
Atropinum sulfuricum Vzf

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Atropinum sulfuricum Vzf

How to use Atropinum sulfuricum Vzf
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF, 0.5 mg/ml, solution for injection
Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF, 1 mg/ml, solution for injection
Atropine sulfate
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF
- 3. How to use Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF and what is it used for
Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF contains atropine sulfate, which belongs to the group of anticholinergic drugs. Atropine acts on receptors found in exocrine glands, smooth muscles, heart muscle, and the central nervous system. Atropine causes an increase in heart rate, a decrease in saliva, sweat, and bronchial secretion, a decrease in nasal discharge, tear fluid, and gastric juice, a decrease in intestinal peristalsis, and an inhibition of urination.
Atropine accelerates the sinus rhythm and increases the conduction speed between the atria and ventricles of the heart muscle.
Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF is used:
- in sinus bradycardia (significant slowing of heart contractions resulting from disorders of the vagus nerve, which mediates between the brain and the sinoatrial node in controlling the heart); arrhythmia;
- for induction of general anesthesia (premedication);
- in poisoning with organophosphorus insecticides or cholinomimetic drugs;
- in poisoning with mushrooms containing muscarine;
- for reversing neuromuscular blockade;
- as an auxiliary in spastic conditions of smooth muscle in the abdominal cavity (hepatic colic, renal colic);
- in radiological diagnostics, when it is desirable to induce relaxation of smooth muscle and relieve intestinal passage.
2. Important information before using Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF
When not to use Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF:
- if the patient is allergic to atropine sulfate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has urethral obstruction, e.g. due to prostate enlargement (symptoms: difficulty urinating);
- if the patient has reflux esophagitis (symptoms: heartburn, esophageal mucosa damage);
- if the patient has myasthenia gravis (muscle weakness);
- if the patient has paralytic ileus (symptoms: fever, severe abdominal pain, bloating);
- if the patient has severe ulcerative colitis (symptoms: blood and mucus in stool);
- if the patient has diseases causing gastrointestinal obstruction;
- if the patient has narrow-angle glaucoma (increased eye pressure).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF, the patient should discuss it with their doctor or pharmacist.
- Particular caution should be exercised when using Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF in patients:
- over 40 years old, due to the risk of prostate enlargement and urinary tract obstruction;
- with respiratory diseases, as atropine may worsen shortness of breath;
- with hyperthyroidism, hypertension, tachyarrhythmia (fast, abnormal heart rhythm), congestive heart failure, angina pectoris, autonomic neuropathy, gastrointestinal diseases (e.g. gastric ulcer, esophageal reflux);
- in old age;
- with renal and/or hepatic impairment.
- When using atropine in children, caution should be exercised and the patient should be monitored.
- Administration of the drug to susceptible individuals may cause an acute attack of glaucoma or accelerate the onset of complete obstruction in case of pyloric stenosis.
- Caution should be exercised when administering atropine to patients with elevated body temperature, as it may cause further elevation. During administration of atropine, the patient should not be in a room with high temperatures.
- There have been cases of severe bradycardia (slow heart rate) caused by hyperkalemia, which did not respond to atropine administration.
- The occurrence of paradoxical atrioventricular block or sinus node inhibition has been reported after atropine administration in a few patients after heart transplantation.
- Atropine should be used with particular caution in therapeutic or diagnostic procedures in patients after heart transplantation. During use, ECG monitoring is recommended, and the availability of resuscitation equipment should be ensured.
- Doses of atropine not exceeding 1 mg hardly stimulate the central nervous system. Higher doses may cause mental disorders and inhibition of central nervous system function. Children and the elderly are particularly sensitive.
Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
Medicines that enhance the effects of atropine:
- tricyclic antidepressants,
- antispasmodic drugs (used e.g. in irritable bowel syndrome),
- drugs used in Parkinson's disease,
- certain antihistamines (first-generation),
- phenothiazines (drugs used in mental illnesses),
- disopyramide, quinidine (drugs used in heart diseases).
Atropine, by delaying gastric emptying, may cause slowed or accelerated absorption of some orally administered medicines.
During anesthesia with propofol and concurrent use of atropine, the heart rate response to intravenous atropine administration may be reduced (and cannot be effectively counteracted by administering a large dose of atropine).
Particular caution should be exercised when performing stress echocardiography with dobutamine and atropine or when administering catecholamine amines with atropine in patients who appear to be under strong stress or have a condition called hyperadrenergic (autonomic nervous system malfunction and severe disorders may occur, such as sudden blood pressure drops, accelerated heart rate, fainting, dehydration due to chronic diarrhea).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
The medicine may be used in pregnant women only in cases where the benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
Intravenous administration of atropine to a pregnant woman and during labor may cause fetal tachycardia.
Small amounts of atropine pass into breast milk and may cause side effects in the child. Use of atropine in breastfeeding women requires caution. It may lead to inhibition of milk secretion.
Driving and using machines
The medicine impairs the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. In case of doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF is administered only by medical personnel.
The medicine can be administered subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously.
Detailed information on dosing can be found in the section "Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals".
Using a higher dose of Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF than recommended
Overdose symptoms: dryness in the mouth with a burning sensation, difficulty swallowing, photophobia, redness and dryness of the skin, elevated body temperature, rash, nausea, and vomiting, accelerated heart rate, and elevated blood pressure. Due to central nervous system stimulation, the following may occur: nervousness, tremors, confusion, agitation, hallucinations, delirium. These symptoms may transform into drowsiness, stupor, respiratory and circulatory failure, sometimes life-threatening.
Treatment of severe cases involves intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous administration of 1-4 mg of physostigmine; the dose can be repeated if necessary.
If necessary, the doctor will administer oxygen to the patient and provide respiratory support, as well as ensure the patient receives adequate fluids. In case of photophobia, the patient should be moved to a dark room.
Missing a dose of Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF
A double dose should not be used to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping use of Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF
In case of any further doubts about using this medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects are related to the dose of atropine used and usually disappear after the medicine is discontinued.
After using relatively small doses, atropine reduces saliva, sweat, and bronchial secretion. Dryness in the mouth and reduced or inhibited sweat secretion may occur. Reduced bronchial secretion may cause thickening of the secretions and formation of a bronchial plug, difficult to remove from the airways. The above side effects worsen with increasing doses of atropine.
After using large doses of atropine, the following have been reported: pupil dilation, accommodation disorders, accelerated heart rate with possible occurrence of atrial flutter or fibrillation, atrioventricular block, and ventricular extrasystoles; urinary retention and constipation may occur. Increasing doses of atropine inhibit gastric secretion.
In some patients, anaphylaxis, urticaria, and rash may occur, sometimes with skin peeling.
Other side effects: hallucinations, increased intraocular pressure, loss of taste, headaches, nervousness, drowsiness, weakness, fatigue, dizziness, facial flushing, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, and bloating. Disorientation and/or agitation may occur, especially in elderly patients.
There have been cases of severe bradycardia caused by hyperkalemia, which did not respond to atropine administration.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any not listed in the leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, more information can be gathered on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF
Store at a temperature below 25°C.
Store the ampoules in the outer packaging to protect them from light, do not freeze.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the box and ampoule. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF contains
- The active substance of the medicine is atropine sulfate. Each ml of the solution contains 0.5 mg or 1 mg of atropine sulfate.
- The other ingredients are: diluted hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), water for injections.
What Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF looks like and what the packaging contains
Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF is a clear, transparent liquid.
The packaging contains 10 ampoules of 1 ml each in a cardboard box.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
tel. +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last update of the leaflet:December 2024
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF, 0.5 mg/ml, solution for injection
Atropinum Sulfuricum WZF, 1 mg/ml, solution for injection
Atropine sulfate
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to facilitate the flow of the solution.
A colored dot (see figure 1) is placed on each ampoule as a mark indicating the break point below it.
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, with both hands, with the colored dot facing you - see figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
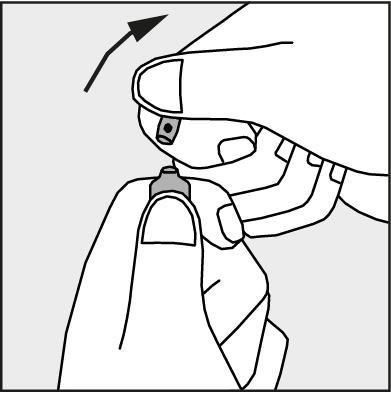
- Press according to the arrow on figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused product should be destroyed in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1.
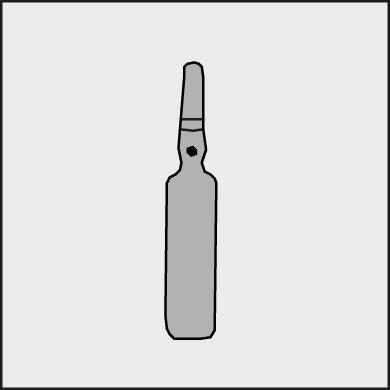
Figure 2.
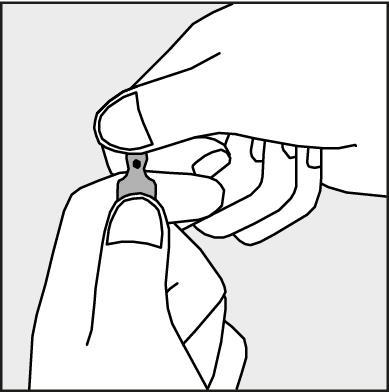
Figure 3.
The medicine can be administered subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously.
Dosing
Adults, adolescents over 12 years old, and elderly patients
Sinus bradycardia, arrhythmia
Intramuscularly or intravenously: 0.3 to 0.6 mg every 4-6 hours, up to a total dose of 2 mg.
In resuscitation: 0.5 mg; the dose can be repeated at 5-minute intervals until the heart rhythm is stabilized.
In case of cardiac arrest: intravenously, a single dose of 3 mg. If atropine cannot be administered intravenously during resuscitation, it should be administered through an endotracheal tube at a dose 2-3 times higher than the dose used intravenously.
Induction of general anesthesia (premedication)
Intramuscularly or subcutaneously: 0.3 to 0.6 mg, administered 30-60 minutes before the procedure or the same dose administered intravenously immediately before the procedure.
Poisoning with organophosphorus insecticides, poisoning with cholinomimetic drugs, poisoning with mushrooms containing muscarine
Intramuscularly or intravenously: 1 to 2 mg, the dose can be repeated every 5 to 60 minutes until the symptoms of poisoning disappear; do not exceed the maximum dose of 100 mg in the first 24 hours.
Reversal of neuromuscular blockade
Intravenously, 0.6 to 1.2 mg, administered a few minutes before or simultaneously with neostigmine at a dose of 0.5 to 2 mg (using separate syringes).
Auxiliary in spastic conditions of smooth muscle in the abdominal cavity (hepatic colic, renal colic)
Intramuscularly or intravenously: 0.5 to 1 mg.
In radiological diagnostics, when it is desirable to induce relaxation of smooth muscle and relieve intestinal passage
Intramuscularly: 1 mg.
Children under 12 years old
Usually, the dose is 10 micrograms/kg body weight (0.01 mg/kg body weight) intramuscularly, intravenously, or subcutaneously; do not exceed 0.4 mg. If necessary, these doses can be repeated every 4-6 hours.
In life-threatening situations in case of severe heart disorders
For life-saving purposes: intravenously, 20 micrograms/kg body weight (0.02 mg/kg body weight); minimum dose: 0.01 mg, which can be repeated every 5 minutes up to a maximum dose of 0.1 mg.
Induction of general anesthesia (premedication)
Intramuscularly or subcutaneously; administer 30-60 minutes before the surgical procedure.
Children with a body weight of up to 3 kilograms: 100 micrograms (0.1 mg).
Children with a body weight of 7 to 9 kilograms: 200 micrograms (0.2 mg).
Children with a body weight of 12 to 16 kilograms: 300 micrograms (0.3 mg).
Children with a body weight over 20 kilograms: doses as for adult patients.
Reversal of neuromuscular blockade
Intravenously; newborns, infants, and children: 20 micrograms/kg body weight (0.02 mg/kg body weight).
Maximum dose: 0.6 mg.
Poisoning with organophosphorus insecticides, poisoning with cholinomimetic drugs, poisoning with mushrooms containing muscarine
Intramuscularly or intravenously: 50 micrograms/kg body weight (0.05 mg/kg body weight) every 10-30 minutes; administer until the symptoms of poisoning disappear.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Atropinum sulfuricum Vzf
Alternatives to Atropinum sulfuricum Vzf in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Atropinum sulfuricum Vzf in Spain
Alternative to Atropinum sulfuricum Vzf in Ukraine
Online doctors for Atropinum sulfuricum Vzf
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Atropinum sulfuricum Vzf – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














