
Betaxolol Pmcs

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Betaxolol Pmcs

How to use Betaxolol Pmcs
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Betaxolol PMCS, 20 mg, Tablets
Betaxolol Hydrochloride
Read the package leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet
- 1. What is Betaxolol PMCS and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Betaxolol PMCS
- 3. How to take Betaxolol PMCS
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Betaxolol PMCS
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Betaxolol PMCS and what is it used for
The active substance of Betaxolol PMCS is betaxolol. Betaxolol belongs to a group of medicines called beta-blockers. These medicines reduce blood pressure, slow down the heart rate, and reduce the heart's oxygen consumption.
Betaxolol PMCS is used to treat mild to moderate high blood pressure (hypertension). In severe cases of hypertension, it may be combined with other antihypertensive medicines.
The medicine is also used for long-term treatment and to prevent the occurrence of stable effort angina (chest pain caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle, occurring in connection with physical exertion or stress).
Betaxolol PMCS is indicated for the treatment of adults.
2. Important information before taking Betaxolol PMCS
When not to take Betaxolol PMCS
- if you are allergic to betaxolol or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- if you have severe asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,
- if you have severe heart failure,
- if you have cardiogenic shock,
- if you have conduction disorders in the heart (second or third degree atrioventricular block, except for patients with a pacemaker),
- if you have Prinzmetal's angina,
- if you have sinoatrial node dysfunction, including sinoatrial block (a disorder of impulse generation and conduction in the heart),
- if you have significant bradycardia,
- if you have severe Raynaud's disease and severe peripheral vascular disease (circulatory disorders in the lower limbs),
- if you have an untreated pheochromocytoma (a tumor of the adrenal gland),
- if you have low blood pressure,
- if you have a history of anaphylactic reactions (severe allergic reactions),
- if you have metabolic acidosis (a disorder of the body's internal environment),
- if you are taking floctafenine or sultopride.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Betaxolol PMCS, discuss it with your doctor
- if you have milder forms of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Before starting treatment, it is recommended to perform a lung function test. However, the risk of side effects is low.
- if you have controlled heart failure or conduction disorders in the heart (first degree atrioventricular block).
- if you have mild peripheral vascular disease, manifested by circulatory disorders in the limbs (Raynaud's syndrome, Raynaud's disease, vasculitis, or chronic lower limb ischemia). Betaxolol PMCS may worsen this condition.
- if you have high blood pressure caused by adrenal disease (pheochromocytoma).
- if you have diabetes with a tendency to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Patients with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels more frequently, especially at the beginning of treatment.
- if you or a family member have a history of psoriasis. Treatment with Betaxolol PMCS may worsen the condition.
- if you are to undergo surgery, inform your anesthesiologist that you are taking Betaxolol PMCS; in patients with severe ischemic heart disease and high blood pressure, it is not recommended to discontinue Betaxolol PMCS due to the risk associated with sudden withdrawal of beta-blockers.
- if you have glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure). Inform your ophthalmologist before the examination that you are taking Betaxolol PMCS.
- if you are an athlete. Betaxolol PMCS contains an active substance that may cause a positive result in a doping test.
- if you have thyroid disease (thyrotoxicosis). Betaxolol PMCS may mask the cardiovascular symptoms of this disease.
- if you have kidney disease.
Consult your doctor if, during treatment, your resting heart rate decreases significantly and you experience symptoms such as chest pain, dizziness, and fatigue.
Your doctor will reduce the dose of the medicine.
If you need to undergo desensitization treatment, replace Betaxolol PMCS with an antihypertensive medicine from a different group, other than beta-blockers.
In elderly patients, start treatment with a low dose.
Never suddenly stop taking Betaxolol PMCS, especially in patients with angina pectoris or ischemic heart disease. If it is necessary to discontinue treatment, consult your doctor, who will recommend gradual dose reduction.
Children and adolescents
Betaxolol PMCS is not recommended for use in children and adolescents.
Betaxolol PMCS and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or plan to take.
The effect of Betaxolol PMCS and the effect of other medicines taken at the same time may influence each other. Therefore, inform your doctor about all medicines you are taking, both those that are prescribed and those that are obtained without a prescription. Before taking any medicine without a prescription, consult your doctor.
Do not take Betaxolol PMCS with floctafenine or sultopride.
It is not recommended to take Betaxolol PMCS with amiodarone, digoxin, and verapamil (medicines used to treat heart diseases) or with fingolimod (a medicine used to treat multiple sclerosis).
Be particularly cautious when taking Betaxolol PMCS with calcium antagonists (bepridil, diltiazem, mibefradil), medicines used to treat arrhythmias (propafenone, quinidine, hydroquinidine, disopyramide), baclofen (a muscle relaxant), lidocaine (a local anesthetic), and contrast agents containing iodine.
Betaxolol PMCS may enhance the effect of concomitantly used antidiabetic medicines.
The effect of betaxolol may mask the clinical symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as increased heart rate and shivering.
Consider the following combinations with medicines whose effectiveness may also be altered during treatment with Betaxolol PMCS: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, calcium channel blockers (nifedipine), antidepressants, corticosteroids and tetracosactide (a type of hormonal treatment), mefloquine (a medicine used to treat malaria), sympathomimetic medicines (medicines used to accelerate heart rate), and clonidine (a medicine used to treat glaucoma).
Betaxolol PMCS with food and drink
Tablets are usually taken in the morning, regardless of food.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Due to possible side effects (fatigue, dizziness), which occur especially at the beginning of treatment, the medicine may affect the performance of tasks that require concentration, coordination, and decision-making speed (e.g., driving vehicles, operating machines, working at heights, etc.). In such cases, these activities can only be performed if the doctor agrees.
Betaxolol PMCS contains sodium
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per tablet, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to take Betaxolol PMCS
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. If you are not sure, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Adults
The dose will be determined individually for each patient, depending on the tolerance of the medicine and its effectiveness.
Usually, the recommended dose for the treatment of high blood pressure is one tablet (20 mg) once a day.
In stable effort angina, the recommended daily dose is 1 tablet. The doctor may adjust the dose from 10 mg to 40 mg (½ tablet to 2 tablets), depending on the patient's clinical condition.
Renal impairment
In patients with mild renal impairment, there is no need to adjust the dosage. In patients with more severe renal impairment or those undergoing dialysis, the doctor will recommend dose reduction. In patients undergoing dialysis, the recommended dose is 10 mg (½ tablet) once a day, regardless of the duration and frequency of dialysis.
Hepatic impairment
In patients with liver dysfunction, there is usually no need to adjust the dosage, but close clinical monitoring is recommended at the beginning of treatment.
Elderly patients
In elderly patients, treatment should be started with a low dose.
Method of administration
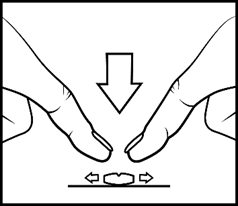
Tablets can be divided into two equal parts, as shown in the picture. To do this, place the tablet on a hard surface, with the dividing line facing up, and then break it into two equal parts, pressing each end down with your index fingers (apply short, strong pressure).
Tablets are usually taken in the morning, regardless of food.
Overdose of Betaxolol PMCS
If you have taken more than the recommended dose of the medicine or if a child has accidentally taken the medicine, seek medical attention immediately.
Missed dose of Betaxolol PMCS
If you miss a morning dose, you can take the medicine during the day and continue treatment the next day according to the recommended dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for the missed dose.
Stopping treatment with Betaxolol PMCS
Never stop treatment with Betaxolol PMCS on your own. If it is necessary to discontinue treatment, consult your doctor, as the dose should be gradually reduced.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Betaxolol PMCS can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Common side effects(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- dizziness, headache,
- weakness, insomnia,
- stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting,
- bradycardia (slow heart rate),
- cold extremities,
- impotence.
Uncommon side effects(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- skin reactions, including exacerbation of existing psoriasis or occurrence of psoriasis-like rash,
- depression,
- heart failure, low blood pressure, conduction disorders in the heart (slow atrioventricular conduction or worsening of existing atrioventricular block),
- discoloration of fingers due to reduced blood flow (Raynaud's syndrome), worsening of pain when walking, related to circulatory disorders in the lower limbs,
- breathing difficulties due to bronchospasm (asthma attack).
Rare side effects(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- peripheral neuropathy (tingling sensation in the limbs),
- vision disorders,
- hallucinations, disorientation, nightmares,
- decreased or increased blood sugar levels.
Side effects of unknown frequency(frequency cannot be estimated from available data)
- lethargy,
- rash, itching, excessive sweating, hair loss.
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products,
Aleje Jerozolimskie 181 C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309,
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Betaxolol PMCS
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and blister after "EXP" or "Expiry date". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Do not store above 30°C.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Betaxolol PMCS contains
- The active substance is betaxolol hydrochloride. Each tablet contains 20 mg of betaxolol hydrochloride.
- The other ingredients are: microcrystalline cellulose, sodium croscarmellose, magnesium stearate, anhydrous colloidal silica.
What Betaxolol PMCS looks like and contents of the pack
Betaxolol PMCS tablets are almost white, round, biconvex, 8 mm in diameter, with a dividing line on one side. The tablet can be divided into equal doses.
Tablets are available in blister packs of 30 and 100 tablets.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
PRO.MED.CS Praha a.s., Telčská 377/1, Michle, 140 00 Praha 4, Czech Republic
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Lithuania
Betaxolol PMCS 20 mg tablets
Latvia
Betaxolol PMCS 20 mg tablets
Poland
Betaxolol PMCS
Czech Republic
Betaxolol PMCS
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 28.05.2023
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterPRO.MED.CS Praha a.s.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Betaxolol Pmcs
Alternatives to Betaxolol Pmcs in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Betaxolol Pmcs in Ukraine
Alternative to Betaxolol Pmcs in Spain
Online doctors for Betaxolol Pmcs
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Betaxolol Pmcs – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










