
Atmina

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Atmina

How to use Atmina
Patient Information Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Atmina, 4.6 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patch
Atmina, 9.5 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patch
Rivastigmine
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet
- 1. What is Atmina and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Atmina
- 3. How to use Atmina
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Atmina
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Atmina and what is it used for
The active substance of Atmina is rivastigmine.
Rivastigmine belongs to a group of substances called cholinesterase inhibitors. In patients with Alzheimer's disease, certain nerve cells in the brain die, which reduces the level of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (a substance that allows nerve cells to communicate with each other). Rivastigmine works by blocking the enzymes that break down acetylcholine: acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.
By blocking the action of these enzymes, rivastigmine allows the level of acetylcholine in the brain to increase, which helps to alleviate the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
Atmina is used to treat adult patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease, which is a progressive brain disease that causes gradual memory, intellectual, and behavioral disorders.
2. Important information before using Atmina
When not to use Atmina
- if the patient is allergic to rivastigmine (the active substance of Atmina) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has ever had an allergic reaction to similar medicines (carbamate derivatives);
- if the patient has a skin reaction that extends beyond the skin area covered by the patch, if the local reaction has worsened (e.g., blisters, exacerbation of skin inflammation, swelling) or if these changes have not resolved within 48 hours after removing the patch. If this situation applies to the patient, they should inform their doctor and not apply the Atmina patch.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Atmina, the patient should discuss it with their doctor or pharmacist:
- if the patient has or has had heart diseases such as irregular or slow heart rhythm, prolonged QT interval, family history of prolonged QT interval, torsades de pointes, or low potassium or magnesium levels in the blood;
if the patient has or has had an active stomach ulcer;
- if the patient has or has had difficulty urinating;
- if the patient has or has had seizures;
- if the patient has or has had asthma or severe respiratory disease;
- if the patient has muscle tremors;
- if the patient has a low body mass;
- if the patient has gastrointestinal reactions such as nausea (vomiting), vomiting, and diarrhea. The patient may become dehydrated (lose too much fluid) if vomiting or diarrhea persists for a longer period;
- if the patient has liver function disorders.
If any of these situations apply to the patient, the doctor may monitor the patient more closely while using this medicine.
If the patient has not applied a patch for more than three days, they should not apply a new patch until they have talked to their doctor.
It is necessary to carefully remove all applied patches before applying a new one. Do not apply more than one patch at the same time. Applying multiple patches to the skin may expose the patient to an excessive amount of medicine, which can be dangerous.
Children and adolescents
Using Atmina in children and adolescents to treat Alzheimer's disease is not appropriate.
Atmina and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
Atmina may affect the action of anticholinergic medicines, some of which are used to relieve stomach cramps (e.g., dicyclomine), to treat Parkinson's disease (e.g., amantadine), or to prevent motion sickness (e.g., diphenhydramine, scopolamine, or meclizine).
Atmina transdermal system, patch should not be used at the same time as metoclopramide (a medicine used to relieve or prevent nausea and vomiting).
Taking these two medicines together may cause disorders such as limb stiffness and hand tremors.
If the patient is to undergo surgery while using Atmina transdermal system, patch, they should tell their doctor about its use, as it may enhance the effect of certain muscle relaxants given during anesthesia.
Care should be taken when Atmina transdermal system, patch is used with beta-adrenergic blockers (medicines such as atenolol, used to treat high blood pressure, angina pectoris, and other heart diseases). Taking these two medicines together may cause disorders such as slow heart rate (bradycardia), leading to fainting or loss of consciousness.
Care should be taken when Atmina is used with other medicines that may affect heart rhythm or the heart's conduction system (prolonged QT interval).
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
If the patient is pregnant, the benefits of using Atmina should be weighed against the possible effects of the medicine on the unborn child. Atmina should not be used during pregnancy unless it is absolutely necessary.
The patient should not breastfeed while using Atmina.
Driving and using machines
The doctor will inform the patient whether their condition allows for safe driving and using machines. Atmina transdermal system, patch may cause fainting or severe confusion. If the patient feels weak or is disoriented, they should not drive vehicles, operate machines, or perform other tasks that require concentration.
3. How to use Atmina
This medicine should always be used exactly as the doctor has instructed. In case of doubts, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
How to start treatment
The doctor will inform the patient which Atmina patch is best for them.
- Treatment usually starts with Atmina 4.6 mg/24 h.
- The recommended, usually used daily dose of Atmina is 9.5 mg/24 h. If this dose is well tolerated, the doctor may consider increasing the dose to 13.3 mg/24 h. It is not possible to achieve a dose of 13.3 mg/24 h with Atmina. For diseases that require the use of such a dose, other transdermal systems containing rivastigmine 13.3 mg/24 h are available.
- Only onerectangular patch and one oval, self-adhesive protective cover should be applied at a time (as described in detail below) and should be changed for new ones twice a week, no later than after 4 days. Patches should be changed on two fixed days:
In each
Monday and Friday OR
Tuesday and Saturday OR
Wednesday and Sunday OR
Thursday and Monday OR
Friday and Tuesday OR
Saturday and Wednesday OR
Sunday and Thursday.
A new patch should always be applied at the same time of day. To make it easier to remember, the patient should note the days and time of patch change.
During treatment, the doctor may adjust the dose of the medicine to the individual patient's needs.
If the patient has not applied a patch for more than three days, they should not apply a new patch until they have talked to their doctor. Patch treatment can be resumed using the same dose if the treatment interruption did not exceed three days. Otherwise, the doctor will recommend resuming treatment with a dose of 4.6 mg/24 h of Atmina.
Atmina can be used with food, drink, and alcohol.
Where to apply Atmina, transdermal system, patch
Before applying the patch, the patient should make sure that the skin in the planned application area is clean, dry, and hairless, free from powder, oils, moisturizing creams, or liquids that could prevent the patch from sticking properly, free from cuts, rashes, and/or irritations.
- Always carefully remove all applied patches before applying a new one.Applying multiple patches to the skin may expose the patient to an excessive amount of medicine, which can be dangerous.
- The patient should apply ONErectangular patch and one oval, self-adhesive protective cover at a time to ONLY ONEof the following areas, as shown in the diagrams below:
- upper part of the left arm orupper part of the right arm
- upper part of the chest on the left side oron the right side (avoid applying patches to the breast)
- upper part of the back on the left side oron the right side
- lower part of the back on the left side oron the right side.
No later than after 4 days, the patient should remove the previous patch before applying ONEnew patch and one self-adhesive protective cover to ONLY ONEof the following possible areas.
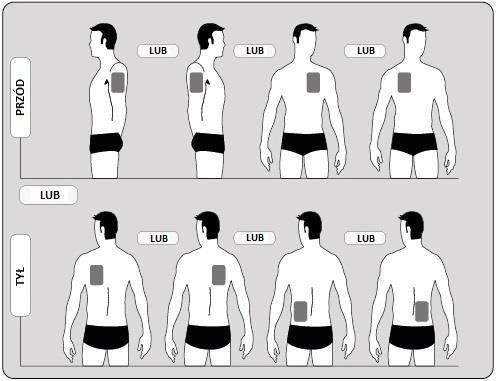
When changing the patch, the patient should remove the previous patch before applying a new patch in a different area (e.g., on the right side of the body for 4 days, then on the left side for 3 days, and on top for 4 days, and then on the bottom for the next 3 days). The patient should not apply a patch to the same area within 14 days.
How the patient should apply Atmina, transdermal system, patch
Atmina is intended for transdermal use.
Atmina consists of two parts:
- one rectangular, semi-transparent patch containing the active substance (transdermal system), which is in a sealed sachet and
- one oval, beige patch made of fabric that does not contain the active substance (self-adhesive protective cover), which is also in a sealed sachet. This sachet is larger than the sachet containing the transdermal system, patch.
 |  |
| Transdermal system, patch containing the active substance | Fabric patch without active substance (for fixation) |
The patient should not open the sachet or remove the patch from the sachet until they are ready to apply it to the skin.
First, the patient should alwaysapply the rectangulartransdermal system, patch.
 | Carefully remove the previous patch before applying a new one. Patients starting treatment (for the first time) and patients resuming treatment with rivastigmine after a break should start with the actions shown in the second diagram. |
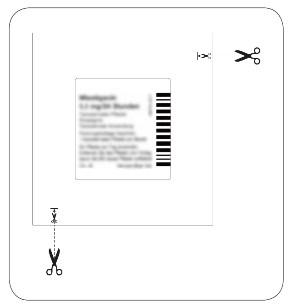 | The patch is in a separate, sealed sachet. The sachet should be opened just before using the patch. Cut the sachet at both places marked with scissors, but no further than the indicated line. Tear the sachet to open it. Do not cut the sachet along its entire length to avoid damaging the patch. Remove the rectangular, semi-transparent transdermal system, patch from the sachet. |
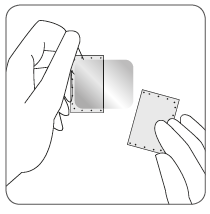 | The adhesive layer of the patch is protected by a protective layer. The patient should remove one part of the protective layer without touching the adhesive surface of the patch with their fingers. |
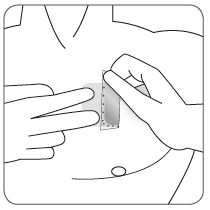 | Apply the adhesive surface of the patch to the upper or lower part of the back, upper part of the arm, or chest, and then remove the second part of the protective layer. |
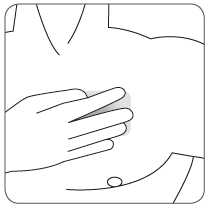 | Press the patch firmly with the palm of the hand for about 15 seconds, making sure its edges stick well to the skin. |
Next, the patient should apply the oval, self-adhesive protective cover.
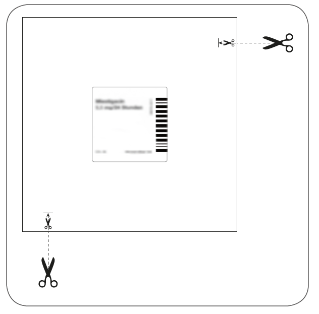 | Cut the sachet at both places marked with scissors, but no further than the indicated line. Tear the sachet to open it. Do not cut the sachet along its entire length to avoid damaging the self-adhesive protective cover without the active substance. Remove the oval, beige, self-adhesive protective cover from the sachet. |
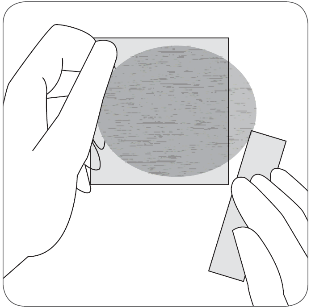 | The adhesive layer of the protective cover is protected by a protective layer. The patient should remove the smaller part of the protective layer without touching the adhesive surface of the patch with their fingers. |
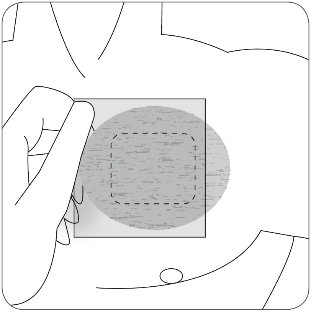 | Apply the adhesive surface of the protective cover to the previously applied transdermal system, patch, so that it is completely covered, and then remove the second part of the protective layer. |
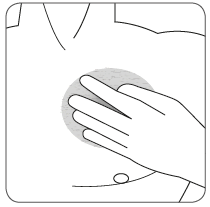 | Press the patch firmly with the palm of the hand for at least 30 seconds, making sure its edges stick well to the skin. |
For some patients, it may be helpful to write the day of the week with a fine pen on the protective cover, e.g., the day of the week.
The patch should be worn continuously until it is time to change it. The patient can try different application areas for the new patch to choose the most convenient and least exposed to abrasion by clothing.
How the patient should remove Atmina, transdermal system, patch
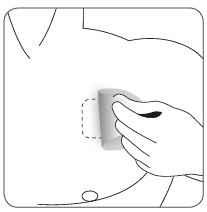
The patient should gently pull one edge of the self-adhesive protective cover and slowly peel it off the skin along with the transdermal system.
If the transdermal system remains on the skin, the patient should gently pull one edge and peel it off the skin.
If there are any adhesive residues on the skin, they can be removed by washing the area with warm water and mild soap or baby oil. The patient should not use alcohol or other solvents (nail polish remover and other products).
After removing the patch, the patient should wash their hands with soap and water. In case of contact with the eyes or eye irritation after contact with the patch, the patient should immediately rinse their eyes with a large amount of water, and if the symptoms do not disappear, they should seek medical attention.
Can the patient use Atmina, transdermal system, patch while bathing, swimming, or in the sun?
- Bathing, swimming, or showering should not affect the patch's action. The patient should make sure that the patch does not come off during these activities.
- The patient should not expose the patch to prolonged external heat sources (e.g., excessive sun exposure, sauna, solarium).
What to do if the patch comes off
If the patch comes off, the patient should apply a new one and then change it at the usual time.
When and for how long should the patient use Atmina, transdermal system, patch?
- To make the treatment effective, the patient should apply a new patch twice a week, no later than after four days, preferably at the same time of day.
The patient should apply only one rectangular transdermal system, patch and one oval, self-adhesive protective cover at a time and change them for new ones on two fixed days of the week.
- The patient should apply a new patch no later than after four days, preferably at the same time of day.
Using more than the recommended dose of Atmina
If the patient accidentally applies more than one rectangulartransdermal system, patch, they should remove all patches and inform their doctor about the accidental application of more than one patch. The patient may need medical attention. In some people who have accidentally taken too much rivastigmine, nausea (vomiting), vomiting, diarrhea, high blood pressure, and hallucinations have occurred. Slow heart rate and fainting may also occur.
Missing a dose of Atmina
If the patient finds that they have forgotten to apply a patch, they should do so immediately, provided that the treatment interruption does not exceed three days.
The next patch can be applied at the usual time on the fixed day to return to the usual dosing schedule. The patient should not apply two patches to make up for a missed patch. If the patient has not had a patch on for more than three days, they should not apply a new patch until they have talked to their doctor.
Stopping treatment with Atmina
If the patient stops using the patches, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist.
In case of any further doubts about using this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Atmina can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects may occur more frequently during the initial period of using the medicine or during dose increase. Side effects usually disappear slowly as the body adapts to the treatment.
In case of any of the following side effects, the patient should remove the patch and immediately tell their doctor, as these effects can be severe:
Frequent(may occur in less than 1 in 10 people)
- loss of appetite
- dizziness
- agitation or drowsiness
- urinary incontinence (inability to properly retain urine).
Uncommon(may occur in less than 1 in 100 people)
- heart rhythm disorders, such as slow heart rate
- seeing things that are not there (hallucinations)
- stomach ulcers
- dehydration (loss of too much fluid)
- excessive restlessness (high level of activity, restlessness)
- aggression.
Rare(may occur in less than 1 in 1000 people)
- falls.
Very rare(may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 people)
- stiffness of the arms or legs
- hand tremors.
Frequency not known(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- allergic reaction at the patch application site, such as blisters or skin inflammation
- worsening of Parkinson's disease symptoms, such as tremors, stiffness, or dragging of the legs
- pancreatitis - symptoms include severe abdominal pain, often with nausea (vomiting) or vomiting
- rapid or irregular heartbeat
- high blood pressure
- seizures (epileptic fits)
- liver function disorders (jaundice, yellowing of the whites of the eyes, unusual dark color of urine, or unexplained nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and loss of appetite)
- changes in liver function test results
- restlessness
- nightmares
- Pisa syndrome (a condition that includes involuntary muscle contraction with abnormal tilting of the body and head to one side).
In case of any of the above side effects, the patient should remove the patch and immediately tell their doctor.
Other side effects reported after using rivastigmine in capsule or oral solution form, which may also occur after using patches:
Frequent(may occur in less than 1 in 10 people)
- excessive salivation
- loss of appetite
- restlessness
- general malaise
- tremors or confusion
- excessive sweating.
Uncommon(may occur in less than 1 in 100 people)
- heart rhythm disorders (e.g., rapid heartbeat)
- difficulty sleeping
- accidental falls.
Rare(may occur in less than 1 in 1000 people)
- seizures (epileptic fits)
- ulcerative disease of the intestines
- chest pain - may be caused by a heart attack.
Very rare(may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 people)
- high blood pressure
- pancreatitis - symptoms include severe abdominal pain, often with nausea (vomiting) or vomiting
- gastrointestinal bleeding - blood in stool or vomit
- seeing things that are not there (hallucinations)
- severe vomiting that can lead to a tear in the esophagus (the tube connecting the mouth to the stomach).
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products; Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, phone: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Atmina
- The medicine should be kept out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and sachet after "Expiry date (EXP)". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
- There are no special precautions for storing the medicine.
- Do not use a patch that is damaged or shows signs of opening.
After removing the patch, the patient should fold it in half with the adhesive side inwards and press firmly. The used patch should be placed in the sachet and then disposed of in a place inaccessible to children. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Atmina contains
The active substance of Atmina is rivastigmine.
Atmina 4.6 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patch:
Each transdermal system, patch releases 4.6 mg of rivastigmine over 24 hours. Each transdermal system, patch with a surface area of 10.8 cm contains 25.92 mg of rivastigmine.
Atmina 9.5 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patch:
Each transdermal system, patch releases 9.5 mg of rivastigmine over 24 hours. Each transdermal system, patch with a surface area of 21.6 cm contains 51.84 mg of rivastigmine.
The other ingredients are:
Outer layer (covering): poly(ethylene terephthalate) film.
Active layer: tocopherol, poly(2-ethylhexyl acrylate, vinyl acetate) (1:1), butyl acrylate, and butyl methacrylate copolymer.
Membrane permeable to the active substance: polyethylene film.
Adhesive layer: polyisobutylene with medium molecular weight, polyisobutylene with high molecular weight, polybutylene with high molecular weight.
Protective layer (removable): silicone-coated polyester film.
Printing ink: blue ink.
What Atmina looks like and contents of the pack
Each transdermal system is a thin, rectangular patch with rounded corners.
The patch is semi-transparent and has the following markings:
Atmina, 4.6 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patch: RID-TDS 4.6 mg/24 h
Atmina, 9.5 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patch: RID-TDS 9.5 mg/24 h
Each transdermal system, patch is in a separate, sealed sachet. The sachets are marked as follows:
Atmina, 4.6 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patch
Atmina, 9.5 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patch
In addition, each carton with the transdermal system, patch contains a protective cover for fixing the transdermal system, patch.
Each protective cover is a thin, beige, oval patch.
The protective covers are in separate, sealed sachets. The sachets are marked as follows:
Self-adhesive protective cover without active substance.
The whole is in a carton.
Atmina, 4.6 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patchand Atmina, 9.5 mg/24 h, transdermal system, patch
are available in packs containing 2, 8, 16, or 24 transdermal systems, patches with 2, 8, 16, or 24 self-adhesive protective covers, respectively.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Exeltis Poland Sp. z o.o.
Szamocka 8
01-748 Warsaw
e-mail: [email protected]
Manufacturer
Luye Pharma AG
Am Windfeld 35
83714 Miesbach
Germany
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Spain
Alzerta dos por semana 4.6 mg/24 h parches transdérmicos
Alzerta dos por semana 9.5 mg/24 h parches transdérmicos
Germany
Rivez zweimal wöchentlich 4.6 mg/24 Stunden Transdermales Pflaster
Rivez zweimal wöchentlich 9.5 mg/24 Stunden Transdermales Pflaster
Poland
Atmina
Date of last revision of the leaflet:06.12.2024
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterLuye Pharma AG
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to AtminaDosage form: System, 4.6 mg/24 hActive substance: rivastigmineManufacturer: Luye Pharma AGPrescription requiredDosage form: System, 4.6 mg/24 hActive substance: rivastigminePrescription requiredDosage form: System, 9.5 mg/24 hActive substance: rivastigmineManufacturer: Luye Pharma AG Zentiva SAPrescription required
Alternatives to Atmina in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Atmina in Spain
Alternative to Atmina in Ukraine
Online doctors for Atmina
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Atmina – subject to medical assessment and local rules.











