

Dexamethasone Kalceks

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Dexamethasone Kalceks

How to use Dexamethasone Kalceks
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Dexamethasone Kalceks, 4 mg/mL, solution for injection/infusion
Dexamethasone phosphate
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Dexamethasone Kalceks and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Dexamethasone Kalceks
- 3. How to use Dexamethasone Kalceks
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Dexamethasone Kalceks
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Dexamethasone Kalceks and what is it used for
Dexamethasone Kalceks contains the active substance dexamethasone phosphate (hereinafter referred to as dexamethasone). Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticoid (adrenal cortex hormone). It reduces inflammatory symptoms and affects significant metabolic processes.
Systemic administration (relating to the whole body)
Dexamethasone Kalceks is often used in the following emergency cases, starting with a high dose:
- Treatment and prevention of brain edema caused by a brain tumor (after surgery and after X-ray irradiation) and after spinal cord injury.
- Shock state caused by a severe allergic reaction called "anaphylactic shock" (e.g. reaction to a contrast agent).
- Shock conditions after severe injuries, prevention of post-traumatic "shock lung" (acute respiratory failure).
- Persistent severe symptoms of an asthma attack.
- Initial treatment of extensive, acute skin diseases with a severe course (e.g. pemphigus vulgaris, erythroderma).
- Severe blood diseases (e.g. acute thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic anemia, as an adjunctive therapy in leukemia treatment).
- As a second-line treatment in patients with impaired adrenal cortex function or its absence (adrenal insufficiency, Addison's crisis).
Dexamethasone Kalceks is used in the treatment of COVID-19 in adult patients and adolescents (aged 12 and older, weighing at least 40 kg), with breathing difficulties and requiring oxygen therapy.
Local administration (relating to specific parts of the body)
- Injection into the area around the joints (periarthricular) and infiltrative tissue treatment, e.g. in shoulder joint inflammation (periarthritis scapulohumeralis), elbow joint inflammation
(epicondylitis), bursitis, tendon sheath inflammation (tendovaginitis) and wrist joint inflammation (styloiditis).
- Injection into the joint (intra-articular injection), e.g. in rheumatoid arthritis, when individual joints are affected or do not respond sufficiently to systemic treatment; accompanying inflammatory reactions in degenerative joint disease (rheumatoid arthritis).
2. Important information before using Dexamethasone Kalceks
When not to use Dexamethasone Kalceks
- If the patient is allergic to dexamethasone or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- Systemic infection, including those that may be caused by fungi (e.g. candidiasis), which are not treated with antibiotics.
- Intra-articular injection is contraindicated in the following cases: infections in or near the treated joint; bacterial arthritis; joint instability requiring treatment; tendency to bleeding (spontaneous or caused by anticoagulant drugs); periarticular calcification; local bone tissue necrosis, especially of the humeral and femoral heads (aseptic bone necrosis); tendon rupture; Charcot's joint disease.
- Intralesional injection is contraindicated without additional causal treatment in the case of infections at the injection site.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with this medicine, the patient should discuss it with their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, as special caution is recommended if:
- The patient has an acute or chronic bacterial infection
- The patient has had tuberculosis
- The patient has a fungal infection with internal organ involvement
- The patient has a parasitic disease (e.g. amoeba infection, pinworms)
- The patient has an acute viral infection (hepatitis B, herpes virus infection, chickenpox)
- The patient (or their child) has been or is to be vaccinated (see "Dexamethasone Kalceks and other medicines"). In particular, the doctor should be informed if the patient has not had chickenpox or measles, or if the child's immune system is weakened
- The patient has stomach or intestinal ulcers
- The patient has osteoporosis (bone mass loss). The doctor may want to determine bone density before starting long-term treatment. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe calcium, vitamin D, and/or drugs for reduced bone density. In patients with severe osteoporosis, this medicine will be used only for life-threatening reasons or for a short period
- The patient has difficulty controlling high blood pressure
- The patient has diabetes
- The patient has a history of mental disorders, including suicidal tendencies
- The patient has increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma with closed and open angle), corneal damage, or eye ulcers (as close monitoring and treatment by an ophthalmologist are required)
- The patient has heart or kidney disorders
- The patient has myasthenia (muscle disease), as its symptoms may initially worsen after dexamethasone administration; the initial dose should be chosen carefully
- The patient has an adrenal gland tumor (pheochromocytoma). If the patient is unsure whether any of the above applies to them, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
The patient should inform their doctor if they notice any of the following symptoms during treatment with this medicine:
- Muscle cramps, muscle weakness, confusion, vision disturbances, or loss of vision and shallow breathing, in the case of a patient with a blood cancer. These may be symptoms of tumor lysis syndrome.
- Blurred vision or other vision disturbances.
Concomitant use of corticosteroids
Do not stop taking other steroid medicines without consulting your doctor.
General precautions for the use of steroids in certain diseases, masking infection, adjunctive therapies, etc. should be in accordance with current recommendations.
Severe allergic reactions
Severe allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis (a potentially life-threatening reaction), may occur, with symptoms such as irregular heartbeat, bronchospasm, decreased or increased blood pressure, circulatory failure, or cardiac arrest.
Adrenal insufficiency
Sudden discontinuation of treatment that has lasted longer than 10 days may lead to the development of acute adrenal insufficiency. Therefore, the dose should be gradually reduced if treatment is to be discontinued. Depending on the dose and duration of treatment, adrenal insufficiency caused by glucocorticoid therapy may persist for several months, and in individual cases, even more than a year after treatment is discontinued.
If special physical stress situations occur during treatment, such as illness with fever, accidents, or surgery, the patient should immediately inform their doctor or emergency doctor about the ongoing dexamethasone treatment. Temporary increase in daily dexamethasone dose may be necessary. Administration of glucocorticoids may also be required in situations of physical stress if adrenal insufficiency persists after treatment is discontinued.
Infection risk
Administration of dexamethasone in doses higher than required for maintenance treatment is associated with a higher risk of infection, possible worsening of existing infection, and possible activation of latent infection. The anti-inflammatory effect may mask infection symptoms until the infection develops.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Due to the risk of intestinal wall perforation with peritonitis, this medicine will be used, with appropriate monitoring, only if there are compelling medical reasons, in the following cases:
- severe colitis (ulcerative colitis) with inevitable perforation;
- abscesses or purulent infections (filled with pus);
- diverticulitis (inflammation of diverticula [outpouchings] on the colon wall);
- after certain types of intestinal surgery (intestinal anastomoses) immediately after surgery. Signs of peritoneal irritation after perforation of a stomach or intestinal ulcer may not occur in patients receiving high doses of glucocorticoids.
Long-term treatment
In long-term therapy, regular medical check-ups (including control eye exams every 3 months) are recommended; after relatively high doses, ensure adequate potassium intake (e.g. vegetables, bananas) and limited sodium intake, and monitor blood potassium levels.
Cautious monitoring is also recommended in patients with severe heart failure (heart failure to deliver the required amount of blood to metabolism, during exercise or even at rest).
Warnings related to specific administration methods
- Into a vein, the medicine will be injected slowly (2-3 minutes), as too rapid injection may cause transient unpleasant tingling or unusual skin sensations lasting up to 3 minutes. These symptoms are harmless in themselves.
- Intra-articular injection of glucocorticoids increases the risk of joint infection. Long-term and repeated use of glucocorticoids in loaded joints may lead to worsening of degenerative changes in the joint. One possible cause is overloading of the affected joint after pain or other symptoms have subsided.
Other warnings
- After high doses, bradycardia (slow heart rate) may occur.
- The risk of tendon disorders, tendonitis, and tendon rupture increases when dexamethasone is used concomitantly with fluoroquinolones (antibiotics).
- Vaccinations with killed (inactivated) vaccines are generally possible. However, it should be noted that the immune response, and thus effective vaccination, may be impaired at higher doses.
- In elderly patients, the doctor will consider the benefit-risk ratio and pay attention to side effects, such as osteoporosis (bone tissue breakdown).
- If dexamethasone is administered prematurely to newborns, it is necessary to monitor cardiac function and structure.
Children and adolescents
Routine use of dexamethasone is not recommended in premature infants with respiratory disorders. In children and adolescents, this medicine can be used only when necessary, due to the risk of growth retardation. Whenever possible, during long-term treatment, an intermittent therapy regimen should be aimed for.
Dexamethasone Kalceks and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
Some medicines may increase the effect of dexamethasone, and the doctor may want to closely monitor the patient's condition if they are taking these medicines (including HIV treatments: ritonavir, cobicistat).
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist if they are taking any of the following medicines:
- medicines used to treat heart failure (cardiac glycosides);
- medicines used to increase urine production;
- medicines that lower blood sugar levels (antidiabetic medicines);
- medicines that prevent blood clots/ thin the blood (coumarin derivatives);
- ephedrine (used in asthma and during poor circulation);
- rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis);
- medicines used to treat seizures and epilepsy (phenytoin, carbamazepine, primidone);
- barbiturates (sleep-inducing medicines);
- ketokonazole, itraconazole (used to treat fungal infections);
- medicines used to treat infections (macrolide antibiotics, e.g. erythromycin, or fluoroquinolones, e.g. ciprofloxacin);
- pain-relieving, anti-inflammatory, and anti-rheumatic medicines (e.g. salicylates and indomethacin);
- oral contraceptives containing estrogen;
- medicines used to combat intestinal parasites (praziquantel);
- medicines used to treat high blood pressure and certain heart diseases (ACE inhibitors);
- antimalarial medicines (chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, mefloquine);
- somatropin (growth hormone);
- laxatives;
- atropine and other anticholinergic medicines (medicines that block the action of a certain brain neurotransmitter);
- muscle relaxants;
- medicines that weaken the immune system (cyclosporine);
- bupropion (used to quit smoking).
Effect on diagnostic tests: Skin reactions to allergy tests may be suppressed. Interactions with the medicine used in thyroid function tests (protirelin: increased thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH] after protirelin administration may be decreased) are possible.
If dexamethasone treatment is initiated approximately 8 weeks before and up to 2 weeks after prophylactic vaccinations with live vaccines, it can be expected that the effectiveness of such vaccination may be reduced or not occur.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Pregnancy
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Dexamethasone crosses the placenta. During pregnancy, especially in the first three months, the medicine should be used only after careful consideration of the benefit-risk ratio. Therefore, if the patient is pregnant or becomes pregnant, they should inform their doctor. In the case of long-term use of glucocorticoids during pregnancy, it cannot be ruled out that growth disorders may occur in the unborn child. In the case of glucocorticoid use in the late stages of pregnancy, the newborn may experience adrenal insufficiency, which may require replacement therapy, which should be gradually discontinued. In newborns of mothers who received Dexamethasone Kalceks at the end of pregnancy, low blood sugar levels may occur after birth.
Breastfeeding
Glucocorticoids pass into human milk. So far, no harmful effects on the infant have been reported. Nevertheless, they should be used only when strictly necessary during breastfeeding. If higher doses are necessary, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Fertility
No fertility studies have been conducted.
Driving and using machines
No studies have been conducted on the effects on driving and using machines.
Dexamethasone Kalceks contains sodium
The medicine contains approximately 3 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per 1 mL of solution. This corresponds to 0.15% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake in adults.
3. How to use Dexamethasone Kalceks
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. The doctor will decide how long the patient should use dexamethasone. In case of doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
This medicine can be administered into a vein, into a muscle, into a joint, or by local injection into soft tissues.
Dosage depends on the indication, severity of symptoms, individual patient response, and, in the case of intra-articular injection, on the size of the joint.
Glucocorticoids should be used only as long as - and only in as small doses as - is absolutely necessary to achieve and maintain the desired effect. The duration of treatment depends on the indication. Long-term use of dexamethasone should not be discontinued abruptly; the dose should be gradually reduced, as directed by the doctor.
Treatment of COVID-19
Adult patients: the recommended dose is 6 mg intravenously once a day, for up to 10 days.
Elderly patients, renal impairment, hepatic impairment (in small doses [6 mg per day] and for a short duration):No dose adjustment is necessary.
Children and adolescents:Pediatric patients (adolescents aged 12 or older with a body weight of at least 40 kg) are recommended to receive 6 mg intravenously once a day for up to 10 days.
The duration of treatment should be based on clinical response and individual patient requirements.
Renal impairment
No dose adjustment is necessary.
Hepatic impairment
In patients with severe hepatic impairment, dose adjustment may be necessary.
Children and adolescents
In children under 14 years of age, during long-term treatment, a 4-day break in treatment should be introduced after each 3-day course, due to the risk of growth disorders.
Use of a higher than recommended dose of Dexamethasone Kalceks
No cases of acute dexamethasone overdose are known. In case of overdose, increased side effects should be expected. If the patient believes they have received too high a dose, they should inform their doctor.
Discontinuation of Dexamethasone Kalceks
Treatment should not be disrupted or discontinued abruptly, unless the doctor advises it. However, if the patient decides to discontinue treatment, e.g. due to side effects or improved well-being, they not only jeopardize the success of treatment but also expose themselves to significant risk.
In particular, patients who have been on long-term treatment should not discontinue this medicine on their own. The patient should always consult their doctor first.
In case of any further doubts regarding the use of this medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
During short-term treatment with dexamethasone, the risk of side effects is low. The following side effects are possible:
- gastric or duodenal ulcers;
- reduced ability to defend against infections;
- increased blood sugar levels (decreased glucose tolerance).
The following side effects may occur, which to a large extent depend on the dose and duration of treatment, and therefore their frequency is unknown (frequency cannot be estimated from available data):
Infections and infestations
Masking of infections, fungal, viral, and other (opportunistic infections) promoting their development or worsening, activation of latent infections (see section 2, "Warnings and precautions").
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Changes in blood morphology (moderate leukocytosis, lymphocytopenia, eosinopenia, erythrocytosis).
Immune system disorders
Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. rash), immune system suppression, allergic reactions, and even anaphylaxis (a life-threatening allergic reaction), with symptoms such as irregular heartbeat, bronchospasm, decreased or increased blood pressure, circulatory failure, or cardiac arrest.
Endocrine disorders
Cushing's syndrome (e.g. moon face, obesity in the upper part of the body), adrenal cortex insufficiency or atrophy.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders
Sodium retention in the body with water accumulation in tissues, increased potassium excretion (note: possible cardiac arrhythmias), weight gain, increased blood sugar levels (decreased glucose tolerance), diabetes, increased blood lipid levels (cholesterol and triglycerides), increased appetite.
Psychiatric disorders
Psychosis, depression, irritability, euphoria (excessive happiness), sleep disturbances, lability, anxiety, mania, hallucinations, suicidal thoughts.
Nervous system disorders
Pseudotumor cerebri (a "false" brain tumor), first-time onset of epilepsy promoted in patients with latent epilepsy (previously "dormant") and increased susceptibility to seizures in previously diagnosed epilepsy (seizures).
Eye disorders
Glaucoma, cataract, worsening of corneal ulcer symptoms, promotion of viral, fungal, and bacterial eye inflammation; worsening of bacterial corneal inflammation, ptosis (drooping eyelid), mydriasis (pupil dilation), conjunctival edema, iatrogenic scleral perforation (eye injury caused by a doctor [white eye wall]), vision disturbances or loss, blurred vision. In rare cases, reversible exophthalmos (bulging eye).
Cardiac disorders
Cardiac hypertrophy (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy) in premature infants, which usually returns to normal after treatment is discontinued.
Vascular disorders
Hypertension, increased risk of atherosclerosis (changes in blood vessel walls) and thrombosis (blockage of blood vessels by a blood clot), vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels), and vascular fragility (vascular fragility).
Gastrointestinal disorders
Gastrointestinal upset, gastric or intestinal ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding, pancreatitis, risk of intestinal perforation in ulcerative colitis (severe colitis).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Stretch marks, skin thinning, petechiae (small blood spots under the skin), bruising, steroid acne, inflammatory conditions around the mouth, superficial vasodilation, excessive body hair, changes in skin pigmentation.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, inflammatory muscle disease, tendon disorders, tendonitis, tendon rupture, bone loss (osteoporosis), delayed growth in children, aseptic bone necrosis (bone tissue death without microbial involvement), increased fat tissue in the spinal canal.
Reproductive system and breast disorders
Disorders of sex hormone secretion, such as amenorrhea, excessive male-type hair growth in women, impotence.
General disorders and administration site conditions
Delayed wound healing.
Local administration
Local irritation and signs of hypersensitivity (burning sensation, persistent pain) may occur, especially after injection into the eye. Tissue atrophy cannot be ruled out if dexamethasone is not properly injected into the joint cavity.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any not listed in this leaflet, the patient should inform their doctor or pharmacist.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Dexamethasone Kalceks
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not store above 30 °C.
Store ampoules in the outer packaging to protect from light.
After opening the ampoule: After opening, the medicine should be used immediately.
Shelf life after dilution
Chemical and physical stability during use has been demonstrated for 48 hours at 25 °C (in light-protected conditions) and 2 to 8 °C.
From a microbiological point of view, the diluted solution should be used immediately. If the solution is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the storage conditions before use, and usually, it should not be longer than 24 hours at 2 to 8 °C, unless the dilution took place in controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the ampoule label after "EXP" and on the carton after "Expiry date (EXP)". The expiry date refers to the last day of the stated month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Dexamethasone Kalceks contains
- The active substance is dexamethasone phosphate.
Each 1 mL ampoule contains dexamethasone sodium phosphate, equivalent to 4 mg of dexamethasone phosphate.
Each 2 mL ampoule contains dexamethasone sodium phosphate, equivalent to 8 mg of dexamethasone phosphate.
- Other ingredients are: creatinine, sodium citrate, disodium edetate, sodium hydroxide, water for injections.
What Dexamethasone Kalceks looks like and contents of the pack
Clear, colorless solution, free from visible particles.
1 mL or 2 mL ampoules made of clear, colorless glass type I with one break point.
Ampoules are marked with a color ring.
Ampoules are packaged in protective covers. Protective covers are packaged in cardboard boxes.
Pack sizes:
3, 10, 25, 50, or 100 ampoules of 1 mL
5, 10, 25, 50, or 100 ampoules of 2 mL
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
AS KALCEKS
Krustpils iela 71E
LV-1057 Rīga
Latvia
Phone: +371 67083320
Email: [email protected]
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Estonia
Dexamethasone Kalceks
Austria, Germany
Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/mL injection/infusion solution
Croatia
Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/mL solution for injection/infusion
Czech Republic, Poland
Dexamethasone Kalceks
Denmark, Norway Dexamethasone phosphate Kalceks
Finland
Dexalcex 4 mg/mL injection/infusion solution, liquid
France
DEXAMETHASONE KALCEKS 4 mg/1 mL, solution for injection/infusion
Hungary
Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/mL solution for injection or infusion
Ireland
Dexamethasone phosphate 4 mg/mL solution for injection/infusion
Italy
Desametasone Kalceks
Latvia
Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/mL solution for injections/infusions
Lithuania
Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/mL injection/infusion solution
Netherlands
Dexamethasone phosphate Kalceks 4 mg/mL solution for injection/infusion
Portugal
Dexametasona Kalceks
Slovenia
Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/mL solution for injection/infusion
Spain
Dexametasona Kalceks 4 mg/mL solution for injection and perfusion EFG
Sweden
Dexalcex
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 01/2022
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Dosage and administration
In cases where high doses are required, consideration should be given to using a medicinal product containing dexamethasone with a higher concentration per unit volume.
- 1. Systemic administration
In treatment and prevention of brain edema in brain tumors (postoperatively and after irradiation) and
after spinal cord injuries
The initial dose is 8-10 mg (up to 80 mg) intravenously, then 16-24 mg (up to 48 mg)/day divided into 3-4 (6) single intravenous doses for 4-8 days. Long-term administration of smaller doses of dexamethasone phosphate may be necessary during radiotherapy and in the conservative treatment of inoperable brain tumors.
In the case of anaphylactic shock, first an adrenaline injection intravenously, then 40-100 mg (children 40 mg) intravenously, repeated as needed.
Shock after severe injury / prevention of post-traumatic shock lung
Initially 40-100 mg (children 40 mg) intravenously, repeated dose after 12 hours, or 16-40 mg every 6 hours for 2-3 days.
In the case of severe asthma exacerbations8-40 mg intravenously as soon as possible; repeated injections of 8 mg every 4 hours if necessary.
In the case of acute, severe dermatoses, severe blood diseases, initial treatment with 20-40 mg of dexamethasone phosphate intravenously and further treatment, depending on the severity of the case, with the same daily dose or smaller doses over the first few days and transition to oral therapy.
In the treatment of acute adrenal insufficiency(Addison's crisis), treatment is started with 4-8 mg of dexamethasone phosphate intravenously.
In the treatment of COVID-19
Adult patients:6 mg intravenously, once a day, for up to 10 days.
Elderly patients, renal impairment, hepatic impairment (in small doses [6 mg per day] and for a short duration):No dose adjustment is necessary.
Children and adolescents:Pediatric patients (adolescents aged 12 or older with a body weight of at least 40 kg) are recommended to receive 6 mg intravenously once a day for up to 10 days.
The duration of treatment should be based on clinical response and individual patient requirements.
- 2. Local administration
In the case of local infiltrative treatment, periarticular and intra-articular injections, in strictly aseptic conditions, injections of 4 mg or 8 mg of dexamethasone phosphate. For injection into a small joint, 2 mg of dexamethasone phosphate is sufficient. Depending on the severity of the disease, no more than 3-4 infiltrations or 3-4 joint injections should be performed. The interval between injections should not be less than 3-4 weeks.
Administration method
For intravenous, intramuscular, intra-articular, or local injection (intralesional injection). Dexamethasone Kalceks solution for injection/infusion is usually administered intravenously slowly (2-3 minutes) in acute conditions, by injection or infusion. However, it can also be administered intramuscularly (only in exceptional cases), as a local intralesional injection, or intra-articularly.
Instructions for use and disposal
For single use only.
After opening, the medicinal product should be used immediately. All unused residues should be discarded.
The ampoule should be inspected visually before use. Only a clear and particle-free solution should be administered.
The pH of the solution is between 7.0 and 8.5
This medicinal product should not be mixed with other medicinal products, except for those listed below.
Dexamethasone Kalceks solution for injection/infusion is best administered as a direct intravenous injection or as an injection into the infusion line. However, the injection solutions are compatible with the following infusion solutions (250 mL and 500 mL):
- 9 mg/mL (0.9%) sodium chloride solution
- 50 mg/mL (5%) glucose solution
- Ringer's solution.
When combining with infusion solutions, the compatibility, contraindications, side effects, and interactions of the respective infusion solutions should be taken into account, including information from the manufacturers.
Ampoule opening instructions
- 1) Turn the ampoule with the colored point upwards. If there is a solution in the upper part of the ampoule, gently tap with your finger to transfer the entire solution to the lower part of the ampoule.
- 2) Use both hands to open the ampoule; holding the lower part of the ampoule in one hand, break off the upper part of the ampoule in the direction of the colored point (see picture below).
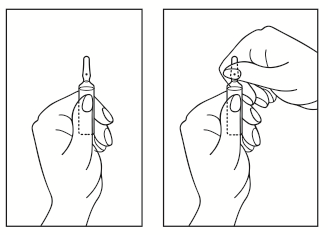
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAS Kalceks
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Dexamethasone KalceksDosage form: Solution, 4 mg/mlActive substance: dexamethasonePrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 4 mg/mlActive substance: dexamethasoneManufacturer: mibe GmbH Arzneimittel Sun-Farm Sp. z o.o.Prescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 8 mg/mlActive substance: dexamethasoneManufacturer: mibe GmbH Arzneimittel Sun-Farm Sp. z o.o.Prescription required
Alternatives to Dexamethasone Kalceks in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Dexamethasone Kalceks in Spain
Alternative to Dexamethasone Kalceks in Ukraine
Online doctors for Dexamethasone Kalceks
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Dexamethasone Kalceks – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










