
Digoxin Vzf

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Digoxin Vzf

How to use Digoxin Vzf
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
DIGOXIN WZF, 0.25 mg/ml, solution for injection
Digoxin
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Digoxin WZF and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Digoxin WZF
- 3. How to use Digoxin WZF
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Digoxin WZF
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Digoxin WZF and what is it used for
Digoxin WZF contains digoxin, an active substance belonging to a group of medicines called cardiac glycosides. The medicine reduces the heart rate and at the same time increases the strength of heart muscle contractions. Digoxin WZF in the form of a solution for injection is administered intravenously by medical personnel.
Digoxin WZF is used in cases such as:
- heart failureThis applies to people whose heart cannot pump blood with sufficient strength to reach all parts of the body. This condition may be accompanied by certain types of heart rhythm disorders (see below).
- certain types of heart rhythm disorders (arrhythmias)This applies to people with disorders involving "fibrillation" and "flutter" of the heart's atria. They are caused by abnormal electrical conduction in the heart and manifest as variable or too rapid heart rate.
2. Important information before using Digoxin WZF
When not to use Digoxin WZF
- if the patient is allergic to digoxin or other medicines called cardiac glycosides, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if the patient has had serious heart problems in the past, known as:
- second-degree heart block (symptoms: the heart does not beat rhythmically, there is significant slowing of heart function);
- periodic complete heart block (symptoms: dissociation of atrial and ventricular work, causing inefficient heart function and potentially requiring a pacemaker);
- certain types of supraventricular arrhythmias (heart rhythm disorders);
- ventricular tachyarrhythmias (rapid ventricular contractions) or ventricular fibrillation;
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (left ventricular hypertrophy, manifesting as shortness of breath after exertion, dizziness, and loss of consciousness);
- arrhythmias caused by digitalis glycoside poisoning.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Digoxin WZF, discuss it with your doctor.
- If the patient is taking this medicine, the doctor may order regular blood tests to determine the amount of Digoxin WZF in the blood. This may be useful in patients with kidney function disorders.
- If digoxin toxicity occurs, it can lead to various forms of heart rhythm disorders, some of which resemble the heart rhythm disorders for which this medicine was prescribed.
- If the patient has an abnormal heart rhythm (heart block) and is taking this medicine, they should contact their doctor immediately if they experience one or more of the following symptoms: fainting, transient loss of consciousness, dizziness, or a feeling of emptiness in the head, fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, or irregular heartbeat.
- If the patient has a sinoatrial conduction disorder; in some patients with this disorder, this medicine may cause slowing and/or irregular heartbeat. Sometimes this leads to fatigue, weakness, and dizziness, and when the heartbeat is very slow, fainting may occur.
- If the patient has had a recent heart attack.
- In the case of heart failure with abnormal protein accumulation in heart tissue (cardiac amyloidosis), the doctor may recommend alternative treatment.
- If the patient has myocarditis, which can rarely cause blood vessel constriction, the doctor may prescribe another medicine.
- If the patient has Beriberi disease (caused by vitamin B deficiency).
- If the patient has constrictive pericarditis (inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart).
- If the patient is taking diuretic medicines (medicines that increase urine production and help reduce water in the body) with an ACE inhibitor (mainly used to treat high blood pressure) or without it, the doctor will recommend a lower dose of Digoxin WZF. Do not stop taking Digoxin WZF without consulting your doctor.
- If the patient is scheduled to have a heart test called an EKG (electrocardiogram), they should tell the person performing the test that they are taking Digoxin WZF, as it may affect the test results.
- If the patient has severe respiratory disease (lung disease), as they may be more sensitive to Digoxin WZF.
- If the patient has low oxygen levels reaching some parts of the body, low potassium, abnormally low magnesium, or elevated calcium levels in the blood.
- If the patient has thyroid disease (such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism), as they may require a dose adjustment of this medicine.
- If the patient has a malabsorption syndrome (cannot properly absorb minerals from food) or has had gastrointestinal reconstruction surgery.
- If the patient is to undergo electrical cardioversion to correct abnormal heart rhythm.
In case of any doubts regarding the above cases, the patient should consult their doctor. The doctor will decide on any dose change or discontinuation of the medicine.
Digoxin WZF and other medicines
Tell your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take. Taking several medicines can sometimes have harmful consequences or lead to unwanted interactions.
Sensitivity to Digoxin WZF may be increased by medicines that lower potassium levels in the blood, such as:
- diuretics (medicines that increase urine production),
- lithium salts (antidepressant medicines),
- corticosteroid-containing medicines,
- carbenoxolone (which acts to strengthen the stomach lining).
The following medicines increase the level of Digoxin WZF in the blood, which may increase the risk of toxicity:
- certain heart medicines: amiodarone, flecainide, prazosin, propafenone, quinidine,
- canagliflozin (used to treat type 2 diabetes),
- certain antibiotics: erythromycin, clarithromycin, tetracycline, gentamicin, trimethoprim,
- daclatasvir (used in combination with other medicines to treat hepatitis C virus infection),
- flibanserin (used to treat low sexual desire in women before menopause),
- isavuconazole (used to treat fungal infections),
- itraconazole (used to treat fungal infections),
- ivacaftor (used to treat cystic fibrosis),
- spironolactone (a medicine that increases urine production),
- alprazolam (a sedative that may be used to treat anxiety),
- indomethacin (used to treat inflammatory conditions),
- quinine (may be used to prevent malaria),
- propantheline (used to prevent muscle spasms),
- mirabegron (used to treat overactive bladder),
- nefazodone (an antidepressant),
- atorvastatin (lowers cholesterol levels in the blood),
- cyclosporine (an immunosuppressive medicine often used to prevent transplant rejection),
- epoprostenol (used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension),
- tolvaptan (used to treat low sodium levels in the blood),
- conivaptan (used to treat low sodium levels in the blood),
- carvedilol (used to treat mild to severe congestive heart failure and high blood pressure),
- ritonavir (used to treat HIV and AIDS infection),
- telaprevir (used to treat hepatitis C virus infection),
- dronedarone (used to treat irregular heartbeat),
- ranolazine (used to treat chest pain),
- simeprevir (used in combination with other medicines to treat hepatitis C virus infection),
- telmisartan (used to treat high blood pressure),
- lapatinib (used to treat breast cancer),
- ticagrelor (used to prevent heart attack or stroke),
- verapamil (used to treat high blood pressure),
- felodipine (used to treat high blood pressure),
- tiapamil (used to treat chest pain),
- vandetanib (used to treat certain types of thyroid cancer),
- velpatasvir (used in combination with other medicines to treat hepatitis C virus infection),
- glycoprotein P inhibitors,
- venetoclax (used to treat patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia),
- vemurafenib (used to treat adult patients with a type of cancer called melanoma),
- proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) (used to alleviate symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)).
The following medicines may increase or have no effect on the level of Digoxin WZF in the blood:
- nifedipine, diltiazem, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), ACE inhibitors (used to treat high blood pressure and congestive heart failure),
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors (used to treat pain and inflammatory conditions).
If the patient is taking Digoxin WZF with the following medicines, there may be an increased risk of irregular heartbeat:
- intravenous calcium,
- beta-blockers,
- sympathomimetics (used to treat heart attack and low blood pressure). If the patient is taking Digoxin WZF and suxamethonium (a medicine used to relax muscles and treat temporary paralysis), there may be an increased risk of high potassium levels in the blood.
Digoxin WZF with food and drink
Not applicable, as Digoxin WZF is intended for intravenous administration.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
The doctor will prescribe this medicine with caution during pregnancy.
If the patient is pregnant, they may need a higher dose of this medicine.
This medicine may be given to the mother to treat abnormally high heart rate and congestive heart failure in the unborn baby.
Side effects of Digoxin WZF treatment in the mother may also affect the unborn baby.
Breastfeeding
This medicine passes into breast milk, but in very small amounts. Therefore, this medicine may be used in breastfeeding women.
Fertility
There is no available information on the effect of Digoxin WZF on fertility.
Driving and using machines
While using Digoxin WZF, dizziness, fatigue, headache, or vision disturbances (blurred vision or yellow vision) may occur. If such symptoms occur, do not drive or operate machinery until they resolve.
Digoxin WZF contains alcohol (96% ethanol) and propylene glycol (E 1520) and sodium
This medicine contains 202.5 mg of alcohol (96% ethanol) in each ampoule (2 ml). The amount of alcohol in 2 ml of this medicine is equivalent to less than 5 ml of beer or 2 ml of wine.
The small amount of alcohol in this medicine is unlikely to have noticeable effects.
The medicine contains 414.8 mg of propylene glycol in each ml, which corresponds to 829.6 mg of propylene glycol in each ampoule (2 ml). Before administering the medicine to a child under 5 years of age, inform the doctor, especially if the child is taking other medicines containing propylene glycol or alcohol.
Children with kidney or liver function disorders should not take this medicine without the doctor's recommendation. The doctor may decide to perform additional tests on such patients.
The medicine contains 1.16 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in each ampoule (2 ml). This corresponds to 0.06% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake in the diet for adults.
The medicine may be diluted - see below "Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals". The sodium content from the diluent should be taken into account when calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, refer to the product characteristics of the diluent used.
3. How to use Digoxin WZF
Use this medicine always as directed by your doctor. In case of doubts, consult your doctor.
This medicine is usually administered by medical personnel.
- Digoxin WZF is administered intravenously.
Dose and administration schedule of Digoxin WZF are determined by the doctor individually for each patient. The dose depends on the type and severity of heart problems, as well as age, body weight, and kidney function. The following are usually used doses for loading and maintenance.
and maintenance.
- Digoxin treatment usually starts with a loading dose (although there may be patients for whom the doctor does not recommend a loading dose), which may be administered according to one of the schemes below. After administering the loading dose, the doctor will recommend taking a maintenance dose of digoxin in another form, e.g., tablets.
- The doctor may recommend increasing or decreasing the dose of Digoxin WZF depending on how the patient tolerates the medicine. To check which dose is suitable for a given patient, the doctor may recommend blood and urine tests.
Recommended dose
Adults and children over 10 years old:
Loading dose:
- Usually 0.5 to 1 mg (2 to 4 ml) administered in divided doses every 4 to 8 hours, strictly according to the doctor's instructions. Before administering each subsequent dose, the doctor will assess the patient's response to the medicine.
Maintenance dose:
- The doctor will decide on a suitable dose for the patient, usually ranging from 0.125 to 0.25 mg (from 125 to 250 micrograms) per day.
Children under 10 years old:
Loading dose:
- Depends on the child's body weight and usually ranges from 0.020 to 0.035 mg (from 20 to 35 micrograms) per kilogram of body weight per day;
- this dose should be administered in divided doses every 4 to 8 hours, strictly according to the doctor's instructions. Before administering each subsequent dose, the doctor will assess the patient's response to the medicine.
Maintenance dose:
- The doctor will decide on a suitable dose for the child, usually one-fifth (1/5) or one-quarter (1/4) of the daily loading dose.
Elderly patients and/or those with kidney disease
In elderly patients and/or those with kidney problems and taking diuretic medicines, the doctor may reduce the dose of the medicine.
Using a higher dose of Digoxin WZF than recommended
The medicine is usually administered by medical personnel - using a higher dose of the medicine than recommended is unlikely. However, if the patient experiences symptoms listed in section 4 "Possible side effects", they should immediately inform the medical personnel.
Missing a dose of Digoxin WZF
The medicine is usually administered by medical personnel - missing a dose is unlikely.
In case of any further doubts regarding the use of this medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
Stopping the use of Digoxin WZF
- The decision to stop taking the medicine is made by the doctor.
- In patients taking diuretic medicines (e.g., furosemide) and/or medicines for high blood pressure (e.g., enalapril, captopril), stopping digoxin may worsen their condition.
In case of any further doubts regarding the use of this medicine, consult a doctor.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects usually occur when too high a dose of the medicine is used.
Immediately report to the doctor or nurse if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- palpitations,
- chest pain,
- breathing difficulties, so-called "shortness of breath",
- excessive sweating.These occur very rarely (less than 1 in 10,000 people). They may be symptoms of serious heart problems caused by the development of new heart rhythm disorders and require immediate consultation with a doctor.
Inform your doctor if you experience any other side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet.
Frequent (less than 1 in 10 people):
- slow or irregular heartbeat;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- itching skin changes (rash);
- drowsiness, dizziness;
- vision disturbances (blurred, unclear vision or yellow vision).
Uncommon (less than 1 in 100 people):
- depression.
Rare (less than 1 in 10,000 people):
- bruises or bleeding more often than usual (may be a sign of reduced platelet count);
- abdominal pain caused by ischemia or intestinal damage;
- mental disorders (apathy; confusion - disorders of consciousness with difficulties in assessing the situation; psychosis);
- weakness, feeling of fatigue or general malaise;
- breast enlargement in men;
- loss of appetite (anorexia);
- headache;
- heart rhythm disorders.
Digoxin WZF may very rarely cause serious irregular heartbeat. In such cases, consult a doctor. The doctor should order regular tests to ensure the medicine is working properly.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any not listed in this leaflet, inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Adverse Reaction Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Digoxin WZF
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Protect from light. Do not freeze.
Keep the medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging and ampoule.
The expiry date stated on the packaging and ampoule is the last day of the specified month.
The notation on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP indicates the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot indicates the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Digoxin WZF contains
- The active substance of the medicine is digoxin. Each ml of the solution contains 0.25 mg of digoxin. Each ampoule (2 ml) contains 0.5 mg of digoxin.
- The other ingredients are: ethanol 96%, propylene glycol (E 1520), disodium phosphate dodecahydrate, citric acid monohydrate, water for injections.
What Digoxin WZF looks like and contents of the packaging
Digoxin WZF is a colorless, clear liquid.
The medicine is available in ampoules made of colorless glass containing 2 ml of the solution, packaged in 5 pieces in a cardboard box.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Polpharma S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
tel. +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
DIGOXIN WZF, 0.25 mg/ml, solution for injection
Digoxin
Refer to the current Summary of Product Characteristics for Digoxin WZF.
Dosing and administration
Intravenous administration.
Doses of the medicine should be determined individually, depending on the patient's age, body weight, and kidney function. The doses given below are for guidance.
In cases where cardiac glycosides were taken within the last two weeks, the doctor should reconsider the initial dosing recommendations for the patient - it is recommended to reduce the dose.
Considering the differences in bioavailability of oral and intravenous digoxin, when switching from tablets to intravenous solution, the dosing should be reduced by 33%.
Adults and children over 10 years old: Parenteral loading
Parenteral loading can only be used in patients who have not received cardiac glycosides within the last 2 weeks:
Total parenteral loading dose: 0.5 mg to 1 mg (2 ml to 4 ml) depending on the patient's age, body weight, and kidney function.
The total loading dose should be administered in divided doses - with the first dose being half of the total dose, and subsequent doses administered every 4 to 8 hours, assessing the clinical effect before administering the next dose.
Each dose should be administered as an intravenous infusion over 10 to 20 minutes - see below "Method of administration".
Maintenance dose
The maintenance dose can be calculated using the following formula:
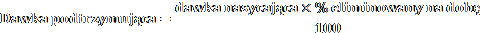
Where:
dose - dose determined individually for the patient
% eliminated per day = 14 + C / 5
- C - is creatinine clearance, corrected for 70 kg body weight or 1.73 m2 body surface area. If only serum creatinine concentration is known, C can be estimated as follows:
- for men:
Ccr =
140 − age
serum creatinine concentration (mg/100ml)
Note: If creatinine is measured in micromoles/l, it can be converted to mg/100 ml (mg%) as follows:
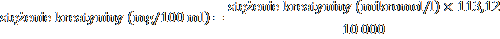
= serum creatinine concentration (micromol/l)
88.4
Where 113.12 is the molecular weight of creatinine.
- for women - the result should be multiplied by 0.85.
Note: The above formulas are not suitable for calculating creatinine clearance in children.
In practice, this means that for most patients, the maintenance dose is between 125 and 250 micrograms (mcg) of digoxin per day. In sensitive patients who experience severe side effects, a smaller dose, i.e., 62.5 mcg per day or less, may be sufficient.
Some patients may require higher doses.
Children
Newborns, infants, and children up to 10 years old
If cardiac glycosides were administered within two weeks prior to starting digoxin treatment, it should be expected that optimal loading doses of digoxin will be lower than those recommended below.
In newborns, especially premature babies, renal clearance is lower, so the dose of the medicine should be reduced, going beyond the general dosing recommendations.
Except for the neonatal period, children generally require proportionally higher doses of digoxin than adult patients, per body weight or surface area, as shown in the scheme below.
In children over 10 years old, the same doses are used as in adults, taking into account body weight.
Parenteral loading dose
The intravenous loading dose should be administered according to the following scheme:
Preterm infants with a body weight of less than 1.5 kg:
20 micrograms/kg body weight per day
Preterm infants with a body weight of 1.5 kg to 2.5 kg:
30 micrograms/kg body weight per day
Newborns and children up to 2 years old:
35 micrograms/kg body weight per day
Children from 2 to 5 years old:
35 micrograms/kg body weight per day
Children from 5 to 10 years old:
25 micrograms/kg body weight per day
The loading dose should be administered in divided doses - with the first dose being half of the total dose, and subsequent doses administered every 4 to 8 hours, assessing the clinical effect before administering the next dose.
Each dose should be administered as an intravenous infusion over 10 to 20 minutes.
Maintenance treatment:
The maintenance dose should be administered according to the following scheme:
Preterm infants: daily dose = 20% of the 24-hour loading dose.
Newborns and children up to 10 years old: daily dose = 25% of the 24-hour loading dose.
The above scheme should be treated as a general guideline, and in these groups of children and adolescents, clinical observation and control of digoxin levels in the serum should be used as the basis for adjusting the dose.
Elderly patients
In elderly patients, it should be taken into account that kidney function may be impaired and lean body mass may be reduced. If necessary, the dose should be reduced and adjusted to the changed pharmacokinetics to prevent increased digoxin levels in the serum and the risk of toxicity. Regular monitoring of digoxin levels in the serum is recommended, and hypokalemia should be avoided.
Renal impairment
Dosing recommendations should be reconsidered if patients are elderly or have other reasons for reduced renal clearance of digoxin. Consider reducing the initial and maintenance doses.
Recommendations for dosing digoxin in patients with kidney disease or taking diuretic medicines
In elderly patients or those with reduced renal clearance, consider reducing the doses, both loading and maintenance.
In patients taking diuretic medicines and/or ACE inhibitors or only diuretic medicines, stopping digoxin may worsen their clinical condition.
Monitoring
Results of tests determining digoxin levels in the serum may be expressed in nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml) or SI units nanomoles per liter (nmol/l). To convert ng/ml to nmol/l, multiply ng/ml by 1.28.
Digoxin levels in the serum can be determined using radioimmunological methods.
Blood for testing should be drawn at least 6 hours after the last dose of digoxin.
There are no strict guidelines for the range of serum levels that are most effective.
Several post-hoc analyses performed in patients with heart failure participating in the Digitalis Investigation Group trials showed that optimal digoxin serum levels are between 0.5 ng/ml (0.64 nmol/l) and 1.0 ng/ml (1.28 nmol/l).
Signs of digoxin toxicity occur more frequently when digoxin levels in the serum are higher than 2 ng/ml, but may occur at lower serum levels.
When interpreting test results, consider the serum potassium level and thyroid function.
However, digoxin levels in the serum should be interpreted in the context of the patient's overall clinical condition.
Toxicity may occur at lower digoxin levels in the serum. When deciding whether the patient's symptoms are caused by digoxin, important factors are the clinical condition, serum potassium level, and thyroid function.
Determining digoxin levels in the serum can be very helpful in deciding on further treatment with digoxin, but other glycosides and endogenous substances similar to digoxin, including digoxin metabolites, may interfere with test results, and one should always be cautious of values that do not seem to match the patient's clinical condition. Temporary discontinuation of digoxin may be more appropriate.
Dilution
The medicine may be administered undiluted or after dilution in a fourfold or larger volume of infusion solution. Dilution in a smaller volume than recommended may lead to precipitation of digoxin.
The following infusion solutions can be used for dilution:
- 0.9% NaCl solution,
- 0.18% NaCl solution and 4% glucose solution,
- 5% glucose solution. The infusion solution should be prepared immediately before administration. If necessary, the prepared solution can be stored, at the user's responsibility, for a maximum of 24 hours at a temperature between 2°C and 8°C, provided that the dilution is prepared in controlled and validated aseptic conditions. Unused solution should be discarded after 24 hours.
Method of administration
Intravenous administration.
Each dose should be administered intravenously. The infusion should be administered over 10 to 20 minutes.
The total loading dose should be administered in divided doses, with approximately half of the total dose administered as the first dose, and subsequent doses administered every 4 to 8 hours, assessing the clinical effect before administering the next dose.
Intramuscular administration is painful and may cause muscle necrosis. Intramuscular administration is not recommended.
Rapid intravenous injection may cause vasoconstriction, leading to high blood pressure and/or reduced coronary blood flow. Slow injection rate is therefore important in congestive heart failure with high blood pressure and in acute myocardial infarction.
Patients taking digoxin should not be given intravenous calcium salts.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to help the solution flow down.
A colored dot is placed on each ampoule (see Figure 1) as a mark indicating the location of the break point below it.
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, with both hands, with the colored dot facing each other - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
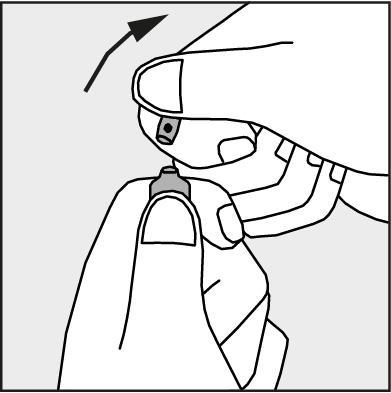
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused medicine should be disposed of in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1.
Figure 2.
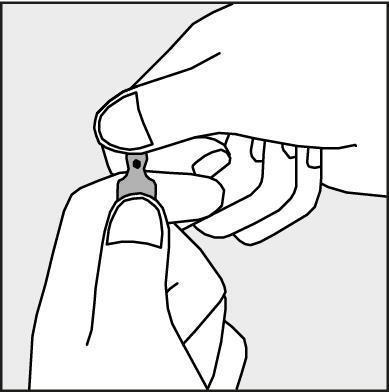
Figure 3.
Information on how to proceed in case of overdose of the medicine
Information on DIGOXIN WZF overdose can be found in the Summary of Product Characteristics.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Digoxin VzfDosage form: Tablets, 250 mcgActive substance: digoxinManufacturer: Teva Operations Polska Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 100 mcgActive substance: digoxinManufacturer: Teva Operations Polska Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 3 mg/mlActive substance: adenosineManufacturer: Cenexi HSC Famar Health Care Services Madrid SAUPrescription not required
Alternatives to Digoxin Vzf in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Digoxin Vzf in Ukraine
Alternative to Digoxin Vzf in Spain
Online doctors for Digoxin Vzf
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Digoxin Vzf – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










