
Biotum
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Biotum

How to use Biotum
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Biotum, 1 g, powder for solution for injection or infusion
Biotum, 2 g, powder for solution for injection or infusion
Ceftazidime
Read the leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Biotum and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Biotum
- 3. How to take Biotum
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Biotum
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Biotum and what is it used for
Biotum is an antibiotic used in adults and children (including newborns). It works bactericidally on bacteria that cause infections. It belongs to a group of medicines called cephalosporins.
Biotum is used to treat severe bacterial infections:
- lower respiratory tract, including lungs
- lungs and bronchi in patients with cystic fibrosis
- brain (meningitis)
- ear
- urinary tract
- skin and soft tissues
- abdominal cavity and abdominal lining (peritonitis)
- bones and joints.
Biotum can also be used:
- to prevent infections during transurethral resection of the prostate in men
- to treat patients with a low white blood cell count (neutropenia) who have a fever due to a bacterial infection.
2. Important information before taking Biotum
When not to take Biotum
- If the patient is allergic to ceftazidime or any other ingredient of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If the patient has ever had a severe allergic reaction to any other antibiotic (penicillins, monobactams, and carbapenems), as they may also be allergic to Biotum.
➢
If the patient suspects that they are affected by the above circumstances, they should inform their doctor before starting treatment with Biotum.
Do not give the patient Biotum.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Biotum, discuss it with a doctor or nurse.
Pay attention to whether the patient experiences any special symptoms during treatment with Biotum, such as allergic reactions, nervous system disorders, and stomach and intestine disorders, including diarrhea. This will reduce the risk of potential problems. See "Symptoms to watch out for" in section 4. If the patient has ever had an allergic reaction to other antibiotics, they may also be allergic to Biotum.
Severe skin reactions have been reported with ceftazidime, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). If the patient experiences any symptoms related to these severe skin reactions, as described in section 4, they should contact their doctor immediately.
Blood and urine tests
Biotum may change the results of urine sugar content tests and blood tests known as the Coombs test. If the patient is to have such tests:
- Tell the person taking the samplethat the patient is taking Biotum.
Biotum and other medicines
Tell the doctor about all medicines the patient is currently taking or has recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
The patient should not take Biotum without consulting their doctor if they are also taking:
- an antibiotic called chloramphenicol
- an antibiotic from a group called aminoglycosides, such as gentamicin or tobramycin
- diuretic tablets containing furosemide.
➢
If the above circumstances apply to the patient, they should inform their doctor.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before taking this medicine.
The doctor will assess whether the benefits of taking Biotum during pregnancy and breastfeeding outweigh the risks to the child.
Driving and using machines
Biotum may cause side effects that affect the ability to drive or operate machinery, such as dizziness (see section 4). The patient should not drive or operate machinery unless they are sure they have not experienced these side effects.
Biotum contains sodium
Each 1 g vial contains 60 mg of sodium. This is 3% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
Each 2 g vial contains 120 mg of sodium. This is 6% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
The medicine contains 60 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per gram of powder. This is 3% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
This should be taken into account in patients with reduced kidney function and in patients controlling their sodium intake.
Preparing the medicine for administration - see the section "Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals" at the end of the leaflet. When calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution, consider the sodium from the diluent. For accurate information on the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, refer to the patient leaflet of the diluent used.
3. How to take Biotum
This medicine should always be taken as directed by the doctor. In case of doubts, consult a doctor.
Biotum is usually administered by a doctor or nurse.
Biotum 1 g can be administered by intravenous infusion or as an injection directly into a vein or intramuscular injection.
Biotum 2 g can be administered by intravenous infusion or as an injection directly into a vein.
Biotum is prepared by a doctor or nurse using water for injections or another suitable infusion fluid.
Usual dose
The doctor will decide on the appropriate dose of Biotum for the patient, taking into account the severity and type of infection, any other antibiotics the patient is taking, their body weight, age, and kidney function.
Newborns and infants (0-2 months old)
For every 1 kg of the infant's body weight, 25-60 mg of Biotum is administered over 24 hours in two divided doses.
Infants (over 2 months old) and childrenweighing less than 40 kg
For every kg of the infant's or child's body weight, 100-150 mg of Biotum is administered over 24 hours in three divided doses. Maximum 6 g per day.
Adults and adolescentsweighing 40 kg or more
1-2 g of Biotum three times a day. Maximum 9 g per day.
Patients over 65 years old
The daily dose should not be higher than 3 g per day, especially in patients over 80 years old.
Patients with kidney disease
The patient may receive a different dose than usual. The doctor or nurse will decide on the dose of Biotum to be administered to the patient, depending on the severity of kidney disease. The doctor will closely monitor the patient and may order more frequent kidney function tests.
Using a higher dose of Biotum than recommended
In case of accidental use of a higher dose of Biotum than prescribed, contact the doctor or go to the nearest hospital immediately.
Missing a dose of Biotum
If the patient misses an injection, it should be administered as soon as possible.
Do not take a double dose (two injections at the same time) to make up for a missed dose, but take the next dose at the usual time.
Stopping treatment with Biotum
Do not stop taking Biotum without consulting a doctor.
In case of any further doubts about taking this medicine, consult a doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Biotum can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Symptoms to watch out for
➢
The severe side effects described below have occurred in a small number of people, but their exact frequency is unknown (the frequency cannot be determined from the available data).
If the patient experiences any of the following symptoms, they should contact their doctor immediately:
- Severe allergic reaction. Symptoms are: swollen, itchy rash, swelling, sometimes of the face or mouth, which can cause difficulty breathing.
- Red spots on the torso, spots resembling a target or circle, often with central blisters, peeling skin, ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes. These severe skin rashes can be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis).
- Widespread rash, high body temperature, and swollen lymph nodes (DRESS or drug hypersensitivity syndrome).
- Red, peeling, widespread rash with bumps under the skin and blisters, and fever at the same time. Symptoms usually occur at the beginning of treatment (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis).
- Nervous system disorders: tremors, seizures, and sometimes coma. These disorders have occurred in patients who received too high doses, especially in patients with kidney disease.
Common side effects
May occur in more than 1 in 10 patients:
- diarrhea
- swelling and redness along the vein
- red, swollen rash on the skin, which may itch
- pain, burning, swelling, or inflammation at the injection site.
➢
If any of the above symptoms concern the patient, they should tell their doctor.
Common side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- increased number of one type of white blood cell (eosinophilia)
- increased number of platelets involved in blood clotting
- increased activity of liver enzymes.
Uncommon side effects
May occur in more than 1 in 100 patients:
- inflammation of the intestines, which can cause pain or diarrhea that may contain blood
- thrush - fungal infections of the mouth or vagina
- headache
- dizziness
- abdominal pain
- nausea or vomiting
- fever and chills.
➢
Tell the doctor if the patient experiences any of the above symptoms.
Uncommon side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- decreased number of white blood cells
- decreased number of platelets (cells involved in blood clotting)
- increased levels of urea, nitrogen, or creatinine in the blood.
Rare side effects
May occur in more than 1 in 10,000 patients:
- inflammation or kidney failure.
Other side effects
Other side effects that have occurred in a small number of patients, but the exact frequency is unknown:
- tingling
- unpleasant taste in the mouth
- yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin.
Other side effects that may be seen in blood tests:
- red blood cells break down too quickly
- increased number of one type of white blood cell in the blood
- significant decrease in the number of white blood cells.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any not listed in this leaflet, tell the doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Biotum
Store the medicine at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Protect from light.
The prepared solution can be stored for 24 hours in the refrigerator, i.e., at a temperature between 2°C and 8°C.
Store the medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask the pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Biotum contains
- The active substance of the medicine is ceftazidime. Each vial contains 1 g or 2 g of ceftazidime in the form of a pentahydrate buffered with sodium carbonate.
- The other ingredient is: sodium carbonate.
What Biotum looks like and what the pack contains
White or light yellow powder in a glass vial, closed with a rubber stopper and secured with an aluminum cap or aluminum cap with a hood, in a cardboard box.
The packaging contains 1 or 10 vials.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Polpharma S.A.
Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Manufacturer
Polpharma S.A.
Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
Polpharma S.A.
Production Plant in Duchnice
Ożarowska 28/30, 05-850 Ożarów Mazowiecki
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals
Biotum, 1 g, powder for solution for injection or infusion
Biotum, 2 g, powder for solution for injection or infusion
Ceftazidime
The pressure in Biotum vials of any size is lower than atmospheric pressure. When dissolving the powder, the pressure increases due to the release of carbon dioxide. Small carbon dioxide bubbles in the prepared solution can be ignored.
Instructions for preparing the medicine for administration
Refer to the table of added volumes and achieved concentrations, which may be useful when partial doses are needed.
| Contents of the vial | Route of administration | Volume of solvent to be added [ml] | Approximate concentration of ceftazidime [mg/ml] |
| 1 g | intramuscular injection | 3 ml | 260 |
| intravenous injection | 10 ml | 90 |
| intravenous infusion | 50 ml* | 20 | |
| 2 g | intravenous injection | 10 ml | 170 |
| intravenous infusion | 50 ml* | 40 |
* Note. Add in two stages
The color of the solution ranges from light yellow to amber, depending on the concentration, type of solvent, and storage conditions. If the recommended conditions are met, the variability of the solution's color does not adversely affect the product's effectiveness.
Preparing a solution for rapid injection
- 1. Pierce the stopper with a needle and inject the recommended volume of solvent into the vial. To pierce the stopper, use a needle with a diameter not larger than 0.8 mm (21 G in the Gauge [G] scale). Insert the needle into the center of the stopper at a 90° angle, as shown below:
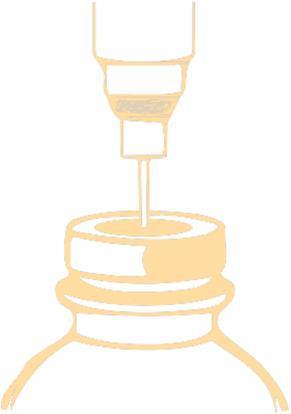
Underpressure inside the vial may facilitate the entry of the solvent. Withdraw the needle with the syringe.
- 2. Shake until dissolved: carbon dioxide is released, and a clear solution is obtained within 1 to 2 minutes.
- 3. Invert the vial. Holding the syringe plunger in a fully depressed position, pierce the vial stopper with the needle and draw the entire volume of the solution into the syringe (the increased pressure in the vial will facilitate this). Keep the needle within the solution to avoid drawing in air. The solution drawn into the syringe may contain small carbon dioxide bubbles.
These solutions can be administered directly into a vein or into an intravenous infusion set, if the patient is receiving intravenous fluids. Ceftazidime is compatible with most commonly used intravenous fluids.
Preparing a solution for intravenous infusion with ceftazidime in a standard vial (mini-bag or burette setup)
Prepare using a total of 50 ml (for 1 g and 2 g vials) of compatible solvent, added in two stages, as described below:
- 1. Pierce the stopper with a needle and inject 10 ml of solvent into the 1 g and 2 g vials.
- 2. Remove the needle and shake the vial until a clear solution is obtained.
- 3. Do not insert a venting needle until the medicine is completely dissolved. Insert a venting needle through the stopper to reduce the pressure inside the vial.
- 4. Transfer the solution to the final container (mini-bag or burette setup), achieving a total volume of not less than 50 ml, and administer by intravenous infusion over 15 to 30 minutes.
Note: To ensure the sterility of the medicine, it is essential not to insert the venting needle through the vial stopper before the medicine is completely dissolved.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Oddział Produkcyjny w Duchnicach
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to BiotumDosage form: Powder, 500 mgActive substance: ceftazidimeManufacturer: Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Oddział Produkcyjny w DuchnicachPrescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 1 gActive substance: ceftazidimeManufacturer: Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Oddział Produkcyjny w DuchnicachPrescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 1 gActive substance: ceftazidimePrescription not required
Alternatives to Biotum in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Biotum in Spain
Alternative to Biotum in Ukraine
Online doctors for Biotum
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Biotum – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














