their doctor if they suspect they are pregnant (or plan to become pregnant).The doctor will usually advise to stop taking Diovan before becoming pregnant or as soon as pregnancy is confirmed, and recommend an alternative medicine instead of Diovan. It is not recommended to take Diovan in early pregnancy, and it should not be taken after the 3rd month of pregnancy, as it may seriously harm the baby if taken at this stage.
- The patient should inform their doctor if they are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed.It is not recommended to take Diovan while breastfeeding; the doctor may choose an alternative treatment for the patient who plans to breastfeed. This applies especially to breastfeeding newborns or premature babies.
Driving and using machines
Before driving, using tools, or operating machinery, or performing other activities that require concentration, the patient should make sure how Diovan affects them. Like many other medicines used to treat high blood pressure, Diovan can cause dizziness and affect concentration.
Diovan contains saccharose, methylparahydroxybenzoate, poloxamer, sodium, and propylene glycol
- Diovan oral solution contains 0.3 g of saccharoseper milliliter. This should be taken into account in patients with diabetes. If the patient has been informed by their doctor that they have intolerance to certain sugars, they should contact their doctor before taking Diovan oral solution. The sugar in Diovan oral solution may be harmful to teeth.
- Diovan oral solution contains methylparahydroxybenzoate (E218). It may cause allergic reactions, which may occur some time after treatment with the solution. Symptoms of these reactions may include rash, itching, hives. If any of these symptoms worsen, the patient should inform their doctor.
- Diovan oral solution contains poloxamer (188), which may cause loose stools.
- Diovan contains 3.72 mg of sodium(the main component of common salt) per milliliter. This corresponds to 0.19% of the maximum daily intake of sodium in the recommended diet for an adult.
- This medicine contains 0.99 g propylene glycol (E1520)per milliliter of oral solution.
3. How to take Diovan
This medicine should always be taken exactly as prescribed by the doctor. In case of doubt, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist again. People with high blood pressure often do not notice any symptoms of this problem. Many of them feel quite well. For this reason, it is especially important to attend doctor's appointments, even if the patient feels well.
Before using the oral syringe or dosing container, read the instructions at the end of the leaflet.
How much to take
Diovan oral solution should be taken once a day
Children from 1 year to less than 6 years
- The usual recommended starting dose is 1 mg/kg body weight per day. The following table shows the dose and corresponding volume of oral solution to be administered:
| Child's body weight | Dose of Diovan (for the usual recommended starting dose of 1 mg/kg body weight) | Volume of oral solution |
| 10 kg | 10 mg | 3.5 ml |
| 15 kg | 15 mg | 5.0 ml |
| 20 kg | 20 mg | 6.5 ml |
| 25 kg | 25 mg | 8.5 ml |
| 30 kg | 30 mg | 10 ml |
- The doctor may recommend a higher starting dose (2 mg/kg body weight) if faster blood pressure reduction is necessary.
- The dose can be increased up to a maximum of 4 mg/kg body weight.
Children and adolescents from 6 years and
- with a body weight below 35 kg:
- The usual recommended starting dose of Diovan oral solution is 20 mg (which corresponds to 7 ml of solution).
- The dose can be increased up to a maximum of 40 mg (which corresponds to 13 ml of solution).
- with a body weight of 35 kg or more:
- The usual recommended starting dose of Diovan oral solution is 40 mg (which corresponds to 13 ml of solution).
- The dose can be increased up to a maximum of 80 mg (which corresponds to 27 ml of solution).
Children who started taking Diovan before the age of 6 may use a higher dose of the medicine than the maximum dose indicated above. In some cases, the doctor may decide to continue using this dose. Diovan can be taken with or without food. Diovan should be taken every day at about the same time.
Taking more Diovan than prescribed
In case of severe dizziness and/or fainting, the patient should contact their doctor immediately and lie down. If more Diovan oral solution is taken than prescribed, the patient should contact their doctor, pharmacist, or hospital.
Missing a dose of Diovan
If a dose is missed, the patient should take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, the patient should skip the missed dose. A double dose should not be taken to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping Diovan treatment
Stopping treatment with Diovan may worsen the disease. The patient should not stop taking Diovan unless their doctor tells them to. If the patient has any further doubts about taking this medicine, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Diovan can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects may be serious and require immediate medical attention:
There may be symptoms of angioedema (a specific allergic reaction), such as:
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat,
- difficulty breathing or swallowing,
- hives, itching.
If any of these symptoms occur, the patient should stop taking Diovan immediately and contact their doctor (see also section 2 "Important information before taking Diovan").
Side effects:
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- dizziness,
- low blood pressure with symptoms such as dizziness and fainting when standing up or without these symptoms,
- kidney problems (symptoms of kidney problems).
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- angioedema (see "Some side effects may be serious and require immediate medical attention"),
- sudden loss of consciousness (fainting),
- feeling of spinning (dizziness),
- severe kidney problems (symptoms of acute kidney failure),
- muscle cramps, heart rhythm disturbances (symptoms of hyperkalemia),
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing when lying down, swelling of the feet or ankles (symptoms of heart failure),
- headache,
- cough,
- abdominal pain,
- nausea,
- diarrhea,
- feeling of tiredness,
- weakness.
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- angioedema of the intestine: swelling in the intestine with symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Unknown(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- blisters on the skin (symptoms of bullous pemphigoid),
- allergic reactions with rash, itching, and hives; symptoms such as fever, swelling, and joint pain, muscle pain, swelling of lymph nodes, and/or flu-like symptoms (symptoms of serum sickness),
- purple-red spots, fever, itching (symptoms of vasculitis),
- unusual bleeding or bruising (symptoms of thrombocytopenia),
- muscle pain (myalgia),
- fever, sore throat, or mouth ulcers due to infection (symptoms of neutropenia),
- decreased hemoglobin and decreased red blood cell count in the blood (which can lead to anemia in severe cases),
- increased potassium levels in the blood (which can cause muscle cramps and heart rhythm disturbances in severe cases),
- increased liver function test results (which may indicate liver damage), including increased bilirubin levels in the blood (which can cause yellowing of the skin and eyes in severe cases),
- increased urea and creatinine levels in the blood (which may indicate kidney problems)
- low sodium levels in the blood (which can cause fatigue, confusion, muscle tremors, and/or seizures in severe cases).
The frequency of some side effects may vary depending on the disease. For example, such side effects as dizziness and kidney problems are less common in adult patients treated for high blood pressure than in adult patients treated for heart failure or after a recent heart attack. Side effects in children and adolescents are similar to those in adult patients.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Monitoring, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Diovan
- The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
- Do not store above 30°C. After opening, the bottle can be stored for up to 3 months at a temperature below 30°C.
- Do not use Diovan after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
- Do not use this medicine if the packaging is damaged or shows signs of tampering.
- Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines they no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Diovan contains
- The active substance of Diovan is valsartan.
- 1 ml of oral solution contains 3 mg of valsartan.
- Other ingredients of the medicine are saccharose, methylparahydroxybenzoate (E218), potassium sorbate, poloxamer (188), citric acid, sodium citrate, strawberry flavor, propylene glycol (E1520), sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, purified water (see also section 2 "Diovan contains saccharose, methylparahydroxybenzoate, poloxamer, sodium, and propylene glycol").
What Diovan looks like and contents of the pack
Diovan 3 mg/ml oral solution is a clear solution with a color from colorless to pale yellow.
- The solution is available in packs containing one brown glass bottle with a capacity of 180 ml, equipped with a child-resistant cap and a yellow or colorless protective ring. The bottle contains 160 ml of solution. The packaging includes a dosing set consisting of one push-on cap for the bottle, one 5 ml oral syringe made of polypropylene, and one polypropylene dosing container with a capacity of 30 ml.
Marketing authorization holder
Novartis Poland Sp. z o.o., ul. Marynarska 15, 02-674 Warsaw, tel. (22) 375 48 88
Manufacturer/Importer
Novartis Pharma GmbH, Roonstrasse 25, D-90429 Nürnberg, Germany
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
| Novartis Pharma GmbH | |
| Sophie-Germain-Strasse 10 | |
| 90443 Nuremberg | |
| Germany | |
| Novartis Farmacéutica S.A. | |
| Gran Via de les Corts Catalanes, 764 | |
| 08013 Barcelona | |
| Spain | |
| Novartis Poland Sp. z o.o. | |
| ul. Marynarska 15 | |
| 02-674 Warsaw | |
| Austria, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Greece, Spain, Netherlands, Ireland, Iceland, Lithuania, Latvia, Malta, Germany, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, Hungary | Diovan |
| Belgium, Luxembourg | Diovane |
| France, Italy | Tareg |
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 04/2025
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF THE ORAL SYRINGE AND DOSING CONTAINER
Before taking the medicine, read this instruction carefully. It will help you use the oral syringe and dosing container correctly.
The set includes:
Push-on cap for the bottle:
- Which is placed on the neck of the bottle.
- Once the cap is placed on the bottle, it should not be removed.
Bottlewith medicine:
- Equipped with a child-resistant cap.
- After taking the medicine, the bottle should always be tightly closed.
Oral dosing syringe:
- Consisting of a transparent plastic cylinder with a plunger.
- The tip of the oral syringe fits into the cap on the bottle and is used to draw the required amount of medicine from the bottle. A new cap and a new oral syringe should be used for each new bottle of medicine.
Dosing container:
- Which can be used if the prescribed dose requires multiple fillings of the syringe.
- After administering the medicine and washing the container, it should always be placed on the bottle cap.
Placing the push-on cap on a new bottle of medicine
- 1. Remove the cap from the bottle by strongly pressing and turning it counterclockwise (according to the drawing on the top of the cap).
- 2. Place the bottle upright on the table and stronglypush the cap onto the neck of the bottle until you feel resistance or as far as possible.
Note:It may not be possible to push the cap all the way down, but this does not matter, as it will be pushed down further by the cap when the bottle is closed.
- 3. Close the bottle.
Preparing the dose
- 4. Remove the cap from the bottle by strongly pressing and turning it counterclockwise (according to the drawing on the top of the cap).
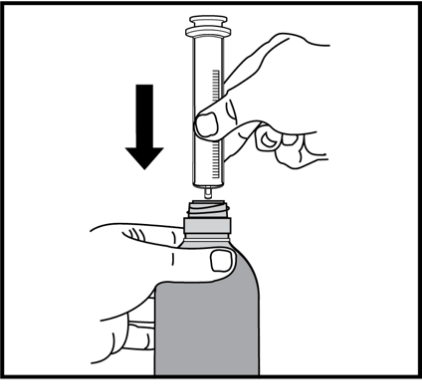
Make sure the plunger is fully pushed into the syringe.
- 5. Make sure the plunger is fully pushed into the syringe.
- 6. Holding the bottle upright, firmlyinsert the syringe into the cap on the bottle neck.
- 7. Carefully turn the bottle upside down with the syringe in it.
Measuring the dose
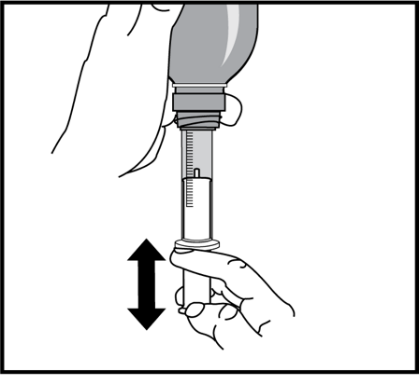
Note: The total amount of solution that can be measured with the oral syringe is 5 ml. Depending on the prescribed dose, it may be necessary to repeat the actions described in points 10-16 several times. For example, if the prescribed dose is 13 ml, it will be necessary to measure the solution three times: 5 ml + 5 ml + 3 ml.
- 8. Find the mark on the syringe that corresponds to the prescribed dose.
- 9. Slowly pull the plunger until the top edge of the plunger is exactly aligned with the corresponding mark on the scale.
- 10. Carefully turn the bottle and syringe upside down.
- 11. Gently pull the syringe out of the cap, turning it slightly.
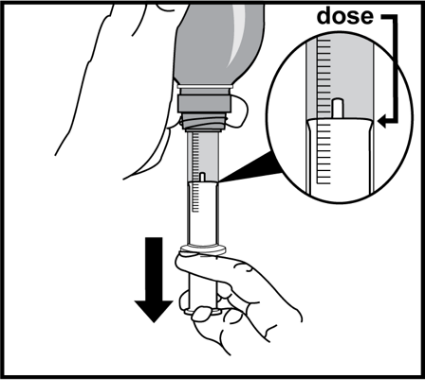
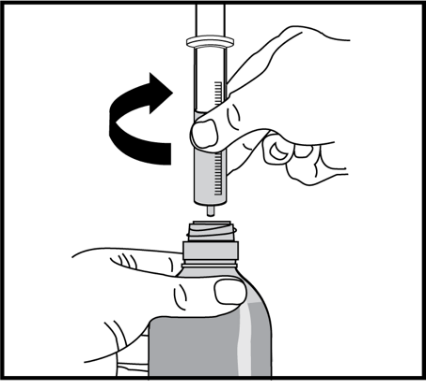
Taking the medicine
- 12. Sit upright.
- 13. Insert the tip of the syringe into your mouth.
- 14. Slowly press the plunger, taking the medicine directly from the syringe.
- 15. If the prescribed dose requires multiple fillings of the syringe, the measured dose of medicine can be transferred from the syringe to the dosing container, and then check if the total amount of measured solution corresponds to the prescribed dose.
- 16. Drink the entire solution at once.
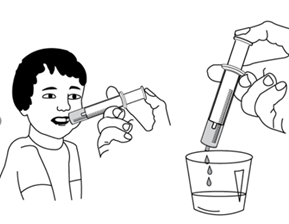
- 17. After taking the medicine, close the bottle.
- 18. Cleaning the oral syringe:
- Wipe the outside of the syringe with a clean, dry cloth.
- The syringe should be cleaned after each use.
- 19. Cleaning the dosing container:
- Rinse the container with clean water.
- Wipe the container with a clean cloth and then place it on the bottle cap.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterNovartis Farmacéutica, S.A. Novartis Pharma GmbH Novartis Pharma GmbH Novartis Poland Sp. z o.o.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DiovanDosage form: Tablets, 80 mgActive substance: valsartanManufacturer: APL Swift Services (Malta) Ltd.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 160 mgActive substance: valsartanManufacturer: APL Swift Services (Malta) Ltd.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 80 mgActive substance: valsartanManufacturer: Polfarmex S.A.Prescription required
Alternatives to Diovan in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Diovan in Spain
Alternative to Diovan in Ukraine
Online doctors for Diovan
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Diovan – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










