
Biotaksim

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Biotaksim

How to use Biotaksim
Leaflet attached to the packaging: information for the user
BIOTAXYM, 1 g, powder for solution for injection or infusion
BIOTAXYM, 2 g, powder for solution for injection or infusion
Cefotaxime
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Biotaxym and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Biotaxym
- 3. How to use Biotaxym
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Biotaxym
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Biotaxym and what is it used for
Biotaxym contains a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic - cefotaxime.
The medicine, after dissolution and proper dilution, is administered intramuscularly or intravenously
(in injection or infusion).
Cefotaxime is used:
- to treat severe infections caused by susceptible bacteria:
- lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia;
- urinary tract infections;
- infections in the pelvic area;
- septicemia;
- skin and soft tissue infections;
- intra-abdominal infections, including peritonitis;
- bone and joint infections;
- central nervous system infections, including meningitis;
- to prevent postoperative infections.
2. Important information before using Biotaxym
When not to use Biotaxym:
- if the patient is allergic to cefotaxime or other cephalosporins;
- if the patient is taking penicillins, due to the possibility of cross-reaction (see section: "Biotaxym and other medicines");
- if the patient has ever had a severe skin rash or exfoliation after taking cefotaxime or other cephalosporins;
- with lidocaine:
- in patients allergic to lidocaine or other amide local anesthetics;
- intravenously;
- in infants under 30 months of age;
- in patients with severe heart failure or heart block (without a pacemaker).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Biotaxym, you should discuss it with your doctor or nurse.
- If the patient has an allergy, especially to cephalosporins and penicillins (and other beta-lactam antibiotics); you should be particularly careful, as people allergic to penicillins may also be allergic to cephalosporins (so-called cross-allergy). There is a risk of a severe allergic reaction. If an allergic reaction occurs, cefotaxime should be discontinued and, if necessary, appropriate treatment should be administered. In the treatment of severe reactions, the use of adrenaline and other anti-shock medications (circulatory supportive medications, corticosteroids, and antihistamines) may be necessary.
- Severe skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), have been reported with cefotaxime. You should discontinue cefotaxime and immediately consult a doctor if any of the symptoms associated with these severe skin reactions occur, as described in section 4.
- If the patient has kidney problems, the doctor may order monitoring and, if necessary, reduce the dose of the medicine.
- If the patient experiences neurological symptoms such as changes in consciousness, abnormal movements, and seizures, they should consult a doctor before continuing treatment.
- If cefotaxime is used for a long time, as with other antibiotics, initially susceptible strains may become resistant, and an increase in bacteria from the Enterococcus spp. family may occur. The doctor may then recommend an antibiogram.
- If the patient experiences diarrhea associated with the use of the medicine, they should consult a doctor, who will recommend appropriate action. Rarely, during or after antibiotic treatment, pseudomembranous colitis may occur, characterized by diarrhea. The inflammation can be mild or severe. Mild cases usually resolve after discontinuation of the medicine. In more severe cases, the doctor may recommend taking metronidazole or vancomycin. You should not take medications that slow down bowel movements or have a constipating effect.
- If the patient has had colitis in the past, especially colitis of the colon.
- If the patient is taking the medicine for more than 7 days, the doctor may recommend monitoring the white blood cell count and liver function.
Children
Children under 2 months of age should be given the medicine only intravenously.
Biotaxym and other medicines
You should tell your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken,
as well as any medicines you plan to take.
You should be careful when taking cefotaxime and:
- bacteriostatic agents (e.g., tetracycline, erythromycin, chloramphenicol, sulfonamides) - they may weaken the antibacterial effect of cefotaxime;
- aminoglycoside antibiotics (e.g., streptomycin) and potent diuretics (e.g., furosemide) - they may increase the harmful effect on kidney function;
- probenecid - it increases the concentration of cefotaxime in the serum and prolongs its action.
Effect on laboratory test results
Taking cefotaxime may cause:
- false positive results of glucose reduction tests in urine;
- false positive Coombs test result.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
Pregnancy
The safety of cefotaxime in pregnant women has not been established. Therefore, cefotaxime should not be used during pregnancy unless the expected benefits outweigh the risks.
Breastfeeding
Cefotaxime passes into breast milk. It cannot be excluded that it may affect the physiological intestinal flora of breastfed infants, leading to diarrhea, colonization of yeast-like fungi. The infant may also experience an allergic reaction.
You should discuss with your doctor whether to stop breastfeeding or discontinue treatment, considering the benefit of breastfeeding for the child and the benefit of treatment for the mother.
Driving and operating machinery
There is no evidence that cefotaxime directly impairs the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. High doses of cefotaxime, especially in patients with kidney failure, may cause changes in consciousness, movement disorders, and seizures. In such cases, you should not drive vehicles or operate machinery.
Biotaxym contains sodium
The medicine contains 48 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per gram. This corresponds to 2.4% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
This should be taken into account in patients with reduced kidney function and in patients controlling their sodium intake in the diet.
Preparation of the medicine for administration - see the section: "Information intended exclusively for medical professionals" at the end of the leaflet. When calculating the total sodium content in the prepared solution, you should take into account the sodium from the diluent. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, you should read the patient information leaflet for the diluent used.
3. How to use Biotaxym
This medicine should always be used as directed by your doctor. If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor.
Dosage and method of administration are determined by the doctor based on the severity and type of infection, age, body weight, and kidney function of the patient.
Detailed dosing and method of administration and preparation of the medicine for administration are given at the end of the leaflet, in the section "Information intended exclusively for medical professionals".
Using a higher dose of Biotaxym than recommended
If you suspect that you have received too high a dose of Biotaxym, you should inform your doctor. Overdose may occur, especially in patients with kidney failure. Seizures, tremors, and coma may occur. In such cases, you should discontinue the medicine and receive appropriate treatment. Hemodialysis removes the medicine from the body.
Missing a dose of Biotaxym
If you suspect that a dose of Biotaxym has been missed, you should tell your doctor as soon as possible.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects and their frequencies are presented below.
You should immediately discontinue cefotaxime and inform your doctorif you notice the occurrence of any of the following symptoms:
- red, non-raised, target-like or round spots on the torso, often with centrally located blisters, exfoliation of the skin, ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes. These severe skin rashes may be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis).
- Widespread rash, high body temperature, and enlarged lymph nodes (DRESS or drug hypersensitivity syndrome).
- Red, scaly, widespread rash with thickening under the skin and blisters, accompanied by fever. Symptoms usually appear at the beginning of treatment (acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis).
Very common (occurring in more than 1 in 10 patients):
- pain at the injection site after intramuscular injection.
Uncommon (occurring in 1 to 10 in 1,000 patients):
- decreased white blood cell count, increased eosinophil count (a type of white blood cell), decreased platelet count, Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction (symptoms that occur within a few weeks of starting treatment for borreliosis, such as skin rash, itching, fever, leukopenia, breathing difficulties, joint problems),
- seizures,
- diarrhea,
- increased liver enzyme activity (ALT, AST, LDH, GGTP, alkaline phosphatase) and (or) bilirubin concentration,
- rash, itching, hives,
- worsening of kidney function and (or) increased creatinine concentration (when used with aminoglycosides),
- fever, inflammatory reactions at the injection site, including phlebitis or thrombophlebitis.
Frequency not known (cannot be determined from available data):
- superinfections, decreased neutrophil count (a type of white blood cell), including life-threatening (neutropenia), hemolytic anemia,
- anaphylactic reactions, angioedema, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock,
- headache, dizziness, encephalopathy (e.g., changes in consciousness, abnormal movements),
- arrhythmia caused by rapid infusion through a central venous catheter,
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain,
- pseudomembranous colitis, hepatitis (sometimes with jaundice), interstitial nephritis, systemic reactions to lidocaine after intramuscular injection (if the solution contains lidocaine).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Biotaxym
The medicine should be stored at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Protect from light.
The prepared solution can be stored for 24 hours in the refrigerator, i.e., at a temperature between
2°C and 8°C.
It is recommended to prepare solutions just before administration.
The medicine should be stored out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste containers. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer used. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Biotaxym contains
- The active substance of the medicine is cefotaxime. Each vial contains 1 g or 2 g of cefotaxime in the form of cefotaxime sodium. The medicine does not contain excipients.
What Biotaxym looks like and what the packaging contains
The medicine is a white or slightly yellowish, hygroscopic powder.
Biotaxym is intended for the preparation of a solution for injection or infusion.
The glass vial is closed with a rubber stopper and protected by an aluminum cap or aluminum cap with a hood, in a cardboard box.
The packaging contains 1 or 10 vials.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Polpharma S.A. Pharmaceutical Works
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Manufacturer
Polpharma S.A. Pharmaceutical Works
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
Polpharma S.A. Pharmaceutical Works
Duchnice Production Plant
ul. Ożarowska 28/30, 05-850 Ożarów Mazowiecki
Date of last revision of the leaflet:April 2024
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended exclusively for medical professionals
BIOTAXYM, 1 g, powder for solution for injection or infusion
BIOTAXYM, 2 g, powder for solution for injection or infusion
Cefotaxime
Dosage
Adults and children over 12 years of age
For mild to moderate infections, 1 g is used every 12 hours.
In severe infections, the daily dose can be increased to 12 g in 3 or 4 divided doses.
Daily doses up to 6 g should be divided into at least two doses, administered every 12 hours. Higher daily doses should be divided into at least 3 to 4 doses, administered every 8 or 6 hours.
Dosing guidelines are given in the table below:
| Type of infection | Single dose of cefotaxime | Interval between doses | Daily dose of cefotaxime |
| Typical infection, when susceptibility of the microorganism is confirmed or suspected | 1 g | 12 hours | 2 g |
| Infections in which multiple microorganisms with high or moderate susceptibility are confirmed or suspected | 2 g | 12 hours | 4 g |
| Unexplained bacterial infections, where the site of infection could not be localized and the patient's condition is critical | 2 to 3 g | 8 hours, 6 hours | from 6 g to 9 g, from 8 g to 12 g |
Infants and children under 12 years of age
In infants and children under 12 years of age, 50 mg to 150 mg/kg body weight per day of cefotaxime is used in 2 or 4 divided doses.
In very severe infections, especially life-threatening ones, it may be necessary to increase the daily dose of cefotaxime to 200 mg/kg body weight per day in divided doses.
Children under 2 months of age should be given the medicine only intravenously.
Preterm and full-term newborns
The dose should not exceed 50 mg/kg body weight per day of cefotaxime in 2 to 4 divided doses.
In severe, life-threatening infections, it may be necessary to increase the daily dose from 150 to 200 mg/kg body weight per day, in divided doses.
In such cases, the dosing recommended in the table below is suggested:
Gonorrhea
Uncomplicated gonorrhea: a single intramuscular injection of 1 g of cefotaxime. Before starting treatment with cefotaxime, appropriate tests should be performed to ensure that there is no concurrent syphilis infection.
| Age of the child | Daily dose of cefotaxime |
| From 0 to 7 days of life | 50 mg/kg body weight every 12 hours intravenously |
| From 8 days to 1 month of life | 50 mg/kg body weight every 8 hours intravenously |
Prophylaxis of postoperative infections
A single dose of 1 g of cefotaxime should be administered 30 to 90 minutes before the surgical procedure.
Depending on the risk of infection, the administration of the medicine may be continued after the procedure.
Dosage in patients with kidney failure
Reducing the dose of the preparation is necessary only in cases of severe kidney failure
(creatinine clearance less than 5 ml/min, serum creatinine concentration 751 micromol/l). After the initial, loading dose of 1 g, the daily dose should be reduced by half without changing the frequency of administration of the medicine, e.g., a dose of 1 g every 12 hours should be reduced to 500 mg every 12 hours, a dose of 1 g every 8 hours should be reduced to 500 mg every 8 hours, a dose of 2 g every 8 hours should be reduced to 1 g every 8 hours, etc.
In some patients, further modification of the dose may be necessary, depending on the course of the infection and the patient's general condition.
Method of administration
The medicine, after proper dilution, is administered intravenously in a 3-5 minute injection or intramuscularly - deeply into the upper, outer quadrant of the gluteus maximus muscle or the lateral thigh.
The medicine can be administered in intravenous infusion.
Method of puncturing the vial
Puncture the stopper with a needle and inject the recommended volume of solvent into the vial. To puncture the stopper, a needle with a diameter not larger than 0,8 mm (21 G in the Gauge [G] scale) should be used. The needle should be inserted into the centrally marked field at an angle of 90°, as shown in the scheme below:
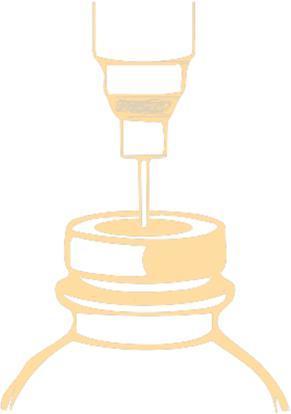
After adding the solvent to the vial, it should be shaken until the preparation dissolves, after 1-2 minutes the solution is clear. Before administering the medicine, you should check if the solution is clear and does not contain insoluble particles. The solution of the medicine may be colorless or light yellow.
Preparation of solutions for injection and infusion
| Content of the antibiotic in the vial | Volume of solvent | ||
| Intramuscular injection | Intravenous injection | Intravenous infusion | |
| 1 g | 4 ml | 10 ml | 50-100 ml |
| 2 g | 10 ml | 50-100 ml | |
Intramuscular injection
The medicine should be administered deeply intramuscularly after dissolution in an appropriate amount of water for injection or 1% lidocaine solution. Do not administer intravenously a solution of the medicine with lidocaine.
Intravenous injection(from 3 to 5 minutes)
The contents of the vial are dissolved in water for injection in a volume dependent on the dose, as shown in the table above.
Intravenous infusion(from 20 to 60 minutes)
To prepare solutions for intravenous infusion, the powder is dissolved in water for injection (as for intravenous injections). The resulting solution should then be diluted with one of the following solutions:
- 0.9% sodium chloride solution,
- 5% glucose solution,
- 5% glucose solution with 0.45% sodium chloride solution,
- 5% glucose solution with 0.2% sodium chloride solution,
- Ringer's lactate solution,
- sodium lactate injection solution (M/6). It is not recommended to use infusion fluids containing sodium bicarbonate, as cefotaxime is unstable in these solutions.
Cefotaxime and aminoglycosides should not be mixed in the same syringe or infusion fluid.
If concurrent administration is necessary, these medicines should be injected at different sites.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Oddział Produkcyjny w Duchnicach
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to BiotaksimDosage form: Powder, 1 gActive substance: cefotaximeManufacturer: Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Oddział Produkcyjny w DuchnicachPrescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 1 gActive substance: cefotaximePrescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 2 gActive substance: cefotaximePrescription not required
Alternatives to Biotaksim in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Biotaksim in Ukraine
Alternative to Biotaksim in Spain
Online doctors for Biotaksim
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Biotaksim – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














